Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrofoil "Hull "
Uploaded by
bourneremembers0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
394 views8 pagesA hydrofoil is a wing-like structure mounted below a boat's hull that lifts the boat partially out of the water during motion to reduce drag. There is no actual hull on a hydrofoil boat - it grazes the water's surface at high speeds due to powerful propulsion and hydrofoil struts angled for lift. Hydrofoils combine the lift of hydrofoil wings with additional lift from planing to gain advantages of both technologies. A challenge is pitch instability as both hydrofoils and hull can increase lift when the bow pitches up, causing an oscillating cycle. A stepped hull design confines planing lift to reduce pitch instability. Hybrid hydrofoils can be propelled through hull-mounted components like jets
Original Description:
This is about the physical meaning behind the hydrofoil
Original Title
Hydrofoil “hull ”
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA hydrofoil is a wing-like structure mounted below a boat's hull that lifts the boat partially out of the water during motion to reduce drag. There is no actual hull on a hydrofoil boat - it grazes the water's surface at high speeds due to powerful propulsion and hydrofoil struts angled for lift. Hydrofoils combine the lift of hydrofoil wings with additional lift from planing to gain advantages of both technologies. A challenge is pitch instability as both hydrofoils and hull can increase lift when the bow pitches up, causing an oscillating cycle. A stepped hull design confines planing lift to reduce pitch instability. Hybrid hydrofoils can be propelled through hull-mounted components like jets
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
394 views8 pagesHydrofoil "Hull "
Uploaded by
bourneremembersA hydrofoil is a wing-like structure mounted below a boat's hull that lifts the boat partially out of the water during motion to reduce drag. There is no actual hull on a hydrofoil boat - it grazes the water's surface at high speeds due to powerful propulsion and hydrofoil struts angled for lift. Hydrofoils combine the lift of hydrofoil wings with additional lift from planing to gain advantages of both technologies. A challenge is pitch instability as both hydrofoils and hull can increase lift when the bow pitches up, causing an oscillating cycle. A stepped hull design confines planing lift to reduce pitch instability. Hybrid hydrofoils can be propelled through hull-mounted components like jets
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
HYDROFOIL “HULL”
BASICS & EXTREMES
HYDROFOIL INTRO
• A hydrofoil is a wing-like structure
mounted on struts below the hull of a
boat, which lifts the boat partially out of
the water during forward motion, in
order to reduce drag.
THE “HULL”
• There is no hull in the hydrofoils, its just
that it just grazes over the water surface
at blinding speeds due to the less
displacement & the t-shaped and the v-
shaped struts. Its just that the engine
propulsion is high and the angle of
attack is changed considering the
situation, that enables the hydrofoils to
whizz past at 80 knots.
CONCEPT
Hydrofoil is a vehicle combining the
dynamic lift of hydrofoils with a significant
amount of lift from some other source,
generally planing lift. The traction of
hydrofoils is the desire to meld the
advantages of two technologies in an
attempt to gain a synthesis that is
better than either one alone. Partially
hydrofoil supported hulls mix hydrofoil
support and planing lift.
PITCH INSTABILITY
Pitch instability is the chief issue in a hybrid hydrofoil. Planing hybrid
hydrofoils can exhibit a dynamic pitch instability similar to
porpoising. This phenomenon can be best understood for a
nominal configuration with a single hydrofoil beneath the center of
gravity of a planing hull. If such a configuration is slightly
disturbed bow up from an equilibrium position, the lift on both the
foil and the hull will increase. The hull accelerates upwards and
the intersection of the water surface and the keel moves aft. This
develops a bow down moment, but at a relatively slow rate. By the
time the bow drops enough to reduce the excess lift, the vessel is
well above the equilibrium position, and the keel V waterline
intersection is well aft. It falls back down toward the equilibrium
position bow down, as if it had tripped on its stem. Then, it carries
through equilibrium, takes a deep dive and springs up again. This
cycle repeats, each time growing more severe. The only way that
this motion can damped is if the hull provides enough damping to
prevent the increasing overshoot. Note that this is a smooth water
instability and occurs with only a nominal initial disturbance.
STEPPED HULL CONCEPT
The foil is at the extreme stern of the vehicle
and a step is provided forward of the CG.
The step confines the planing lift to the
forward part of the hull so that the relative
position of the center of gravity, the step
and the foil control the proportioning of lift
between hull and foil. Bow up pitch of the
vehicle produces a strong bow down
moment, directly proportional to pitch, that
reduces the pitch much more rapidly than
the movement of the center of planing lift.
The step also means that the running
attitude of the planing hull can be set at a
trim producing optimum lift. (This is the
whole point of a stepped planing hull.)
PROPULSION
Getting the force into the water often requires passing it
through the struts which is costly in terms of money,
appendage drag, complexity and efficiency. Hydrofoils use
mechanical, electric and hydraulic drives to props on foil
pods, jets taking suction through the foil, and shafts from
the hull. Each of these methods has problems. There is
some consolation that the struts of a hybrid are somewhat
shorter, but this is only important for through-strut jet
drives, and jet drives require higher flow rates for efficiency
at the lower speeds of a hybrid. However, unlike a pure
hydrofoil, a hybrid can be propelled by hull mounted
components. A jet drive could be mounted in the forward
planing hull and discharge at the step. A prop shaft could
penetrate through the step as well or surface piercing props
could be mounted on or below the raised tail and dip down
to the water. This gives some added versatility to the hybrid
concept that a pure hydrofoil doesn't have.
Questions or comments????
PLEASE!!!!
Done by,
K.Mallikarjun
You might also like
- Robots User Manual (CE) - EnglishDocument170 pagesRobots User Manual (CE) - EnglishVlad-Andrei Cucuteanu100% (3)
- Boat Ed Unit 1 and 2Document71 pagesBoat Ed Unit 1 and 2Esper SorianoNo ratings yet
- Catana 471 ArticleDocument2 pagesCatana 471 ArticleerindycNo ratings yet
- Arvel Gentry - Studies of Mast Section AerodynamicsDocument10 pagesArvel Gentry - Studies of Mast Section AerodynamicsklzsailingNo ratings yet
- Sailing Drills Presentation (Compatibility Mode)Document38 pagesSailing Drills Presentation (Compatibility Mode)Stu GilfillenNo ratings yet
- Open 5.70 User GuideDocument30 pagesOpen 5.70 User GuideOpen Sailing, IncNo ratings yet
- 49er Owner ManualDocument27 pages49er Owner Manualj_abendstern4688No ratings yet
- Deckhand Job Guide - Secrets To Employment On A Super YachtDocument26 pagesDeckhand Job Guide - Secrets To Employment On A Super YachtDan SevetsNo ratings yet
- Montacargas GP 25Document496 pagesMontacargas GP 25Jose Andres100% (2)
- BoatingDocument28 pagesBoatingHortan100% (1)
- Boat Design GlossaryDocument10 pagesBoat Design GlossaryTarek MohamedNo ratings yet
- Motorboating Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Motorboating SkillsFrom EverandMotorboating Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Motorboating SkillsNo ratings yet
- Dinghy Sailing Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Sailing SkillsFrom EverandDinghy Sailing Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Sailing SkillsNo ratings yet
- Yachting Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Yachting SkillsFrom EverandYachting Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Yachting SkillsNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Sail & Rig Tuning: Genoa & mainsail trim, spinnaker & gennaker, rig tuningFrom EverandIllustrated Sail & Rig Tuning: Genoa & mainsail trim, spinnaker & gennaker, rig tuningRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ST196 Boat Test Allures39 DK V6Document3 pagesST196 Boat Test Allures39 DK V6Gomez GomezNo ratings yet
- IS-346 Unit-1 (ch01)Document28 pagesIS-346 Unit-1 (ch01)Abrar Al-OtaibiNo ratings yet
- North Sails Rigging Manual 2008 WaveDocument25 pagesNorth Sails Rigging Manual 2008 Wavenorthsails100% (1)
- Arvel Gentry-10-Sailing - To - WindwardDocument3 pagesArvel Gentry-10-Sailing - To - WindwardTom Bee100% (1)
- Hull With Midplane BoatDocument4 pagesHull With Midplane BoatVictor Jesus RiosNo ratings yet
- General Boat Hoist PDFDocument9 pagesGeneral Boat Hoist PDFpasanac77No ratings yet
- 2 - The MastDocument11 pages2 - The Mastgiuseppegaribaldi100% (2)
- Schilling Rudder - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesSchilling Rudder - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAhmad HajivandNo ratings yet
- Dehler 42 Brochure DS 181101Document35 pagesDehler 42 Brochure DS 181101AlchemistasNo ratings yet
- Temple University Boat House ProposalDocument27 pagesTemple University Boat House ProposalParks_RecCommissionNo ratings yet
- North Sails Rigging Manual 2008 CamDocument25 pagesNorth Sails Rigging Manual 2008 CamnorthsailsNo ratings yet
- First VoyageDocument103 pagesFirst VoyageJ WolstenholmeNo ratings yet
- WindvaneDocument11 pagesWindvaneapi-334370926No ratings yet
- Mariner Issue 191Document28 pagesMariner Issue 191Pat ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Sailing Hydrofoil: Typical Configurations Foiling ClassesDocument5 pagesSailing Hydrofoil: Typical Configurations Foiling ClassesbogdanNo ratings yet
- Mast & Sail in Europe and AsiaDocument260 pagesMast & Sail in Europe and AsiaJairo MejiaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Yacht and Boat Sailing and Architecture - KempDocument331 pagesManual of Yacht and Boat Sailing and Architecture - KempIvano BossNo ratings yet
- Heel Leeway On Resistance and SideforceDocument10 pagesHeel Leeway On Resistance and SideforceklzsailingNo ratings yet
- Selene62 Standard European SpecificationsDocument7 pagesSelene62 Standard European SpecificationsGomez GomezNo ratings yet
- Foam Sandwich Construction: How To Build A Foam Sandwich Composite BoatDocument24 pagesFoam Sandwich Construction: How To Build A Foam Sandwich Composite BoatPhong TuanNo ratings yet
- Coro BoatDocument15 pagesCoro BoatNeven SandicNo ratings yet
- Multihull Seamanship: An A-Z of skills for catamarans & trimarans / cruising & racingFrom EverandMultihull Seamanship: An A-Z of skills for catamarans & trimarans / cruising & racingNo ratings yet
- Choosing HullDocument16 pagesChoosing Hullnyaungzin100% (1)
- 2012 Open 5.70 Class RulesDocument10 pages2012 Open 5.70 Class RulesOpen Sailing, IncNo ratings yet
- HydrofoilDocument12 pagesHydrofoilbogdan0% (1)
- Worldarc 2016 Information Pack EngDocument10 pagesWorldarc 2016 Information Pack EngBlakee Griffinn Jr.No ratings yet
- Manual Victron EnergyDocument191 pagesManual Victron EnergycezarbucurNo ratings yet
- Manual in Mast FurlingDocument8 pagesManual in Mast FurlingAnne Lymn100% (1)
- How To Repair Big Holes in GRP Boats - Practical Boat OwnerDocument21 pagesHow To Repair Big Holes in GRP Boats - Practical Boat OwnerRODRIGONo ratings yet
- Boat Lift SystemDocument44 pagesBoat Lift Systemteccvm50% (2)
- Boating HandbookDocument180 pagesBoating Handbookmn5kjdwwrfNo ratings yet
- Bavaria - 30 Cruiser BrochureDocument4 pagesBavaria - 30 Cruiser BrochureJason QuekNo ratings yet
- Racing Basics For CatamaransDocument51 pagesRacing Basics For Catamaransolimpiu vesaNo ratings yet
- Navigation & PilotingDocument20 pagesNavigation & PilotingSaif MultaniNo ratings yet
- Span Squared?: Article by Paul BogatajDocument6 pagesSpan Squared?: Article by Paul BogatajRoger AdamsNo ratings yet
- Anchoring Boat SafelyDocument2 pagesAnchoring Boat SafelyFajar IslamNo ratings yet
- (En) Jasic Evo20 Tig Acdc LCD User Manual Tig200pacdc PFC (E2s23) Tig200pacdc (E2s13)Document61 pages(En) Jasic Evo20 Tig Acdc LCD User Manual Tig200pacdc PFC (E2s23) Tig200pacdc (E2s13)sotirisinNo ratings yet
- Rigging The Weta TrimaranDocument6 pagesRigging The Weta TrimaranunforyoppableNo ratings yet
- Seagoing Dinghy 3Document4 pagesSeagoing Dinghy 3Paul BrownNo ratings yet
- GrandBanks 76 Yacht Dolcenera - Longrange Yacht For SaleDocument25 pagesGrandBanks 76 Yacht Dolcenera - Longrange Yacht For SaleEast Coast Yacht BrokersNo ratings yet
- The Aerodynamics of Sail InteractionDocument12 pagesThe Aerodynamics of Sail InteractionFernando GamboaNo ratings yet
- Sky SailsDocument22 pagesSky Sailsroy thomas100% (2)
- Anchor TheoryDocument7 pagesAnchor TheorymadbakingNo ratings yet
- Sailing Manual IntermediateDocument22 pagesSailing Manual IntermediateEmilNo ratings yet
- Roll Motion of Trimaran ShipsDocument273 pagesRoll Motion of Trimaran ShipsPhilSelborNo ratings yet
- Diwali/Deepavali Speech: The Triumph of Good Over Evil!Document1 pageDiwali/Deepavali Speech: The Triumph of Good Over Evil!bourneremembersNo ratings yet
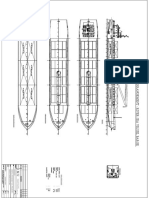
- Main Particulars: General Arrangement Plan (Preliminary)Document1 pageMain Particulars: General Arrangement Plan (Preliminary)bourneremembersNo ratings yet
- NAME5141-Linesplan and curves-MK5Document6 pagesNAME5141-Linesplan and curves-MK5bourneremembersNo ratings yet
- RSV General Arrangement - MK5Document1 pageRSV General Arrangement - MK5bourneremembersNo ratings yet
- Small-Craft Power PredictionsDocument33 pagesSmall-Craft Power PredictionsbourneremembersNo ratings yet
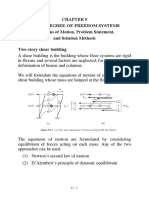
- Two Storeys Hear FrameDocument27 pagesTwo Storeys Hear FramebourneremembersNo ratings yet
- t,E,ρ,damping ratio,L,B,N ,N, restraintsDocument1 paget,E,ρ,damping ratio,L,B,N ,N, restraintsbourneremembersNo ratings yet
- C87SDocument7 pagesC87SbourneremembersNo ratings yet
- DWT Double Hull Bulk Carrier - Brief - SpecDocument10 pagesDWT Double Hull Bulk Carrier - Brief - Specroy thomasNo ratings yet
- Summary of Nurbs-Advantages and DrawbacksDocument1 pageSummary of Nurbs-Advantages and DrawbacksbourneremembersNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 1700Document10 pagesTechnical Specification 1700bourneremembersNo ratings yet
- Intact and Damage Stability CodeDocument111 pagesIntact and Damage Stability CodebourneremembersNo ratings yet
- Dredge AutomationDocument8 pagesDredge AutomationbourneremembersNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument13 pagesCorrosionbourneremembersNo ratings yet
- AMI Organics LTD Unit II 100 TRDocument18 pagesAMI Organics LTD Unit II 100 TRVatsal VermaNo ratings yet
- API Plans FlowserveDocument56 pagesAPI Plans Flowservewwast72100% (5)
- Format - CISDocument8 pagesFormat - CISgopichandallakaNo ratings yet
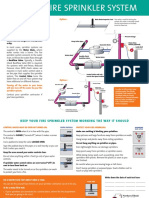
- Fire Sprinkler System GuideDocument2 pagesFire Sprinkler System GuideMike LojoNo ratings yet
- Memo LubDocument57 pagesMemo LubjoelNo ratings yet
- XE145F Presentation AUMDocument21 pagesXE145F Presentation AUMrudyNo ratings yet
- Subject: Structural Design III Introduction of Subject: Examination SchemeDocument63 pagesSubject: Structural Design III Introduction of Subject: Examination SchemeKiran BandeNo ratings yet
- 4 Laws of MotionDocument15 pages4 Laws of MotionHimanshu Gupta100% (1)
- Evo Transmission InformationDocument13 pagesEvo Transmission InformationReynaldo Juanito Ludo LafortezaNo ratings yet
- Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge Model 213.53, Liquid Filling, Stainless Steel CaseDocument2 pagesBourdon Tube Pressure Gauge Model 213.53, Liquid Filling, Stainless Steel Casedidin MuhidinNo ratings yet
- Surging & Blow Out of Loop Seals in A CFBC BoilerDocument9 pagesSurging & Blow Out of Loop Seals in A CFBC Boilermohamed faragNo ratings yet
- Biddle - VRVDocument31 pagesBiddle - VRVutzu_yooNo ratings yet
- Iso 3506 1 2020Document46 pagesIso 3506 1 2020Anna BubblegumNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation-Inia-Pergola 1Document10 pagesDesign Calculation-Inia-Pergola 1Glastal EngineersNo ratings yet
- Gas Lift Valve MechanicsDocument22 pagesGas Lift Valve Mechanicsاسلام الشتيوي100% (1)
- Work and Heat InteractionsDocument13 pagesWork and Heat InteractionsAtharva SawantNo ratings yet
- Bombas en El Libro de Re Metallica 1556Document4 pagesBombas en El Libro de Re Metallica 1556Carlos DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Warehouse 2Document1 pageWarehouse 2aliNo ratings yet
- PC130-8 Parte 2Document440 pagesPC130-8 Parte 2Renata MansanoNo ratings yet
- Dumper Caterpillar 772Document32 pagesDumper Caterpillar 772Foromaquinas100% (2)
- ENSC 3233 HW #1 Solution PDFDocument10 pagesENSC 3233 HW #1 Solution PDFheem bashaNo ratings yet
- ValveTypesSelection - ControlsWikiDocument42 pagesValveTypesSelection - ControlsWikiMayur PatelNo ratings yet
- Module V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesDocument17 pagesModule V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- BOOM Camion (165 297)Document133 pagesBOOM Camion (165 297)David BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Problems With FEM Solution: Heat TransferDocument34 pagesProblems With FEM Solution: Heat Transfermailsk123No ratings yet
- Service Parts List: M18™ 1/4" Hex Impact Driver - Single SpeedDocument2 pagesService Parts List: M18™ 1/4" Hex Impact Driver - Single SpeedhiramfgarciaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual MIL-9000 and MIL-12000: Electric WinchesDocument29 pagesService Manual MIL-9000 and MIL-12000: Electric WinchesGlen C. ChadwickNo ratings yet
- 2015 Ducati Monster 795 16Document155 pages2015 Ducati Monster 795 16Superleggera upmapNo ratings yet