Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GBO 007 E1 1 GSM Signaling System-48
Uploaded by
Sudheera IndrajithCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GBO 007 E1 1 GSM Signaling System-48
Uploaded by
Sudheera IndrajithCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM Signaling System
ZTE University
Objectives
At the end of this course, you will be able to:
Know GSM system signaling model
State various types of GSM protocol messages
Understand GSM system basic signaling procedure
Content
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM protocol message
Basic Signaling Procedure
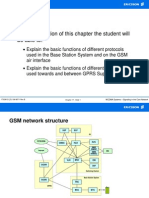
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM Interface
Um
Abis
GGSN
SGSN
BTS
HLR/AUC
BTS
Qx
Gb
EIR
SMC
OMC
BTS
NSMU
FSMU TRAU
BSC
BTS
Ater
MSC/VLR/GMSC
PSTN/PLMN/
PSPDN/ISDN
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM system signaling model adopts the lowest three
layer of OSI seven layer protocol model, from low to
high:
Application layer
Link layer/Network layer
Physical layer
GSM System Signaling Model
Physical Layer
The physical layer provides error protection transmission. It defines
the electric parameters of transmission.
In ZTE-GSM digital mobile communication systems, The physical
layer of Um interface between MS and BTS is Radio link. Abis
interface physical layer adopts 75-ohm coaxial cable or 120-ohm
symmetrical twisted pair whose rate is 2Mbit/s.
GSM System Signaling Model
Data Link Layer
The data link layer major functions: frame transmission errorfree transmission and realize end-to-end bits transfer between
two connective entities. Open maintenance and close the
connection of two connective entities.
The link layer protocol used by the GSM system at the radio
interface is the LAPDm protocol (Dm channel link access
procedure). The data link layer of Abis interface between BTS
and BSC is LAPD (D channel link access procedure).
GSM System Signaling Model
Application Layer
ApplicationLayer
CC
CM
MM
SS
SMS
RR
GSM System Signaling Model
Application Layer
Radio Resources (RR) management handles the
establishment, maintenance and release of physical
channels. Its major functions are performed by BSC. Part
of functions are performed by BTS.
Mobility Management (MM) deals with the mobile stations
register and the identify of the mobile subscriber, The
function are performed by MSC.
The CM Layer is composed of three functional entities:
Call Control (CC), deals with the functions to establish
maintenance and release the call Short Message
Service support (SMS) and Supplementary Service
support (SS).
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM protocol
Public Switched
Telephone Network
(PSTN)
Mobile
Switching
Centre
(MSC)
MAP/TCAP + ISUP/TUP
))
Mobile
Switching
Centre
(MSC)
DTAP + BSSMAP
A interface
Base
Station
Controller
(BSC)
BTSM
A-bis interface
MAP/TCAP
Authentication
Centre
(AUC)
Home
Location
Register
(HLR)
Visitor
Location
Register
(VLR)
Equipment
ID
Register
(EIR)
To other VLR
MAP/TCAP
MAP/TCAP
ISUP/TUP
Base
Transceiver
Station
(BTS)
))
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM Protocol Architecture
MS
BSC
BTS
CM
(CM)
(CM)
(CM)
MSC
DTAP
CM
MM
(MM)
(MM)
(RR)
(RR)
RR
(MM)
RR
RR'
BTSM
BTSM
Sig. layer 2
(LAPDm)
Sig. layer 2
(LAPDm)
Sig. layer 2
(LAPD)
Sig. layer 2
(LAPD)
Layer 1 (air)
Layer 1 (air) Sig. layer 1
Sig. layer 1
Um Interface
Abis Interface
DTAP Direct Transfer Application Part
BSSMAP BSS Management Application Part
CM Call Management
MM Mobile Management
RR Radio Resource Management
BTSM BTS Management
(CM+MM)
BSSMAP
MM
BSSMAP
I
S
MAP U
TCAP P
SCCP
SCCP
SCCP
MTP
MTP
MTP
A Interface
SCCP Signalling Connection Control Part
MAP Mobile Application Part
TCAP Transaction Capability Application Part
ISUP ISDN User Part
MTP Message Transfer Part
Inter-MSC
Interface
Content
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM protocol message
Basic Signaling Procedure
GSM protocol message
Um interface protocol stack
Um interface
CM
MM
RR
RR
LAPDm
LAPDm
Layer1
Layer1
MS
BTS
GSM protocol message
LAPDm frame format
The address field contains the service
access point identifier (SAPI).
SAPI = 0 represents the signaling link
SAPI = 3 represents the short message link
In the control field,
N (S) represents the sending serial number
N (R) represents the receiving serial number
Address
SAPI
Control
N(S)
Information
N(R)
GSM protocol message
Operation mode
Acknowledged mode: Requires the confirmation
from the receiver. This mode provides a whole set of
control mechanism for error recovering and flow
control, the establishment mechanism and release
mechanism for multi-frame operations.
Unacknowledged mode: The receiver is not required
to send a confirmation upon reception of a UI frame.
This operation mode does not provide flow control or
error recovering mechanism.
GSM protocol message
RR messages
Type
Message
Channel establishment message
Immediate assignment
Immediate assignment reject
Ciphering message
Ciphering mode command
Ciphering mode complete
Handover command
Handover message
Handover complete
Handover failure
Handover access
Channel release message
Channel release
Paging message
Paging request
Paging response
System info
System info:1 8
GSM protocol message
MM messages
Type
Message
IMSI detach indication
Registration messages
Location updating accept
Location updating reject
Location updating request
Authentication reject
Authentication request
Security messages
Authentication response
Identity request
Identity response
TMSI reallocation command
TMSI reallocation complete
CM service accept
Connection-management messages
CM service reject
CM service request
GSM protocol message
CC messages
Type
Message
Alerting
Call confirmed
Call establishment messages
Call proceeding
Connect
Disconnect
Call clearing messages
Release
Release complete
Congestion control notify
Miscellaneous messages
Start DTMF
Stop DTMF
GSM protocol message
Abis Interface Protocol stack
GSM protocol message
LAPD Protocol
SAPI = 0 represents the signaling link,
SAPI = 62 represents the O&M link,
SAPI = 63 represents the management link of the LapD layer.
GSM protocol message
A interface protocol stack
CM
A interface
BSC
RR
MM
BSSAP
BSSAP
SCCP
SCCP
MTP3
MTP3
MTP2
MTP2
Layer1
Layer1
MSC
GSM protocol message
Relationship between SCCP and OSI model
HLR
INAP
OMAP
Layer 7
TCAP
46
ISP
VLR
MAP
BSSAP
SCCP
Layer3
MTP-3
Layer2
MTP-2
Layer1
MTP-1
ISUP
TUP
GSM protocol message
BSSAP
MSC
MS
BSS
CC
CC
DTAP
MM
MM
RR
BSSAP
DTAP
BSSMAP
RR
BSSAP
BSSMAP
DTAP
Distribution
Distribution
SCCP
SCCP
MTP
MTP
BSSMAP
RR
LAPDm
LAPDm
L1
L1
DTAP
GSM protocol message
SCCP message
CR Connection request
CC Connection confirm
CREF Connection refused
RLSD
Released
RLC
Release complete
DT1
Data form 1
UDT
Unit data
UDTS Unit data service
GSM protocol message
BSSMAP Message -1
Assignment messages (setup of traffic channels)
Assignment request
Assignment complete
Assignment failure
Handover messages
Handover request
(to BSC: request for handover to that BSC)
Handover required
(to MSC: inter BSC/MSC handover required)
Handover request ack.
Handover command (to BSC: contains new radio channel/BTS for the MS)
Handover complete
(to MSC: commanded handover successful)
Handover failure
(to MSC: commanded handover unsuccessful)
Handover performed (to MSC: BSC has performed internal handover)
Handover candidate enquiry
handed
(to MSC: acknowledge of handover request)
(to BSC: MSC requests list of MS that could be
over to another cell)
Handover candidate response (to MSC: answer to handover candidate enquiry)
Handover required reject
Handover detect
(to BSC: required handover unsuccessful)
(to MSC: commanded handover successful)
GSM protocol message
BSSMAP Message -2
Release messages
Clear command
(release of traffic channel)
Clear complete
Clear request
SAPI n clear command
SAPI n clear complete
SAPI n reject
(control of layer 2 SAPI n on the radio interface)
General messages
Reset
(initialisation of BSS or MSC due to failure)
Reset acknowledge
Overload
Trace invocation
Reset circuit (initialisation of single circuit due to failure)
(processor or CCCH overload)
(start production of trace record
Terrestrial resource messages
Block
(management of circuits/time slots between MSC and BTS)
Blocking acknowledge
Unblock
Unblocking acknowledge
GSM protocol message
BSSMAP Message -2
Radio resource messages
Resource request
in BSS cells)
Resource indication
Paging
Cipher mode command
Classmark update
class)
Cipher mode complete
Queuing indication
assignment of tch)
(available radio channels
(paging of MS)
(start encryption)
(change of MS power
(indicates delay in
Content
GSM System Signaling Model
GSM protocol message
Basic Signaling Procedure
Basic Signaling Procedure
Mobile Originating Call Establishment Procedure -1
Basic Signaling Procedure
Mobile Originating Call Establishment Procedure -2
Basic Signaling Procedure
Mobile Originating Call Establishment Procedure -3
Basic Signaling Procedure
Mobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure -1
Basic Signaling Procedure
Mobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure -2
Basic Signaling Procedure
Mobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure -3
Basic Signaling Procedure
Location Update Procedure -1
Basic Signaling Procedure
Location Update Procedure -2
Basic Signaling Procedure
Intra Cell Handover Procedure
Basic Signaling Procedure
Intra BSC Handover Procedure
Basic Signaling Procedure
Inter BSC Handover Procedure
Basic Signaling Procedure
Call Re-establishment Procedure
Basic Signaling Procedure
Directed Retry Procedure
Basic Signaling Procedure
Short Message Procedure On SDCCH When MS Is
Calling -1
Basic Signaling Procedure
Short Message Procedure On SDCCH When MS Is
Calling -2
Basic Signaling Procedure
Short Message Procedure On SDCCH When MS Is
Called -1
Basic Signaling Procedure
Short Message Procedure On SDCCH When MS Is
Called -2
Basic Signaling Procedure
Short Message Procedure On SACCH When
MS Is Calling
Basic Signaling Procedure
Short Message Procedure On SACCH When
MS Is Called
You might also like
- RYA-MCA Coastal Skipper-Yachtmaster Offshore Shorebased 2008 AnswersDocument28 pagesRYA-MCA Coastal Skipper-Yachtmaster Offshore Shorebased 2008 AnswersSerban Sebe100% (4)
- Satellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandSatellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Call FlowsDocument103 pagesCall Flows742952100% (3)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- HRD DilemmaDocument4 pagesHRD DilemmaAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Abu Hamza Al Masri Wolf Notice of Compliance With SAMs AffirmationDocument27 pagesAbu Hamza Al Masri Wolf Notice of Compliance With SAMs AffirmationPaulWolfNo ratings yet
- The Art of Blues SolosDocument51 pagesThe Art of Blues SolosEnrique Maldonado100% (8)
- GSM Signaling System-48Document48 pagesGSM Signaling System-48sburki89No ratings yet
- GBO - 013 - E1 - 1 GSM Signaling System-48Document48 pagesGBO - 013 - E1 - 1 GSM Signaling System-48Clive MangwiroNo ratings yet
- GSM Signalling ProcedureDocument60 pagesGSM Signalling ProcedureSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Map Call Flow ImportantDocument22 pagesMap Call Flow ImportantPham Thanh TamNo ratings yet
- GSM Call Flow ProceduresDocument54 pagesGSM Call Flow ProceduresKafayat Aheer100% (5)
- GBC - 001 - E1 - 1 GSM Basic: ZTE University GSM-BSS TeamDocument40 pagesGBC - 001 - E1 - 1 GSM Basic: ZTE University GSM-BSS Teambahuguna_45No ratings yet
- Gbo 001 E1 1 GSM Basic-40Document40 pagesGbo 001 E1 1 GSM Basic-40Clive MangwiroNo ratings yet
- GB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-01Document40 pagesGB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-01JaneYinNo ratings yet
- GB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-40Document40 pagesGB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-40Didier TangaNo ratings yet
- GSM GPRS: Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument55 pagesGSM GPRS: Global System For Mobile CommunicationArrul InsaniNo ratings yet
- 2G - GSMDocument47 pages2G - GSMMuhammad Rauf AkramNo ratings yet
- GSM Overview UpdatedDocument131 pagesGSM Overview UpdatedSandip DasNo ratings yet
- GSM, GPRS, Umts, Hsdpa and HSUPA Protocols and Call Flow by Kiran KoonaDocument103 pagesGSM, GPRS, Umts, Hsdpa and HSUPA Protocols and Call Flow by Kiran KoonaZin MaungNo ratings yet
- CdmaDocument1 pageCdmaflatelecom938No ratings yet
- Signalling and Control in GSMDocument22 pagesSignalling and Control in GSMFebri DoangNo ratings yet
- 2 5-GSMDocument47 pages2 5-GSMTanveer Akram100% (1)
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Document25 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Smart VinayNo ratings yet
- The Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Document32 pagesThe Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)devajeet_nerist2840No ratings yet
- GSM BasesDocument9 pagesGSM BasesBasel wesamNo ratings yet
- SigleRAN Abbreviations V1.0 (With Description)Document20 pagesSigleRAN Abbreviations V1.0 (With Description)Francesco TrebbiNo ratings yet
- GSM NetworkDocument40 pagesGSM NetworkSandeep P BhaskarNo ratings yet
- GSM Call FlowsDocument40 pagesGSM Call FlowsNitin Jain100% (9)
- UMTS FamilyDocument92 pagesUMTS FamilyAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Umts PosterDocument2 pagesUmts Posterand_2012No ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) and ExtensionsDocument33 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) and Extensionsਗੁਰਪਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੂਰਾਪੁਰੀNo ratings yet
- GSM System TheoryDocument83 pagesGSM System TheoryMuhammad Saqib JadoonNo ratings yet
- PDF GSMDocument6 pagesPDF GSMMahabub AhmedNo ratings yet
- GSM Protocol Layers For SignalingDocument5 pagesGSM Protocol Layers For SignalingProf. P. P. AdivarekarNo ratings yet
- AbbreviationsDocument6 pagesAbbreviationsChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of GSM Network - AppendixDocument9 pagesBasic Components of GSM Network - AppendixBasel wesamNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document44 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)المهندس غالبNo ratings yet
- GSM ProtocolsDocument12 pagesGSM ProtocolsraymondushrayNo ratings yet
- Presentation On GSM NetworkDocument39 pagesPresentation On GSM NetworkSonu TripathiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On GSM NetworkDocument40 pagesPresentation On GSM NetworkNgoy SaroNo ratings yet
- 3GRAN 07 6272 Appendix RFDocument14 pages3GRAN 07 6272 Appendix RFhungpm2013No ratings yet
- 946169657-اختصارات هندسة الاتصالاتDocument14 pages946169657-اختصارات هندسة الاتصالاتICCB2006No ratings yet
- CS 9059 Mobile ComputingDocument107 pagesCS 9059 Mobile Computingkarthi_gopalNo ratings yet
- Various Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarDocument43 pagesVarious Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarKuldeep BishtNo ratings yet
- GSM Signalling ConceptsDocument25 pagesGSM Signalling ConceptsThirupathi SubbaiahNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 - GSM - NetworkDocument21 pagesCurs 1 - GSM - NetworkDarius DaKiddNo ratings yet
- IP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureFrom EverandIP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemFrom EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsFrom EverandThe Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chipless Radio Frequency Identification Reader Signal ProcessingFrom EverandChipless Radio Frequency Identification Reader Signal ProcessingNo ratings yet
- BRS End of The Week Results Snapshot - 21.10.2022Document9 pagesBRS End of The Week Results Snapshot - 21.10.2022Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- BRS Weekly Report 14.10.2022Document13 pagesBRS Weekly Report 14.10.2022Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Trader's Daily Digest 15.11.2022Document8 pagesTrader's Daily Digest 15.11.2022Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Trader's Daily Digest 30.08.21Document7 pagesTrader's Daily Digest 30.08.21Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Trader's Daily Digest 14.09.2021Document8 pagesTrader's Daily Digest 14.09.2021Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- GO - BT1004 - E01 - 0 GPRS and EDGE Introduction-41Document38 pagesGO - BT1004 - E01 - 0 GPRS and EDGE Introduction-41Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- BRS Market Report: Week IVDocument7 pagesBRS Market Report: Week IVSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- 2058-34 15.02.2018 Public Officer PermitDocument2 pages2058-34 15.02.2018 Public Officer PermitSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Licence Rene Val ApplicationformDocument3 pagesLicence Rene Val ApplicationformSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Trader's Daily Digest - 15.05.2019Document7 pagesTrader's Daily Digest - 15.05.2019Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- GERAN ZGB-02!01!001 Paging Feature GuideDocument17 pagesGERAN ZGB-02!01!001 Paging Feature GuideSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Tems Cel File FormatDocument2 pagesTems Cel File FormatSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- BRS Morning Shout 10 08 2016Document5 pagesBRS Morning Shout 10 08 2016Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Chess Results ListDocument8 pagesChess Results ListSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- 1-WO - NP2001 - E01 - 1 UMTS Radio Network Planning Process-++-P65Document65 pages1-WO - NP2001 - E01 - 1 UMTS Radio Network Planning Process-++-P65Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Filename Cellid Secno. Rru Number Ant Number Antinfo Ul FrequencDocument3 pagesFilename Cellid Secno. Rru Number Ant Number Antinfo Ul FrequencSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Comment:-: Page 1 of 1Document1 pageComment:-: Page 1 of 1Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- BRS Morning Shout 11.10.2016Document3 pagesBRS Morning Shout 11.10.2016Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Brs Morning Shout 22 September 2016: 65, Braybrooke Place, Colombo 2, Sri LankaDocument3 pagesBrs Morning Shout 22 September 2016: 65, Braybrooke Place, Colombo 2, Sri LankaSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Company Update: Brs Morning Shout 29 July 2016Document7 pagesCompany Update: Brs Morning Shout 29 July 2016Sudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Ikea AnalysisDocument33 pagesIkea AnalysisVinod BridglalsinghNo ratings yet
- Hager Pricelist May 2014Document64 pagesHager Pricelist May 2014rajinipre-1No ratings yet
- Profile On Sheep and Goat FarmDocument14 pagesProfile On Sheep and Goat FarmFikirie MogesNo ratings yet
- BMA Recital Hall Booking FormDocument2 pagesBMA Recital Hall Booking FormPaul Michael BakerNo ratings yet
- Sweet Biscuits Snack Bars and Fruit Snacks in MexicoDocument17 pagesSweet Biscuits Snack Bars and Fruit Snacks in MexicoSantiagoNo ratings yet
- Mat Boundary Spring Generator With KX Ky KZ KMX KMy KMZDocument3 pagesMat Boundary Spring Generator With KX Ky KZ KMX KMy KMZcesar rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Securitron M38 Data SheetDocument1 pageSecuritron M38 Data SheetJMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- Tinplate CompanyDocument32 pagesTinplate CompanysnbtccaNo ratings yet
- Discover Mecosta 2011Document40 pagesDiscover Mecosta 2011Pioneer GroupNo ratings yet
- D - MMDA vs. Concerned Residents of Manila BayDocument13 pagesD - MMDA vs. Concerned Residents of Manila BayMia VinuyaNo ratings yet
- Daraman vs. DENRDocument2 pagesDaraman vs. DENRJeng GacalNo ratings yet
- Simoreg ErrorDocument30 pagesSimoreg Errorphth411No ratings yet
- 6 V 6 PlexiDocument8 pages6 V 6 PlexiFlyinGaitNo ratings yet
- Employees' Pension Scheme, 1995: Form No. 10 C (E.P.S)Document4 pagesEmployees' Pension Scheme, 1995: Form No. 10 C (E.P.S)nasir ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Electricity Act - 2003Document84 pagesThe Electricity Act - 2003Anshul PandeyNo ratings yet
- General Financial RulesDocument9 pagesGeneral Financial RulesmskNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2: Fundamentals of Management Science For Built EnvironmentDocument23 pagesAssignment - 2: Fundamentals of Management Science For Built EnvironmentVarma LakkamrajuNo ratings yet
- Activity Description Predecessor Time (Days) Activity Description Predecessor ADocument4 pagesActivity Description Predecessor Time (Days) Activity Description Predecessor AAlvin LuisaNo ratings yet
- MOTOR INSURANCE - Two Wheeler Liability Only SCHEDULEDocument1 pageMOTOR INSURANCE - Two Wheeler Liability Only SCHEDULESuhail V VNo ratings yet
- Online Learning Interactions During The Level I Covid-19 Pandemic Community Activity Restriction: What Are The Important Determinants and Complaints?Document16 pagesOnline Learning Interactions During The Level I Covid-19 Pandemic Community Activity Restriction: What Are The Important Determinants and Complaints?Maulana Adhi Setyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Voice Controlled Robot: Aditya Chaudhry, Manas Batra, Prakhar Gupta, Sahil Lamba, Suyash GuptaDocument3 pagesArduino Based Voice Controlled Robot: Aditya Chaudhry, Manas Batra, Prakhar Gupta, Sahil Lamba, Suyash Guptaabhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- PFI High Flow Series Single Cartridge Filter Housing For CleaningDocument2 pagesPFI High Flow Series Single Cartridge Filter Housing For Cleaningbennypartono407No ratings yet
- RENCANA KERJA Serious Inspeksi#3 Maret-April 2019Document2 pagesRENCANA KERJA Serious Inspeksi#3 Maret-April 2019Nur Ali SaidNo ratings yet
- How Yaffs WorksDocument25 pagesHow Yaffs WorkseemkutayNo ratings yet
- Capital Expenditure DecisionDocument10 pagesCapital Expenditure DecisionRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Government of West Bengal Finance (Audit) Department: NABANNA', HOWRAH-711102 No. Dated, The 13 May, 2020Document2 pagesGovernment of West Bengal Finance (Audit) Department: NABANNA', HOWRAH-711102 No. Dated, The 13 May, 2020Satyaki Prasad MaitiNo ratings yet