Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.3: Summation Notation and Area
Uploaded by
Rose JonesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.3: Summation Notation and Area
Uploaded by
Rose JonesCopyright:
Available Formats
5.
3: Summation Notation and Area
(Def 5.9): Summation Notation
1 2 3
1
n
k n
k
a a a a a
=
= + + + +
(Th 5.10):
1
n
k
c nc
=
=
1 2
n
k b b b n
k b
a a a a a
+ +
=
= + + + +
Example: Evaluate .
10
1
3
i =
3 10 = 30 =
10
1
3
i =
A common mistake is to write
1
n
i
c c
=
=
(Th 5.11): Summation Properties
(i) ( )
1 1 1
n n n
i i i i
i i i
a b a b
= = =
=
(ii) ( )
1 1
n n
i i
i i
c a c a
= =
=
(Th 5.12): Summation Formulas
(i)
( )
1
1
2
n
i
n n
i
=
+
=
(ii)
( )( )
2
1
1 2 1
6
n
i
n n n
i
=
+ +
=
(iii)
( )
2
3
1
1
2
n
i
n n
i
=
| | +
=
|
\ .
You may have fond
memories of proving
these formulas last year
with induction.
We will be using them
this year, not proving
them again
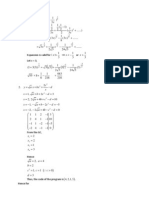
Example: Express in terms of .
3 2
1
2 5
n
k
k k
=
+
n
3 2
1
2 5
n
k
k k
=
+
3 2
1 1 1
2 5
n n n
k k k
k k
= = =
= +
3 2
1 1 1
2 5
n n n
k k k
k k
= = =
= +
( ) ( )( )
2
1 1 2 1
2 5
2 6
n n n n n
n
| | | | + + +
= +
| |
\ . \ .
4 3 2 3 2
2 2 3
5
4 3
n n n n n n
n
| | | |
+ + + +
= +
| |
\ . \ .
4 3 2
3 2 9 56
12
n n n n +
=
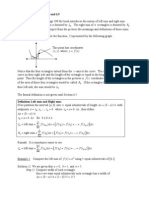
Investigating Area
a b
( )
y f x =
x A
i
x
Approximation for
area under the curve
from a to b:
( )
1
n
i
i
f x x
=
A
height
width
number of rectangles
as , . 0 x A n
Area under curve: ( )
0
1
lim
n
i
x
i
f x x
A
=
A
Inscribed Rectangles
a b
( )
y f x =
x A
i
x
Approximation for
area under the curve
from a to b:
( )
1
n
IP i
i
A f x x
=
= A
height
width
number of rectangles
is the minimum height of
in each subinterval.
( )
i
f x f
IP
A = Area by method of
Inscribed
Rectangular Polygons
Circumscribed Rectangles
a b
( )
y f x =
x A
i
x
Approximation for
area under the curve
from a to b:
( )
1
n
CP i
i
A f x x
=
= A
height
width
number of rectangles
is the maximum height of
in each subinterval.
( )
i
f x f
CP
A = Area by method of
Circumscribed
Rectangular Polygons
Inscribed rectangles give an underestimate for area.
Circumscribed rectangles give an overestimate for area.
Example: Approximate the area under the graph of
from 1 to 5 using inscribed rectangles and .
( )
2
1 f x x = +
1 x A =
( )
1
n
IP i
i
A f x x
=
= A
( )
4
1
1
i
i
f x
=
=
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2 2
1 1 1 2 1 1 3 1 1 4 1 1 = + + + + + + +
2 5 10 17 = + + + 34 =
Inscribed rectangles give an underestimate for area.
Circumscribed rectangles give an overestimate for area.
Example: Approximate the area under the graph of
from 1 to 5 using circumscribed rectangles and .
( )
2
1 f x x = +
1 x A =
( )
1
n
CP i
i
A f x x
=
= A
( )
4
1
1
i
i
f x
=
=
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2 2
2 1 1 3 1 1 4 1 1 5 1 1 = + + + + + + +
5 10 17 26 = + + + 58 =
Example: Approximate the area under the graph of
from to using circumscribed rectangles and four equal
subintervals.
( )
sin f x x =
0 t
4
x
t
A = ( )
1
n
CP i
i
A f x x
=
= A
t
4
t
2
t 3
4
t
( )
4
1
sin
4
CP i
i
A x
t
=
| |
=
|
\ .
sin
4 4
t t
| |
=
|
\ .
sin
2 4
t t
| |
+
|
\ .
sin
2 4
t t
| |
+
|
\ .
3
sin
4 4
t t
| |
+
|
\ .
2 2
1 1
4 2 2
t
| |
= + + +
|
|
\ .
( )
2 2
4
t
= +
Example: Approximate the area under the graph of
from to using inscribed rectangles and four equal subintervals.
( )
sin f x x =
0 t
4
x
t
A = ( )
1
n
IP i
i
A f x x
=
= A
t
4
t
2
t 3
4
t
( )
4
1
sin
4
IP i
i
A x
t
=
| |
=
|
\ .
( )
sin0
4
t
=
sin
4 4
t t
| |
+
|
\ .
3
sin
4 4
t t
| |
+
|
\ .
( )
sin
4
t
t +
2 2
0 0
4 2 2
t
| |
= + + +
|
|
\ .
2
4
t
=
Example: Find the area under the graph of from to .
( )
2
f x x = 0 b
( )
1
n
i
i
A f x x
=
= A
1
x
2
x
3
x
i
x
n
x
b
2
1
n
i
i
x x
=
= A
b
x
n
A =
b
i
n
2
1
n
i
bi b
n n
=
| |
=
|
\ .
3
2
3
1
n
i
b
i
n
=
=
( )( )
3
3
1 2 1
6
n n n
b
n
| | + +
=
|
\ .
3 2 3 3
2
2 3
6
b n b n b
n
+ +
=
0 x A
n
3
0
lim
3
x
b
A
A
=
Example: Find the area under the graph of from to .
( )
2
f x x = 3 7
3
7
We use the result of the previous
example to aid us in our search.
A
(Area from 0 to 7) (Area from 0 to 3) (Area from 3 to 7)
( )
3
0
1
lim
3
n
i
x
i
b
f x x
A
=
A =
3
7
3
3
3
3
3 3
7 3
3 3
316
3
=
1
3
105 =
You might also like
- Supplement To 6-4 PDFDocument8 pagesSupplement To 6-4 PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxNo ratings yet
- Blue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question PaperDocument14 pagesBlue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question Paperapi-243565143No ratings yet
- Numerical Differentiation: X X X H X H X HDocument19 pagesNumerical Differentiation: X X X H X H X HDini AryantiNo ratings yet
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument10 pagesNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Additional Maths NoteDocument10 pagesForm 5 Additional Maths NoteEric WongNo ratings yet
- CALCULATING AREA UNDER A GRAPHDocument20 pagesCALCULATING AREA UNDER A GRAPHnkmarshNo ratings yet
- MATH1151 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesMATH1151 Final Exam ReviewtravissaronNo ratings yet
- AP Review Chapter 4Document20 pagesAP Review Chapter 4DSaulBNo ratings yet
- Y MX B: Linearization and Newton's MethodDocument7 pagesY MX B: Linearization and Newton's MethodTony CaoNo ratings yet
- Section 3.1 Exponential FunctionsDocument21 pagesSection 3.1 Exponential FunctionsdavogezuNo ratings yet
- W5 IntegrationDocument37 pagesW5 IntegrationYuri ParkNo ratings yet
- 2sem 2 Project WoekDocument31 pages2sem 2 Project WoekHui Li TehNo ratings yet
- HCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesHCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 Solutionsnej200695No ratings yet
- Obj. 5 Vertex Form (Presentation)Document17 pagesObj. 5 Vertex Form (Presentation)Sandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Ajc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument11 pagesAjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Essential Calculus, James Stewart: Techniques of IntegrationDocument36 pagesEssential Calculus, James Stewart: Techniques of IntegrationChuc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Calculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsDocument11 pagesCalculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsRaymond BalladNo ratings yet
- (3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Document10 pages(3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Matthew ShiaNo ratings yet
- Approximation Methods for IntegralsDocument16 pagesApproximation Methods for IntegralsEric MoralesNo ratings yet
- Materi PolynomialDocument20 pagesMateri PolynomialnormasulasaNo ratings yet
- Section 6 IntegrationDocument16 pagesSection 6 IntegrationpraveshNo ratings yet
- 2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2Document12 pages2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2lacewingNo ratings yet
- LIMITS AND CONTINUITYDocument41 pagesLIMITS AND CONTINUITYAan SajaNo ratings yet
- Math DiskritDocument46 pagesMath DiskritnenaibrahimNo ratings yet
- 101 Math Short Cuts-Mental Ability PDFDocument20 pages101 Math Short Cuts-Mental Ability PDFsanits591100% (1)
- Circular FunctionsDocument44 pagesCircular Functionsrica_marquezNo ratings yet
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Interpolation Produces That Matches Exactly. The Function Then Can Be Utilized To ApproximateDocument44 pagesInterpolation Produces That Matches Exactly. The Function Then Can Be Utilized To ApproximategraphicalguruNo ratings yet
- MTE 01 EngDocument5 pagesMTE 01 EngdesperadomarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2:: Evaluating FunctionsDocument21 pagesLesson 2:: Evaluating FunctionsTerence Guiritan0% (1)
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDocument12 pagesHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- FPT. Integration 2022Document112 pagesFPT. Integration 2022Cao Nhật ThiênNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityDocument57 pagesLimits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityPol EboyNo ratings yet
- Calc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.7 1 of 8: FXDXM FC X Ba X N C A XiDocument8 pagesCalc 1 Lecture Notes Section 4.7 1 of 8: FXDXM FC X Ba X N C A Ximasyuki1979No ratings yet
- 2013 12 SP Mathematics 05Document30 pages2013 12 SP Mathematics 05Akanksha Yash KathuriaNo ratings yet
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solDocument12 pages2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoNo ratings yet
- EEM2036 Numerical Methods TutorialDocument8 pagesEEM2036 Numerical Methods TutorialSivanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Second Puc Mathematics Model Question Papers 2013 New Syllabus - Subject Code: 35Document34 pagesSecond Puc Mathematics Model Question Papers 2013 New Syllabus - Subject Code: 35Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Document3 pages151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniNo ratings yet
- I F C F: Pure Math SummaryDocument4 pagesI F C F: Pure Math SummaryRuijia ZengNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SPM 2011.powerpointDocument55 pagesMathematics SPM 2011.powerpointuzai88No ratings yet
- UCSB Math34B HomeworkDocument5 pagesUCSB Math34B Homeworklex7396No ratings yet
- Application of Determinant To Determine The Area of PlaneDocument14 pagesApplication of Determinant To Determine The Area of PlanekanasaputrasNo ratings yet
- J2 Common Test 2 SolutionsDocument14 pagesJ2 Common Test 2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- FX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- LPP- Aldehyde & Ketone Single CorrectDocument6 pagesLPP- Aldehyde & Ketone Single CorrectSamisha JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Hammer Call Master FAQsDocument8 pagesHammer Call Master FAQsPriya NavaneethanNo ratings yet
- Inbound 7651129928954348636Document6 pagesInbound 7651129928954348636IoanaNo ratings yet
- S2 - Lesson 10 (Tone and Style)Document8 pagesS2 - Lesson 10 (Tone and Style)Muhammad Harist Murdani0% (1)
- Parallel Programming IntroductionDocument17 pagesParallel Programming IntroductionYang YiNo ratings yet
- A2 Writing Booklet (Answer Key)Document93 pagesA2 Writing Booklet (Answer Key)jul123456No ratings yet
- Own Cloud Admin ManualDocument87 pagesOwn Cloud Admin ManualNagraj NagNo ratings yet
- Seborg - Process Dynamics and ControlDocument2 pagesSeborg - Process Dynamics and ControlJedielson GirardiNo ratings yet
- Basic Examples: Figure 1. Copybook INQINTCDocument2 pagesBasic Examples: Figure 1. Copybook INQINTCSatyabrata DashNo ratings yet
- Once There Were Wolves - AnalysisDocument5 pagesOnce There Were Wolves - AnalysisДаниела ИсаевичNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech With Reporting VerbsDocument2 pagesReported Speech With Reporting Verbsklaid proctorNo ratings yet
- SSD Buying Guide ListDocument18 pagesSSD Buying Guide Listriski arrixki2No ratings yet
- Pdfmergerfreecom Ms Excel 2007 Formulas With Examples PDF in Hindi WordpresscomcompressDocument4 pagesPdfmergerfreecom Ms Excel 2007 Formulas With Examples PDF in Hindi WordpresscomcompressRitesh NimjeNo ratings yet
- Juan de Tovar's history of the indigenous peoplesDocument4 pagesJuan de Tovar's history of the indigenous peoplesTörök Levente BélaNo ratings yet
- Soda Chapter 7Document20 pagesSoda Chapter 7dinesh9866119219No ratings yet
- Meeting people in ITDocument8 pagesMeeting people in ITDavid ValenzNo ratings yet
- Othello by William ShakespeareDocument5 pagesOthello by William ShakespearerajeshNo ratings yet
- 1 Rounding Decimal Places and Significant FiguresDocument10 pages1 Rounding Decimal Places and Significant Figuresapi-258749062No ratings yet
- Lec7matrixnorm Part2Document12 pagesLec7matrixnorm Part2Somnath DasNo ratings yet
- Learn basic Mirpuri phrases and vocabularyDocument9 pagesLearn basic Mirpuri phrases and vocabularyInder M NagiNo ratings yet
- Learn Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in CDocument39 pagesLearn Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in CkarijghfdNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 4, Wk.8 - Module 2Document29 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4, Wk.8 - Module 2Jennifer JuatcoNo ratings yet
- Raihan Fuadi Tugas 3 Bhs InggrisDocument5 pagesRaihan Fuadi Tugas 3 Bhs InggrisRaihan FuadiNo ratings yet
- ESC Shahadah 2Document14 pagesESC Shahadah 2fatimah.kamal013No ratings yet
- Arie Rahmawati Hadiyanti 06202244042-DikonversiDocument192 pagesArie Rahmawati Hadiyanti 06202244042-DikonversiHana Nurul KarimahNo ratings yet
- Project Crime Scene Investigation Creative DramaDocument16 pagesProject Crime Scene Investigation Creative DramaPaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Owen tiamtingNo ratings yet
- 500 Most Used Russian Nouns - With Genders Marked 4Document3 pages500 Most Used Russian Nouns - With Genders Marked 4Chrystian SilvaNo ratings yet
- Protel DXP BeginnersDocument38 pagesProtel DXP BeginnersandreskapazNo ratings yet
- Teste - Marinheiro 2 ClasseDocument6 pagesTeste - Marinheiro 2 Classeanita_ribeiro825No ratings yet



















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)


































