Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Memory Book NURSING
Uploaded by
Pedz Romano99%(156)99% found this document useful (156 votes)
22K views109 pagesMemory guide for Nurses.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMemory guide for Nurses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF or read online from Scribd
99%(156)99% found this document useful (156 votes)
22K views109 pagesMemory Book NURSING
Uploaded by
Pedz RomanoMemory guide for Nurses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 109
ACUTE LARYNGOTRACHEOBRONCHITIS
LTB (Croup)
¢ Slow Onset.
* Commonly Occurs
Before Age 5
© Barking Cough
¢ “Crowing Sounds”
© URL's Frequently
Precede LTB
* Restlessness
* Supra-sternal
© Ingpiratory
Stridor
© Occurs at Night
in Fall and Winter
Retractions
¢ TRespiratory Rate
© May Progress to
Hypoxic State
© May Have Slight
Temperature (<102")
TURP
(Iransurethral Resection of the Prostate)
* Continuous or intermittent Bladder Irrigation (C.B.|.)
(Usually DC'd after 24 houre, if No Clots). “uy Oe
* Close observation of drainage system-
(T Bladder Distention causes Pain & Bleeding).
* Maintain Catheter Patency
* Bladder Spasms
* Pain Control: Analgesics & | Activity first 24 houre.
* Avoid otraining with BMs. T Fiber diet & Laxatives.
* Complications:
+ Hemorrhage - Bleeding should gradually |
ta light pink in 24 hrs.
* Urinary Incontinence - Kegal Exercioeo
* Infections = T Fluide
*# Prevertt Deep Vein Thrombosis
+ Sequential compression stockings
* Discourage sitting for prolonged periods
@Nursing Education Consultant, In.
POST MASTECTOMY
NURSING CARE
+ Elevate affected side with distal joint higher than proxima
joint.
* No BR, injections or venipunctures on affected side,
Watch for S & & of edema on affected arm.
+ Lymphedema can occur any time after
axillary node disection.
* Flexion and extension exercises of the hand in recovery.
* Abduction and external rotation arm exercises
after wound has healed.
* Assess dressing for drainage.
* Assess wound drain for amount: and color.
© Provide privacy when patient looks at incision,
*c)
iotherapy, Radiation therapy.
* Monitor for Complications ~ hemorrhage, hematoma,
lymphedema, infection, pootmastectomy pain syndrome,
* Feychological concerns:
Altered body image
Altered sexuality
ton Conauttante In Fear of disease outcome
Nursing Eau
SUICIDE PRECAUTIONS
SECURE ROOM:
~ Windows Locked
- Breakproof Glass & Mirrors
- Plastic Flatware
- Cords - Phone
- Extension
- Equipment
- Curtains
- Belts/Shoelaces/Drawstring Pants
- Matches or Cigarettes
- Sharps/Razors
PATIENT CARE:
- Frequent Observation...
Preferably1to1
- Staff Communication — Constant
Risk Assessment/Documentation
- Develop Therapeutic Relationship
- Written Behavior Contract with Pt.
- Restraints as Necessary
- Medications
- Monitor and Restrict Visitors
OG Sy
SCHIZOPHRENIA
- Illogical Thinking - Auditory Hallucinations
& Impaired Judgment - Delusions — Persecutory or Grandiose
- Lows of Ego Boundaries - Hypersensitivity to Sound, Sight & Smell
- Inability to Trust - Difficulty Relating to Others
- Bizarre Behavior
- Indifferent - Aloof
- Love/Hate Feelings
- Feelings of: ) - Behavior — Disorganized,
Rejection (gate Motor Agitation,
- Negativism
- Religiosity
- Lack of Social Awareness
Lack of Self-Respect Catatonic
Loneliness,
Hopelessness - Retreat to
Speech Incoherent Fantasy World
& Rambling - Autiom
- Disorganized
Thinking
BB etisrsin Education Conouleants, ic
Recent Difficulties / Alterations In:
Relationships In Patient’s Own Words - Why le He Seeking Help?
+ Ueual level of functioning ee es eee eS
Behavior a
Ferceptions Z
Cognitive abilities a
tFeelings OF:
Depression
Anxlety
Hopelessnese
Being overwhelmed
Suspiciousness
Confusion |
Name
icity & Cultural lmpications
= Marital Status
#6 Ages Children
= # &. Ages Siblings
+ Living Arrangements
+ Occupation
Education
Religious Affiliations
Sphritual Needs
5 Previous illness / Hospitalization
Education - highest grade completed
Childhood
Caregiver
Physical Abuse ?
Parents Substance Uce/ Abuset
J
Occupational background
pation eee
How long employed
What joe
Social patterns:
Friend - importance
__ Somatic Changes |
Ss Constipation ‘Ageibacen Usual day
bo Diarrhea ey Use OF Drugs Sowal Fatgerns
E insormia pores mana te
ae Lonely Etegt on family ore
> Weight Lort aN a Incereste & Abilities
pias Happy Family Physical eae aa
srenie Rebellious Or Feychosocial Problems $Gives pleasure
= Nausea Who? Substance abuse - Meds
Nausea ubetance abuse - Mede
mi What: problem? i
[Yomiting Howitt aftccked Bare,
Drug use problems
meade the family Seraes coping wiethods
@Nuesing Education Consutante, fo.
MENTAL REWARD ATION
=
a
Repetition
Reinforcement
Routine
Repetition
Reinforcement
Routine
Repetition
Reinforcement
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
yao ea aac)
ue
[oa NN oy OL
REAL STIMULI
MISINTERPRETED...
FALSE FIXED
BELIEF.
EATING DISORDERS
Views self as fat — regardless of weight
Intenge fear of becoming fat
Anxious about losing control
Weight is¥85% of normal
Feels powerless
Associated with obsessive compulsive disorder
BULIMIA
Recurrent binge eating followed by
self-induced vomiting, misuse oF laxatives
and enemas
Depressed mood following binge eating
T Anxiety and compulsivity
PICA
Fersietent eating of non-nutritive food and non-food substances
Food — cornstarch, baking powder, coffee grounds
Non-food — clay, soils, laundry starch paint chips
More common in children, pregnant women, individuals with autism or
cognitive Impairment, patients in chronic renal failure.
Influenced by cultural background.
Associated with Iron and zinc deficiency.
FB onursng Eavcation Constanta ne
Datety Precautions
Remove harmful objects
Clase observation
Encourage expression
Norejudgmental support
Kind pleasant ntbresved approach
Frequent contact
ticipation ns
ont ~ Activities Assist in decision making
Westen contract = ee ieeunsir
Self-Esteem
Cognitive
Suicidal preoccupation
Crying
Poverty of ideae
Negative view - Self
= World
- Future
Prevent constipation
Encourage exerciee
Maintain hygienic
Mood
Dysphoric
Depressive
Despair
[Intereat
in pleasure
Feychomotor
=] Agitation
“Gad Persone Scale or
[= (genden)t ¢ malos At Risk retardation of movement
Ago 419 Adolescente & elderly Fatigue
Depression Recent. crisis - stress - loos {Appetite
Previous euicide attem) Slotarce sues, Canstipation
Chronic or painful tiness Step veturbarees
Frevious suicide attempts
ETOH (alcohol) abuse
Rational thinking impaired
ftir i
Sante pan a Ea
Hallucinating
@Nuroing Education Consultant, ne
Sicknese (chronic)
BIPOLAR DISORDER
MANIC
* Onset between 18-30 yrs old
* Mood:
Elevated
Expansive
Irritable
* Speech:
Loud-Rapid
Punning
Poor Judgment.
Clanging
Vulgar
©? Wr. loss
* Grandiose
delusions
* Distracted
* Hyperactive
«1 Need for sleep
* Inappropriate Dress
# Flight of ideas
DEPRESSIVE
* Previous manic
episodes
* Feelings of
Worthlessness
Guilt
Hopelessness
+ TAnger & Irritability
eLinterest in
pleasure
* Negative views
* Fatigue & | Energy
© LAppetite
* Constipation
* Insomnia
etLibido
* Suicidal
preoccupation
* May be agitated
or have movement
retardation
cy
BBB chars education Conus inc
BASIC COMPONENTS OF A PSYCH ASSESSMENT
Why is Patient
Ethnicity Seeking help?
3 Mattel Statue Recent Difficutties
ay Living Arrangements Relevant Family History
& Creda bon f Feelings of - Depression
o Education Anxiety
Cultural implications [eee cence
Religious & Spiritual Suspiciousness:
Beliefs/Affiiations
Being Overwhelmed
Somatic Changes
Previous liness:
and Hospitalizations Chilahood
Growth and Adolescence
eco Patterns Brug We
E\ Social Patterns - Family
‘S\\ BFrienas Physical, Emotional
Sonal Freterence(Practice| of Setual Abuse
Interests.
Substance Use & Abuee|
Family Physical
Judgment
Affect
Memory
Cognition
Orientation
BB enierstg Education Consultant ic
ALTERATIONS OF BODY IMAGE
IMPACT / SHOCK / DENIA\
Despair
Digcouragement
Withd a
DEPRESSION
Insomnia
Refusal to participate in self-care
Sadness
R
Refusal to discuss change
or lose
+Self Esteem
Hostile / Irritable
GRIEF
Normal reaction to loos
Regression can and does occur
Provide safe environment for :
expression of feelings Acceptance and Adaption
Common Ini patients who have Active participant in therapy / care
experienced mastectomy, ampu- D i
Feber aABteatece Aerated CA cna Con ae
surgery, or spinal cord injury
HG onarsingtarcoton constant
ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL DELIRIUM
“Delirium Tremens (DTs)”
Begin DT9 After Hospitalization,
Surgery or Procedure.
EAR DROPS ADMINISTRATION
Adult
Pull ear back
and up for
Older Children
and Adults Pull ear down
and back for Infants
and Childrent3 yrs.
Child
Oo
STROKE
(Brain Attack, CVA)
© Headache
* Mental Changes
~ Confusion
- Disorientation
- Memory impairment
© Aphasia (,24.¢%,)
ete
* Resp Probleme
(4 Neuromuscular Contrel)
# bough / Swallow
Reflex
* Agnosia (tierctacen)
# Incontinence
* Seizures
* Hemiparesia or Hemiplegia
© Emotional Lability
* Vigual Changeo
(Homorymous Hemiamopsia)
* Diplopia, Ptosis, and Lose
of Corneal Reflex
* Vomiting
* Spatial-Ferceptual Defects
(CVA Right Hemisphere)
* Hypertension
* Apraxia
(tlearnea Movements)
4
i
i
DIAGNOSTICS
Neuro Exam, CT Sear, MRI
‘Angiography
Intea-Artieral Digital Subtraction
“Angegrapy (B5A)
nocranial Doppler (TCD)
iltrasoncaraphy
ur,
ticox
Monitoring
SEPNURSING GOALS |
* Airway - Oxygenation
o$icr
* Nutrition
+ Preserve Function
° Rehabilitation
* Safety
+ Education
‘#Right-Sided Weaknees
eAphasia
LEFT HEMISPHERE
&
PUPILLARY ABNORMALITIES]
Typically Larger on the
Side Opposite the Lesion
* Conjugate Deviation
(Looks toward lesion)
* Homonyrigus Hemisnopsia
BZwey
e
Temporary Vein ae
Tiere orsparese
‘Vertigo & Conk
* Typeally Last Lees
= Hypotonia “® Hypertonia
1 Spatial-Rerceptual Defects,
© Aprania
© Lose of Voluntary
Movement On One Sie
eb Neuromusculer Control
Reape
2 Swallow - Cough
© Bladder - Bowels
© Communication
Probleme
* Emotional Lability
impaired Judgement
and Memory
* Atherosclerosie
* Thrombosie
* Emboligm
* Cerebral Hemorrhage
(Tissue DamagerTraura)
RIGHT HEMISPHERE
*Left-Sided Weakness
° Spatial-Ferceptual Deficita
(Vulnerable to Accidents)
Bi ottursing Edvcatim Consultant
PARKINSON’S DISEASE
© Onget usually gradual, after age 50.
(Slowly progressive)
* Mask-Like, Blank
Expression >
* Stooped Fosture
© Pill Rolling Tremors
4 * Possible Mental Deterioration
* Depression
* Has Familial Incidence:
More Common in Men
* Shuffiing, Propulsive
Gait
ques
‘@Nureing Education Consultants, lnc.
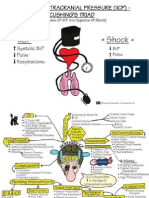
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
© Changes in LOC ¢ Headache
= Flattening of Affect
"JOrientation & Attention ¢ Seizures
"Coma * Impaired Seneory
& Motor Function
° Eyes - ;
* Fapilledema ¢ Changes in Vital Signs:
Cushing’s Triad
= Systolic BP
“Widering Pulse Freseure”
* Pupillary Changes
* Impaired Eye Movement:
*UPulse
¢ Fosturing * Irregular Resp Pattern
" Decerebrate
"Decorticate ¢ Vomiting
"Flaccia * Not Preceded by Nausea
"May be Projectile
° Decreased
Motor Function * Changes in Speech
= Change in Motor Ability
*" Fosturing ©lnfants: ° Bulging Fontanels
°Cranial Suture Separation
et Head Circumference
BBB cturcing Eekication Concuttants, in High Pitched Cry
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE (IICP) -
CUSHING’S TRIAD
(Symptoms OF ICP Are Opposite OF Shock)
* ICP *
* Shock «
t Systolic B/P Vere
¥ Pulse t Pulse
‘ Respirations t Respirations
(2a
scl Scan MRI ‘
* PET, EEG, Angiography)
*LiGOx Brain Tissue
xygenation Catheter
* Transcranial Doppler
Studios TP
+ Evokod Potential Studios
\t intracranial Blood Vol. Cerebral Hemorrhage
tesr Sale Toxine
Cerebral Edema lechomic Cells
Dilated Cerebral Arteries PCO
“‘Acidotic State
# Secondary to Initial Damage
# Brain Tumor
* Closed Head Injury
ured Blood Vessels
Ruy
os (TTS) holon
mange in L * Thrombosis & lechemia
uching’s Tad ‘\s Hyarocephalue
° Pupillary Changes ‘y e
* Fafledema
Fs \cP Monitoring Ventriculostomy)
+ Cerebral Orggerattion Mon torr (LICOX)
1 Sipertone aire Ve
# Medleateg= Osmotic Dretios
Corncosterode
Artioctaure Drage
‘->Infants_
* Bulging Fontanels
* Cranial Suture
Separation
« THead Circumference
* High Pitched Cry
* Ingert Urinary
i Catheter
Avoid Straining
‘Sensory & Motor
leacache
*Vomizrg
TGR Occurs With
Tin The Size OF
intracranial Contents
(pale DR sore Prcesvone
© Airway Fatency SF From Ears/Nose?
leurov's *FCO2 OK? * Prevent Aspiration
"© Hemniation
erebral Perfusion
* Diabetes Ineipidue
* Som-Fowlers Minimum Suctioning § Guice Envkormens, ° Explain Neuro 's During BM
* Charge Rosition Slowly * Ventilator? * Provent Eye Damage * ypceurage Fears ROM
¢ Maigean Hoaration ‘Light Sedativea for santa Realty * Presoure Ulcer Prevention
sgitation Orientation * Avoid Extreme Hip Flexion
* 2 Coughing, Sneezing, or Valesiva Manewer i andioace
* Maintain Nutritional Needs - Enteral or Parenteral Feedings Gk te Unconscious « Assess Motor Responses
and Movement
* Giascow Coma Scale
# TSize infant's Head
* Work Thru Feelings
FAST RECOGNITION OF A STROKE
CRANIAL NERVE MNEMONIC
S = Sensory
Olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
Facial
Acoustic
Gloseopharyngeal
Vague Nerve
Spinal
Hypogloseal
ZOAA000
BEB onireing Education Coneuttants, ni
rrr
TO445000
M = Motor
On
Old
Olympus
Towering
Tope
A
Finn
And
German
Viewed
Some
Hops
B= Both
3
6
M
M
B
M
5
&
B
8
M
M
Some
Say
Marry
Money
But
My
Brother
Says
Bad
Business
Marry
Money
BELL’S PALSY
Forehead Not Wrinkled
Eyeball Rolls Up
Eyelid Does Not Close
Flat Nasgolabial Fold
Paralysis of Lower Face
Etiology:
Possible reactivation
of herpes vesicles in
and around the ear will
proceed facial paralysis.
Treatment:
* Corticosteroids
° Antivirale
e Full Recovery by Most Patients
in 6 Months, Especially if
Treatment is Started Immediately
ABNORMAL POSTURING
NURSING CARE FOR
SPRAINS AND STRAINS
R Rest
Ice
C Compression
E Elevation
Thickened Synovial
Al Membranes
4 Inflammation
Synovitia|
rN
Ot Stages Sprannus +> Cartilage Destruction
Fibrous —p Fibrous tissue
‘Ankylosia * which evolves
into scar tissue
«Ayan aa pala
2.
ASSESSMENT.
NSAIDS, Cox2 Inhibitors
* Disease Modifying Antirneumatic Drugs (DMARDs) Af
Flaqueni, Methotrexate, Enbrel, Remicade
* Heat /Colt Applcacions + Bilateral joint involvement
© Detontity roventing Dovicoe + Joint stitfness, pain, limitation of movement
# Prysical Therapy * Morning stiffness lasting >thr
* Fain increases with movement
«@Serum —emm) + Commonly affects joints of hands and fingers
Rheumatod Factor # Extraarticular symptoms
+ Teor ‘Rheumatoid nodules (located on extensor
oT C-Reactive Protein surface of joints)
Poatthe Antinulear * Sjdigrar's syndrome (decreased tearing,
‘Antibody dry mouth, photosensitivity)
**Felty oyndrome (oplenomegaly,
blood dyscraciae)
BS ohiirsing Education Coeutcant he
I can't sit up straight
and | got this pillow
Doing pretty good — between my legs!
can’t crose my legs
or stand too long — got to keep JOINT
REPLACEMENTS
MAIN COURSE
me Crrar nee)
Nm
Knee — CPM, neutral
ear
DT aCe Cay
do not bend hip 7 96°
008 2* post op day
Incision care
Asoose
Extremity For
‘Color
‘T Tolerance To Meds —+ Prevent: Oversedation
* LV Rate Avoid CHF
fronn
pee ue ae -
ae Imntblity compicatons " Contractures
baat Disorientation
ies Seen,
Gre Frobleme + Thrombophlebitio
Safety —> Side Ralls ana Prevent Falls:
Poor Nutrition Constipation - Fluid &
eotrolyte Imbalance,
Foor Healing
Motor Function
Pain, Muscle Spas
* Circulatory Compromice ¢ Infection
immobility Complications * Embol
Delayed Union - Non Union # Avazcular
at Emcolism Necrosis
‘Nerve and Vascular Injury
TAge
+ Treat cooxisting
medical cisorcers
Cardiac problems
Peripheral Vascular
Disease
Neurologic disorders
TFemale
Buckle Tractipn SiMe ose
to Relieve Spasmo Para * Presence
up t0 24-48 Hours TaN] Wsiian Revcvon Charge Chronic Condition
Depend itor 42 Hrs nad Nici Sos
coraiaan & ame + Use Asdtion Pilon Beowoon Leg ¢ Tat, Muscle Spagme,
Tolge Steep Benue Acted Leg onortaned
oe ‘» Adduction of Affected Leg
Sutyery = Exercice When OF Estemal Rotation
v * Ghent teaching, Self Care Fremenion * Deformity Along Lateral
ental Foation # Avoid Extreme Hip Flexion pace, pera
ins - Screws - Plates) + Prevent External Rotation is Displaces
Prosthctice, ate ae + Ecchymosio
HG Ovirsing Education Conoltanta ne
ZOrAQNFAH
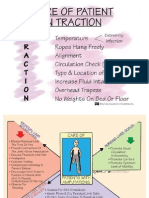
CARE OF PATIENT
IN TRACTION
Extremit
Temperature 2
Infection
Ropes Hang Freely
Alignment
Circulation Check (5 F’s)
Type & Location of Fracture
Increase Fluid Intake
Overhead Trapeze
No Weights On Pea Or Floor
fe.
134 oe
eS %. CARE OF ys Rs
eo ©
* Elevate Residual Limb
The First 24 Hre
* Prevent Contracture Of * Promote Good
The Joint Avove Amputation Circulation
* Discuss Phantom Limb Pain In Extremity
* Analgesics * Promote Comfort
* Evaluate Healing
* Compression Dressing To
Prevent Edema
* Discourage Semi-Fower’s
Position In Patient With
AKA To Prevent PATIENTS WITH
Contractures Of The Hip
* Observe For La AMPUTATIONS
gS
"29+ Aosese For Skin Breakdown
* Wash, Rinse & Dry Residual Limb Daily
2 * Do Not Apply Anything To Residual Lim
KO AlcoholmempDries Lotions Skin Too Som
oy) * Encourage Patient To Wear Prosthesis When He Gets
Up & All Day To Prevent Residual Limb Swelling
«Teach Patient that Leather and Metal Farts of Prosthesis
| Should Not Get Wet
* Promote Optimum
Level of Mobility
TRACHEAL - ESOPHAGEAL FISTULA
(3C*)
C- Choking
C- Coughing
C ° Cyanosis
BB ottreing Education Conouttant in
STAGES OF LABOR
(Stage of Cervical Dilation) Begins
with onset of regular contractions
and ends with complete dilation
Latent—> Active—> Transitional
-Firet Stage - en) (ee
(Stage of Expulsion) Begins with
complete cervical dilation and ende
with delivery of fetus.
y - Second Stage -
(Placental Stage) Begins immediately
after fetus ie born and ende when
the placenta io delivered.
- Third Stage -
(Maternal Homeostatic Stabilization
Stage) Beging after the delivery of
the placenta and continues for one
to four hours after delivery. = Fourth Stage -
PRENATAL CARE
Presum
Foriods
N&V
Sears
Urination
Breast Changes
Quickening
Probable
OPG Tet
Enlarged Abdomen
Hegar's Sign
Softening of Uterus
Chadwick's Sign
Bluish Vagina
Goodel's Sign
Softening of the Cervical Lip
Ballottement - Fetus Rebounds
Braxton-Hicks Contractions
Fositive
FHR
Fetal Movement
~Visible
+ Felt By Examiner
Fetal Sonography
RH@or .
VORURPR
CBC
UA
Hepatitis B Screen
18. Skin Teot
HY Screen
Glucose Screening
Lab Test? | 7-10 Days After Conception
Radloreceptor Asoay (RRA)
Radioimmunoassay (RIA)
Enzyme Linkes
Immunosorbent Aeeay (ELISA)
History & Physical
Ciaiiais > x Obstetric History
Schedule Prenatal Visits
Vitals Fara’ Gravida
uA
Weight: L G
Height of Fundus
FHR
POSTPARTUM ASSESSMENT
Mev» c
Breasts
Uterus
Bowels
Bladder
Lochia
Episiotomy/Laceration/
C-Section Incision
PHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES Sesisttnsiiti
Ta ee cca
*T Need for H.0- os
* Tidal Volume
ites IN PREGNANCY
‘Meg Sten" fh
# T Lumbosacral Curve
* Altered Center of Gravity
© Duck Wading Gait.
#1 Breast Size
* Heaviness, Tingling
* Darkening of Nipple
* Colostrum
{ Blood Volume ~ 40-50%
* THR 10-19 beateimn
#1 Cardiac Palpitations
+ Slight @BEnurgerent
* Murmurs
Pregnancy GingMile * Poeuscanomia
tae ~ Ptyaliom
Gastric Keidiny
NY, Heartburn
# [Tone & Motilty of Smooth Muscles
lcmorrhcide & Constipation
Lemptying of the gallbladcer
Estrogen Influence
‘# Smooth Muscle Hypertrophy
lyperplasia of Lining
hick White Secretion ~ Loukorrh:
ecrequerey
*T Biba tone
1 [Reval noshold for Sugar
2 Glomerular eteraton
‘arical Sottering ~ Goodall's Sign
Mucus Piug
Color of Mucosa
© T Skin Pigmentation
Facial Mask — Chioaoma
re Vulgario
ty
Bonel Metabolc Rate
ermatitis
fascular Spider Novi TFacachyroia Actiy
© ABD - Stretch Marke ~ Striae Gravidsrum
Linea Nigra Produces FEM, LM, Thyrotropin
Aarenoseopin & Prolactin
@Nursig EAication Consultants, nc
NON-STRESS TEST
3 Negatives in a row to interpret results
of non-stress test
N Non-Reactive
N Non-Stress is
N Not Good
BH eisring Education Conetantn a
HE ary t
ge Sleeps 16-20 hours a day
the first 2 weeks,
General Characterietice:
ree
ff W810 52cm
ae
Circulatory System:
Blood Aow from uel
vessels & plecenta stops
Clogure OF at orth
fe Ductus Arterceus
SFeramen Ovele
*
»
Dictus Venza.
+ Pulmonary Circulation
ransitory Murmurs
Hands & Fact =
Ph ectee res: 6
Heat Rate 120 10160 Beataltin RO? \
Sj Temp Heat Loss Due To:
Evaporatior Persie from ont ign Lung Maturation <" 26th Week Gectation
Convection - Body heat to cool air flow. Pe de uatocten Rak
Conduction - Body heat to blankets, atc. Aelia 38th Weok Gestation
Radiation - Heat lose to cool temps, ©
Reap fore «|
02 Consumption
t Utilization of Glucose (Hypoglycemia < 45mgis)
‘& Brown Fat
Need for Calories
tRivk Metabolic Acidosio
1 Surfactant Production e
3.400 grams (Average) or Tle. Bor:
Usually to 10% wt, lose tot fow days.
Regained within 10-14 days
ieadt > Molding 3 Elongated
as Caput Succedaneum>Edema
> Measurement >33,cm. to 35 om (15-14 in.).
Circumference
x (ised w2to em than oo)
> Fontanels » Bulging? or Sunker?
Extremes in Size May Indicate
mi Microcephaly, Hydrocephaly or ICF_ 9
* Umbilical Cord = 2 Arteries & 1 Vein
Obeain cord blood sample
ery oom.
Lung Function after
BS onersng eacation consitanta in
Within the Tet minute of birch
“lous Busty Cry
“Ne Byspnea
26 Retlactlons
Roep Rate 30-60 / Min
Kaphragmatic & Abcominal Muscle ised
lose Breathor
SS HIGH RISK NEWBORN
TEMPERATURE NURSING INTERVE} ITIONS
BR Minimize Cold Stress. !
PK Maintain Skin Temp. 36.1°- 36.7°C (96.8°-97.7°F)
Continuously Monitor Ternp,
We Prevent Rapid Warming
or Cooling
Pe Use A Cap To Prevent
Heat Loss From Head.
RESP FUNCTION
¥ Position T 02 - Semiprone/Side Lying.
Maintain Resp Tract Fatency.
ee ee We Stimulate > Remind to Breathe.
4K Monitor For Hypoglycemia. $ Monitor O2 Therapy.
# Assess Tolerance Of Oral Or Tube Feedings. $® Access Resp Effort.
$#X Monitor Hydration Closely. © Grunting
WE Assess For Gastric Residual, Bowel Sounds, * Nasal Flaring
Change In Stool Pattern, Abdominal Girth. * Cyanosis
Monitor Weight Gain Or Loss. © Apnea
iri Eascaton Conon is
HELLP Syndrome
(Preeclampsia with Liver Involvement)
Hemolysis
Elevated Liver Function Tests
Low Platelet Count
EVALUATION OF
EPISIOTOMY HEALING
Redness
Edema
Ecchymosis
Discharge, Drainage
>UMMA
Approximation
DEVELOPMENTAL DYSPLASIA OF THE HIP
lAsymetrical gluteal
and thigh folds.
Affected side)
Shortening of leg.
on Conoutantes he
FB ow
Threatened
+ inevitable
* Incomplete
* Complete
° Miseed AB
+ Recurrent
Control Hemorrhage
Vaginal Bleeding
or Concealed
Hemorrhage
Painese Bright
Red Bleeding During Mild to Severe
28 &3" Trimester
Abdominal Pain
Has Presumptwe Signe:
Of Pregnancy
High hCG levels
Passage of
Vesicles
Fiyperemesio
Gravidarur
Kaa)
s
Proteinuria TBP
i>
Faeries. ‘Aniniotic Fluid Index (AFI) >24-25om
Watch Galt Intske Develops 3” Trimester in Diabetica
180 Complications — Abruptio Placenta,
Fost Partal Hemorrhage
CLEFT LIP - POST OP CARE
C Choking
L Lie on Back
E Evaluate Airway
F Feed Slowly
T Teaching
L Larger Nipple Opening ;
I Incidence t Males
P Prevent Crust Formation
Prevent Aspiration
BEB on uroing eaicotion concuivants, ine
ASSESSMENT TESTS FOR
FETAL WELL-BEING
* BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE *
Choice for
Follow Up Fetal
Evaluations
Fetal Breathing Movements -
4 episode of 30 2ec, in 3O min
B. Fetal Tone - At leaet | epicode
of extremity extension and flexion
C. Body Mavemert - 3 episodes
over 30 min
BIOPHYSICAL TESTS
* Daily Fetal Movement: Count: (DFMC)
* Ultrazongraphy
* Biophysical Frofile (BP?)
D. Amniotic Fluid Volume -
MRI At least 1 pocket measure 20m
BIOCHEMICAL TESTS
in 2 perpendicular planes
E. Non-Strese Test - Reactive -
FHR T with activity.
Each hae a possible
score of 2
Max Score =10 ©)
* Amniocentesio
* Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
* Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling (FUBS)
‘* Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP)
© Indirect Coombs Test
Nursing Education Conuitants Ine
HEPATITIS A & E
Hepatitis with
avowel... Comes
from the bowel.
Fil onursing Education Concur in
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
HEPATIC COMA
@ Changes
in LOC
* Progressive Confusion
* Stuporous
os © Impaired Thinking & Judgment
Se Neuromuscular
Disturbances
eAsterixis _,,
“Liver Flap” 8
Hyperreflexia “
¢ Fetor Hepaticus
Problem Td By:
* Constipation
e
* Infection Treatment * Administer Vancomycin
* Hypovolemia & Lactulose
* Hypokalemia (LK) Aa a ates
* Gl Bleeding © Promote Diet Tin
© Ovioi Carbohydrates
Opioid Meds & Adequate Fluide
CIRRHOSIS:
LATER CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
|_ Changes in Mental
Responsiveness & Memory
Jaundice
Spider Angiomas
Face - Neck - Shoulders
Esophageal Varices Anemia, Leukopenia
—— Thrombocytopenia
Coagulation Disorders
iN Super heial Veins Visible
In Abdominal Wall
“Caput Medueae”
Palmar Erythema
Ascites
Hepatomegaly
Splenomegaly
Sexual Characteristics
Changes
Gynecomastia
Hirsutism
Edema
Feripheral Neuropathy
BEB ONursing Education Consultants, Inc. FI uee
CHOLECYSTITIS
Jaundice
Fever & Leukocytosis
Nausea & Vomiting
Anorexia
Pain
@ Right Upper Quad . . .
oF Right Shdulder Abdominal Distention
* May Radiate To Back
wleraaseein Dae Feeling of Fullness
Breath
Fat Intolerance
CMe
@tising EAcaton Constr In
PREVENTION OF INFECTION
+ Safe Injection Practices
* Use a Single Dose Syringe
re and Needle 1 Time and Discard
* Do NOT Recap a * Hand
Needle Hygiene
* Discard in Sharpe
Container . We
*DoNOT Force a covet
Syringe into Barriere
a Full Sharps (28 Wdicaved)
Container ip ° Give
© Mas!
* Do NOT Place a Syringe and Needle — © Eye Shield
‘own
in your pocket
on bedside table * Consider ALL
Body Fluids to be
Contaminated. AD
J
ona meal tray
% Clean Up Spills
of Body Fluids Immediately, * Avoid Contaminating
Then Cleanse Area with the Outside of
Germicidal Solution.
nursing Education Consultant, ine
Specimen Containers.
INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS
“Mono”
Known ae thi
« Fatigue, Decreased
Energy
* Sore Throat (severe)
* Tonsil Enlarged
and Reddened
— ote
“es wise gt
Transmission:
Most common in young people
425 yrs old
Predominantly tranemitted via ealiva,
° Headache
° Fever
«
Treatment:
- Rest
- Throat Soothing
Measures
Cause:
Epstein Barr Virus
(EBV)
© Skin Rash
© Swollen Lymph Glands
© Fain in LUQ—
Splenomegaly
* Loss of Appetite
- Low Energy / |mpact Activity
- Gradual TActivity
- Course is Self-limiting
- Acetaminophen / Ibuprofen
FEB oNrina Education Concuranta he
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) INFECTION
Transmisei
Stealer pexual intercourse Early Chronic Infection
© Cortact with Blood and Blood Praducts ‘* HIV infection to development of
‘AIDS ~ average M1 years
*# Symptom ~ fatigue, headache,
lymphadenopathy, low grade
fever
«© Normal CD4* Cell count
*thoreased infections
Intermediate Chronic Infection
'* CD4* T-Cell court b 260-600 cello
‘Increased viral load
‘Perinatal - during pregnancy, delvery, or breastfeeding
Sereening
* Enzyme inmuncassay (EIA) at 3 wks, 6 wis,
mo after exposure
“= Rapid HIV Anbody Testing ~ tests for antigens,
not antibodies, if positive, nead follow-up with EIA,
andlor Antibody/Antigen teot
‘Seroconversion — development of HIV
specific antibodies
* Window Period ~ may be 2 months between
infection ara detection of antboaies
(CHV positive)
Acquited Immunodeficiency Disease
‘Syndrome — (AIDS) presence of at least:
one or more:
© D4 Teall count 4 200 caloful
(compromised immune syoters)
* Opportunistic infections —
Fungal ~ Candiaiasie, Preumocystisfroveci
preumoria (PCP)
Viral ~ Gytomagalovirus (CMY)
Bacterial ~ Mycobacterium tuberculesis, pneumonia
Protazoal — Toxoplasmosis of brain, intestine
Cancer
‘Increased infection, earlier
symptoms more severe
Late Chronic infection |
"= Diagnose of AIDS
Treatment:
‘© Antiretroviral therapy (ART) begins
with confirmation of HIV
Goal
Decrease viral load
© Maintain of t CD4° T-Cell count:
* Delay onset of HIV related
Invasive conical pt
‘symptoms
Kaposi's sarcoma =
eae * Prevent or delay opportunistic
Lymphoma Y RP
eye infections
‘© Wasting Syndrome © AIDS Dementia Complex.
TES on urcing eavcavion Consultants
BLOOD TRANSFUSION REACTION
Febrl i Hemolytic Transfusion
*Chille * Fever * Headache Reaction:
* Flushing © Tachycardia *T Anxiety + TAnxiety
+ Low Back Fain
+ Hypotension
* Tachycardia
+ Fever and Chills
Allergi jon:
ld:
* Hives ¢ Fruritus
* Facial Fluehing + Chest Fain
Severe: * Tachypnea
* Shortness + Hemogiobinuria
of Breath + May Have Immediate Onset
* Bronchospasm
© Anxiety
ge Nursing Implications:
* Stop Transfusion and notify Physician
«Change IV tubing at hub and begin NS
+ Treat symptoms if present 02, fluids, epinephrine
* Check vital signs every 15 minutes
* Recheck crossmatch record with unit and send blood bag/tubing to the lab
* Obtain blood sample
* Obtain urine sample for hemoglobinuria
* Monitor fluid/electrolyte balance
+ Evaluate serum calcium levelo THB ovursing Eascation Comouttanta, te.
BLOOD ADMINISTRATION
* Determine Fatient’e
* Allergies + Check Crossmatch
© Previous Transfusion Record With
Reactione 2 Nurses:
*AB0-Group
ss m 5 © 8H Type
% Administer Within 30 Minutes of SR aaa
Receiving From Blood Bank 1D Blood Bana
* Hospital #
* Expiration Date
* Do NOT Warm Unless
* Never Add ANY
Meds to Blood Products
Risk of
Hypothermic Response
THEN Only By Specific
* Verify Patient’ Blood Warming Equipment.
° Check she D's Order
* Check labels on blood bag & 4% Infuse Each Unit Over
blood bank transfusion record 2-4 Hours BUT
* Baseline vitals - (Then per policy) No Longer Than 4 Houre
* #18G or #20G gauge needle
Normal saline IV solution
* Blood administration set with filter
* Severe reactions most likely
first 15 min & first 50ce
* Blood tubing shauld be changed after 4 hours SUN a cli CSeaacg
€tlureing Education Consultant, inc,
- Pain Over Area
- Presence of a Cause
- Abdominal Guarding
- Abd Distention
- Fever (>100 °F)
~ Anoreria
“N&V
- TPulse ater
- }Bowel Sounds Z
- Dehydration
~ Shock Feritoneal Aspiration
0d Feritoneoscopy
Ultracound
Identify Cause
Antibiotics & Antiemetics
IV Fluids
5 JAbad Distention
he. ass, Surgery to Close
Electrolyte Replacement Ferforation
Feristalsis->¢ Bowel Sounds
1&0
'S & S Dehydration - Hypovolemia
with Knees Flexed
Quiet Environment.
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD
~ 7h,
“S,
wn
>.
© Streed
+H. pylori
* Alcohol
* Weight Loss © Smoking
‘© Acid - Normal or * Gastritie
Hyposecretion
© Pain Ye - 1 hr After
Meals
* Vomiting
* Eating may
— * Most Common
reo * Well Nourished
Shock | * Fain 2-SHre
Cushina’s
ve Brain After Meals
g * Food May
4 Fain
Murcia Eevoation Consultants Ine
CROHN’S DISEASE
* Occurs Teens to Mid-30s
© Second Feak After Age GO
© @ Autoimmune
Factors
* Nausea & Vomiting
* Severe Diarrhea
* Low Grade Fever
* Infrequent Rectal
Bleeding
° Weight Loss
* Severe Malabsorption
© Abdominal Fain
and Distention
© Tenderness in RLQ
* Complications *
© Ferineal Abscesseo
* Intestinal Fistulas
« Feritonitio
* Later S & S's *
Hypoxia
3 * Rapid, Shallow * Drowsiness, Dizziness,
i Respirations Disorientation
: el BP * Muscle Weakness,
j Hyperreflexia
2 © Skin/Mucoga Pale to ° Causes:
2 Syanorl’ f AD\ Respiratory Depression
E (Anesthesia,
* Headache Overdose, tICP)
, Airway Obstruction
* Hyperkalemia +Alveolar Capillary
Diffusion (Pheumonia,
. COPD, ARDS, PE)
© Dysrhythmias 1
(Tk)
METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
* Confusion * Dizzy, T Irritability
¢ Dysrhythmias
N , Vomiting,
(Tachycardia from +K*) ane
Diarrhea
* Compensatory
Hypoventilation © TAnxiety,
Seizures
° Cgulece
HCOs (Antacids, _
Le © Tremors, Muscle Cramps,
bicarbonate) Tingling of Fingers & Toes
SH (NG Suctioning, (tserum Ca**)
Prolonged Vomiting,
Hypercortigolism)
HB ones tsscaton Constance
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
© Headache « tMuscle Tone,
4Reflexes
(Confusion, TDroweiness)
«LBP
¢ Hyperkalemia * Kussmaul
‘P Respirations
‘Compensatory )
* Muscle Twitching Hoporertl att
¢ Causes:
° Warm THY Producti
s Too much H*(acid) hE
Flushed Too little Bicarb Geeaston
a iryetabollom)
+H Elimination
(Vasodilation) (renal failure)
HCO. Production
(dehydration, liver
* Nausea, ¥ailure)
Vomiting THCOs Elimination
(diarrhea, fistulas)
BE or rsingEaicaton Constance
@hrsng Education Concent, a Adapted from Dolores Graceffa, RN, MS
ACID BASE MNEMONIC
B#e ep
(ROME)
Respiratory
Opposite
pH t PCO, 1 Alkalosis
pH | PCO; ft Acidosis
Metabolic
Equal
pH t HCO, F Alkalosis
pH | HCO, | Acidosis
TRIANGLE OF
DIABETES MANAGEMENT
EXERCISE
Glucose Monitoring
MEDICATION ~ DIET
METABOLIC SYNDROME - SYNDROME X
Avoid the X Factor
Leads to: Diabetes, Stroke
and Heart Disease.
Fasting BS
2110 mg/l
or on
Diabetic Medo
fen E 6 Os.
BMI > 25 Kain
(Body Mage Index) IBW t 20%
(Ideal Body Weight)
Taking Lipid
Medication
Triglycerides
> 150 mg/al
HDL < 40 mg/dl"
HDL < 35 ma/alQ
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Intolerance to Cold
Receding Hairline
Facial & Eyelid Edema
7 Dull-Blank Expression
Hair Li ?
eatin Generalized Edema
pay Thick Tongue -
Lethargy/Fatigue } Slow Speech
Dry Skin . ia Anorexia
{Carnes Brittle Naile
Muscle Aches & Hair
& Weakness
Constipation Menstrual Disturbances
Late Clinical Manifestations
Subniormal Temp
Bradycardia
Weight Gain
+Loc
Thickened Skin
Cardiac Complications
UmMma--aA
HYPOGLYCEMIA
Tachycardia
Irritable
Restless
Excessive Hunger
Diaphoresis
Depression
HYPERTHYROIDISM
Bulging Eyeg®
AS
Fine, Straight Hair
a Dyspnea on Exertion
f
a Weight Loss
Muscle Wasting
Menstrual Changes
(Amenorrhea)
DIABETES MELLITUS - TYPE 1
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS:
Polyuria
Urination
Polydipsia
Mhirst
Polyphagia
Hunger
FW ontursing education Consultants, inc.
© Weight Loss
° Fatigue
of Frequency
of Infections
¢ Rapid Onset
elnsulin ==
Dependent
° Familial Tendency
° Feak Incidence
From 10 to 15
Years
+ B noun Produced ;
© Most Often Before Age 15 . eeutncene neale eaiewa
© Was Called Juvenile Diabet * Ketoacidosia Not Common
Pads iagebandes + Adults p40 Most Ofzen
«Familial & Lifelong * Was Called Adult Onset Diabetes
1 Je Familial
xs z Se + May Need —S== Insulin
Gestational
+ Dug Pregnancy
* Goes Anay 5 Pregnancy
‘May Noe Reaceur
May Have Big, Baby
Trick or poz
Mature Onset. * Impalred Insulin Production
+ Keteacidosia Not Common
Diabetes of” S Strong Family 1X of ype 2
the Young (MODY) * Game Characteriotlce ae Type 2
“Lor @ Insulin”
Secretion Type 1 & 2
aie
\yphagia
Reps
Insulin Folyuria
= Hypoaticeria Fatigue
* Semogyi Eft porty Contra
* Allergic Reaction Diabetes _ Wet WE.
* Diabet Ketonciaosi (Tye 1) Eye Probims = Wh 4
nyse revere = Slow Qnoet a ee Ng
-hetotic Coma ("ype :
Flu & Eectro¥te Imbalance ; Rapid Onset
Long Term
* Angiopatiy Sutin G2 126 mg/al contiemed by repeat
“ferret Vaccine Gpliraen —«PRGRRE pia rr sa
+ Retinopathy Diet
ual oF cose & 200 mala + eymy
* Nephropathy insulin Need with t Exercise a i 6 RR RE EOLA REE
* Neuropathy 4Glucose Fluctuation wo he ‘glicose 2 200 mafal during
* Infections Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OG™)
| eNersin Education Conatant in Sea
DIABETES INSIPIDUS (DI
(ve Se @& , BE
decrease the ies or Pruteary ‘Bianiatony
in mor fark
5 1 2
Central DI (neurogenic)
Treatment:
Vasopressin
DDAVP
CUSHING’S SYNDROME
Corticosteroid Excess
Personality Changes Hyperalycemia
Moon Face CNS Irritability
T Susceptibility . ;
to Infection NA* & Fluid Retention
(Edema)
Thin
Extremities
Males:
eneconaetl/ 4
Fat Deposits on Face |
and Back of Stovaen f/
Gl Distress -TAcid
Amenorrhea, Hireutism
| Thin Skin
+— Purple Striae
Bruises & Fetechiae
Osteoporosis
FB ONervirg Eavcation Corman ne
BLOOD SUGAR MNEMONIC
HOT & DRY = SUGAR HIGH
COLD & CLAMMY =
NEED SOME CANDY
FB onsrsing Education Consultants Ie
ADRENAL GLAND HORMONES
S Sugar (Glucocorticoids)
S Salt (Mineralcorticoids)
S Sex (Androgens)
BiB 6rursngEaiction Connitara
ADDISON’S DISEASE
Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Depression
Bronze ep
Pigmentation
of Skin. — Hypoglycemia
a 2)— Fostural
Tachycardia Hypotension
G| Disturbances
— Weight Loss,
Weakness, Anorexia
Fatique
Adrenal Crisis:
Profound Fatigue
Dehydration
Vascular Collapse (HBP)
Serum NA*
TSerum KY ee
re
RVISORY COM
ag
MAND
oe
STEPS IN THE
NURSING PROCESS
A Delicious PIE: AnApple PIE:
Assessment Assessment
Diagnosis Analysio
Planning Planning
Amplementation Implementation
Evaluation Evaluation
PRE OP CHECKLIST
DAY OF SURGERY
Wo Hospital Gown
W Allergy Band
7 \D Bana
o Preoperative Education
Completed
wv Informed Consent Signed
NPO — Bowel Pr
A NPO- Bowel Prep wv Dentures, Eyeglasseo,
Hearing Aids, Contacts —
Wo Skin Prep - Shower Left in Place or Removed
or Bath in Anti- |
microbial Soap ov Makeup and Nail Polish
Removed
a Documentation /
Checklist of W Vital Signs Before Tranafer
Valuable
ona w Fre Op Lab Work on Chart
S Woided orto'tiansior Surgeon Notified of Abnormal Values
vo Medications
wv Pre Op Meds — Given and Charted History
MAR on Chart
W Side Ralls After Pre Op EHR/EMR up-to-date
Bed in Low Position Fgh Alert Meds Noted
Nursing Education Conaurtants In.
u
e
jf o
2
é eo
S. ° xo
te t o
oe |
Ms ah oad
V6 94 Hee Early Ambulation
WFluid 8 Rate
Adequate Hydration
Electrolytes
GI Drainage
Renal Function ‘
Lab Values Nutrition &
A
"Olaesicg
Antiemetics
soe "um.
ce a Sug
gf 4% 20 0h rey, Oh
gf & ei Reapiratory 5,
é S piratory Din,
Function
Ba,
Bowel Sounds
Check NFO Status
NG Tube?
Encourage Fluids
‘Assess Fluld Tolerance
Progressive Diet
Monitor for Flatue or BM
Assess Output
ey
o “a
BB rong Eaacation Conca Ic
+ Should Vola Within
G-6 Hre Foot Op
*Falpable Bladder
«Frequent, Small Amount
icing
*Pain Suprapubic Area
chennai hohe
Fever
* Wet Breath Sounds
* Asymmetrical Chest Movement:
* Productive Cough
* Hypoxia
Tachycardia
* Leukoaytosis
eco
"Redness
+Vosre
+ Chest Fain ee +Purulent Drainage
+ Dyspnea + Weak Pulse se
+ TResp Rate "Cool Clammy “Tachycardia
Tachycardia “Reotlese *Leukoeytosis
“tAriety "TBlecing
Diaphoresio + Thirst
+ sOrientation —
te
“Blood Gas Changes *Separation of Incision
+ Evidence of Bowel
Through Incision
+ Tain
+ Nausea & Vorniting
* Abd Distention
RESPIRATORY
a “No Stool or Flatue
10. Sate & 420, “Nausea
*4Breath Sounds “Yomiting
+ Asymmetrical Chest Movement *Abd Distention
+ Tachycardia * Abd Tenderness
+ TRestlessneso
lurcing Eaucoton Consultants ic
Evaluate Reet
General Assesoment
‘Affective Behavior
Yerval Behavior
BP & Reopirations Ariety
Nursing DX Alteration
in comfort:
Fear
Plan ———> Implement
Cutaneous Stimulation i
Distraction
Relaxation Techniques
z
beaes**
* Rel = ean”
Nursing Education Gonoultanta
Ghroric heath probleme
Age Currentdriae ©
Weight Allergies
Suacaltceiwes interview Cone Sat
Catheterization ‘Religion
Significant others
Faychological needs
3. Medications
Nursing Avseoement
Lab studies
Injections
Infusions
Dressing changes
rine patient nfo
2. Evaluate paviert's
+e Breathing Wao Dr. gues patient explanation
jarring Uereiepeters stared by: De, Patient & Witness
Fain Meds bir? agile (Nurse may witness)
* Equipment 4. Dont overstelm. Signed prior to Pre-Op med
«NFO Policy NB baeive any remains permaners part | gy
Wachart
# Leg Exercises
ape
@Nursing Education Coeattants, inc
MASLOW’S HIEARCHY OF BASIC HUMAN NEEDS
| feel on top
of the world
, fed and a a
rested ~ | = 3 ES
vS
Respiratory Status
Assessment [ Color
Fluid Intake
Special Equipment.
Dressing
ide King Position
Airway until gag refiex OK
Fosition
rep runcton ‘Suction (PRN)
Cough/Deep Breathe
02& O2Gats
neato ? Mechanical Support
re “ereath Soundk"
Prevent.
Aspiration
Speak Caimly
Oren cia
Fluid Status
Quiet Atmosphere sychological Li
Body Alignment Equilibrium Blood Loss?
Explain Actions, W Rave
Last to Go ber iste
ks 4 Electrolyte Levels
Awake Patient returns: Hydration
Dressings OF +o room if: neiolonal Area Branage
= Drainage? NG Tube
x = Record output’ Nav?
erasing Eciceton Coneutarta nc. from drains
DEHISCENCE / EVISCERATION
Dehigcence
Separation or splitting
open of layers of a
surgical wound
Evisceration
Extrusion of viscera or
intestine through a
surgical wound
TB on eringEavcaton Cooutonta be,
Informed consent signed
Record vital signs prior to transfer
Remove jewelry and valuables
Remove nail polish arid makeup
Dentures, eye glasses, heating aide —
removed or left in place?
NFO - tine patient began
Bath/shower in antimicrobial soap
Family aware of surgical waiting area
ive teachin
— Appropriate to developmental age
~ Preoperative routines
Belamrenen tren conser orm
len pryical preparation =
cttoceNEO
Discuss procedures immediately prior to
Sanopbrt and wat co peck WOR
—Fostoperative routines
Reeplratory care ~ coughing, turning
Leg exercises to increase venous return
‘Activity ~ out of bed, ambulation
Pain control
Fluids and nutrition
Nursing Considerations
General
cit ag
y
ev azz
& ‘Geren
nal —Resmsemoreo pont
or rag Concer
= ends ier
~ Protect area of Learsation Respiratory depression &
~ Monitor return of sensation Patent airway
Vomiina, prevent aepration
Rotum of consciousness
Hydration ta prevent $B
Urinary output
BiB ovine cascaton conse e
CHARTING BODY FLUIDS
“Coach”
C Consistency
Ti: How The Fatient
is Tolerating It.
CARE OF THE CHRONICALLY ILL CHILD
3X Decline in mortality rate increases
in number of children with special
health care needs. rn
F hile’ ( Maximize independence while minimizing
‘Pr Fecue on chide elie AN atsooa oR
age.
$x Family Centered Care:
‘Aseeoe family response to lncoe
Involve famiy in care
asi fay procs
‘arowen ard develogman
Y Promote, Maintain,
or Restore Health.
¢ Most Common Chronic
Childhood Conditions —
2 1, Reapiratory (Asthma)
aa ip 2. Specch and Bensory
5 impairments
jrinne
da actuate 3, Merital and Nervous
$< Hospitalization —
Baie Wer aNde card tr ae ares ers
& maintain routines
* Respect family's expertise in care of child
* Be attentive to parents’ or caregiver's input
are conferences for planning & eharing mutual concerns
‘# Encourage independence and self-care
Nursing Education Conoutants, ne
RIGHT SIDED® FAILURE
(Cor Pulmonale)
© May be secondary to
chronic pulmonary
° Fatigue
a problems (COPD)
eT Feripheral
Venous Pressure Distended
Jugular
i Veing
° Ascites
© Anorexia &
Complaints of
© Enlarged p
Liver & Spleen Gl Distress
(Hepatosplenomegaly) § WelgntiGain
* Dependent Edema
tsa eanseniconucwasi nc
PRELOAD AND AFTERLOAD
Afterload:
Resistance left
ventricle must
overcome to
circulate blood
Pressure from volume
of blood in ventricles
at end of diastole
(end diastolic pressure)
Increased in:
Increased in: Hypertension
Hypervolermia Vasoconstriction
Regurgitation of
cyiten TAfterload =
cardiac valves
Heart Failure fT Cardiac workload
FB onsrving Caicaton on
- Reduces number of
pathogens
- Referred to as
“Clean technique”
- Used in administration of:
Medications
Enemas
Tube feedings
Daily hygiene
Hand Hygiene is number 4
MEDICAL ASEPSIS~
- Eliminates all pathogens
- Referred to as
“Oterile technique”
- Used in:
Dressing changes
Catheterizations
Surgical Procedures
SURGICAL ASEPSIS
- MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (MI) -
- CORONARY OCCLUSION -
- Pain: - -
eS udelan Onset HEART ATIACK
Substernal
Crushing
Tightness
Severe
Unrelieved by Nitro
May Radiate To: Back
Neck
Jaw/Tooth
= Dyspnea Shoulder
- Syncope (LBP) Arm
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Extreme Weakness THO, IV Meds
- Diaphoresis Monitor
~ Denial is Dietary Restrictions
Common a INA‘ Cholesterol,
-T Pulse " 1 Caffeine
PCI? Surgery? Pacemaker?
~ Changes in ST segment
LEFT SIDED Y FAILURE
* Paroxysmal Nocturnal
Dyspnea Qa © Restlessness
* Elevated Pulmonary as -
Capillary Wedge wa > * Confusion
Pressure
* Orthopnea
* Pulmonary Congestion
- Cough
3 * Tachycardia
- Crackles
- Wheezes Exertional
- Blood-Tinged Dyspnea
Sputum
* Fatigue
~ Tachypnea
© Cyanosis
LDL/HDL
Want LOW (J 100mg/al)
= or it will lower you
into the ground.
Low Deneity Liproprotein
Want HIGH (fT 40mg/dl)
= for patient to feel
healthy.
High Deneity Liproprotein BEB orurcing eavcoron conounante ne
To Calculate
Heart Rate:
Count the number of
“R” waves in 6 seconds.
(6 large blocks X's 10 =
1 min rate)
= Wwe
@ peretie MHEMONE
W_DEFECTS MNEMONIC
CONGENITAL® DEFECTS
4Pulmonary Blood Flow
lam
doing the
Cyanotic
Squat.
Example:
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tricuspid Atresia
Squatting
Cyanosis
Clubbing
Syncope
cation Coneutant, be
CONGENITALW DEFECTS
Tt Pulmonary Blood Flow
hot blue, just.
O (tired all the
Example:
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
* T Fatigue
* Murmur
* TRisk Endocarditis
* CHF
* Growth Retardation
BRS ote rsing Faction Constants,
CONGENITAL & DEFECT
SYMPTOMS
eT Pulse
@ T Respirations
wy Retarded Growth
Dyspnea, Orthopnea
Y Fatigue
¥uRI
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
‘ORS
~, | |COMPLEX
Se of rhc
Conduction of impulee
through the bundle oF HiS to
Purkinje fiers causing
AUSCULTATING “ttle alrone
HEART SOUNDS \7Z
APE
Tricuspid — FO
verte —Mla nN
Dose Ordered
Oty of Sol =
Dose on Hana YF Sel
Maximum safe dose
based on child's weight =
Sate dose / Kg x Child's wt, in Kg
‘Amt, to infuse
Hour rate
Amt to infuee
Dene inher el A oe
Infusion time i
= # of hours
Total mle
‘xe Minutes
mi / Hour.
ae = mi
oo rnin
= mil xgtt factor =gt /pnin
BRB onroing Education Conauitanta nc
Can the patient follow directions?
Can the patlent swallow? (intothe Blood) __ (Just below skin)
ume ad)
teem? Pe TB Testing
Inritatin
Rectal 9 gP Locals
Se ner
Sublingual Sassi,
Nacal
Eyes
Ears
* Medication
* Dose To Prove Leaking
Pe Administer only
= paso weal ee Stang of
hem Pe Be familiar Desires response HO OF) seromay Su0-O Tleoue
+ Route with med or Nepitaers ieou
i copa Fla
ites F Document: mede ety precautions ee
P evaluate ec totlen’s condzion cuppostones
ed compat array
S ° ee
y Aileralee
* Aseptic technique
* Hand hygiene after removing gloves &
between patients Emulelone
Spine
’o Review med administration if seus
Glient is to do by himself oEhere
* ugpnsons
HEPARIN & COUMADIN
LAB TESTS
HEPARIN + PTT = 10 LETTERS
COUMADIN + PT = 10 LETTERS
Wow, this is a good way
to remember which lab goes
with which medication.
ATROPINE OVERDOSE
Hot as a Hare
(decreased sweating = temperature)
Mad asa taro Fe
(confusion, delirium)
Red as a Beet
(flushed face)
Dry as a Bone
(decreased secretions, thirsty)
You might also like
- Presentation Nursing 4Document10 pagesPresentation Nursing 4Pedz Romano100% (6)
- Presentation Nursing 3Document10 pagesPresentation Nursing 3Pedz Romano100% (11)
- Presentation Nursing 2Document10 pagesPresentation Nursing 2Pedz Romano100% (4)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument48 pagesFundamentals of Nursinganon-429003100% (31)
- Presentation Nursing 1Document10 pagesPresentation Nursing 1Pedz Romano80% (5)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument48 pagesFundamentals of Nursinganon-429003100% (31)
- TestDocument2 pagesTestPedz Romano0% (2)
- Newborn Hal ManualDocument74 pagesNewborn Hal ManualPedz RomanoNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument1 pageNursingPedz RomanoNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument1 pageNursingPedz RomanoNo ratings yet
- TestDocument2 pagesTestPedz Romano0% (2)
- NursingDocument1 pageNursingPedz RomanoNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)