Professional Documents
Culture Documents
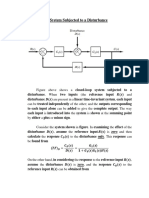
Advanced Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Eme Elibe Johnson EmestarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Eme Elibe Johnson EmestarCopyright:
Available Formats
ADVANCED FLUID
MECHANICS
SUPERVI SED BY:
DR. SAMEH SHAABAN
DONE BY:
ENG. AMI R AL- BATAL
ABSTRACT
At the first an introduction about the
advantages of CFD will be presented and
then I am going to show the CFD analysis
for the solved case which it is a duct with a
nozzle at the end and air flow in it with 3m/s
starting from the drawing on solidworks and
importing on pointwise to create the mesh
and exporting to the fluent as a solver then
reading the case using the fluent to solve
the case.
WHY WE WANT TO STUDY CFD ?
- Relatively low cost.
Using physical experiments and tests to get essential
engineering data for design can be expensive.
CFD simulations are relatively inexpensive, and costs are likely
to decrease as computers become more powerful.
- Speed.
CFD simulations can be executed in a short period of time.
Quick turnaround means engineering data can be introduced
early in the design process.
- Ability to simulate real conditions.
Many flow and heat transfer processes can not be (easily)
tested, e.g. hypersonic flow.
CFD provides the ability to theoretically simulate any physical
condition.
Because of its advantages, which is
ADVANTAGES OF CFD (2)
- Ability to simulate ideal conditions.
CFD allows great control over the physical process, and provides
the ability to isolate specific phenomena for study.
Example: a heat transfer process can be idealized with adiabatic,
constant heat flux, or constant temperature boundaries.
- Comprehensive information.
Experiments only permit data to be extracted at a limited
number of locations in the system (e.g. pressure and
temperature probes, heat flux gauges, LDV, etc.).
CFD allows the analyst to examine a large number of
locations in the region of interest, and yields a
comprehensive set of flow parameters for examination.
THE USED STEPS FOR SOLVING THE CASE :
1. Using solidworks.
2. Using pointwise.
3. Solving the case on the fluent.
1-THE SOLIDWORKS PRODUCT
I AM SAVING IN A .IGS FORMAT THAT POINTWISE CAN
IMPORT AS DATABASE
2. USING POINTWISE
IMPORTING THE DATABASE
AFTER IMPORTING
SELECTING SOLVER
CREATING CONNECTORS ON DATABASE ENTITIES
ASSEMBLING DOMAINS
DOMAINS
AFTER ASSEMBLING ALL DOMAINS
ASSEMBLING BLOCKS
THE BLOCKS
CALCULATING Y+
APPLYING S
AND THIS VIEW AFTER APPLYING S
THIS IS THE VIEW OF THE MESH
CHECKING EQUIANGLE SKEWENESS
CHECKING THE WALL ORTHOGONALITY
SETTING THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
SETTING THE VOLUME CONDITION
THE VOLUME CONDITIONS
EXPORTING CAE
3. SOLVING THE CASE ON THE FLUENT.
READING THE CASE
SCALING THE GRID
DEFINING THE SOLVER
SCALING THE VISCOUS MODEL
DEFINING THE OPERATING CONDITIONS
DEFINING THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
SETTING THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
DEFINING THE SOLUTION CONTROLS
MONITORING THE RESIDUALS AND EDITING THE
ABSOLUTE CRITERIA
CHECKING THE CASE
AND FINALLY SOLVING THE CASE
Then start to iterate
AND THE FLUENT STARTS TO PLOT THE SOLUTION
.
CONTINUING .
AND HERE WE CAN SEE IT IS GOING TOWARDS
CONVERGENCE
AND HERE IS THE SOLUTION
POST ANALYSIS
The contours of static pressure
The inlet
the outlet
The contours of Turbulent kinetic energy
The contours of velocity magnitude
THANK YOU
QUESTIONS ARE WELCOME
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- System CircuitsDocument234 pagesSystem CircuitsEme Elibe Johnson EmestarNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hydrocyclones For Particle Size SeparationDocument7 pagesHydrocyclones For Particle Size SeparationJean DejardinNo ratings yet
- GD&T PDFDocument109 pagesGD&T PDFBikash Chandra SahooNo ratings yet
- Axelrod SummaryDocument3 pagesAxelrod SummaryLuuk JanssenNo ratings yet
- GR 4 Mathematics 1st 4thDocument230 pagesGR 4 Mathematics 1st 4thGolden SunriseNo ratings yet
- Principles of Form and DesignDocument350 pagesPrinciples of Form and DesignNora Maloku100% (8)
- XYZ Data Analysis ReportDocument14 pagesXYZ Data Analysis ReportAshwini Kumar Maurya100% (1)
- Math8 - q1 - Mod12 - Finding The Equations of A Line - 08092020Document17 pagesMath8 - q1 - Mod12 - Finding The Equations of A Line - 08092020Cassandra Nicole FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Toyota CorollaDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Toyota CorollaEme Elibe Johnson EmestarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 AC Generators Transformers AC MotorsDocument57 pagesModule 3 AC Generators Transformers AC MotorsEme Elibe Johnson EmestarNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Induction MotorsDocument14 pagesTroubleshooting Induction MotorsImelda LadrilloNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On: Federal University of TechnologyDocument32 pagesTerm Paper On: Federal University of TechnologyEme Elibe Johnson EmestarNo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Analysis: Ujvnl Ae 2016Document7 pagesQuality Control and Analysis: Ujvnl Ae 2016Sagar ThengilNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate P90 (Or Other PXX) PV Energy Yield Estimates - SolargisDocument8 pagesHow To Calculate P90 (Or Other PXX) PV Energy Yield Estimates - SolargisgoyalmanojNo ratings yet
- Aits 2021 FT Ix Jeem.Document16 pagesAits 2021 FT Ix Jeem.Atharv AtoleNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument56 pagesStatisticsdimeNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Block DiagramDocument6 pagesHow To Draw Block DiagramAbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- PyBaMM PaperDocument9 pagesPyBaMM PapervishnuNo ratings yet
- DWDM R19 Unit 1Document27 pagesDWDM R19 Unit 1GAYATHRI KAMMARA 19MIS7006No ratings yet
- Acoustics Lab: Selected Topics On Acoustics-CommunicationDocument138 pagesAcoustics Lab: Selected Topics On Acoustics-CommunicationHeba Noweir100% (1)
- 2009-10 T.Y.B.SC. ElectronicsDocument26 pages2009-10 T.Y.B.SC. Electronicshys0671No ratings yet
- OOPM Theory QuestionsDocument7 pagesOOPM Theory Questionssheenam_bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Modelacion Calida Agua Parte 1Document14 pagesModelacion Calida Agua Parte 1Gisell AguilarNo ratings yet
- Cis110 12sp MidtermDocument8 pagesCis110 12sp Midtermdodoman666No ratings yet
- Representation of Numeric Data in Computer-1Document3 pagesRepresentation of Numeric Data in Computer-1Anthony LoñezNo ratings yet
- A Meta-Analysis of Research On Sensory Integration TreatmentDocument10 pagesA Meta-Analysis of Research On Sensory Integration TreatmentPaula CelsieNo ratings yet
- WRM Y6 Autumn b3 Four Operations Assessment BDocument2 pagesWRM Y6 Autumn b3 Four Operations Assessment BĐặng Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Tutorial 1Document2 pagesDynamics Tutorial 1ethanNo ratings yet
- Virtual Work (Deflection)Document46 pagesVirtual Work (Deflection)Rovic JayNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Acceleration Due To Gravity LabDocument6 pagesMeasuring The Acceleration Due To Gravity Labapi-616433899No ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment PDFMoazzam HussainNo ratings yet
- Phys 31 Module 4Document42 pagesPhys 31 Module 4Coyzz de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Analytical Dynamics - WikipediaDocument5 pagesAnalytical Dynamics - WikipediaHEIN HTETNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016Document3 pages1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016api-292307509No ratings yet
- Magnetic ForcesDocument6 pagesMagnetic ForcesJevaughn SmithNo ratings yet