Professional Documents
Culture Documents
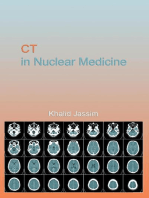
Resolution: All Remote Sensing Systems Have Four Types of Resolution
Uploaded by
Yugandhar Damalla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views22 pagesThe document discusses the four types of resolution that all remote sensing systems have: spatial, spectral, temporal, and radiometric. It also outlines the key elements used in image interpretation, including shape, shadow, tone and color, texture, pattern, height and depth, and association. These elements provide important visual cues when analyzing imagery from remote sensing.
Original Description:
All remote sensing systems have four types of resolution:
Spatial
Spectral
Temporal
Radiometric
Original Title
Resolution Visual Interpretation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the four types of resolution that all remote sensing systems have: spatial, spectral, temporal, and radiometric. It also outlines the key elements used in image interpretation, including shape, shadow, tone and color, texture, pattern, height and depth, and association. These elements provide important visual cues when analyzing imagery from remote sensing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views22 pagesResolution: All Remote Sensing Systems Have Four Types of Resolution
Uploaded by
Yugandhar DamallaThe document discusses the four types of resolution that all remote sensing systems have: spatial, spectral, temporal, and radiometric. It also outlines the key elements used in image interpretation, including shape, shadow, tone and color, texture, pattern, height and depth, and association. These elements provide important visual cues when analyzing imagery from remote sensing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Resolution
All remote sensing systems have four types of
resolution:
Spatial
Spectral
Temporal
Radiometric
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
High vs. Low?
Spatial Resolution
Source: Jensen (2000)
Source: Jensen (2000)
Spectral
Resolution
Temporal Resolution
Time
July 1
July 12
July 23 August 3
11 days
16 days
July 2 July 18 August 3
Radiometric Resolution
6-bit range
0
63
8-bit range
0 255
0
10-bit range
1023
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Shape:
Many natural and human-made features have
unique shapes.
Often used are adjectives like linear,
curvilinear, circular, elliptical, radial, square,
rectangular, triangular, hexagonal, star,
elongated, and amorphous.
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Jensen (2000)
Shape
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Shadow:
Shadow reduction is of concern in remote sensing
because shadows tend to obscure objects that
might otherwise be detected.
However, the shadow cast by an object may be
the only real clue to its identity.
Shadows can also provide information on the
height of an object either qualitatively or
quantitatively.
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Jensen (2000)
Shadow
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Tone and Color:
A band of EMR recorded by a remote sensing
instrument can be displayed on an image in
shades of gray ranging from black to white.
These shades are called tones, and can be
qualitatively referred to as dark, light, or
intermediate (humans can see 40-50 tones).
Tone is related to the amount of light reflected
from the scene in a specific wavelength interval
(band).
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Jensen (2000)
Tone and Color
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Texture:
Texture refers to the arrangement of tone or color
in an image.
Useful because Earth features that exhibit similar
tones often exhibit different textures.
Adjectives include smooth (uniform,
homogeneous), intermediate, and rough (coarse,
heterogeneous).
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Jensen (2000)
Texture
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Pattern:
Pattern is the spatial arrangement of objects on
the landscape.
General descriptions include random and
systematic; natural and human-made.
More specific descriptions include circular, oval,
curvilinear, linear, radiating, rectangular, etc.
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Jensen (2000)
Pattern
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Height and Depth:
As discussed, shadows can often offer clues to the
height of objects.
In turn, relative heights can be used to interpret
objects.
In a similar fashion, relative depths can often be
interpreted.
Descriptions include tall, intermediate, and short;
deep, intermediate, and shallow.
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Height and Depth
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Elements of Image Interpretation
Association:
This is very important when trying to
interpret an object or activity.
Association refers to the fact that certain
features and activities are almost always
related to the presence of certain other
features and activities.
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Jensen (2000)
Association
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
ND GIS Users Workshop
Bismarck, ND October 24-26,
2005
Imaging Tools and Data
Google Earth
ERDAS Imagine
Digital Northern Great
Plains
You might also like
- LEC5 - Interpreting Earth Surface DigitallyDocument64 pagesLEC5 - Interpreting Earth Surface DigitallyNaim LotfiNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing Introduction to Image InterpretationDocument25 pagesRemote Sensing Introduction to Image InterpretationAKASH MAURYANo ratings yet
- Visual Image Interpretation Techniques and ApplicationsDocument37 pagesVisual Image Interpretation Techniques and ApplicationslahiyaNo ratings yet
- Hyperspectral Edge Filtering For Measuring Homogeneity of Surface Cover Types BakkerDocument11 pagesHyperspectral Edge Filtering For Measuring Homogeneity of Surface Cover Types BakkerAmarjargal DavaadorjNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument8 pagesAnswersAnonymous lt2LFZHNo ratings yet
- Ec1009 Digital Image ProcessingDocument37 pagesEc1009 Digital Image Processinganon-694871100% (15)
- Motivation For Ip: Rakesh Soni M.E. (CSE) Assistant Professor, PietDocument87 pagesMotivation For Ip: Rakesh Soni M.E. (CSE) Assistant Professor, PietRakeshSoniNo ratings yet
- EC2029 Digital Image Processing Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument34 pagesEC2029 Digital Image Processing Two Mark Questions and AnswerspoongodiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 DIP Fall 2019Document82 pagesLecture 02 DIP Fall 2019Naimal MasoodNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1.3 AGP-316Document6 pagesExperiment 1.3 AGP-316Tej pattaNo ratings yet
- Blur and DisorderDocument8 pagesBlur and DisorderdavidrojasvNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument37 pagesQuestion BankViren PatelNo ratings yet
- A Review On Image Segmentation Techniques: Abstract - ManyDocument18 pagesA Review On Image Segmentation Techniques: Abstract - ManyMili MiliNo ratings yet
- A Review On Image Denoising TechniquesDocument6 pagesA Review On Image Denoising TechniquesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- EC2029-Digital Image Processing Two Marks Questions and Answers - New PDFDocument20 pagesEC2029-Digital Image Processing Two Marks Questions and Answers - New PDFNathan Bose Thiruvaimalar NathanNo ratings yet
- Digital Imaging FundamentalsDocument158 pagesDigital Imaging Fundamentalsexample exampleNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Tutorial Questions AnswersDocument38 pagesDigital Image Processing Tutorial Questions Answersanandbabugopathoti100% (1)
- KUET EEE CourseDocument27 pagesKUET EEE CourseShoikotNo ratings yet
- Advanced Methods For Image Segmentation: Ilya Pollak Purdue UniversityDocument49 pagesAdvanced Methods For Image Segmentation: Ilya Pollak Purdue UniversityGaurav ParwalNo ratings yet
- 391-B0001Document10 pages391-B0001Mohamed KaramNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Image Denoising Method Using SVM ClassificationDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Image Denoising Method Using SVM ClassificationGRENZE Scientific SocietyNo ratings yet
- Geo-Informatics (CE-287) : Misbah Kiran MCE-Risalpur NustDocument37 pagesGeo-Informatics (CE-287) : Misbah Kiran MCE-Risalpur NustIsrar KhanNo ratings yet
- Geospatial Data Acquisition Using Unmanned Aerial Systems (Uas) A Paradigm For Mapping The Built Environment of The Niger Delta Region of NigeriaDocument14 pagesGeospatial Data Acquisition Using Unmanned Aerial Systems (Uas) A Paradigm For Mapping The Built Environment of The Niger Delta Region of NigeriaIEREKPRESSNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Digital Image ProcessingDocument37 pages2 Marks Digital Image Processingrajat287100% (1)
- At-Satellite Reflectance: A First Order Normalization of Landsat 7 Etm+ ImagesDocument9 pagesAt-Satellite Reflectance: A First Order Normalization of Landsat 7 Etm+ ImagesHerie WidiyantoNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing: Week # 2 Lecture # 4-6Document42 pagesDigital Image Processing: Week # 2 Lecture # 4-6Aamir ChohanNo ratings yet
- Abhishek KushDocument17 pagesAbhishek KushAbhishek KushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Digital Image FundamentalsDocument51 pagesChapter 2: Digital Image FundamentalsMộtConMèoNo ratings yet
- B.Tech-Information Technology Sixth Semester Digital Image Processing (IT 603) NotesDocument19 pagesB.Tech-Information Technology Sixth Semester Digital Image Processing (IT 603) NotesnannurahNo ratings yet
- Basic Relationships between pixels, Geometric Transformation and Pin hole CameraDocument11 pagesBasic Relationships between pixels, Geometric Transformation and Pin hole CameraAlRowad Team technologyNo ratings yet
- ST - Joseph's College of Engineering, Chennai-119 Department of ECE Digital Image Processing (Ec2029)Document19 pagesST - Joseph's College of Engineering, Chennai-119 Department of ECE Digital Image Processing (Ec2029)Shenthur PandianNo ratings yet
- Evren ImageclassificationDocument78 pagesEvren ImageclassificationtechmoorthiNo ratings yet
- 02 Topic ImageDataDocument61 pages02 Topic ImageDatadevenderNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Question Answer BankDocument69 pagesDigital Image Processing Question Answer Bankkarpagamkj759590% (72)
- Saliency Map PresentationDocument38 pagesSaliency Map PresentationhassamaliNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUESDocument27 pagesDIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUESJomin PjoseNo ratings yet
- Image Processing Question Answer BankDocument54 pagesImage Processing Question Answer Bankchris rubishaNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Question Answer BankDocument3 pagesDigital Image Processing Question Answer BankJerryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4brev - Digital Image ProcessingDocument85 pagesChapter 4brev - Digital Image ProcessingFaran MasoodNo ratings yet
- Color-Based Object RecognitionDocument12 pagesColor-Based Object RecognitionAndrada CirneanuNo ratings yet
- Measure Texture Content in Multi-Spectral ImagesDocument20 pagesMeasure Texture Content in Multi-Spectral ImagesAlejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- (Main Concepts) : Digital Image ProcessingDocument7 pages(Main Concepts) : Digital Image ProcessingalshabotiNo ratings yet
- Edge Detection-Application of (First and Second) Order Derivative in Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesEdge Detection-Application of (First and Second) Order Derivative in Image ProcessingBhuviNo ratings yet
- RS & GIS Image Enhancement: Contrast StretchingDocument20 pagesRS & GIS Image Enhancement: Contrast StretchingSatya Chandra PernidiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document34 pagesLecture 11An TranNo ratings yet
- LED Source Modeling For Optical Design Workbook Davis 2004Document66 pagesLED Source Modeling For Optical Design Workbook Davis 2004FabocciNo ratings yet
- Transformada Distancia ArticuloDocument6 pagesTransformada Distancia ArticuloGustavo ColimbaNo ratings yet
- An Extensive Survey On Edge Detection Techniques: AbstractDocument7 pagesAn Extensive Survey On Edge Detection Techniques: AbstractInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Denoising of SAR Image: Y. Murali Mohan Babu, Dr. M.V. Subramanyam, Dr. M.N. Giri PrasadDocument3 pagesBayesian Denoising of SAR Image: Y. Murali Mohan Babu, Dr. M.V. Subramanyam, Dr. M.N. Giri PrasadsakethmohanNo ratings yet
- Raffel (2015)Document17 pagesRaffel (2015)jan tasyNo ratings yet
- Techniques for Image Processing and Classifications in Remote SensingFrom EverandTechniques for Image Processing and Classifications in Remote SensingNo ratings yet
- General Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusFrom EverandGeneral Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- New Approaches to Image Processing based Failure Analysis of Nano-Scale ULSI DevicesFrom EverandNew Approaches to Image Processing based Failure Analysis of Nano-Scale ULSI DevicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lighting Fittings Performance and Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringFrom EverandLighting Fittings Performance and Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 2BHK Guidelines GO No 10 Date15.10.2015 PDFDocument5 pages2BHK Guidelines GO No 10 Date15.10.2015 PDFbokkaramesh1979No ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Properties Lecture1 PDFDocument4 pagesDynamic Soil Properties Lecture1 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- The Vision For Civil Engineering in 2025 Author Various AuthorsDocument1 pageThe Vision For Civil Engineering in 2025 Author Various AuthorsYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- GO IR TG - Steel & Cement RatesDocument1 pageGO IR TG - Steel & Cement RatesYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Vibrations Lecture4 PDFDocument4 pagesTheory of Vibrations Lecture4 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- River Training WorksDocument34 pagesRiver Training WorksBia MughalNo ratings yet
- DataStructure (13 14)Document35 pagesDataStructure (13 14)Yugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- 2BHK Guidelines GO No 10 Date15.10.2015 PDFDocument5 pages2BHK Guidelines GO No 10 Date15.10.2015 PDFbokkaramesh1979No ratings yet
- 2BHK Guidelines GO No 10 Date15.10.2015 PDFDocument5 pages2BHK Guidelines GO No 10 Date15.10.2015 PDFbokkaramesh1979No ratings yet
- River Training WorksDocument34 pagesRiver Training WorksBia MughalNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Download PDFDocument2 pagesData Structure Download PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Lecture1 PDFDocument5 pagesIntroduction Lecture1 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- UPSC IAS Mains LAST 10 Year Papers Public Administration OptionalDocument25 pagesUPSC IAS Mains LAST 10 Year Papers Public Administration OptionalKumar TrimukheNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Crushing Value TestDocument22 pagesAggregate Crushing Value TestYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Lecture2 PDFDocument4 pagesIntroduction Lecture2 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Properties Lecture2 PDFDocument3 pagesDynamic Soil Properties Lecture2 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Lecture3 PDFDocument3 pagesIntroduction Lecture3 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Properties Lecture3 PDFDocument2 pagesDynamic Soil Properties Lecture3 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Spillway 140901101155 Phpapp02Document10 pagesSpillway 140901101155 Phpapp02Yugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Properties Lecture1 PDFDocument4 pagesDynamic Soil Properties Lecture1 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Vibrations Lecture3 PDFDocument4 pagesTheory of Vibrations Lecture3 PDFYugandhar DamallaNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture1 PDFHIMANSHUNo ratings yet
- Theory of Vibrations Lecture2 PDFDocument4 pagesTheory of Vibrations Lecture2 PDFYugandhar Damalla100% (1)
- m4l08-ENERGY DISSIPATOR IITDocument75 pagesm4l08-ENERGY DISSIPATOR IITRajendra Shah Shah100% (1)
- Spillway DesignDocument18 pagesSpillway DesignFrancisco Alves100% (2)
- m4l08-ENERGY DISSIPATOR IITDocument75 pagesm4l08-ENERGY DISSIPATOR IITRajendra Shah Shah100% (1)
- Diversion Headworks: CEL351: Design of Hydraulic StructuresDocument78 pagesDiversion Headworks: CEL351: Design of Hydraulic StructuresAlvaro Rodrigo Chavez Viveros100% (1)
- Irrigation Structures - Diversion Head Works ComponentsDocument13 pagesIrrigation Structures - Diversion Head Works Componentslakumas15No ratings yet
- Diversion Head Works: Prepared by Bibhabasu Mohanty Dept. of Civil EngineeringDocument66 pagesDiversion Head Works: Prepared by Bibhabasu Mohanty Dept. of Civil EngineeringhNo ratings yet
- 9 - Diversion Head Works PDFDocument24 pages9 - Diversion Head Works PDFYugandhar Damalla50% (2)
- Stepper Motor 57HS8430A4D8 / NEMA 23 3ADocument2 pagesStepper Motor 57HS8430A4D8 / NEMA 23 3AMuhammad Ghiyats MukminNo ratings yet
- Oracle Service Procurement Advisory & ConsultingDocument22 pagesOracle Service Procurement Advisory & ConsultingPrakashNo ratings yet
- Greddy E-Manage Installation ManualDocument6 pagesGreddy E-Manage Installation ManualTHMotorsports.net100% (2)
- AbzenoDocument7 pagesAbzenojykhgpdrc5No ratings yet
- Transportation System, Analysis and Modelling (CE-632) : Carried Out by Group-3Document15 pagesTransportation System, Analysis and Modelling (CE-632) : Carried Out by Group-3Naman Kumar100% (2)
- Certification Authorities Software Team (CAST) Cast 10Document8 pagesCertification Authorities Software Team (CAST) Cast 10Anastasia SuckallahNo ratings yet
- Nitya Parayana Slokas MalayalamDocument3 pagesNitya Parayana Slokas MalayalamGopakumar NairNo ratings yet
- Grand Rapids Controls LPA Checksheet AuditDocument7 pagesGrand Rapids Controls LPA Checksheet Auditalliceyew100% (3)
- Centrifugal PumpsDocument20 pagesCentrifugal PumpsPiccollo640780% (5)
- SR.11.10961 - Sour Well Design GuideDocument52 pagesSR.11.10961 - Sour Well Design GuideMahmoud Ahmed Ali Abdelrazik100% (1)
- BDC Program To Create Routings Through BDCDocument10 pagesBDC Program To Create Routings Through BDCswapnil_265051509No ratings yet
- BS Basics Boundary Scan PDFDocument2 pagesBS Basics Boundary Scan PDFShankar ArunmozhiNo ratings yet
- Safety Analysis of Mooring Hawser of FSO and SPM B PDFDocument10 pagesSafety Analysis of Mooring Hawser of FSO and SPM B PDFORUGANo ratings yet
- MCQ - QuestionsTM P-1 PDFDocument8 pagesMCQ - QuestionsTM P-1 PDFRislan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Rfid Based Attendance SystemDocument16 pagesRfid Based Attendance Systemhim chauNo ratings yet
- Range and Angle Tracking Techniques for Moving Target EstimationDocument34 pagesRange and Angle Tracking Techniques for Moving Target Estimationmykingboody2156No ratings yet
- AKA DP Close Bus Ring SolutionsDocument2 pagesAKA DP Close Bus Ring Solutionssun qiNo ratings yet
- Civilstrips Installation NotesDocument3 pagesCivilstrips Installation NotesKoeswara SofyanNo ratings yet
- Feature Setup Description: Software Basic Data Mcs - TCBCDocument77 pagesFeature Setup Description: Software Basic Data Mcs - TCBCAlexis MauricioNo ratings yet
- Lot Inspection Report For LPG New CylindersDocument3 pagesLot Inspection Report For LPG New CylindersJagannath MajhiNo ratings yet
- Ansi B 16.34Document22 pagesAnsi B 16.34Vinoth Rajendra100% (2)
- Post TensioningDocument13 pagesPost TensioningAbdullah AhamedNo ratings yet
- SCC Development, Applications and InvestigationsDocument5 pagesSCC Development, Applications and InvestigationslauravoineagNo ratings yet
- J) Method Statement For Discharge of Stormwater and Rain WaterDocument4 pagesJ) Method Statement For Discharge of Stormwater and Rain WaterLee Tin YanNo ratings yet
- Monocrystalline - 50Wp - 200Wp: 50W - 200W 17.20V - 30.10V 27.5A - 7.85A 21.10V - 36.10V 2.95A - 8.34ADocument2 pagesMonocrystalline - 50Wp - 200Wp: 50W - 200W 17.20V - 30.10V 27.5A - 7.85A 21.10V - 36.10V 2.95A - 8.34ARia IndahNo ratings yet
- Em 2 SupplyDocument4 pagesEm 2 Supplykrishn murariNo ratings yet
- Petr Zamostny Tablet CompressionDocument57 pagesPetr Zamostny Tablet CompressionIka AniNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Sony MHC-V5Document122 pagesService Manual Sony MHC-V5Enya Andrea Ribba HernandezNo ratings yet
- MMDS Indoor/Outdoor Transmitter Manual: Chengdu Tengyue Electronics Co., LTDDocument6 pagesMMDS Indoor/Outdoor Transmitter Manual: Chengdu Tengyue Electronics Co., LTDHenry Jose OlavarrietaNo ratings yet
- Bringing Industrial Automation Environment Into Classroom: A Didactic Three-Tank and Heat Exchanger ModuleDocument5 pagesBringing Industrial Automation Environment Into Classroom: A Didactic Three-Tank and Heat Exchanger Modulenicacio_89507470No ratings yet