Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiratory System Anaphy Lab
Uploaded by
NicoleTrishiaDeparine0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Laboratory powerpoint presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnatomy and Physiology Laboratory powerpoint presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views15 pagesRespiratory System Anaphy Lab
Uploaded by
NicoleTrishiaDeparineAnatomy and Physiology Laboratory powerpoint presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
The Respiratory
System
Respiration: Three Major
Steps
1. Pulmonary ventilation
Moving air in and out of lungs
2. External respiration
Gas exchange between alveoli and blood
3. nternal respiration
Gas exchange between blood and cells
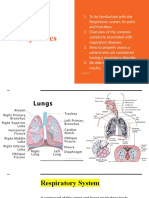
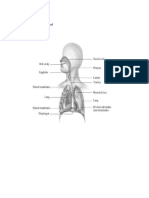
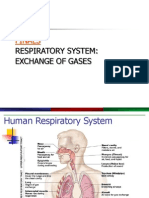
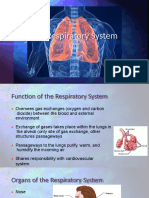
Organs of the Respiratory
System
!pper respiratory system
"ose and pharynx
#ower respiratory system
#arynx$ trachea$ bronchi$ bronchioles$ and lungs
%&onducting 'one( consists of
)ll airways that carry air to lungs*
"ose$ pharynx$ trachea$ larynx$ bronchi$ bronchioles$ and
terminal bronchioles
%+espiratory 'one(
,ites within lungs where gas exchange occurs
+espiratory bronchioles$ alveolar ducts$ alveolar sacs$
and alveoli
Organs of the Respiratory
System
Upper Respiratory System:
Nose
-unctions
.arm$ humidify$ filter/trap dust and microbes
Mucus and cilia of epithelial cells lining nose
0etect olfactory stimuli
Modify vocal sounds
Upper Respiratory System:
Pharynx
1nown as the %throat(
,tructure
-unnel2shaped tube from internal nares to larynx
3 parts
3hree regions
!pper* nasopharynx4 posterior to nose
Middle* oropharynx4 posterior to mouth
#ower* laryngeal pharynx
&onnects with both esophagus and larynx* food and air
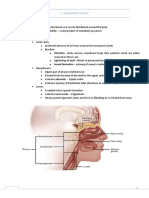
Respiratory System: Head
and Neck
Loer Respiratory System:
Larynx
%5oice box(
Made largely of cartilage
3hyroid cartilage* 52shaped
%)dam6s apple(* pro7ects more anteriorly in males
5ocal cords %strung( here 8and to arytenoids9
Epiglottis* leaf2shaped piece4 covers airway
0uring swallowing$ larynx moves up so epiglottis covers
opening into trachea
&ricoid cartilage* inferior most portion
)rytenoids 8paired$ small9 superior to cricoid
Loer Respiratory System:
Larynx
Loer Respiratory System:
Trachea
%.indpipe(
#ocation
)nterior to esophagus and thoracic vertebrae
Extends from end of larynx to primary bronchi
Loer Respiratory System: !ronchi"
!ronchio#es
,tructure of bronchial tree
:ronchi contain cartilage rings
Primary bronchi enter the lungs medially
n lungs$ branching secondary bronchi
Tertiary bronchi terminal bronchioles
3hese smaller airways
;ave less cartilage$ more smooth muscle. n
asthma, these airways can close.
&an be bronchodilated by sympathetic nerves$
epinephrine$ or related medications.
$o#%me&Press%re 'hanges in
L%ngs
5olume and pressure are inversely related
)s lung volume alveolar pressure
)s lung volume alveolar pressure
&ontraction of diaphragm lowers diaphragm
lung volume alveolar pressure so it is <
atmospheric pressure air enters lungs =
inhalation
+elaxation of diaphragm raises diaphragm
lung volume alveolar pressure so it is >
atmospheric pressure air leaves lungs =
exhalation
L%ng $o#%mes
Measured by spirometer
nspiratory reserve volume 8+59 = volume of air
that can be inhaled beyond tidal volume 8359
Expiratory reserve volume 8E+59 = volume of air
that can be exhaled beyond 35
)ir remaining in lungs after a maximum expiration
= residual volume 8+59
L%ng 'apacities
nspiratory capacity = 35 ? +5
-unctional residual capacity 8-+&9 =
+5 ? E+5
5ital capacity 85&9 = +5 ? 35 ? E+5
3otal lung capacity 83#&9 = 5& ? +5
You might also like
- Roses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.Document249 pagesRoses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.MabesNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument249 pagesRespiratoryBulborea MihaelaNo ratings yet
- 16 Respiratory SystemDocument40 pages16 Respiratory SystemchromaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument117 pagesThe Respiratory SystemPark chin-haeNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesBronchial AsthmaMoonNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory SystemAngela Ylagan100% (1)
- Pulmonary Ventilation: Dr. Mohamed HassanDocument29 pagesPulmonary Ventilation: Dr. Mohamed HassanSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- Alterations in OxygenationDocument104 pagesAlterations in OxygenationMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- Respira SiDocument80 pagesRespira SiIlaJako StefanaticNo ratings yet
- Problems With OxygenationDocument92 pagesProblems With OxygenationEbiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System-Review PathoDocument100 pagesRespiratory System-Review PathoSadiePartington-RiopelleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Kulpak UPN - Fisiologi Respirasi 1Document64 pagesKulpak UPN - Fisiologi Respirasi 1NabilaNo ratings yet
- NCM103 15th Respi IDocument10 pagesNCM103 15th Respi IKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesChapter 13 - Respiratory SystemCess Abad AgcongNo ratings yet
- Therespiratorysystem Grade 9Document19 pagesTherespiratorysystem Grade 9ClarkBautistaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemMonica VelascoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesRespiratory SystemdjokerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument12 pagesRespiratory AssessmentAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Wa0107.Document177 pagesWa0107.Dikachi ExcellentNo ratings yet
- Funda LecDocument5 pagesFunda LecJoannalyn FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesHuman Biology: Respiratory SystemSaikrishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemALYZZA JANE BUNANo ratings yet
- Fundamentalof Ventilation & PacemakerDocument22 pagesFundamentalof Ventilation & PacemakerLucila Lugo100% (1)
- The Respiratory System or Pulmonary SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory System or Pulmonary Systemfharidaismail47No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Respiratory SystemDocument63 pagesPathophysiology Respiratory SystemAli Basha QudahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemKatherineMysterieuxNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Human Breathing SystemDocument37 pagesLesson 1 Human Breathing SystemDavid Lawrence GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Anatomy & Physiology-Training HandoutDocument20 pages2012 Anatomy & Physiology-Training HandoutAkshay SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- 1.oxygenation DisordersDocument8 pages1.oxygenation Disorders2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemКрістіна БаландаNo ratings yet
- Respiiiraatatoory SystemDocument78 pagesRespiiiraatatoory Systempriyanshuraj717No ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document10 pagesChapter 17Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Handouts)Document5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Handouts)bluecindy87No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory SystembettyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesRespiratory SystemNahid ParveenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PreDocument11 pagesRespiratory System PrecontehamosaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument56 pagesRespiratory SystemSalma NawazNo ratings yet
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesIngles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Group1 Review of Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesGroup1 Review of Respiratory Systemjohn obinaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PDFDocument16 pagesRespiratory System PDFMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument55 pagesThe Respiratory SystemChuy Cantu RdzNo ratings yet
- Functional Human Physiology: The Respiratory SystemDocument64 pagesFunctional Human Physiology: The Respiratory SystemnashqonashNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Assignment 3Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Assignment 3api-238869728No ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory Systemangel demonyoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - NotessNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Respirstory SystemDocument35 pagesGrade 9 Science Respirstory SystemMark Anthony ClavillasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystempptDocument26 pagesRespiratory SystempptRinaliza BogsulenNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument77 pagesThe Respiratory SystemPridas GidNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Aam Amarullah, M.PDDocument42 pagesThe Respiratory System: Aam Amarullah, M.PDUniversal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory System: Anatomy and Physiology ReviewTerry Mae Atilazal SarciaNo ratings yet
- Humb1000 Compendium NotesDocument9 pagesHumb1000 Compendium NotesZeba ZiaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument17 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArjun ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material 3.1 Basic Concepts and Assessment (N) - 2Document13 pagesSupplementary Material 3.1 Basic Concepts and Assessment (N) - 2Kent Borro CantomayorNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory Systemjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument20 pagesOxygenationKhie-An OcampoNo ratings yet
- 1-The Respiratory SystemDocument7 pages1-The Respiratory SystemEma FröhlichováNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Catalogo GatesDocument255 pagesCatalogo GatesBenjamin HedoneweNo ratings yet
- Niir Integrated Organic Farming Handbook PDFDocument13 pagesNiir Integrated Organic Farming Handbook PDFNatalieNo ratings yet
- 14p-220 Mud PumpDocument2 pages14p-220 Mud PumpMurali Sambandan50% (2)
- PEH Q3 Long QuizDocument1 pagePEH Q3 Long QuizBenedict LumagueNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Marketing Mansi 4Document39 pagesLab Report Marketing Mansi 4Mansi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Irina Maleeva - Ariel Snowflake x6 - ENG - FreeDocument4 pagesIrina Maleeva - Ariel Snowflake x6 - ENG - FreeMarinaKorzinaNo ratings yet
- Crouse Hinds XPL Led BrochureDocument12 pagesCrouse Hinds XPL Led BrochureBrayan Galaz BelmarNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Self Contained Breathing ApparatusDocument4 pagesTraining Report On Self Contained Breathing ApparatusHiren MahetaNo ratings yet
- JKJKJDocument3 pagesJKJKJjosecarlosvjNo ratings yet
- Ensemble Averaging (Machine Learning)Document3 pagesEnsemble Averaging (Machine Learning)emma698No ratings yet
- Surface TensionDocument13 pagesSurface TensionElizebeth GNo ratings yet
- Awakened Citizen Programme-Report-class VII-2014Document4 pagesAwakened Citizen Programme-Report-class VII-2014bhsgeneral r m saraswathi50% (4)
- Electricity NotesDocument35 pagesElectricity Notesapi-277818647No ratings yet
- Murata High Voltage CeramicDocument38 pagesMurata High Voltage CeramictycristinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Geriatric Nursing 6th Edition Williams Test BankDocument10 pagesBasic Geriatric Nursing 6th Edition Williams Test Bankmaryrodriguezxsntrogkwd100% (49)
- The Indian Mining Sector: Effects On The Environment & FDI InflowsDocument10 pagesThe Indian Mining Sector: Effects On The Environment & FDI InflowsMehul MandanakaNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsDocument118 pagesStructural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsRISHABH JAMBHULKARNo ratings yet
- Updated Factory Profile of Aleya Apparels LTDDocument25 pagesUpdated Factory Profile of Aleya Apparels LTDJahangir Hosen0% (1)
- Someone Who Believes in YouDocument1 pageSomeone Who Believes in YouMANOLO C. LUCENECIONo ratings yet
- Flow Chart - QCDocument2 pagesFlow Chart - QCKarthikeyan Shanmugavel100% (1)
- AssessmentDocument9 pagesAssessmentJuan Miguel Sapad AlpañoNo ratings yet
- Data Bulletin Group Motor Installations:: Understanding National Electrical Code (NEC) 430.53 RequirementsDocument8 pagesData Bulletin Group Motor Installations:: Understanding National Electrical Code (NEC) 430.53 RequirementsshoaibNo ratings yet
- 07ercoskun 05 01 PDFDocument23 pages07ercoskun 05 01 PDFjagmadridNo ratings yet
- Fyp-Hydraulic Brakes CompleteDocument32 pagesFyp-Hydraulic Brakes CompleteRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Harmonics PatternsDocument4 pagesHarmonics PatternsIzzadAfif1990No ratings yet
- Presentation On 4G TechnologyDocument23 pagesPresentation On 4G TechnologyFresh EpicNo ratings yet
- 1762 Ob8 PDFDocument16 pages1762 Ob8 PDFRodríguez EdwardNo ratings yet
- Cross Talk Details and RoutingDocument29 pagesCross Talk Details and RoutingRohith RajNo ratings yet
- Poly 103Document20 pagesPoly 103Sharifah Zulaikha BenYahyaNo ratings yet
- 3-History Rock Cut MonumentDocument136 pages3-History Rock Cut MonumentkrishnaNo ratings yet