Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Intellectual Property Rights
Uploaded by
sahildhingali0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
392 views11 pagesipr ppt
Original Title
Introduction to Intellectual Property Rights
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentipr ppt
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
392 views11 pagesIntroduction To Intellectual Property Rights
Uploaded by
sahildhingaliipr ppt
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Introduction to intellectual
property rights
Definition :- Anything resulting from the
exercise of human intellect is intellectual
property and right of possession of the
same is intellectual property rights.
Trade related aspects ( by WTO)
§ Patents
§ Integrated circuits
§ Geographical indications
§ Copyright
§ Trade marks
§ Designs
§ Trade secrets
Basis of Patentability
•
(1)Novelty
(2)
(3)Utility
(4)
(5)Inventive Step / Non obviousness
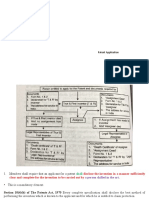
Patent Application Procedure in
India
•
(1)Ordinary Patents
(2)
(3)Patent of Addition
(4)
(5)Patent Granted under Convention
Agreement
Step 1 Application for the
Patents
Step 2 Examination of the
Application
Step 3 Opposition to the grant
of Patent
Step 4 Grant & sealing of
Patent
Step 1 Includes following
parts
A.Form of Application
B.
C.Specification
a.Provisional Specification
b.Complete Specification
D.
E.Priority Date
F.
G.Publication of Application
Step 2 Consist of two
components
•
1)Request for Examination under
section 11B
2)
3)Final Examination under section 12
Step 3 Have following
Reasons
a) Obtaining wrongfully
b) Prior publication
c) Prior claim in a concurrent application
d) Prior public use or public knowledge in India
e) Obviousness and lack of inventive step
f) Non-patentable invention
g) Insufficient description of the invention
h) Failure to disclose information relating to foreign
applications
i) If convention application, not made within the
prescribed time
j) Wrong mention of origin
k) Available of knowledge in locality
Details about Step 4
• This is the last and final step of grant
of patent
Exclusive Marketing Rights
• Definition:- When the patent application is pending
then statutory body of the country gives approval to drug
makers to sell the drug exclusively while the patent
application is still pending is called exclusive marketing
right.
•
• Examples:-
Section 24A – Application for grant of Exclusive Rights
Section 24B – Grant of Exclusive Rights
Section 24C – Compulsory Licences in relation to Exclusive Rights to sell or
distribute
Section 24D – Special provision for selling or distribution
Section 24E – Suits relating to infringements
Compulsory Licence
• It is different from ordinary licence.
• The reason for providing such licence
in India is obvious, from the fact
that patents are grated to
encourage invention.
• They are not granted merely to
enable the patentee to enjoy a
monopoly for the importation of the
patented article.
Infringement of Patents
The law does not define infringement
Relief in Suits for Infringement
Article 44 – Injunction
Article 45 – Damages
Article 46 – Other remedies
Article 47 – Right to information
Article 48 – indemnification of the
defendant
You might also like
- Introduction to IPR RightsDocument13 pagesIntroduction to IPR RightslilliputNo ratings yet
- IP 1st Exam NotesDocument19 pagesIP 1st Exam NotesErika Cristel DiazNo ratings yet
- Rights of The PatenteeDocument9 pagesRights of The PatenteeAunneshaa DeyNo ratings yet
- Patent Law and BiotechnologyDocument12 pagesPatent Law and BiotechnologyAadhityaNo ratings yet
- IP RIGHTS PROCEDURES AND COSTSDocument19 pagesIP RIGHTS PROCEDURES AND COSTSSharon DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Ipr Workshop ReportDocument12 pagesIpr Workshop ReportSwarna PrabaNo ratings yet
- C. Ra 6969 - Engr. Czes BongcoDocument87 pagesC. Ra 6969 - Engr. Czes Bongcorandell vasquezNo ratings yet
- Dustin Che Law R.A 318 Vs 9297Document3 pagesDustin Che Law R.A 318 Vs 9297lenlee cedelesNo ratings yet
- Technology Transfer Principle & EstrstegyDocument10 pagesTechnology Transfer Principle & EstrstegyJorge Rodriguez MNo ratings yet
- 012-Patent Basics 101Document27 pages012-Patent Basics 101bunty_jagiwalaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Code of The PH Cpe Laws Lesson 2Document31 pagesIntellectual Property Code of The PH Cpe Laws Lesson 2Kent Harry VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property LawDocument10 pagesIntellectual Property LawSarthak ShankarNo ratings yet
- Technological EnvironmentDocument15 pagesTechnological EnvironmentTejaswi ReddyNo ratings yet
- CHE LAW OF 2004 AND CODE OF ETHICSDocument45 pagesCHE LAW OF 2004 AND CODE OF ETHICSjestlejNo ratings yet
- Patent Trolling in IndiaDocument3 pagesPatent Trolling in IndiaM VridhiNo ratings yet
- Geographical IndicationDocument51 pagesGeographical IndicationmymadhavaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology and IprDocument27 pagesResearch Methodology and IprSreepradha100% (2)
- Lecture 16 Theories of Reaction RatesDocument13 pagesLecture 16 Theories of Reaction RatesAmeelaDNo ratings yet
- Lessons from innovation studies in manufacturingDocument21 pagesLessons from innovation studies in manufacturingMoeshfieq WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Leagal Challenges For The Customs Regarding The Counterfeit Goods in Transit - A Study With Refernce To The Nokia CaseDocument49 pagesLeagal Challenges For The Customs Regarding The Counterfeit Goods in Transit - A Study With Refernce To The Nokia CaseAmit Sudarsan/ VideaimIPNo ratings yet
- Ipr SyllabusDocument3 pagesIpr SyllabusArman Rocky100% (1)
- What Is A Patent ?Document33 pagesWhat Is A Patent ?RajanSharmaNo ratings yet
- History of Patent LawDocument14 pagesHistory of Patent LawNasif MustahidNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On "Patent Drafting" by Ms. Vinita RadhakrishnanDocument75 pagesA Presentation On "Patent Drafting" by Ms. Vinita RadhakrishnanBrain League100% (2)
- FinalDocument8 pagesFinalMelvin DanginNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Requirements For Contract Research Organization in IndiaDocument13 pagesRegulatory Requirements For Contract Research Organization in IndiaNeelam100% (1)
- Supplier Accreditation Requirements Checklist: Collaborative Industrial Revolution IncDocument2 pagesSupplier Accreditation Requirements Checklist: Collaborative Industrial Revolution Incamiel pugatNo ratings yet
- 03 FINAL - TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER PROTOCOL OF THE DOST-RDIs PDFDocument21 pages03 FINAL - TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER PROTOCOL OF THE DOST-RDIs PDFWalter PeraltaNo ratings yet
- HMT Unit 4Document21 pagesHMT Unit 4Muthuvel MNo ratings yet
- Intellual Property RightDocument25 pagesIntellual Property RightsinghalshilpiNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Rights QBDocument8 pagesIntellectual Property Rights QBSandeepNo ratings yet
- Unit V Patents 1Document26 pagesUnit V Patents 1MANIKANDAN.CNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Course Matterial Ipcomp Relation Between Ipr and Competition LawDocument36 pagesModule 3 Course Matterial Ipcomp Relation Between Ipr and Competition LawAnkush JadaunNo ratings yet
- Patent Lecture 1Document20 pagesPatent Lecture 1BinithaNo ratings yet
- Technoprenuership 101 1Document5 pagesTechnoprenuership 101 1Warren PineNo ratings yet
- Cases TortsDocument84 pagesCases TortsniyatijigyasiNo ratings yet
- PPTXDocument132 pagesPPTXKimNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument12 pagesIntellectual Property RightsAkash KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis - IiDocument12 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis - IiMae Quenie Abadingo TiroNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Indian Patent ActDocument74 pages1.1 Indian Patent ActBhavya NarangNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyMicaella GalanzaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument35 pagesIntellectual Property RightsUjjwal AnandNo ratings yet
- IPR Protection and Enforcement in IndiaDocument3 pagesIPR Protection and Enforcement in Indiatulasinad123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Tin PlateDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Tin PlateProf C.S.Purushothaman100% (1)
- Ip Due DiligenceDocument5 pagesIp Due DiligencePradnya PatilNo ratings yet
- Keywords Search: Ma. Winelma M. GarciaDocument60 pagesKeywords Search: Ma. Winelma M. GarciaIñaki Zuriel Constantino100% (1)
- Solution 4Document3 pagesSolution 4D.VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Patent Mapping and LandscapingDocument24 pagesPatent Mapping and LandscapingKESETHANo ratings yet
- The Vision and Mission of the Claro M. Recto AcademyDocument3 pagesThe Vision and Mission of the Claro M. Recto Academyadriane aquinoNo ratings yet
- Recent Patent Litigation CasesDocument4 pagesRecent Patent Litigation CasesMedha AvasiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Peptides: A Coupling Reaction in Peptide SynthesisDocument14 pagesChemistry of Peptides: A Coupling Reaction in Peptide SynthesisRakesh KoreNo ratings yet
- Invention SpottingDocument42 pagesInvention SpottingMichelle RomulNo ratings yet
- Iic Celebration Activities 2021-22Document1 pageIic Celebration Activities 2021-22Srushti JainNo ratings yet
- RMIPR - Unit 4 - Study MaterialsDocument23 pagesRMIPR - Unit 4 - Study Materialsdrmsrmurty9473No ratings yet
- Biomedical Literature Evaluation SkillsDocument24 pagesBiomedical Literature Evaluation SkillsPauline TayabanNo ratings yet
- Alaire CorporationDocument2 pagesAlaire CorporationChleo EsperaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic ProductsDocument17 pagesOphthalmic ProductsAmrit GaireNo ratings yet
- Ethics Chapter 1Document6 pagesEthics Chapter 1Echizen KinichiNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Components and Testing MethodsDocument3 pagesAerosol Components and Testing MethodsSwaroopSinghJakharNo ratings yet
- IP and Technology: Department of Biotechnology, IIT GuwahatiDocument27 pagesIP and Technology: Department of Biotechnology, IIT GuwahatiAgradaNo ratings yet
- 9.4 Implied Volatility 149Document2 pages9.4 Implied Volatility 149api-3754054No ratings yet
- FinValley 5.0 Case StudyDocument3 pagesFinValley 5.0 Case StudyBrennan BarnettNo ratings yet
- Worldlessness in ArendtDocument24 pagesWorldlessness in ArendtCarmen CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Rights and obligations of parties to negotiable instrumentsDocument4 pagesRights and obligations of parties to negotiable instrumentsAgatha de Castro100% (2)
- Securities Regulation Code 8799 PDFDocument20 pagesSecurities Regulation Code 8799 PDFKAYE VIENNANo ratings yet
- Merger AgreementDocument5 pagesMerger AgreementGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Non-Disclosure and Confidentiality AgreementDocument2 pagesNon-Disclosure and Confidentiality AgreementAnn SCNo ratings yet
- 62 LQRev 375Document13 pages62 LQRev 375me elkNo ratings yet
- Brand Ambassador AgreementDocument2 pagesBrand Ambassador AgreementKristel Sales-Medel67% (3)
- Nunelon R. Marquez v. Elisan Credit CorporationDocument3 pagesNunelon R. Marquez v. Elisan Credit CorporationmltoqueroNo ratings yet
- Auto Secure Private Car Package Policy: Tata AIG General Insurance Company LimitedDocument6 pagesAuto Secure Private Car Package Policy: Tata AIG General Insurance Company LimitedSuffah Education CenterNo ratings yet
- 1 Engro Code of Business Conduct PDFDocument61 pages1 Engro Code of Business Conduct PDFQamber HoathNo ratings yet
- SCHMID & OBERLY, INC. vs. RJL MARTINEZ FISHING CORPORATIONDocument2 pagesSCHMID & OBERLY, INC. vs. RJL MARTINEZ FISHING CORPORATIONEmi Sicat100% (1)
- Revised Corporation Code of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesRevised Corporation Code of The PhilippinesJon MickNo ratings yet
- Set Up A Business in Angola PDFDocument3 pagesSet Up A Business in Angola PDFSoiab KhanNo ratings yet
- United States Contract Law - WikipediaDocument18 pagesUnited States Contract Law - WikipediaEl Tio100% (1)
- Diwakar Nath Jogi PDFDocument3 pagesDiwakar Nath Jogi PDFblack kobraNo ratings yet
- 5021 Solutions 7Document7 pages5021 Solutions 7karsten_fdsNo ratings yet
- IMICL Dighi Maritime LTDDocument28 pagesIMICL Dighi Maritime LTDPrachi JainNo ratings yet
- Statement OF Financial Interests: ?C J H KDocument4 pagesStatement OF Financial Interests: ?C J H KnebraskawatchdogNo ratings yet
- Pro PerDocument47 pagesPro Perxlrider530No ratings yet
- Associated Bank Liable for Payment of Crossed Checks to Unauthorized PersonDocument2 pagesAssociated Bank Liable for Payment of Crossed Checks to Unauthorized PersonmmaNo ratings yet
- Secured Party Affirms Ownership of Birth CertificateDocument3 pagesSecured Party Affirms Ownership of Birth Certificateron homan90% (29)
- Breach of ContractDocument18 pagesBreach of ContractGRACE100% (1)
- Letter of Indemnity For Maturity - Survival ClaimDocument2 pagesLetter of Indemnity For Maturity - Survival Claimsajeer n FORWARDNo ratings yet
- 34 City State Savings Bank Vs Teresita Tobias 3 7 18 G.R. No. 227990Document4 pages34 City State Savings Bank Vs Teresita Tobias 3 7 18 G.R. No. 227990RubenNo ratings yet
- General Growth Properties' Bankruptcy FilingDocument56 pagesGeneral Growth Properties' Bankruptcy FilingDealBook100% (12)
- Partnership Notes 1Document4 pagesPartnership Notes 1Joylyn CombongNo ratings yet
- Parties To A Negotiable InstrumentDocument4 pagesParties To A Negotiable InstrumentAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Company Directors Disqualification Act 1986 - ACCA Qualification - Students - ACCA GlobalDocument3 pagesCompany Directors Disqualification Act 1986 - ACCA Qualification - Students - ACCA Globalpepe23112No ratings yet