Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SPPTChap 005
Uploaded by
iLeegendOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SPPTChap 005
Uploaded by
iLeegendCopyright:
Available Formats
5- 1
Accounting for Merchandising
Operations
Chapter 5
PowerPoint Authors:
Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA
Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA
Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA
Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA
Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
5- 2
C1
Reporting Income for a
Merchandiser
Merchandising companies sell products to
earn revenue.
Examples: sporting goods, clothing, and auto parts stores
5- 3
C2
Operating Cycle for
a Merchandiser
Begins with the purchase of merchandise and
ends with the collection of cash from the sale
of merchandise.
5- 4
C2
Inventory Systems
5- 5
C2
Inventory Systems
Perpetual systems
continually update
accounting records for
merchandising
transactions
Periodic systems
accounting records
relating to merchandise
transactions are updated
only at the end of the
accounting period
5- 6
P1
Trade Discounts
Used by manufacturers and wholesalers to
offer better prices for greater quantities
purchased.
Example
Z-Mart offers a 30% trade
discount for orders of 1,000
units or more on its popular
product Racer. Each
Racer has a list price of $5.25.
Quantity sold
Price per unit
Total
Less 30% discount
Invoice price
1,000
$ 5.25
5,250
(1,575)
$ 3,675
5- 7
P1
Accounting for Merchandise
Purchases
5- 8
P1
Purchase Discounts
A deduction from the invoice price granted
to induce early payment of the amount due.
5- 9
Purchase Discounts
P1
2/10,n/30
Discount
Percent
Number of
Days
Discount Is
Available
Otherwise,
Net (or All)
Is Due in 30
Days
Credit
Period
P1
Purchase Returns and
Allowances
Purchase Return . . .
Merchandise returned by the purchaser to the
supplier.
Purchase Allowance . . .
A reduction in the cost of defective or
unacceptable merchandise received by a
purchaser from a supplier.
5- 10
5- 11
P1
Transportation Costs and
Ownership Transfer
5- 12
P1
Accounting for Merchandise
P2
Accounting for Merchandise
Sales
5- 13
5- 14
P2
Sales of Merchandise
Each sales transaction for a seller of
merchandise involves two parts:
Revenue received in
the form of an asset
from a customer.
Recognition of the
cost of merchandise
sold to a customer.
5- 15
P2
Sales Discounts
Sales discounts on credit sales can benefit a seller by
decreasing the delay in receiving cash and reducing future
collection efforts.
5- 16
P2
Sales Returns and Allowances
Sales returns and allowances usually involve
dissatisfied customers and the possibility of
lost future sales.
Sales returns refer
to merchandise that
customers return to
the seller after a
sale.
Sales allowances
refer to reductions in
the selling price of
merchandise sold to
customers.
5- 17
P2
Merchandising Cost Flow in
the Accounting Cycle
5- 18
P3
Closing Entries for Merchandisers
5- 19
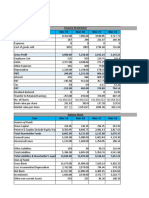
P4
A multiple-step
income
statement
format shows
detailed
computations
of net sales
and other
costs and
expenses, and
reports
subtotals for
various
classes of
items.
5- 20
P4
Single-Step Income Statement
5- 21
Classified Balance Sheet
Highly
Liquid
Less
Liquid
5- 22
End of Chapter 5
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CH 8 Practice HomeworkDocument11 pagesCH 8 Practice HomeworkNCT100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Financial FormationDocument60 pagesFinancial FormationSandeep Soni100% (1)
- Adj. EntriesDocument41 pagesAdj. EntriesElizabeth Espinosa Manilag100% (2)
- 19 ConceptsandTheories CashflowForecasting OkDocument9 pages19 ConceptsandTheories CashflowForecasting OkPrecious J Alolod ImportanteNo ratings yet
- OPS - SP009 - Project ReportingDocument22 pagesOPS - SP009 - Project Reportingpuput utomoNo ratings yet
- Bata India LTD PDFDocument4 pagesBata India LTD PDFparchure123No ratings yet
- Grant Thornton Patisserie Valerie Final ReportDocument65 pagesGrant Thornton Patisserie Valerie Final ReportJason Bramwell100% (1)
- Balakrishnan MGRL Solutions Ch09Document53 pagesBalakrishnan MGRL Solutions Ch09Rachna Menon100% (1)
- Financial PlanDocument18 pagesFinancial Planashura08No ratings yet
- My Report Internal AssessmentDocument18 pagesMy Report Internal AssessmentGlenn John BalongagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Glossary: Shareholders or StockholdersDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Glossary: Shareholders or StockholdersiLeegendNo ratings yet
- Acct 2301 Exam 2 - v2 Key2Document11 pagesAcct 2301 Exam 2 - v2 Key2iLeegendNo ratings yet
- Investments and International OperationsDocument15 pagesInvestments and International OperationsiLeegendNo ratings yet
- Cima Online Calculator ManualDocument44 pagesCima Online Calculator ManualWalakulage Dilan Urban PereraNo ratings yet
- Respuesta Capt 1 LibroDocument20 pagesRespuesta Capt 1 LibroiLeegendNo ratings yet
- Textbook Chap 1 PDFDocument39 pagesTextbook Chap 1 PDFiLeegend100% (2)
- Textbook Chap 1 PDFDocument39 pagesTextbook Chap 1 PDFiLeegend100% (2)
- Far0 ReviewerDocument8 pagesFar0 ReviewerAshianna KimNo ratings yet
- PSO & SHELL ComparisonDocument22 pagesPSO & SHELL ComparisonSabeen JavaidNo ratings yet
- 3.6 ExercisesDocument8 pages3.6 ExercisesGeorgios MilitsisNo ratings yet
- Transaction Analysis: Transaction 1. Investment by Owner Ray Neal Decides ToDocument31 pagesTransaction Analysis: Transaction 1. Investment by Owner Ray Neal Decides ToSophia LocreNo ratings yet
- Dalmia Cement (Bharat) LTDDocument8 pagesDalmia Cement (Bharat) LTDRemonNo ratings yet
- SMCH 05Document42 pagesSMCH 05Lara Lewis AchillesNo ratings yet
- F2 - Financial ManagementDocument20 pagesF2 - Financial ManagementRobert MunyaradziNo ratings yet
- 2014 Dse Bafs 2a MSDocument8 pages2014 Dse Bafs 2a MSryanNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisJamil SalibioNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1. Accounting PracticesDocument3 pagesActivity No. 1. Accounting PracticesNalin SNo ratings yet
- CHAP - 5 - Measuring and Evaluating The Performance of BanksDocument7 pagesCHAP - 5 - Measuring and Evaluating The Performance of BanksNgoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Module - Principless of Accounting IDocument205 pagesModule - Principless of Accounting Iወሬ ነጋሪ- oduu himaaNo ratings yet
- Earning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)Document20 pagesEarning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)Jamie Rose AragonesNo ratings yet
- Hoor GheeDocument32 pagesHoor GheeHaider Sarwar50% (4)
- NYRA Board Meeting AgendaDocument75 pagesNYRA Board Meeting AgendaDavid LombardoNo ratings yet
- ACTBAS1 - Lecture 9 (Adjusting Entries) RevisedDocument44 pagesACTBAS1 - Lecture 9 (Adjusting Entries) RevisedAlejandra MigallosNo ratings yet
- ComprehensiveexamDocument14 pagesComprehensiveexamLeah BakerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Ngô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- Obillos v. CIRDocument7 pagesObillos v. CIRmceline19No ratings yet
- Tafi Jbga 2017-18Document22 pagesTafi Jbga 2017-18Naveen RajputNo ratings yet