Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MOSFET DC Analysis Quiz Solutions
Uploaded by
Allen ChandlerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MOSFET DC Analysis Quiz Solutions
Uploaded by
Allen ChandlerCopyright:
Available Formats
L-29, 23.09.
2014
MOSFET DC Analysis
Quiz II
Date: 24.09.2014
Syllabus
Unit II BJT
Unit III MOSFET (L-28 & L-29)
Best Wishes for a Fine Performance!
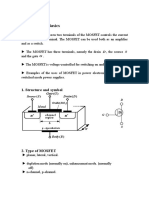
Symbols for MOSFET
The i
D
vs v
DS
Relationship
For the MOSFET to establish a channel, we give a
minimum voltage of V
t
(threshold voltage) to the gate.
Hence it is known as enhancement-type MOSFET.
Correspondingly, we also have a depletion-type
MOSFET.
i
D
= k
n
(W/L){(V
GS
- V
t
)v
DS
v
DS
2
} (Triode Region)
i
D
= [k
n
(W/L)(V
GS
- V
t
)
2
](Saturation Region)
k
n
=
n
C
ox
and is called the process transconductance*
parameter.
W/L is the aspect ratio of the MOSFET.
V
OV
= (V
GS
- V
t
) is the gate-to-source overdrive voltage.
Temperature Effect and Breakdown:
Both k
n
and V
t
are temperature sensitive.
V
t
increases with temperature 2 mV per C.
However k
n
decreases with temperature rise and
dominantly so.
Overall there is a reduction in i
D
as temperature goes up.
This is one of the favorable attributes of a MOSFET.
At about 20 V, the device suffers punch through, when
the depletion region extends from drain to the source
and a rapid increase in drain current causes the effect.
This is normally not destructive.
BD also occurs when V
GS
exceeds 30 V. The gate oxide
(tiny as it is) may breakdown. The damage is permanent.
This can be caused by static voltage (?).
MOSFET ICs are protected by clipper diodes and by steel
wool while packaging.
Exercise
4.4/343: An NMOS transistor with V
t
= 0.7 V, has its source
terminal grounded and a 1.5 V is applied at the gate. In
what region does the device operate for a) V
D
= +0.5 V?
b) 0.9 V? and c) 3 V?
If
n
C
ox
= 100 A/V
2
, W = 10 m and L = 1 m, find the
drain current in each of the three cases.
V
DS
V
GS
- V
t
triode region; a) V
GS
= 1.5 V, V
DS
= 0.5 V, V
t
= 0.7 V
i
D
= k
n
(W/L){(V
GS
- V
t
)v
DS
v
DS
2
} = ?
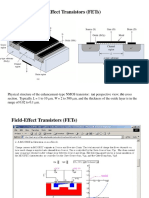
i
D
vs V
GS
Characteristics
Similar to base width modulation in BJT, MOSFET has channel
length modulation, resulting in an r
o
.
Large Signal (DC)Equivalent Circuit Model
Large Signal Equivalent Circuit Model under Saturation
Analyze the circuit to determine the voltages at all nodes and currents in
all branches, for V
t
= 1 V and k
n
(W/L) = 1 mA/V
2
. Assume = 0.
V
G
= [R
G2
/(R
G1
+R
G2
)]V
DD
= ?
Assuming the transistor is in
saturation,
i
D
= [k
n
(W/L)(V
GS
- V
t
)
2
].
Substitute the values and get
the quadratic equation in i
D
.
Solve for i
D
. two roots -
choose the one that will fit into
your solution.
Confirm your assumption is true
or otherwise.
Find the values of V
D
and V
S
.
Design the circuit so that the transistor operates at I
D
= 0.4 mA and V
D
=
+0.5 V. It has V
t
= 0.7 V,
n
C
ox
= 100 A/V
2
, L = 1 m, W = 1 m. Neglect
the channel length modulation (i.e. = 0)
R
D
= (V
DD
- V
D
)/ I
D
= ?
i
D
= [k
n
(W/L)(V
GS
- V
t
)
2
]
Plugging in the values, V
GS
= ?
V
GS
= V
G
- V
S
; V
S
= ?
R
S
= (V
S
- V
SS
)/i
D
= ?
You might also like
- Electronics Ch5Document30 pagesElectronics Ch5Santi Navarro MoralNo ratings yet
- Mosfet (Iii) - I-V CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesMosfet (Iii) - I-V Characteristics許博凱No ratings yet
- Detailed Notes: IC Fabrication ProcessDocument81 pagesDetailed Notes: IC Fabrication ProcessimmadiuttejNo ratings yet
- VLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORDocument162 pagesVLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORBasheer V.PNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23Document6 pagesLecture 23Rakesh AshokNo ratings yet
- EC410 Fall 2012 FinalDocument8 pagesEC410 Fall 2012 FinalRabee Adil JamshedNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Lab 1Document11 pagesMosfet Lab 1Pramod SnkrNo ratings yet
- ENGG*3450 Lab Manual MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesENGG*3450 Lab Manual MOSFET Characteristicsdlat94No ratings yet
- 3.5 MOSFET Scaling and Small-Geometry EffectsDocument19 pages3.5 MOSFET Scaling and Small-Geometry Effectspraritlamba25No ratings yet
- Lecture - MOS & MOSFET-1Document21 pagesLecture - MOS & MOSFET-1Kartika MunirNo ratings yet
- GIKINST-ME203-Lec27-MOSFETsDocument28 pagesGIKINST-ME203-Lec27-MOSFETsBilal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument40 pagesField Effect TransistorsRatanNo ratings yet
- AmplfierDocument7 pagesAmplfierCharuka WeerasekaraNo ratings yet
- VLSIDocument86 pagesVLSILorelei VasiloaiaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet BasicsDocument14 pagesMosfet BasicsFazal AkbarNo ratings yet
- 08ece Ee331 Group 6 Le Van Hai Lab3Document19 pages08ece Ee331 Group 6 Le Van Hai Lab3Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture17 080213-FDocument35 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture17 080213-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- MOS Rabaey PDFDocument32 pagesMOS Rabaey PDFalamgirNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering: American University of BeirutDocument10 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering: American University of BeirutadgjkinghackNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Scaling and Its Effects in 40 CharactersDocument109 pagesMOSFET Scaling and Its Effects in 40 CharactersLiferNo ratings yet
- FETDocument49 pagesFETPalak Agrawal100% (2)
- L #5: Mosfet C A: Sfsu - E 301 - E L AB Haracteristics and PplicationsDocument14 pagesL #5: Mosfet C A: Sfsu - E 301 - E L AB Haracteristics and PplicationsRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Ned Mohan Slides Ch22Document35 pagesPower Electronics Ned Mohan Slides Ch22Anoop MathewNo ratings yet
- Microdevices: Mosfets - Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors N MosfetDocument11 pagesMicrodevices: Mosfets - Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors N Mosfetblue7nicoNo ratings yet
- Analog Ders 1Document77 pagesAnalog Ders 1Eren TelifNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Electronics Devices AssignmentDocument5 pagesMOSFET Electronics Devices AssignmentShaheer ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Lec17 MOSFET IVDocument49 pagesLec17 MOSFET IVBlanca MeLendezNo ratings yet
- MOS Transistor Theory: OutlineDocument24 pagesMOS Transistor Theory: OutlineCarlos AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryDocument25 pagesChapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryrasheeenNo ratings yet
- I. Instructional Objectives: D S G D GDocument4 pagesI. Instructional Objectives: D S G D Gcokelat_kNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: Ph-218 Lec-26: Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors (Mosfets)Document16 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: Ph-218 Lec-26: Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors (Mosfets)Udai SinghNo ratings yet
- Mos ModelsDocument39 pagesMos Modelsch0071No ratings yet
- Mos Transistor Review: 3D Band Diagram of A Long Channel Enhancement Mode NMOS TransistorDocument14 pagesMos Transistor Review: 3D Band Diagram of A Long Channel Enhancement Mode NMOS TransistorKumar Amit VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document42 pagesChapter 12Felipe SouzaNo ratings yet
- 1.characteristics of MOSFETDocument8 pages1.characteristics of MOSFETabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistors Analysis Mr. Zeeshan Ali, Asst. Professor Department: B.E. Electronic & Telecommunication Subject: Analog Electronics - I Semester: IIIDocument84 pagesField Effect Transistors Analysis Mr. Zeeshan Ali, Asst. Professor Department: B.E. Electronic & Telecommunication Subject: Analog Electronics - I Semester: IIIAqilAbbasiNo ratings yet
- MOS Field-Effect Transistor MOSFETDocument34 pagesMOS Field-Effect Transistor MOSFETFrank WanderiNo ratings yet
- Mosfet DC AnalysisDocument13 pagesMosfet DC AnalysiswaqarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Field-Effect Transistors (Fets)Document129 pagesChapter 5 - Field-Effect Transistors (Fets)Srie WidodoNo ratings yet
- Mosfet PowerPoint PresentationDocument71 pagesMosfet PowerPoint PresentationMohammad Rameez100% (7)
- Inv 120923Document29 pagesInv 120923Aman KumarNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Amplifier DC AnalysisDocument4 pagesMOSFET Amplifier DC AnalysisMichael AlbanianNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Model MOSFETDocument8 pagesSmall Signal Model MOSFETRAHUL100% (1)
- Unit 4Document45 pagesUnit 4321910402038 gitamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital ElectronicsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Digital ElectronicsLeandroRicardoNo ratings yet
- The Cmos Inverter: Slides Adapted From: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design,, 3/e, 2004Document40 pagesThe Cmos Inverter: Slides Adapted From: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design,, 3/e, 2004SrasVelNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument22 pagesElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNo ratings yet
- Lec24 2003Document16 pagesLec24 2003cassNo ratings yet
- MOS Transistor Operation: S/D GateDocument10 pagesMOS Transistor Operation: S/D GateConcetto CantoneNo ratings yet
- MOS PPTDocument13 pagesMOS PPTRenju TjNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Biasing Using A Current MirrorDocument5 pagesMOSFET Biasing Using A Current MirrorSandeep Pandey100% (1)
- Lesson 7 MOSFETDocument30 pagesLesson 7 MOSFETAlbert OmondiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 77 S Mosfet CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesExperiment 77 S Mosfet CharacteristicsviltrumiteNo ratings yet
- 9 MOSFETs EDocument51 pages9 MOSFETs EPapp RichárdNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design Notes-2Document85 pagesAnalog Circuit Design Notes-2itsnirosNo ratings yet
- Lect13 MosfetDocument8 pagesLect13 MosfetAbhay ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Engineering BiotechnologyDocument2 pagesEngineering BiotechnologyNikhil PatidarNo ratings yet
- Brochure GATE2017Document62 pagesBrochure GATE2017mohitNo ratings yet
- Hum103 Business-Economics TH 1.10 Ac26Document1 pageHum103 Business-Economics TH 1.10 Ac26Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Ece101 Electron-Devices-And-circuits Eth 1.20 Ac29Document2 pagesEce101 Electron-Devices-And-circuits Eth 1.20 Ac29Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- User Manual - TDSL300W2Document60 pagesUser Manual - TDSL300W2dugdugdugdugi67% (3)
- Model Question Paper 2014Document3 pagesModel Question Paper 2014Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Random Process Important QuestionsDocument1 pageRandom Process Important QuestionsAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations For Long Endurance Unmanned Aerial VehiclesDocument55 pagesDesign Considerations For Long Endurance Unmanned Aerial Vehiclesnivas_mechNo ratings yet
- DSL-2750U V1 Manual v1.00 (IN)Document65 pagesDSL-2750U V1 Manual v1.00 (IN)Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 27 Oct 2014 RM01 Moral HazardDocument18 pages27 Oct 2014 RM01 Moral HazardAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2014 15 CP1269 TB01 DLD Hardware Manual Win 14 15Document25 pagesWINSEM2014 15 CP1269 TB01 DLD Hardware Manual Win 14 15Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Https Academics - Vit.ac - in Student Pi Change PrintDocument1 pageHttps Academics - Vit.ac - in Student Pi Change PrintAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Sedra/Smith Microelectronic Circuits 6/E: Chapter 4-A Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Document61 pagesSedra/Smith Microelectronic Circuits 6/E: Chapter 4-A Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2014 15 Cp0737 Tb02 Text Books EdcDocument1 pageFallsem2014 15 Cp0737 Tb02 Text Books EdcAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 25 Jul 2014 - RM01 - L 7 Zener ProbDocument5 pages25 Jul 2014 - RM01 - L 7 Zener ProbAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 23 Jul 2014 RM01 L 6 Modeling DiodesDocument9 pages23 Jul 2014 RM01 L 6 Modeling DiodesAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2014 15 Cp0737 Tb02 Text Books EdcDocument1 pageFallsem2014 15 Cp0737 Tb02 Text Books EdcAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 30 Jul 2014 RM01 L 7 Diode Model ContDocument10 pages30 Jul 2014 RM01 L 7 Diode Model ContAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Ref EDC 13Document1 pageRef EDC 13Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- L 1 IntroductionDocument32 pagesL 1 IntroductionAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Noun Phrase ApproachDocument3 pagesNoun Phrase ApproachShabeer Ac75% (4)
- Model Question Paper 2014Document3 pagesModel Question Paper 2014Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Universal Coupling Parts List and DrawingDocument2 pagesUniversal Coupling Parts List and DrawingAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 5 Design Classes 2Document53 pages5 Design Classes 2Allen Chandler100% (1)
- 6 Access Layer PDFDocument84 pages6 Access Layer PDFAllen Chandler50% (2)
- BTech (Mechanical Engineering) Curriculum For 2012 - 2013Document103 pagesBTech (Mechanical Engineering) Curriculum For 2012 - 2013Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- 1 Unit 3Document101 pages1 Unit 3Allen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Is Our Gateway To A Prosperous FutureDocument2 pagesNuclear Power Is Our Gateway To A Prosperous FutureAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Random VariablesDocument13 pagesTwo-Dimensional Random VariablesAllen ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Application of EbwDocument11 pagesApplication of Ebwsuman kumarNo ratings yet
- The historical evolution of organizational behavior and how it shaped modern managementDocument3 pagesThe historical evolution of organizational behavior and how it shaped modern managementSaravanan Swagger100% (1)
- Grupo Stoncor Description - Stonhard Carboline Fibergrate PDFDocument22 pagesGrupo Stoncor Description - Stonhard Carboline Fibergrate PDFAndres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Creative IndustriesDocument433 pagesCreative IndustriesDanielTavaresNo ratings yet
- Caring Seedlings TLE Weekly PlanDocument3 pagesCaring Seedlings TLE Weekly PlanMarjorie RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Assembly Transmission Volvo A40GDocument52 pagesAssembly Transmission Volvo A40GNanang SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Risk and Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk and Risk ManagementMARY JUSTINE PAQUIBOTNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Production of Acetic AnhydrideDocument7 pagesAdiabatic Production of Acetic AnhydrideSunilParjapatiNo ratings yet
- DUPLICATE BILL TITLEDocument8 pagesDUPLICATE BILL TITLEMohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- ManupptDocument65 pagesManupptKrishanarju VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Delhi University SEC Exam Date Sheet March 2023Document2 pagesDelhi University SEC Exam Date Sheet March 2023aamir9ali-42No ratings yet
- CP QB PT-3 Harish KumarDocument3 pagesCP QB PT-3 Harish KumarVISHNU7 77No ratings yet
- ZXJ 10 SPCDocument7 pagesZXJ 10 SPCMuhammad Yaseen100% (1)
- The Chair As Health Hazard Part II J of PDFDocument11 pagesThe Chair As Health Hazard Part II J of PDFPablo BuniakNo ratings yet
- IIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthyDocument1 pageIIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthySathyamoorthy VenkateshNo ratings yet
- 6907 6 52 0040Document35 pages6907 6 52 0040amitkumar8946No ratings yet
- MN00119 Unicom LT User ManualDocument45 pagesMN00119 Unicom LT User ManualPhilipp A IslaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science (Solar System)Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science (Solar System)Angelique Pabillona88% (51)
- Halo Outdoor slmt1000 - slmt1000wDocument1 pageHalo Outdoor slmt1000 - slmt1000wFrank MoyaNo ratings yet
- ETEC 520 - Assignment 2 Group ProjectDocument19 pagesETEC 520 - Assignment 2 Group ProjectjennbosNo ratings yet
- Manhattan Project SummaryDocument5 pagesManhattan Project Summaryapi-302406762No ratings yet
- Report Card of Army Public School StudentDocument2 pagesReport Card of Army Public School StudentRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cropprotectionequipment-Rocker Sprayer - Specification (: Indian StandardDocument9 pagesCropprotectionequipment-Rocker Sprayer - Specification (: Indian Standardgini associatesNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Repair ManualDocument162 pagesBicycle Repair Manualrazvancc89% (9)
- Acer Veriton S480G Service ManualDocument90 pagesAcer Veriton S480G Service ManualAndreea Georgiana ChirilaNo ratings yet
- OSC - 2015 - Revised - Oct (Power Cables) PDFDocument118 pagesOSC - 2015 - Revised - Oct (Power Cables) PDFIván P. MorenoNo ratings yet
- Check For Palindrome: Compute GCD and LCMDocument3 pagesCheck For Palindrome: Compute GCD and LCMAadhi JNo ratings yet
- Strategic Investment Plan ForDocument78 pagesStrategic Investment Plan Forapi-3833112No ratings yet
- Fish HatcheryDocument14 pagesFish HatcheryYared Mesfin FikaduNo ratings yet
- Samsung GT-I8160 Galaxy Ace 2 08 Level 3 Repair - Block-, PCB Diagrams, Flow Chart of TroubleshootingDocument47 pagesSamsung GT-I8160 Galaxy Ace 2 08 Level 3 Repair - Block-, PCB Diagrams, Flow Chart of TroubleshootingOuadghiri Badre Ddine50% (2)