Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Chain - Shawqi
Uploaded by
Shawqi batranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Chain - Shawqi
Uploaded by
Shawqi batranCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Chain Department
ASIA
Pharmaceutical
Industries
Eng. Shawqi A. Al.Batran
Supply Chain Manager
2
Supply Chain-Definitions
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the management of a network of
interconnected businesses involved in the ultimate provision of product and
service packages required by end customers.
Supply Chain Management spans all movement and storage of raw
materials, work in process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin
to point of consumption.
SCM is a cross functional interenterprise system that uses information
technology to help support and manage links between some of a companys
key business processes and those of its suppliers, customers, and business
partners.
Supply chain management has generated much interest in recent years for
a number of reasons. Many managers now realize that actions taken by one
member of the chain can influence the profitability of all others in the chain.
3
Supply Chain
4
Supply Chain Department Structure
Supply Chain
ERP
Department
Procurement
Department
Demand
Planning
Department
Supply
Planning
Department
Tenders
Department
Warehouses
CAPEX
Department
Logistics
Department Objectives
5
Create an awareness of the supply chain structure including
organizations, capabilities, strengths, weaknesses and opportunities for
Improvement.
Build a stronger supply chain through the development of bonded and
collaborative relationships with business partners
Increase supply chain end-to-end visibility with real time communications of
inventory requirements, orders, shipments, payments and performance.
Improve forecast, planning and replenishment accuracy
Reduce costs and increase profits through increased efficiencies,
negotiations and compliance
Reduce inventory levels through inventory management disciplines
Improve service levels through performance management
Get the right product in the right place at the right time with the right quality
Implementing ERP System
6
Ordering RM
7
8
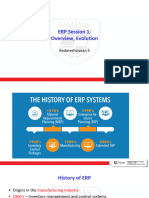
ERP Systems
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) integrates
internal and external management information
across an entire organization, embracing
finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and
service, etc.
ERP systems automate this activity with an
integrated software application. Its purpose is to
facilitate the flow of information between all
business functions inside the boundaries of the
organization and manage the connections to outside
stakeholders.
What is ERP
Two common things that people usually talk
about ERP are ERP system and ERP software.
ERP system refers to all components required
to establish the system, such as ERP software,
IT Infrastructure, business process and so on.
Thus, ERP software is part of the ERP system.
But sometime people do not distinguish ERP
system and ERP software.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Why Do We Need an ERP System?
Increased operational effectiveness & Productivity
Timely and targeted information feedback system for
decision support
Efficient inventory management
Improved Planning
Improved customer service
Compliant to cGMPs /21 CFR Part 11
Control of your finances top to bottom
ERP Modules
There are many ERP modules in ERP software
solution. Each ERP software module
corresponds to a major functional area of an
organization. Generally it includes, modules
for material purchasing, inventory control,
product planning, product distribution,
tracking the order, financial ERP module,
accounting, marketing, quality and human
resource
A "module" is a group of related programs performing a major function within an ERP
ERP Process Flow
S
a
l
e
s
F
o
r
e
c
a
s
t
Sales Forecast
Production
Planning & Control
Scheduling
P
a
c
k
a
g
in
g
Production
Stores
Warehouse
(Finished Products)
Dispatch
Master
Recipe
Workcentre
Hierarchy
Shop Floor
In-Process
Control
cGMP
guidelines
Computer Aided
Manufacturing
Routing
Capacity
Planning
Materials
Management
(Inventory)
BOM
cGMP
guidelines
Inspection
Plan
Inspection
Record
Audit Report
cGMP
Warehouse
Management
System
Finished
Goods
Raw Material
Qurantine,Approved,
Rejected
Purchase
Management
Finance
Management
Costing
Receivable
Payable
Process
Flow
Quality
Assurance
ERP Vendors
Do you know how many ERP vendor worldwide?
They are more than fifty and could be more than
one hundred including local ERP software.
Which ones are considered as Top ERP vendor?
Most people will tell that SAP is the most top ERP
vendor because one of the reasons is they have
had a lot of enterprise scale clients.
ERP Market Share and Vendor
Evaluation
Vendor Sales by Industry
Vendor Sales by Industry
Vendor Sales by Industry
Vendor Sales by Industry
Vendor Sales by Industry
ERP Selection Criteria
Selection Template
Materials requirement planning
MRP
The main objective of MRP is to guarantee material
availability.
MRP is required to procure or produce the required
quantities on time for internal purpose or for SALES.
WHY MRP ?
Optimizing service level
Minimizing costs and capital lockup.
MRP 1
MRP 2
MRP 3
MRP 4
Stock Requirements List
27
You might also like
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Presented By: Makansingh ChauhanDocument28 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Presented By: Makansingh ChauhanGuru Darshan0% (1)
- Business Processing ReengineeringDocument3 pagesBusiness Processing ReengineeringAAYUSHI MOONKANo ratings yet
- ERP ConceptsDocument27 pagesERP ConceptsLaxmi PaiNo ratings yet
- Session 01Document23 pagesSession 01Anket SinghNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource and Planning - ERPDocument20 pagesEnterprise Resource and Planning - ERPyogendra reddyNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal OF ERPDocument7 pagesProject Proposal OF ERPbik00090% (5)
- An Overview of Enterprise Resource Planning (Erp)Document13 pagesAn Overview of Enterprise Resource Planning (Erp)sunnygangisettiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Categories of PEAS New (Compatibility Mode)Document34 pages2.2 Categories of PEAS New (Compatibility Mode)Magarsa BedasaNo ratings yet
- "Erp Uses in Management and Supply Chain": Project Report OnDocument19 pages"Erp Uses in Management and Supply Chain": Project Report OnAman KumarNo ratings yet
- Erp - Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument22 pagesErp - Enterprise Resource PlanningShravana ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Q-A SCMDocument4 pagesQ-A SCMDil FarzanaNo ratings yet
- CRM Program Using Oracle EBS - Student GuideDocument589 pagesCRM Program Using Oracle EBS - Student GuideShakti NaiduNo ratings yet
- ERPgDocument24 pagesERPgLokesh ShewaniNo ratings yet
- ERPDocument55 pagesERPSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- SCM & ErpDocument31 pagesSCM & ErpVrinda MadhuNo ratings yet
- LectraDocument38 pagesLectraNiharika SinhaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument19 pagesEnterprise Resource PlanningAswanNo ratings yet
- ERP ConceptsDocument27 pagesERP ConceptsPranav JainNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning June 2023 Assignment SolutionDocument10 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning June 2023 Assignment SolutionAnket SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal OF ERPDocument7 pagesProject Proposal OF ERPsecurics0% (1)
- Erp-Boon To Supply Chain Management - Sastra UniversityDocument14 pagesErp-Boon To Supply Chain Management - Sastra UniversityPradeesh Kumar.ANo ratings yet
- ERP OverviewDocument16 pagesERP OverviewAtanu GhoshNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 SCM BDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 SCM BGurlal SinghNo ratings yet
- Finally ErpDocument37 pagesFinally Erpsadiaf507No ratings yet
- 3108 - MIS Assignment 3Document14 pages3108 - MIS Assignment 3Nirvana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- ERP Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesERP Supply Chain ManagementJoms LucerioNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument44 pagesEnterprise Resource PlanningDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain ManagementDocument4 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain ManagementsahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Why ERP Important for EngineersDocument26 pagesWhy ERP Important for EngineersHassan AzizNo ratings yet
- Ms Office Mod 2Document12 pagesMs Office Mod 2MADHULIKA SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument6 pagesEnterprise Resource PlanningKAUSHIK SUNDARARAJANNo ratings yet
- Business ProcessDocument34 pagesBusiness Processjoyce plandNo ratings yet
- ERP in Inventory ManagementDocument36 pagesERP in Inventory ManagementVicky VigneshNo ratings yet
- R12 Finance Student GuideDocument479 pagesR12 Finance Student Guidemandeeppathak100% (3)
- Module 5Document23 pagesModule 5PREJA PATELNo ratings yet
- Quiz GSCMDocument3 pagesQuiz GSCMGurlal SinghNo ratings yet
- Apparel Quality Management 2: Assignment: 2Document16 pagesApparel Quality Management 2: Assignment: 2AnushkaNo ratings yet
- Erp 1Document39 pagesErp 1Samson GoaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document30 pagesModule 5PREJA PATELNo ratings yet
- ERPDocument33 pagesERPLovepreetSidhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document20 pagesChapter 07Nusa FarhaNo ratings yet
- ITM7-Group2 PepsiAmericasDocument11 pagesITM7-Group2 PepsiAmericasSneha Lundia AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document37 pagesModule 5zkharuri7220No ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Erp Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Is An Integrated Computer-Based SystemDocument51 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Erp Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Is An Integrated Computer-Based Systemchandru5g100% (4)
- Enterprise Management System (ERP)Document23 pagesEnterprise Management System (ERP)Ramesh SafareNo ratings yet
- Erp - MtaDocument47 pagesErp - MtaAnik KararNo ratings yet
- Erp AssignmentDocument15 pagesErp AssignmentAfrah Abdul AzeezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part ADocument42 pagesUnit 1 Part AShanthiNo ratings yet
- ERPDocument11 pagesERPaskmeeNo ratings yet
- ERP Unit 12 Benefits of ERPDocument14 pagesERP Unit 12 Benefits of ERPAnonymous bTh744z7E60% (1)
- Phases of Erp ImplementationDocument20 pagesPhases of Erp ImplementationSuda Aravindnath ReddyNo ratings yet
- ERP - DefinitionDocument55 pagesERP - DefinitionasaNo ratings yet
- Top 20 Erp PDFDocument8 pagesTop 20 Erp PDFCardeas XuNo ratings yet
- ERP For Retail Sector: Presented By: Astha Priyamvada Roll No. 38 IM 18 Section ADocument12 pagesERP For Retail Sector: Presented By: Astha Priyamvada Roll No. 38 IM 18 Section AAstha PriyamvadaNo ratings yet
- Erp Prasent and FeaturesDocument46 pagesErp Prasent and FeaturesPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain and Procurement Quick Reference: How to navigate and be successful in structured organizationsFrom EverandSupply Chain and Procurement Quick Reference: How to navigate and be successful in structured organizationsNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning (Erp) the Great Gamble: An Executive’S Guide to Understanding an Erp ProjectFrom EverandEnterprise Resource Planning (Erp) the Great Gamble: An Executive’S Guide to Understanding an Erp ProjectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Customer-Anchored Supply Chains: An Executive’S Guide to Building Competitive Advantage in the Oil PatchFrom EverandCustomer-Anchored Supply Chains: An Executive’S Guide to Building Competitive Advantage in the Oil PatchNo ratings yet
- The German Tradition of Psychology in Literature and Thought 1700-1840 PDFDocument316 pagesThe German Tradition of Psychology in Literature and Thought 1700-1840 PDFerhan savasNo ratings yet
- Quraani Nabatat K Khwas o Afadiat Tib e Jadeed K Nuqta e Nazar Se Fayaz Ahmed PH.D 2010Document542 pagesQuraani Nabatat K Khwas o Afadiat Tib e Jadeed K Nuqta e Nazar Se Fayaz Ahmed PH.D 2010Muhammad Ahmed Tarazi100% (1)
- Activity 1.docx AjDocument2 pagesActivity 1.docx AjMaya BabaoNo ratings yet
- Past Progressive WorksheetDocument3 pagesPast Progressive WorksheetSantiago VargasNo ratings yet
- Nucor at A CrossroadsDocument10 pagesNucor at A CrossroadsAlok C100% (2)
- School Name Address Contact No. List of Formal Schools: WebsiteDocument8 pagesSchool Name Address Contact No. List of Formal Schools: WebsiteShravya NEMELAKANTINo ratings yet
- Met Worksheet Atmosphere QuestionsDocument4 pagesMet Worksheet Atmosphere QuestionsSujan IyerNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper About Educational Administration (Ivy M. Peralta)Document1 pageReflection Paper About Educational Administration (Ivy M. Peralta)Ivy peraltaNo ratings yet
- Rail Section As Per IrsDocument6 pagesRail Section As Per IrskarnagaNo ratings yet
- 201233646Document48 pages201233646The Myanmar TimesNo ratings yet
- Development of Overall Audit StrategyDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Overall Audit StrategyPhrexilyn PajarilloNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion Throughout The Life Span 8Th Edition Edelman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesHealth Promotion Throughout The Life Span 8Th Edition Edelman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDeborahAndersonmkpy100% (10)
- Class XII PHY - EDDocument7 pagesClass XII PHY - EDsampoornaswayamNo ratings yet
- Intrrogative: Untuk Memenuhi Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris DasarDocument9 pagesIntrrogative: Untuk Memenuhi Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris DasarRachvitaNo ratings yet
- Open NNDocument2 pagesOpen NNsophia787No ratings yet
- Aits 2223 PT III Jeea Paper 1Document15 pagesAits 2223 PT III Jeea Paper 1Suvrajyoti TaraphdarNo ratings yet
- Reading - Zeeshan UsmaniDocument25 pagesReading - Zeeshan UsmaniHanif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Mammals of South America, Vol. 2 PDFDocument1,363 pagesMammals of South America, Vol. 2 PDFJose Jaime Henao OsorioNo ratings yet
- Write EssayDocument141 pagesWrite Essayamsyous100% (1)
- Vacuum Pump Manual (English)Document12 pagesVacuum Pump Manual (English)nguyen lam An100% (1)
- Pageant Questions For Miss IntramuralsDocument2 pagesPageant Questions For Miss Intramuralsqueen baguinaon86% (29)
- Pavement Design and Maintenance: Asset Management Guidance For Footways and Cycle RoutesDocument60 pagesPavement Design and Maintenance: Asset Management Guidance For Footways and Cycle RoutesGaneshmohiteNo ratings yet
- Management of Chronic ITP: TPO-R Agonist Vs ImmunosuppressantDocument29 pagesManagement of Chronic ITP: TPO-R Agonist Vs ImmunosuppressantNiken AmritaNo ratings yet
- Under DronesDocument336 pagesUnder DronesRobert LewisNo ratings yet
- Job - RFP - Icheck Connect Beta TestingDocument10 pagesJob - RFP - Icheck Connect Beta TestingWaqar MemonNo ratings yet
- Cotton-Top Tamarin - Husbandry - ManualDocument98 pagesCotton-Top Tamarin - Husbandry - Manualjoaquin chan100% (1)
- Eichhornia Crassipes or Water HyacinthDocument5 pagesEichhornia Crassipes or Water HyacinthJamilah AbdulmaguidNo ratings yet
- Abcdef Ghijkl Mnopq Rstuv Wxyz Alphabet Backpack Book Bookcase CalculatorDocument4 pagesAbcdef Ghijkl Mnopq Rstuv Wxyz Alphabet Backpack Book Bookcase Calculatornutka88No ratings yet
- Study Guide For Kawabata's "Of Birds and Beasts"Document3 pagesStudy Guide For Kawabata's "Of Birds and Beasts"BeholdmyswarthyfaceNo ratings yet
- RMET Score Sheet AnalysisDocument1 pageRMET Score Sheet AnalysisJohnNo ratings yet