Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AKF Carbohydrat Lipid
Uploaded by
ahmadhelmiase76210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views19 pagesCarbohydrate is one of the major compound as source of energy and also the primary source of brain, erythrocytes and retinal cell. Control of blood glucose is under two major hormones : insulin and glucagons both produced by pancreas. Their action appose each other. Diabetes Mellitus is actually a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defect in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCarbohydrate is one of the major compound as source of energy and also the primary source of brain, erythrocytes and retinal cell. Control of blood glucose is under two major hormones : insulin and glucagons both produced by pancreas. Their action appose each other. Diabetes Mellitus is actually a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defect in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views19 pagesAKF Carbohydrat Lipid
Uploaded by
ahmadhelmiase7621Carbohydrate is one of the major compound as source of energy and also the primary source of brain, erythrocytes and retinal cell. Control of blood glucose is under two major hormones : insulin and glucagons both produced by pancreas. Their action appose each other. Diabetes Mellitus is actually a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defect in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Carbohydrates are compounds containing C, H
and O. Carbohydrate is one of the major
compound as source of energy and also the
primary source of brain, erythrocytes and
retinal cell. Carbohydrates are stored primarily
as liver and muscle glycogen.
The classification of carbohydrate is based on
four different properties
The size of the base carbon chain
The location of the CO function group
The number of sugar unit
The stereochemistry of the compound
The nervous system including brain totally
depends on glucose from surrounding
extra cellular fluid (ECF) for energy
The liver, pancreas, and other endocrine
glands are all involved in the controlling the
blood glucose concentration within a narrow
range. During a brief fast, glucose is supplied
to the ECF from liver through glycogenolysis.
Control of blood glucose is under two major
hormones : insulin and glucagons both
produced by pancreas. Their action appose
each other.
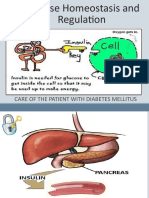
Insulin is the primary hormones
responsible for the entry of glucose into
cell. It is synthesized by the ß-cell of
islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
When these cell detect an increase in
body glucose, they release insulin and
causes an increased movement of glucose
into the cells and increasesd glucose
metabolism.
Insulin is normally released when glucose
levels are high and is not released when
glucose levels are decreased. It decreased
plasma glucose levels by increasing the
transport entry of glucose in muscle and
adipose tissue by way of non specific
receptor.
Glucagon is the primary hormone responsible
for increasing glucose levels. It is synthesized
by the α-cells of islet of Langerhans in the
pancreas and is released during stress and
fasting states. When these cells detect a
decrease in body glucose, they release
glucacon. Glucagon acts by increasing plasma
glucose levels by glycogenolysis in the liver
and an increase in gluconeogenesis. It can be
referred to as a hyperglycemic agent.
Hyperglycemia is an increase in plasma
glucose levels caused by an imbalance of
hormones. This condition known as
diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Mellitus is actually a group of
metabolic diseases characterized by
hyperglycemia resulting from defect in
insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
Classification of diabetes Mellitus :
1. Diabetes type 1, is characterized by
inappropriate hyperglycemia primarily due to
pancreatic islet ß-cell destruction and proneness
to ketoacidosis caused an absolute deficiency.
This case constitutes only 10%-20% of all diabetes
and commonly occurs in childhood and
adolescence
2. Diabetes type 2, is characterized by
hyperglycemia due to an individual's resistance
to insulin with an insulin secretory defect. This
resistance result in a relative, not an absolute
insulin deficiency. This type is the majority of
diabetes case.
Most patient in this type are obese or have
abdominal fat
3.Other Specific types of diabetes, associated
with secondary conditions including genetic
defect of ß-cell function or insulin action,
pancreatic disease, endocrine disease, drug
and chemical induced and certain genetic
syndrome
4. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), is any
degree of glucose intolerance with onset or
first recognition during pregnancy due to
metabolic and hormonal changes
Laboratory Finding in Hyperglycemia
Increased glucose in plasma and urine
Increased urine specific gravity (Density)
Increased serum and urine osmolality
Ketones in serum and urine
Decreased blood and urine pH
Electrolytes imbalance
Hypoglycemia involves decreased plasma glucose
levels and can have many causes, most reactive
(postprandial) and fasting (postabsorbtive). The
warning signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia are all
related to the central nervous system.
reactive (postprandial) such as
alimentary/gastrointestinal surgery characteristics
include a nonsuppressible insulin like activity in
which glucose levels drops below normal fasting
level fasting (postabsorbtive), individual has a loss
of glycemic control during in fasting state. This case
including insulin excess, oral hypoglycemic drugs
and prolonged alcoholic ingestion. Neonatal,
congenital and ketotic hypoglycemia occur in
children.
Glucose oxidase : glucose react oxygen and
water with the present glucose axidase produce
gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen
peroxide react reduced chromogen by peroxidase
produced oxidized chromogen and water
Hexokinase : Glucose and ATP with hexokinase
produced glucose-6-phosphat react NADP
become NADPH which has strong absorbance at
340 nm
Clinitest/ Benedict : Glucose and some reducing
substance react Cu(II) produced Cu(I)oxide
The major lipids of the body triglycerides,
cholesterol, phospholipids and glycolipids
play a variety of biologic roles. Lipoprotein
are complex particles that interact with
many other metabolic pathway of the body.
Cholesterol is an unsaturated steroid alcohol
of high molecular weigh consisting of a
perhydrocyclopenthanthro-line ring and a
side chain of eight carbon atoms.
Characteristics of human lipoprotein :
Chylomicron :diameter 80-1200 nm, density
<0,93 g/ml
VLDL ; diameter 40-80 nm, density 0,93-
1,006 g/ml
IDL : diameter 30-40 nm, density 1.006-1,019
g/ml
LDL : diameter 18-30 nm, density 1,019-
1,063 g/ml
HDL : diameter 5-12 nm, density 1,063-1,21
g/ml
Arteriosclerosis caused by cholesterols in the
wall of arteries. This lipid deposition starts
with thin layers called fatty streaks. The
fatty streaks develop over time into plaques
which partially block blood flow.
When plaques develop in legs or arm called
Peripheral Vascular disease (PVD), in heart
called Coronary Artery disease (CAD), in
vessel brain called Cerebrovascular disease
(CVD) associated with Stroke
Hyperlipoproteinemia are disease associated
with elevated lipoprotein levels while
Hypolipoproteinemia are disease associated
with decreased lipoprotein level. Devided into
low LDL and low HDL caused by physiology
stress, acute infection, surgical procedure
Hyperlipoproteinemia including
hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia
and combined hyperlipidemia. All associated
with heart disease
Lipid Measurement used isolation/extraction
from samples and use some enzymes to
convert into substance to be measured.
Total lipid measurement used gravimetric
method but other substance like cholesterol
need spectrophotometric method like mass
spectrometry. Now, bioassay such as Enzyme
Like Immunobsorbent assay (ELISA), radio
immunodetection (RID) and radioimmuno
assay (RIA) prefer and more available.
VLDL, IDL, LDL and HDL characterized by
separation centrifugal method. The
supernatant analized by enzyme assay.
Fatty acid analysis is less used commonly
in routine clinical test. Usually use Gas
chromatography.
You might also like
- Reaction Kinetics (5) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen UniversityDocument27 pagesReaction Kinetics (5) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen Universityahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics (3) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen UniversityDocument35 pagesReaction Kinetics (3) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen Universityahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- Process For The Preparation of Monosodium GlutamateDocument18 pagesProcess For The Preparation of Monosodium Glutamateahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics (1) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen UniversityDocument28 pagesReaction Kinetics (1) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen Universityahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- AKF ProteinDocument17 pagesAKF Proteinahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- AKF Carbohydrat LipidDocument19 pagesAKF Carbohydrat Lipidahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- Woodwardrulestructural Analysis (Application of Woodward-Fieser Rules) of SpectrosDocument20 pagesWoodwardrulestructural Analysis (Application of Woodward-Fieser Rules) of Spectrosahmadhelmiase7621100% (3)
- Organic Analysis Chemistry Part - 4Document35 pagesOrganic Analysis Chemistry Part - 4ahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- Organic Analysis Chemistry Part - 3Document33 pagesOrganic Analysis Chemistry Part - 3ahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- Organic Analysis Chemistry Part - 2Document32 pagesOrganic Analysis Chemistry Part - 2ahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Reversing Diabetes in 21 Days - Nandita ShahDocument229 pagesReversing Diabetes in 21 Days - Nandita ShahLaray Roy100% (3)
- Lets Talk About Fasting PDFDocument28 pagesLets Talk About Fasting PDFlearnafren100% (2)
- Diabetes in The ElderlyDocument24 pagesDiabetes in The ElderlyRAJEEVNo ratings yet
- Vol 4 - Autocoids Diagnostics - and Drugs From New BiologyDocument716 pagesVol 4 - Autocoids Diagnostics - and Drugs From New Biologyjoshigauta100% (1)
- Anp 120 Test 2Document22 pagesAnp 120 Test 2Joseph A MwitupaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Davidson Shortlisted 24 Ed (Hira - Fj'23)Document30 pagesDiabetes Davidson Shortlisted 24 Ed (Hira - Fj'23)saifsaffa2No ratings yet
- Obesity As Disruptor of The Female Fertility: Review Open AccessDocument13 pagesObesity As Disruptor of The Female Fertility: Review Open Accessirfan dwiputra rNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology TestDocument88 pagesPharmacology TestIrinotecanNo ratings yet
- 2614 PDFDocument11 pages2614 PDFAdriani HasyimNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Glycogen.Document17 pagesFundamentals of Glycogen.Kevin VillaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 1 - Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument4 pagesBIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 1 - Nervous and Endocrine SystemsMayaNo ratings yet
- Volume 2, Issue 4Document133 pagesVolume 2, Issue 4Asfandyar SheikhNo ratings yet
- Jejunoileal Shunt in Surgical Treatment of Morbid ObesityDocument11 pagesJejunoileal Shunt in Surgical Treatment of Morbid ObesityTiago VieiraNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 06 01782Document27 pagesNutrients 06 01782jasonc13No ratings yet
- Effect of Tilapia Bile Extract As Blood Sugar Lowering Agent in MiceDocument37 pagesEffect of Tilapia Bile Extract As Blood Sugar Lowering Agent in MiceJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- 7 Proven Anti Aging Secrets For A Long and Healthy LifeDocument31 pages7 Proven Anti Aging Secrets For A Long and Healthy LifeBerchades100% (1)
- BCH301Document19 pagesBCH301yabdallahNo ratings yet
- Study of Antidiabetic Drug GlyburideDocument19 pagesStudy of Antidiabetic Drug GlyburideRaviNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris, JJHDocument2 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris, JJHNova Novitarini100% (1)
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesChapter 34 The Endocrine SystemCarl Agape Davis100% (3)
- Apbio 45 LectoutDocument15 pagesApbio 45 LectoutSimone Alexis GuinocorNo ratings yet
- NR 325 Diabetes Power-Student Copy1118Document39 pagesNR 325 Diabetes Power-Student Copy1118John MixerNo ratings yet
- Lec11 Feedback & ControlDocument54 pagesLec11 Feedback & ControlMuh ArifinNo ratings yet
- RosiglitazoneDocument2 pagesRosiglitazoneAngelica Alburo PenionNo ratings yet
- P 174 Insulin TherapyDocument3 pagesP 174 Insulin TherapyJeane ClerkNo ratings yet
- 8th Icse Endocrine & TransportDocument2 pages8th Icse Endocrine & TransportManoj BhatiaNo ratings yet
- PMWS27 PDFDocument140 pagesPMWS27 PDFMark Joseph NoolNo ratings yet
- Ada Soc Diabetes in Hospital SettingDocument10 pagesAda Soc Diabetes in Hospital SettingOchie YecyecanNo ratings yet
- Treatment & Management of DiabetesDocument9 pagesTreatment & Management of DiabetesakupunadaNo ratings yet
- Classification Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management of Diabetesmellitus 2155 6156 1000541Document9 pagesClassification Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management of Diabetesmellitus 2155 6156 1000541AldaniaNo ratings yet