Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Electronics
Uploaded by
bojjasaigowthamiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Electronics
Uploaded by
bojjasaigowthamiCopyright:
Available Formats
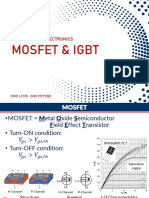
Power Electronics- EEE341
10/11/2014 1
10/11/2014
2
Relationship of Power Electronics
Power Electronics Application
Power Electronics defined as the application of solid-state
(devices) electronics for the control and conversion of electric
power.
Power electronics have already found an important place in
modern technology and are now used in a great variety of
high-power product, including heat controls, light controls,
electric motor control, power supplies, vehicle propulsion
system and high voltage direct current (HVDC) systems.
1.Uncontrolled turn on and off (Power Diode)
2.Controlled turn on uncontrolled turn off (Thyristors)
3.Controlled turn on and off characteristic (Power Transistor, BJT,
MOSFET, GTO, IGBT)
4.Continuous gate signal requirement (BJT, MOSFET, IGBT)
5.Pulse gate requirement (SCR(Silicon-Controlled Rectifier) , GTO)
6.Bidirectional current capability (TRIAC)
7.Undirectionalcurrent capability (SCR, GTO, BJT, MOSFET, IGBT)
POWER ELECTRONIC SWITCHING DEVICES
Diagram Block of Converters
6
7
8
9
10
10/11/2014 11
11
12
Diode Rectifiers. A diode rectifier circuit converts AC voltage into a
fixed DC voltage. The input voltage to rectifier could be either single
phase or three phase.
AC to DC Converters. An AC to DC converter circuit can convert AC
voltage into a DC voltage. The DC output voltage can be controlled by
varying the firing angle of the thyristors. The AC input voltage could
be a single phase or three phase.
AC to AC Converters. This converters can convert from a fixed ac input
voltage into variable AC output voltage. The output voltage is
controlled by varying firing angle of TRIAC. These type converters are
known as AC voltage regulators.
TYPES OF POWER ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
DC to DC Converters . These converters can converter a fixed DC
input voltage into variable DC voltage or vice versa. The DC output
voltage is controlled by varying of duty cycle.
DC-AC converters. It is also known as an INVERTER. The output
voltage is of alternating form and output can be controlled by
varying conduction time of transistors.
Static switches. The power devices which is operated with with
static switches or contactors and the supply to the switches can be
either ac or dc. A number of conversion stages are often cascaded
to produce desired output.
10/11/2014 14
10/11/2014 15
Diode Rectifiers
16
AC-DC Converter
10/11/2014 17
AC-AC Converter
10/11/2014 18
DC-AC Converter
19
20
21
22
10/11/2014 23
IGBT in DC-DC Converter
10/11/2014 24
DC-DC CONVERTER (DC Chopper)
In many industrial application , DC-DC converter is required to convert a
fixed-voltage DC source into a variable-voltage DC source. Like a
transformer, DC-DC converter can be used to step down or step up a DC
voltage source.
Application :
Traction motor control in electric automobiles, trolley cars, marine hoists,
forklift trucks, mine haulers, etc
Advantages :
High Efficiency and fast dynamic response
10/11/2014 25
UPS System
26
27
28
29
10/11/2014 30
Examples of Some
Applications
10/11/2014 31
History of Power Electronics
10/11/2014 32
Types of Power Devices
10/11/2014 33
General Purposes Diodes
10/11/2014 34
Thyristors
10/11/2014 35
GTOs
10/11/2014 36
Power Ratings of Devices
10/11/2014 37
Ratings of Power Devices
10/11/2014 38
Devices Symbols and Characteristics
10/11/2014 39
Devices Symbols and Characteristics
10/11/2014 40
Applications of Power Devices
10/11/2014 41
Control Characteristics of Devices
10/11/2014 42
Control Characteristics of Devices
10/11/2014 43
Switching Characteristics
10/11/2014 44
Ideal Characteristics
Ideal
Characteristics
10/11/2014 45
Voltage and Current Waveforms
10/11/2014 46
Power Converter System
10/11/2014 47
Smart Power System
10/11/2014 48
Fin-type Heat Sink
SCR (hokey-puck-type) on power pak kits
SCR (stud-type) on air-cooled kits
Assembly of power converters
10/11/2014 49
Power Diodes
Stud type
Hockey-puck type
IGBT
Module type: Full
bridge and three
phase
IGCT
Integrated with its
driver
10/11/2014 50
Summary
The characteristics of the power devices play a major role in the speed and
effectiveness of the power conversion.
Power electronics uses low power electronics (ICs), control, and switching power
devices for power converter and/or processing from one form to another.
SPECIFICATION OF THE SWITCH
10/11/2014 51
Voltage ratings: Forward and reverse repetitive peak voltage and on state
forward voltage drop.
Current ratings: Average, root mean square , repetitive peak, non repetitive
peak and off state leakage currents
Switching speed or frequency: switching period or frequency
di/dt rating
Minimum amount of time before its whole conducting surface comes into play in
carrying the full current.
If the current rises rapidly the current flow may be concentrated to a certain area
and the device may be damaged.
This can be limited by connecting a small inductor in series with the device called
series snubber.
dv/dt rating :
Semiconductor device has internal junction capacitance Cj
When the voltage across the switch changes rapidly during turn on and
turn off and while connecting to the main supply the initial current will be
very high. This damages the device.
This can be limited by connecting RC circuit across the device called shunt
snubber
Switching losses: Power losses during turn on and turn off.
Gate drive requirement:
Safe operating area(SOA)
I
2
t rating for fuse
Temperature
Thermal resistance
10/11/2014 52
10/11/2014 53
10/11/2014 54
10/11/2014 55
10/11/2014 56
10/11/2014 57
10/11/2014 58
10/11/2014 59
You might also like
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Guide Covering Rectification, Inverters, Choppers & MoreDocument276 pagesPower Electronics Guide Covering Rectification, Inverters, Choppers & MoreBikrant PoudelNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument38 pagesLec 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsAfiqah Zainuddin100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument90 pagesPower ElectronicsPalanisamy NagappanNo ratings yet
- Solar-Powered Battery Charging With Highly Efficient Buck ConverterDocument20 pagesSolar-Powered Battery Charging With Highly Efficient Buck ConverterSusanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualDocument77 pagesElectronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualpdnkiranNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Comparison of Three Level Inverter-392Document10 pagesSimulation and Comparison of Three Level Inverter-392Đức Khánh Đức KhánhNo ratings yet
- GTO RectifierDocument13 pagesGTO RectifierBijay PoudelNo ratings yet
- R-2R DAC and ADC AnalysisDocument27 pagesR-2R DAC and ADC Analysiskaka_huzefa100% (1)
- IOT Using Arduino IDE to Monitor Temperature and HumidityDocument20 pagesIOT Using Arduino IDE to Monitor Temperature and HumidityPrabir dasNo ratings yet
- Types of Inverters and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesTypes of Inverters and Their Applicationsaa bbNo ratings yet
- Books PDFDocument1 pageBooks PDFDivanshu InsaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics in Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageAdvanced Topics in Power Electronicsdileepk1989No ratings yet
- DC Power Monitor With INA209 and ArduinoDocument57 pagesDC Power Monitor With INA209 and Arduinojp2udhaya100% (2)
- 10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument69 pages10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualVinita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Nano ElectronicsDocument16 pagesNano Electronicssmartsecuritycamera senderNo ratings yet
- Workshop ON Ltspice: Fabrice WATEAUDocument60 pagesWorkshop ON Ltspice: Fabrice WATEAUkalimbaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DC To DC Converters: OutlineDocument27 pagesChapter 3 DC To DC Converters: OutlineAMARNATHNAIDU77No ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions For DSDDocument17 pagesTwo Mark Questions For DSDvnirmalacseNo ratings yet
- Vlsi PDFDocument81 pagesVlsi PDFShruthiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Tutorial PDFDocument16 pagesPower Electronics Tutorial PDFPrem100% (2)
- EI2353-Digital System DesignDocument13 pagesEI2353-Digital System DesignSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Real Time DC Motor Speed Control Using PID in LabVIEWDocument3 pagesReal Time DC Motor Speed Control Using PID in LabVIEWabsalnabiNo ratings yet
- Ranganathan Polytechnic College Coimbatore.: Simulation Practical Lab ManualDocument32 pagesRanganathan Polytechnic College Coimbatore.: Simulation Practical Lab ManualBala SVD100% (1)
- UPS Power 10 KVA, 20kva, 30 Kva, 40kva Redundant UPS - Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument4 pagesUPS Power 10 KVA, 20kva, 30 Kva, 40kva Redundant UPS - Uninterruptible Power SupplyGamatronicNo ratings yet
- DC to DC Converter FundamentalsDocument40 pagesDC to DC Converter FundamentalsJamir CalNo ratings yet
- 8MS Three-Phase Synchronous MotorsDocument163 pages8MS Three-Phase Synchronous MotorsrrrNo ratings yet
- EE6604-DESIGN of Electrical MachinesDocument9 pagesEE6604-DESIGN of Electrical Machinesdishore312No ratings yet
- PWM TechniquesDocument27 pagesPWM TechniquesDanny ChuNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Radar SystemDocument22 pagesArduino Based Radar SystemMayank MrinalNo ratings yet
- DC To DCDocument11 pagesDC To DCsiddhartha_anirbanNo ratings yet
- Foot Step Based Power GeneratorDocument15 pagesFoot Step Based Power Generatorchanda SindhuraNo ratings yet
- Display DeviceDocument16 pagesDisplay DevicekvtrivediNo ratings yet
- Advanced Courses in Power ElectronicDocument147 pagesAdvanced Courses in Power ElectronicCHOUDERNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectsDocument55 pagesMini ProjectsSampath KumarNo ratings yet
- Raghu Institute of Technology ECE Lab ManualDocument150 pagesRaghu Institute of Technology ECE Lab ManualMad DamnNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 DC-DC Converters 2016Document113 pagesChapter3 DC-DC Converters 2016ShawnNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT)Document3 pagesLinear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT)SE ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Multimeter ReportDocument15 pagesMultimeter Reportapi-244226518No ratings yet
- EE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankDocument11 pagesEE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankAnbarasan Annamalai100% (1)
- Power Electronics 2010-2011Document68 pagesPower Electronics 2010-2011Adnan Younus100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesPower Electronicsgrbavithra100% (1)
- Chopper 2003Document40 pagesChopper 2003Agus SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Powe Electronics Unit 1Document65 pagesPowe Electronics Unit 1Ajju K AjjuNo ratings yet
- Ec 2254 Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument376 pagesEc 2254 Linear Integrated CircuitsPavan Kumar100% (1)
- Washing Machine Control Using 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesWashing Machine Control Using 8051 MicrocontrollerPrasath MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Operational AmplifiersDocument26 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Operational AmplifiersLarry CubillasNo ratings yet
- Project Status Review Semester: 7 EE (Group No: 2) Project I (2170001)Document51 pagesProject Status Review Semester: 7 EE (Group No: 2) Project I (2170001)UmangNo ratings yet
- IR Sensor Circuit Diagram and Working Principle ExplainedDocument7 pagesIR Sensor Circuit Diagram and Working Principle ExplainedKirz SerranoNo ratings yet
- Digital Phase Selector: A Mini-Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Requirements For The Award ofDocument53 pagesDigital Phase Selector: A Mini-Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Requirements For The Award ofdondbNo ratings yet
- Report of Induction ProgramDocument23 pagesReport of Induction ProgramDhruv Chunawala100% (1)
- Effect of Current On EDMDocument58 pagesEffect of Current On EDMAli M. ElghawailNo ratings yet
- 21 Toma EmanoilDocument6 pages21 Toma EmanoilFredy Peñafiel PazNo ratings yet
- Mosfet & Igbt: Ee3147 Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesMosfet & Igbt: Ee3147 Power ElectronicsHoàng TúNo ratings yet
- 02 Uncontrolled AC To DC Converters3Document46 pages02 Uncontrolled AC To DC Converters3siegfred sicatNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet Opus A6 Standard Full: Wachendorff Elektronik GMBH & Co. KGDocument7 pagesTechnical Data Sheet Opus A6 Standard Full: Wachendorff Elektronik GMBH & Co. KGLe Viet ThanhNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dryer Fyp DKM 07Document53 pagesShoe Dryer Fyp DKM 07Dasir Baluan AsiriNo ratings yet
- PDF Document (569802)Document120 pagesPDF Document (569802)Elvira RodNo ratings yet
- Single Stage Isolated Bridgeless PFC Converter Achieves 98 Percent EfficiencyDocument10 pagesSingle Stage Isolated Bridgeless PFC Converter Achieves 98 Percent EfficiencyJosip LuetichNo ratings yet
- CPU fan controller project uses PSOC for temperature-based speed controlDocument4 pagesCPU fan controller project uses PSOC for temperature-based speed controlmantoruleNo ratings yet
- Company Standing Order Engine RoomDocument4 pagesCompany Standing Order Engine Roomreka Shipping0% (1)
- Expression of Interest (E.O.I.) Fire Fighting System BOQ (NSRDocument3 pagesExpression of Interest (E.O.I.) Fire Fighting System BOQ (NSRKarthick MahadevanNo ratings yet
- Index ChillDocument95 pagesIndex Chillreezqee100% (1)
- Schneider PLC Module Bmxdra1605 PDFDocument4 pagesSchneider PLC Module Bmxdra1605 PDFjoapmeNo ratings yet
- Terberg Fifth Wheel Service ManualDocument11 pagesTerberg Fifth Wheel Service ManualSyed Danyal SalamNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: TAC-42CF TAC-42CHFDocument17 pagesService Manual: TAC-42CF TAC-42CHFMuhammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- H.E. 6-Week 3 Sewing Tools LECTUREDocument30 pagesH.E. 6-Week 3 Sewing Tools LECTUREChezca CumilangNo ratings yet
- Oferta KR 805-3g Kd1624Document6 pagesOferta KR 805-3g Kd1624Denisson Lopes Monteiro100% (1)
- CabineDocument29 pagesCabineFaustoNo ratings yet
- LIAISSON24 MIXBAAL MANUAL (English) YOMN4850-001 - RevE PDFDocument178 pagesLIAISSON24 MIXBAAL MANUAL (English) YOMN4850-001 - RevE PDFJuan Milton GardunoNo ratings yet
- 24-12 Switch Shutter Actuator V1.1-EnDocument46 pages24-12 Switch Shutter Actuator V1.1-EnYoga Nur HuzainiNo ratings yet
- Blackcore Raptor Lake Spec SheetDocument3 pagesBlackcore Raptor Lake Spec SheetNadendla mastan raoNo ratings yet
- Tanker Pipeline SystemsDocument22 pagesTanker Pipeline SystemsLogovaz91% (11)
- CDHD2 ECT CAN fw2.15.x Rev.1.0 PDFDocument499 pagesCDHD2 ECT CAN fw2.15.x Rev.1.0 PDFDon BozarthNo ratings yet
- XH320 Operations Manual Rev J (Eng)Document370 pagesXH320 Operations Manual Rev J (Eng)Goran BogdanoskiNo ratings yet
- Eng BD Tds4600b-Be-BsDocument4 pagesEng BD Tds4600b-Be-Bsguerouaz el madjidNo ratings yet
- Fuchs-Terex MHL 320-0965-1141-5-14.08.12-2Document944 pagesFuchs-Terex MHL 320-0965-1141-5-14.08.12-2Andrés Aroca100% (13)
- M 325 D (1) ElectDocument4 pagesM 325 D (1) ElectJesus CortesNo ratings yet
- Parallel Parking InstructionsDocument5 pagesParallel Parking Instructionsbra9tee9tiniNo ratings yet
- Rockwell JointerDocument18 pagesRockwell Jointernotjustsomeone100% (2)
- Belts and PulleysDocument28 pagesBelts and PulleysIwan SurachwantoNo ratings yet
- Fits and Clearances - Contents: Propeller Maintenance Manual 132ADocument8 pagesFits and Clearances - Contents: Propeller Maintenance Manual 132AAlexis KidemaNo ratings yet
- Land Rover Factory D3 Air Suspension DescriptionDocument22 pagesLand Rover Factory D3 Air Suspension Descriptionhelen100% (1)
- Airworthiness Directive Schedule: Helicopters Bell 47 Series & Kawasaki Bell 47 Series 25 June 2009Document12 pagesAirworthiness Directive Schedule: Helicopters Bell 47 Series & Kawasaki Bell 47 Series 25 June 2009Cristian PugaNo ratings yet