Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diaper Rash: Bagian Ilmu Kesehatan Kulit Dan Kelamin Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hasanudin
Uploaded by
Vithaa'TetaaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diaper Rash: Bagian Ilmu Kesehatan Kulit Dan Kelamin Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hasanudin
Uploaded by
Vithaa'TetaaCopyright:
Available Formats
BAGIAN ILMU KESEHATAN KULIT DAN KELAMIN
FAKULTAS KEDOKTERAN
UNIVERSITAS HASANUDIN
DIAPER RASH
Oleh:
Stanly Pieter Thenu (2008-83-047)
Chresta D. Illintutu (2008-83-048
Jeane P. Andries (2008-83-035)
Pembimbing:
Dr. Dinie Ramdhani K
Konsulen:
Dr. Safruddin Amin, Sp.KK(K), MARS
DIBAWAKAN DALAM RANGKA TUGAS KEPANITERAAN KLINIK
BAGIAN ILMU KESEHATAN KULIT DAN KELAMIN
UNIVERSITAS PATTIMURA
1
AMBON
2014
Introduction
Diaper Rash/Diaper Dermatitis/napkin dermatitis:
Inflammatory eruption of the napkin area
highly prevalent condition in infancy, although the
reported prevalence varies greatly between different
studies.
Jordan et al.1 reported that half of children of age 1 20
months had nappy rash
highest reported prevalence of diaper dermatitis is in the
9 12-month age group
Introduction
Diaper dermatitis
is the result of progressive barrier compromise and
is characterized by dryness/scaling, aberrant
desquamation and erythema.
When the stratum corneum is exposed to prolonged
wetness in an occlusive nappy environment
Introduction
The following factors need to be considered in any
etiology:
Maceration by water
Excessive wetness has several effects on the stratum corneum
Prolonged occlusion of the skin can itself produce erythema,
particularly if water is kept in contact with the skin surface
Friction
Urine
Feces
The combination of these factors breakdown of the
stratum corneum predisposes the skin to opportunistic
infection by faecal microbes diaper dermatitis
Introduction
Clinical manifestasion
onset : during the third to the 12th week (most often),
peak prevalence : between the seventh and 12th months.
The most common form primary irritant napkin
dermatitis
confluent erythema of the convex surfaces in closest contact
with the napkin
that is the buttocks, the genitalia, the lower abdomen and
pubic area, and the upper thighs.
The deeper parts of the groin flexures are generally spared.
Introduction
Clinical Manifestation
erosive form (Jacquets dermatitis) : small vesicles and
erosions, shallow, round ulcers with raised crater-like
edges.
variants of primary irritant napkin dermatitis secondary
invasion by C. albicans.
secondary invasion by C. albicans
erythema may be more intense,
will no longer spare the deeper parts of the flexural folds.
Introduction
Treatment:
Prevention is the best treatment
emolient
Zinc oxide
Topical corticosteroid
Anti-fungi
Diagnosis
History
High prevalence between 6 and 12 month
history concerning skin & diaper care predisposing
factors
history of present illness,
associated symptoms, & physical examination a clinical
diagnosis of irritant contact diaper dermatitis
Other condition :
mouth must be inspected for thrush
skin and nails examined for other lesions
Anamnesis
A complete history includes gestational and birth history
family history
Exposures during pregnancy
medications,
illicit drugs, and
infectious diseases such as varicella and
sexually transmitted diseases
Physical examintation
Irritant diaper dermatitis (Classic findings)
redness and scaling or maceration of the groin with sparing of
the skin creases
erythematous, moist, and sometimes scaly patches on the
convexities area (genitalia and buttocks
areas in closest contact with the diaper.
Shallow erosions sometimes.
Diaper rash in
convex area
Candida secondary infection
second most common type
bright red erythematous,
moist papules,
patches, and plaques that tend to involve body folds
seborrheic dermatitis ,
confluent erythema with greasy, white-yellow scale,
on the scalp (cradle cap)
intertriginous areas are often moist or macerated
Jacquets dermatitis
well-demarcated,
punched-out ulcers
erosions with elevated borders.
A)
diaper dermatitis seboroik.
B)
Jacquets diaper dermatitis.
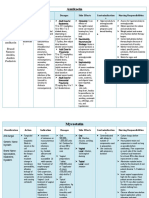
Additional Exam
KOH candida
infeksi herpes Tzanck
Virus direct fluorescent antibody (DFA)
Algorithm diagnosis diaper dermatitis
Treatment
Prevention is the best treatment
Elements of successful treatment include the following:
1.
Attention to the napkins
Disposable napkins
Continuous administration of emollient from certain
disposable napkins.
Frequency of napkin changes
Care of washable napkins
2.
Routine skin care in the napkin area.
3.
Specific therapy
Specific therapy
Topical corticosteroid
Hidrokortison 1%
Strong corticosteroid should be avoided
Covered by emollient
Antifungal
Nystatin
Clotrimazone, Ketokonazole, Miconazone
Covered by emollient
Consider adding hydrocortisone 1%
Topical and systemic Antibiotic
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Psittacine Birds 2eDocument13 pagesPsittacine Birds 2epana0048No ratings yet
- The Dangers of Faecal Incontinence in The At-Risk PatientDocument6 pagesThe Dangers of Faecal Incontinence in The At-Risk PatientRicardo BalauNo ratings yet
- REFERAT Napkin EzcemaDocument20 pagesREFERAT Napkin Ezcemaade nusrayaNo ratings yet
- Napkin Dermatitis PDFDocument14 pagesNapkin Dermatitis PDFGhani AbdurahimNo ratings yet
- D. Diaper 1Document4 pagesD. Diaper 1Merinda Ajeng Arum PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Manejo de Dermatitis Del Pañal 2004Document5 pagesManejo de Dermatitis Del Pañal 2004Estefanía Castañeda MoralesNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument31 pagesImpetigoUmmu Insyirah100% (1)
- Candidiasis (Candidosis)Document17 pagesCandidiasis (Candidosis)h8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- Campbell Etal IntWoundJ 2014Document9 pagesCampbell Etal IntWoundJ 2014SDNo ratings yet
- Diaper Rash: Practice EssentialsDocument17 pagesDiaper Rash: Practice EssentialsXimena MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ccid 11 175Document11 pagesCcid 11 175Remo Alnovryanda PutraNo ratings yet
- TrachomaDocument16 pagesTrachomaabidmc110404No ratings yet
- Cap. 10. SKIN DISEASES PDFDocument14 pagesCap. 10. SKIN DISEASES PDFoana policarpovNo ratings yet
- Referat: Department Dermato - Venereologist Faculty of Medicine Universitas Al-Khairaat Palu 2017Document27 pagesReferat: Department Dermato - Venereologist Faculty of Medicine Universitas Al-Khairaat Palu 2017Elvis HusainNo ratings yet
- PP Diaper RashDocument21 pagesPP Diaper RashAli RumiNo ratings yet
- Candidosis A New ChallengeDocument7 pagesCandidosis A New ChallengeSalvador contreras huertaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Diaper Dermatitis Bernard Cohen, MDDocument11 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Diaper Dermatitis Bernard Cohen, MDRohmah DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Superficial Mycoses Associated With Diaper DermatitisDocument9 pagesSuperficial Mycoses Associated With Diaper DermatitisIntan FajrinNo ratings yet
- Full TextDocument8 pagesFull TextMuammar AhyarNo ratings yet
- Fungal Skin Infections-1Document27 pagesFungal Skin Infections-1Fabb Nelson100% (1)
- Dermatitis: Management: Diaper Differential andDocument4 pagesDermatitis: Management: Diaper Differential andRatna OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Candida-Associateddenturestomatitis - Aetiologyand Management: Areview - Part2.Oraldiseasescausedby Candida SpeciesDocument7 pagesCandida-Associateddenturestomatitis - Aetiologyand Management: Areview - Part2.Oraldiseasescausedby Candida SpeciesDentist HereNo ratings yet
- Tinea Kruris BahanDocument11 pagesTinea Kruris BahanFebridayanti Nur FitriannisaNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Fungal InfectionsDocument8 pagesCutaneous Fungal InfectionsJudith GraalNo ratings yet
- Mucocutaneus Candidiasis: Dosen Pembimbing: DR - Dr.anni Andriani, SP - KK Pembimbing Residen: Dr. EvelynDocument37 pagesMucocutaneus Candidiasis: Dosen Pembimbing: DR - Dr.anni Andriani, SP - KK Pembimbing Residen: Dr. EvelynHamizah Hasbullah100% (1)
- Clinical Heterogeneity and Differential Diagnosis of Atopic DermatitisDocument5 pagesClinical Heterogeneity and Differential Diagnosis of Atopic DermatitisAlina BoiangiuNo ratings yet
- Jacquet Erosive DermatitisDocument15 pagesJacquet Erosive DermatitisRitchie StefanusNo ratings yet
- Infantile Perineal Protrusion.: ChildhoodDocument4 pagesInfantile Perineal Protrusion.: Childhoodcahaya tinggiNo ratings yet
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: January 2014Document4 pagesDyshidrotic Eczema: January 2014Strawberry ShortcakeNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Epidemiology and Latest ResearchDocument10 pagesBacterial Skin Infections: Epidemiology and Latest ResearchIndira DeviNo ratings yet
- Diaper DermatitisjDocument11 pagesDiaper DermatitisjSarah M PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Uncommon Presentations of Tinea Versicolor: Dermatology Practical & ConceptualDocument4 pagesUncommon Presentations of Tinea Versicolor: Dermatology Practical & ConceptualAinun Zamira HabieNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument4 pagesPDF DocumentAditya Yudha PratamaNo ratings yet
- CANDIDIASISDocument20 pagesCANDIDIASISKylie GolindangNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis: International Class MakalahDocument16 pagesCandidiasis: International Class MakalahIrwan AzizNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan DermatitisDocument18 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan DermatitisIRGZI AULIAHAQNo ratings yet
- Diaper Dermatitis Clinical Characteristics and Differential DiagnosisDocument6 pagesDiaper Dermatitis Clinical Characteristics and Differential DiagnosisVicky Pérez KlalaNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox & ChlamydialDocument5 pagesChickenpox & ChlamydialEliezah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Master Plan Onn Skin DisordersDocument5 pagesMaster Plan Onn Skin DisordersSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading - Nurul Nadifa Erza - 2010221012 - Insight Into ScabiesDocument24 pagesJournal Reading - Nurul Nadifa Erza - 2010221012 - Insight Into ScabiesNurul Nadifa ErzaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesChronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis: A Case Reportselandia nisrinaNo ratings yet
- Irritant Diaper DermatitisDocument3 pagesIrritant Diaper DermatitisintanphNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Skin in ChildrenDocument47 pagesDisorders of Skin in Childrensmriti boraNo ratings yet
- Hallopeau 10.1001@jamadermatol.2019.3515Document1 pageHallopeau 10.1001@jamadermatol.2019.3515Faten HayderNo ratings yet
- Jurnal - Fisiologi Kulit NeonatusDocument36 pagesJurnal - Fisiologi Kulit NeonatusMudrikahHaniyahNo ratings yet
- East Africa University Bosaso, Puntland Somalia Faculty of Medicine Communicable Disease MR Buruj Ali SaladDocument42 pagesEast Africa University Bosaso, Puntland Somalia Faculty of Medicine Communicable Disease MR Buruj Ali SaladShaimaa AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis: Management: Diaper Differential andDocument4 pagesDermatitis: Management: Diaper Differential anddoni anandaNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis: (Infantile and Childhood Eczema)Document17 pagesAtopic Dermatitis: (Infantile and Childhood Eczema)Ageededin HartNo ratings yet
- Diaper (Napkin) Dermatitis A FoldDocument6 pagesDiaper (Napkin) Dermatitis A FoldLina Mahayaty SembiringNo ratings yet
- Hand Foot and Mouth DiseaseDocument3 pagesHand Foot and Mouth DiseaseAisah AisahNo ratings yet
- Bullous Impetigo Case Series: An Updated Review: Mariam Hasan Rizvi, Sina AzizDocument5 pagesBullous Impetigo Case Series: An Updated Review: Mariam Hasan Rizvi, Sina AzizsayasajaNo ratings yet
- Inkontinensia Urine DermatitisDocument15 pagesInkontinensia Urine DermatitisAnnisah Ika NurhayatiNo ratings yet
- M13 - Dermatology - Chapter 4Document11 pagesM13 - Dermatology - Chapter 4Idham BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Atopic Dermatitis For Primary Care ProvidersDocument10 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Atopic Dermatitis For Primary Care ProvidersMira GNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative Cheilitis: Case ReportsDocument4 pagesExfoliative Cheilitis: Case ReportsAsep J PermanaNo ratings yet
- Nassef2015 PDFDocument6 pagesNassef2015 PDFBilel DhaouadiNo ratings yet
- Fungal Skin Infections: Education GapDocument17 pagesFungal Skin Infections: Education GapAncuta CalimentNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxNorhana LangiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Epidemiology and Latest ResearchDocument10 pagesBacterial Skin Infections: Epidemiology and Latest ResearchRatih KimNo ratings yet
- Practical Insights into Atopic DermatitisFrom EverandPractical Insights into Atopic DermatitisKwang Hoon LeeNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Jawaban Bahan Ajar 4 Asking & Giving OpinionDocument2 pagesJawaban Bahan Ajar 4 Asking & Giving OpinionVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac Asam Mefanamat: InjeksiDocument12 pagesKetorolac Asam Mefanamat: InjeksiVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Ep. 6 Formularium ObatDocument11 pagesEp. 6 Formularium ObatVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Pidsto Bahasa Inggris VicoDocument2 pagesPidsto Bahasa Inggris VicoVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Contusions and LacerationsDocument19 pagesCerebral Contusions and LacerationsVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Contusions and LacerationsDocument19 pagesCerebral Contusions and LacerationsVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Contusions and LacerationDocument5 pagesCerebral Contusions and LacerationVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Diffuse Vascular Injury (Dvi) : JournalDocument12 pagesDiffuse Vascular Injury (Dvi) : JournalVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Efficacy ClotrimazoleDocument4 pagesEfficacy ClotrimazoleAlexandra ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- (PCH400 T6) AntifungalsDocument10 pages(PCH400 T6) Antifungalsqjamolin210000000237No ratings yet
- Kodamaea Ohmeri InfectionDocument8 pagesKodamaea Ohmeri InfectionMufti DindaNo ratings yet
- Garlic: Nat Ure's Amazing Nut Rit Ional and Medicinal Wonder FoodDocument32 pagesGarlic: Nat Ure's Amazing Nut Rit Ional and Medicinal Wonder FoodABDIEL ADRIAZOLA MURIELNo ratings yet
- Clinical Validation of A Test For The Diagnosis of VaginitisDocument9 pagesClinical Validation of A Test For The Diagnosis of Vaginitiserna utamiNo ratings yet
- Clabsi DR - RonaldDocument19 pagesClabsi DR - RonaldsilviNo ratings yet
- Modern Homoeopathy Speciallity For Following DiseasesDocument2 pagesModern Homoeopathy Speciallity For Following DiseasesAnchal KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Ef Cacy and Safety of A Single Oral 150 MG Dose of Uconazole For The Treatment of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis in JapanDocument7 pagesEf Cacy and Safety of A Single Oral 150 MG Dose of Uconazole For The Treatment of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis in JapanMuhammad IkbarNo ratings yet
- Pros Tho Don Tic Considerations in Diabetes MellitusDocument16 pagesPros Tho Don Tic Considerations in Diabetes MellitusNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Womens Health Care 11th Edition Lowdermilk Test BankDocument38 pagesMaternity and Womens Health Care 11th Edition Lowdermilk Test Bankhenrycpwcooper100% (16)
- Cutaneous Candidiasis Treatment & Management: Medical CareDocument3 pagesCutaneous Candidiasis Treatment & Management: Medical CarerajatinaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Prevention and ControlDocument197 pagesCommunicable Disease Prevention and Controldennisjamesbartz100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Part II Diseases (1) 2Document21 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Part II Diseases (1) 2MK LiNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic Infections: Genet Gebremedhin (MD) Assistant Prof of Gynecology & Obstetrics University of Gondar March 4 2012Document91 pagesGynecologic Infections: Genet Gebremedhin (MD) Assistant Prof of Gynecology & Obstetrics University of Gondar March 4 2012Degefaw BikoyNo ratings yet
- GLOMNDocument17 pagesGLOMNIce 69No ratings yet
- AntifungalDocument3 pagesAntifungalDarren WilliamNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between HIV and AidsDocument14 pagesThe Difference Between HIV and AidsAnonymous bq4KY0mcWGNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument4 pagesAmikacinkristineK100% (1)
- Polly Hattemer Book 2 TtreatmentsDocument100 pagesPolly Hattemer Book 2 Ttreatmentssusilorini100% (1)
- 1.oral Infectious DiseasesDocument68 pages1.oral Infectious DiseasesDrMohamed AssadawyNo ratings yet
- Imran Khan Autoimmune Disease The Flame WithinDocument290 pagesImran Khan Autoimmune Disease The Flame WithinpaulxeNo ratings yet
- Agents of Opportunistic MycosesDocument13 pagesAgents of Opportunistic MycosesMUNDER OMAIRA NASRA D.No ratings yet
- Dermatovenerology CM 388 PDFDocument54 pagesDermatovenerology CM 388 PDFIvanes IgorNo ratings yet
- Block 1 (40) Infectious Diseases As-CompressedDocument173 pagesBlock 1 (40) Infectious Diseases As-CompressedanweridrisejazNo ratings yet
- Trichomoniasis and CandidiasisDocument5 pagesTrichomoniasis and CandidiasisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- SHC Heme Onc Antimicrobial ProphylaxisDocument4 pagesSHC Heme Onc Antimicrobial ProphylaxisTala MahmoudNo ratings yet
- IMCI Chart 2014 EditionDocument80 pagesIMCI Chart 2014 EditionHarold DiasanaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Chapter 42 zp-1-3Document42 pagesPharmacology Chapter 42 zp-1-3sho bartNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AntibioticsDocument16 pagesAntifungal AntibioticsLyadelou FortuNo ratings yet