Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 - Rate Laws and Stoichiometry - Stu
Uploaded by
Tiệp Matíc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views62 pagesToday's lecture covers three blocks:
1) Mole balances and reaction kinetics for CSTRs and PFRs.
2) Chemical reaction rates, orders, and the Arrhenius equation.
3) Stoichiometry, including stoichiometric tables and equilibrium conversion.
Original Description:
Original Title
4- Rate Laws and Stoichiometry_stu.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentToday's lecture covers three blocks:
1) Mole balances and reaction kinetics for CSTRs and PFRs.
2) Chemical reaction rates, orders, and the Arrhenius equation.
3) Stoichiometry, including stoichiometric tables and equilibrium conversion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views62 pages4 - Rate Laws and Stoichiometry - Stu
Uploaded by
Tiệp MatícToday's lecture covers three blocks:
1) Mole balances and reaction kinetics for CSTRs and PFRs.
2) Chemical reaction rates, orders, and the Arrhenius equation.
3) Stoichiometry, including stoichiometric tables and equilibrium conversion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 62
Todays Lecture
Block 1: Mole Balances (Review)
Size CSTRs and PFRs given r
A
=f(X)
Conversion for Reactors in Series
Block 2: Rate Laws
Reaction Orders
Arrhenius Equation
Activation Energy
Effect of Temperature
Block 3: Stoichiometry
Stoichiometric Table
Definitions of Concentration
Calculate the Equilibrium Conversion, X
e
Review of Mole Balances
Review of Conversion
A general reaction:
fed A moles
reacted A moles
X
D
a
d
C
a
c
B
a
b
A
n calculatio of basis as A reactant limiting Choose
D d C c B b A a
=
+ +
+ +
Levenspiel Plot (Review)
F
A0
r
A
X
CSTR(Review)
F
A0
r
A
X
Area = Volume of CSTR
X
1
V =
F
A0
r
A
|
.
|
X
1
- X
1
PFR(Review)
F
A0
r
A
Area = Volume of PFR
V =
0
X
1
}
F
A0
r
A
|
\
|
.
|
dX
X
1
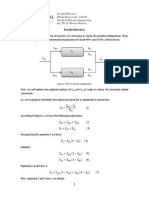
Reactors in Series (Review)
Two steps to get
Step 1: Rate Law
Step 2: Stoichiometry
Step 3: Combine to get
r
A
= f X
( )
r
A
= g C
i
( )
C
i
( )
= h X
( )
r
A
= f X
( )
10
Collision Theory
When one substance
is mixed with
another, the two
substances .
According to collision theory, atoms, ions, and
molecules can react to form ...
Rates of chemical reactions are often measured as ...
15
The factors that affect how ...
16
Factors influencing the likelyhood
of a reaction occurring:
1)
17
2)
18
3)
19
20
21
22
In order for the reaction to occur, the
particles involved must collide with
each other,
. Not every collision
results in a reaction.
activated complex
The is the temporary
arrangement of atoms as they
change from reactants into products.
23
Orientation
24
The colliding molecules
must have enough energy
to react and form an
. This minimum
amount of energy is called
the ..
activation energy
25
Rate of a Reaction = speed of reactants
turning into products
Can be measured in :
or
26
27
Effect of the Nature of the Reactant
The nature of the reactants involved will
determine the kind of reaction that occurs.
Reactions with bond rearrangements or
electron transfer take longer than reactions
without these changes
28
Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate
Increasing the temperature increases
the rate of a reaction. At higher
temperatures, the particles have more
energy, move faster and collide more
frequently. .
29
Effect of Concentration on Reaction Rate
Increasing the concentration of the
reactants increases the rate of a
reaction. ..
30
Effect of Particle Size/Surface Area
Decreasing particle size/increasing surface
area increases the rate of a reaction.
When .
31
Simulation
32
Not Cattle List!!
33
Catalyst
- any substance that is added to the reaction to
the rate. The catalyst .. react with any
substance to produce product.
Inhibitor
- Any substance added to . the rate of reaction.
Works against the catalyst.
34
C
2
H
2
H
2
C
2
H
4
35
A catalyst increases the rate of a
reaction by lowering the activation
energy.
36
Stoichiometry
Batch Systems
Batch Systems (Stoichiometric Table)
Batch Systems (Constant Volume)
Batch Systems (Example)
E
x
p
r
e
s
s
i
n
g
c
o
n
c
e
n
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
a
s
a
f
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
c
o
n
c
e
n
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
Example 1
Example2
Homework1
Homework2
Homework3
You might also like
- Chapter 3 Rates Law and StoichiometryDocument60 pagesChapter 3 Rates Law and StoichiometryMalek Marry AnneNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals and Applications of Lithium-ion Batteries in Electric Drive VehiclesFrom EverandFundamentals and Applications of Lithium-ion Batteries in Electric Drive VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Rate LawsDocument19 pagesRate LawsEli BerkowitzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction.Document38 pagesChapter 1 Introduction.yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Experimental Thermodynamics: Experimental Thermodynamics of Non-Reacting FluidsFrom EverandExperimental Thermodynamics: Experimental Thermodynamics of Non-Reacting FluidsB. Le NeindreNo ratings yet
- 1.cre IntroDocument33 pages1.cre IntroArunPThomasNo ratings yet
- CHEM 212: Phase EquilibriaDocument68 pagesCHEM 212: Phase EquilibriaSerwan BamerniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Phase EquilibriaDocument57 pagesLecture 2 - Phase Equilibria20-02259No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document41 pagesChapter 6Hotib PerwiraNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Homogeneous Reactions Simple Reactor TypesDocument9 pagesKinetics of Homogeneous Reactions Simple Reactor TypesNikai Hermawan AmrullahNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Homogeneous ReactionDocument56 pagesKinetics of Homogeneous ReactionSahel SahraeeNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design Sample ExamDocument7 pagesReactor Design Sample ExamAugustine BrockNo ratings yet
- Chemical Potential in Mixtures: Partial Molar Quantities Thermodynamics of Mixing The Chemical Potentials of LiquidsDocument61 pagesChemical Potential in Mixtures: Partial Molar Quantities Thermodynamics of Mixing The Chemical Potentials of Liquidsjayven minguillanNo ratings yet
- Isothermal Reactor Design: 1. Batch OperationDocument3 pagesIsothermal Reactor Design: 1. Batch Operationنزار الدهاميNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Particlesizeand Distribution 2019Document2 pagesTutorial Particlesizeand Distribution 2019GauravKinngNo ratings yet
- Partial Molar Heat Content and Chemical Potential, Significance and Factors Affecting, Gibb's-Duhem EquationDocument11 pagesPartial Molar Heat Content and Chemical Potential, Significance and Factors Affecting, Gibb's-Duhem EquationRhakhoNo ratings yet
- Entropy ChangeDocument13 pagesEntropy ChangeAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- Group Assignment Q1Document2 pagesGroup Assignment Q1Muhdhadi SajariNo ratings yet
- r05220802 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics IDocument6 pagesr05220802 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics ISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- ChE 471 EXAM 1 2005Document2 pagesChE 471 EXAM 1 2005HungDoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Properties of A Pure Substance: ThermodynamicsDocument62 pagesChapter 3: Properties of A Pure Substance: ThermodynamicsAnurag PanditNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document23 pagesLecture 9amirmasoudNo ratings yet
- 14 EquilibriumDocument6 pages14 EquilibriumAgam HanasichulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture W12 20232Document29 pagesLecture W12 2023214Adi Zawawi AzmanNo ratings yet
- 8 3 Packed Bed ReactorsDocument20 pages8 3 Packed Bed ReactorsridhajamelNo ratings yet
- Accident and Loss StatisticsDocument41 pagesAccident and Loss StatisticsudjilNo ratings yet
- DWA OptimizationsDocument12 pagesDWA OptimizationssannyzhouNo ratings yet
- Green ChemistryDocument17 pagesGreen ChemistryTo BinhNo ratings yet
- Smit Ds Chapter 2Document29 pagesSmit Ds Chapter 2alinoriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ChE 126Document94 pagesChapter 9 ChE 126Roque LeccioNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Design of Reaction/Separation ProcessesDocument8 pagesHeuristic Design of Reaction/Separation ProcessesAndrea VittoNo ratings yet
- Notes5 Simple ReactorsDocument40 pagesNotes5 Simple ReactorsstorkjjNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument101 pagesChemical Reaction EngineeringGerard Toby CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Heat Ingeration of ReactorsDocument29 pagesHeat Ingeration of ReactorsSharmimi RazakNo ratings yet
- Assignment WWTD 2Document9 pagesAssignment WWTD 2imranNo ratings yet
- Surface Phenomena PDFDocument5 pagesSurface Phenomena PDFDurga Prasad KalamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium NotesDocument11 pagesChemical Equilibrium NotesNeha Kaur SinhaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Reaction - Lecture 1Document39 pagesAdvanced Reaction - Lecture 1nahomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Process Control (P1)Document30 pagesLecture 2 - Process Control (P1)Elia SaadNo ratings yet
- Ex0 Questions SolutionsDocument7 pagesEx0 Questions SolutionsBiniyam haileNo ratings yet
- Ugpa3033 Process Optimization and Simulation Tutorial 4Document1 pageUgpa3033 Process Optimization and Simulation Tutorial 4Tko Kai OnnNo ratings yet
- Material Balances 1Document25 pagesMaterial Balances 1Jemimah IshayaNo ratings yet
- Unit Outline and Introduction To Design: © HB Vuthaluru 2006Document41 pagesUnit Outline and Introduction To Design: © HB Vuthaluru 2006Adrian John Soe MyintNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 Chapter1 Molebalancepart1Document42 pagesLecture2 Chapter1 Molebalancepart1Nur SafiahNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemical Engineering CalculationsDocument7 pagesApplied Chemical Engineering Calculationsmbolantenaina100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document35 pagesChapter 4Leon TanNo ratings yet
- Sequential Modular and Simultaneous Modular StrategiesDocument13 pagesSequential Modular and Simultaneous Modular Strategieskim haksongNo ratings yet
- PROP6020 PDocument20 pagesPROP6020 PlukeneerNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design Input Out Structure 2020Document41 pagesConceptual Design Input Out Structure 2020Leencie SandeNo ratings yet
- Derive Perfectly Stirred ReactorDocument3 pagesDerive Perfectly Stirred ReactorTiefu ZhuNo ratings yet
- Parallel Reactors Daniel Sierra Cód.: 244706 Chemical Reaction Engineering Ing. Ph. D. Herney RamírezDocument6 pagesParallel Reactors Daniel Sierra Cód.: 244706 Chemical Reaction Engineering Ing. Ph. D. Herney RamírezDaniel Sierra SantofimioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Collection and Analysis of Rate DataDocument13 pagesLecture 9 - Collection and Analysis of Rate DataSabrina AzharNo ratings yet
- Test 1 CKB 30103 July 2017 Answer Scheme Rev 1Document9 pagesTest 1 CKB 30103 July 2017 Answer Scheme Rev 1nur hidayatiNo ratings yet
- 3K4 2013 Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument9 pages3K4 2013 Assignment 2 SolutionsKhalil LasferNo ratings yet
- Recycle. Process EngineeringDocument20 pagesRecycle. Process EngineeringDarel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 4 - Rate Laws and Stoichiometry - StuDocument62 pages4 - Rate Laws and Stoichiometry - StuNguyễn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Chap 05 NewDocument83 pagesChemistry Form 6 Chap 05 Newmusafir24No ratings yet
- 2.kinetics Homogenous ReactionsDocument33 pages2.kinetics Homogenous ReactionsArief Al Imam HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Tài Loeeuj Thầy HaitDocument237 pagesTài Loeeuj Thầy HaitTiệp Matíc100% (2)
- 5 - Collection and Analysis of Rate Data - StuDocument26 pages5 - Collection and Analysis of Rate Data - StuTiệp MatícNo ratings yet
- ECH 146 Homework 1 Due Friday, 17/1/2014Document1 pageECH 146 Homework 1 Due Friday, 17/1/2014Tiệp MatícNo ratings yet
- 2 - Mole Balances - StuDocument31 pages2 - Mole Balances - StuTiệp MatícNo ratings yet
- EY Commercial Real Estate DebtDocument16 pagesEY Commercial Real Estate DebtPaul BalbinNo ratings yet
- Finra Bond InfoDocument151 pagesFinra Bond InfoPropertywizzNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Kimia Organik - 2Document40 pagesReaksi Kimia Organik - 2Galaxy Abdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. L1. Structure & BondingDocument35 pagesChapter 1. L1. Structure & BondingMohammad Al-KhoderNo ratings yet
- EnzEng 2 EnzymeKinetics C V VIIDocument43 pagesEnzEng 2 EnzymeKinetics C V VIIEkuino Simanungkalit100% (1)
- 9701 s16 QP 41Document20 pages9701 s16 QP 41ابرارفاروقNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument16 pagesExamnicolas dionisio ordonez barruetaNo ratings yet
- An Alternative To Conventional Bond-Swap Curve PositionsDocument45 pagesAn Alternative To Conventional Bond-Swap Curve PositionsJay Prakash SavageNo ratings yet
- Theory of Interest Kellison Solutions Chapter 011Document15 pagesTheory of Interest Kellison Solutions Chapter 011Virna Cristina Lazo100% (1)
- 2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 2Document8 pages2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 2Prasad C M100% (1)
- Organic Acids & Organic BasesDocument20 pagesOrganic Acids & Organic BasesCheng KathyNo ratings yet
- Gmo 7 Year Asset Class Forecast (1q2017)Document1 pageGmo 7 Year Asset Class Forecast (1q2017)superinvestorbulletiNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document3 pagesHW 4api-368121935No ratings yet
- Sovereign Gold Bond 8Document3 pagesSovereign Gold Bond 8sriniNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Chennai Region Class Xii - Revision - Chemistry Scoring KeyDocument12 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Chennai Region Class Xii - Revision - Chemistry Scoring Keyilias1973No ratings yet
- 9701 w15 Ms 41Document13 pages9701 w15 Ms 41MCH100% (1)
- Corporate Finance QuizDocument9 pagesCorporate Finance QuizRahul TiwariNo ratings yet
- Csir Ugc JRF Net Chemistry Paper 1 (Part B) Series - 1Document22 pagesCsir Ugc JRF Net Chemistry Paper 1 (Part B) Series - 1polamrajuNo ratings yet
- Hehre, W. J. Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Theory. Acc. Chem. Res.Document8 pagesHehre, W. J. Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Theory. Acc. Chem. Res.Carlos PezoNo ratings yet
- BFM Collection From FBDocument13 pagesBFM Collection From FBnavneet gauravNo ratings yet
- Stability of Minerals PDFDocument380 pagesStability of Minerals PDFcemalbalciNo ratings yet
- Amorphous PolymerDocument14 pagesAmorphous PolymerWahyu SulistyoNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation Version 1.XlsbDocument14 pagesBond Valuation Version 1.XlsbAlie Dys100% (1)
- What Is A Bond Pricing AgencyDocument61 pagesWhat Is A Bond Pricing AgencyMeor Amri100% (4)
- Microbiology NotesDocument177 pagesMicrobiology NotesMarichu Rogas91% (11)
- JAIIB Accounting Module A NotesDocument205 pagesJAIIB Accounting Module A NotesAkanksha MNo ratings yet
- CH (8) L209 PDFDocument6 pagesCH (8) L209 PDFbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Mind Map ChemistryDocument3 pagesMind Map ChemistryTheesha SophieNo ratings yet
- Horie Adhesivesglossary PDFDocument11 pagesHorie Adhesivesglossary PDFDan Octavian Paul100% (1)