Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Structure of A Business Enterprise Why Do We Need To Study Business Organization
Uploaded by
jf katigbac0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views14 pageschapter 5
Original Title
management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchapter 5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views14 pagesBasic Structure of A Business Enterprise Why Do We Need To Study Business Organization
Uploaded by
jf katigbacchapter 5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
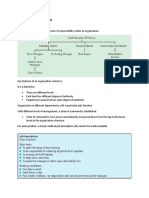
BASIC STRUCTURE OF A BUSINESS ENTERPRISE
Why do we need to study Business Organization
Successful managers need not be products of study any
particular course of study like business administration,
education, engineering, the humanities, liberal arts, or law, they
must at least have a working knowledge and understanding of
the basic principles of business organization and management
more particularly the relationship between departments which
are vital in achieving the objectives of the entire organization.
Organization - the process of identifying and grouping the work
to be performed, defining and delegating responsibility and
authority, and establishing relationships for the purpose of
enabling people to work most effectively together in
accomplishing objectives.
What is Organizational Structure - is the framework by which
the activities of an enterprise, as determined by the managers
are performed.
= It is the arrangement of the functions performed by the
various personnel in the different units usually, classified into
division, departments, sections, and the rank and file workers.
Basic Requirements of Good Organization
To be effective, an organizational set-up must conform to
certain based requirements:
1) To define the basic objectives of the organization.
2) There must be a division of labour so that no member of
the organization will duplicate the work of another.
3)Directing authority to plan, coordinate, and control the
functions and activities of the enterprise.
Define line of responsibility and limits of authority can then be
established.
Directing Authority - it guides the work of the different
divisions as members of a well-integrated team.
4)To established the relationships among the members of
the business.
A pertinent questions on the organization are:
a) What is the relationship of employees to one another and
to
the whole organization?
b) Does each member of the organization know whom he
reports and who should report to him?
c) Does one employee report more than one superior?
The organization is divided into different levels of authority, each
with specific function and responsibilities, contributing to the
attainment of the organizations objectives.
Principles of Good Organization
The basic principles are essential to activities, coordination, and
harmonious relationship among the members of the organization.
The most important of these principles are:
1) Principles of departmentation or division of labor
Departmentation - refers to the particular groupings of functions
or activities in an organization, showing their relationships and the
people doing them.
The groupings establish the logical arrangement of the functions
and activities into levels in the organizational structures facilitating
the assignment of personnel according to their abilities and fields of
specialization.
The organizational structure as indicated by divisions,
departmentations and it breaks up the work into manageable units.
The organizational structure is necessary because of the limitations
of both human ability, time and specialization.
Levels of Management:
a) Top Management - group in large firm consists of the
executives, and managers which authority and responsibility
covers the entire company.
In a corporation, this group includes:
a) board of directors representing the stockholders
b) the president
c) the secretary
d) the treasurer
e) the general manager
The function of this group is to make the major plans and policies
for the company and to formulate the major decisions affecting
such matters as: finance, production, marketing and research.
It is also top managements responsibility to:
1) establish relations with stockholders, labor and customers
2) set up public and legal relations both internally and
externally
3) fix the responsibility and authority of each division and
department manager.
b) Operating Management - group includes personnel of
widely different ranks and responsibilities. This group includes
the: a) superintendent
b) the production manage
c) the personnel manager
d) the office manager
e) other department heads of equivalent ranks
The functions of this group is to interprets and carries out
policies, formulate plans, and utilizes management.
It
coordinates follows up and training subordinate
They are accountable to the chief executives of the firm;
c) Operating Supervision - a group is composed of the
members of the management who deal directly with the workers.
It includes the: a) supervisors
b) foremen
c) section chiefs
d) unit chiefs who are accountable to the operating
management
Also known as first line supervisors. The function of this
group, they have immediate control and supervision over the
work of the operating personnel. They:
a) direct and carry out the programs and goals of their
department or section;
b) analyzed department needs and train personnel under
them;
c) follow up and see to it that employee under them do their
work satisfactory.
d) Operating Personnel - are not part of management and are
the most numerous in the organization. Their task is to
accomplish the work assigned to them and to carry out the
decisions and policies made by the top and operating
management.
The rank and file employees and workers belong to this
group and they are at the bottom of the organizational
structure.
2) Principles of Unity of Command - when a member has
only one direct boss or supervisor. No employee can work
effectively for more than one immediate supervisors at the same
time because two superiors are liable to give their common
subordinates assignments which the latter cannot accomplish
simultaneously.
This principles date back to the time of Christ, who said: No
man can serve two masters; for either he will hate one and love
the other, or else he will be loyal to one and despise the other.
The principle should be applied in two ways:
a) each employee must know to whom he reports
b) a supervisor must know whom he directs
3) Span of Control or Span of Supervision - refers to the
number of subordinates who reports directly to a higher
executive. Because of limitations of the human capacity to
attend to and supervise different activities and workers, an
individual can adequately supervise only a certain number of
people. The larger the number of reporting to an executive
directly the less attention require3 to each subordinates.
4) Homogeneous Assignments - means that workers must be
assigned similar or related functions.
This principles limits the variety of jobs a person can successfully
accomplish. In delegating responsibility the functions to be
assigned should be grouped on the basis of similarity, that is the
duties should be sufficiently related to one another to take
advantage of specialization of skills and knowledge.
5)Delegation of Responsibility with Corresponding Limit of
Authority
Delegation - means conferring of a certain amount of authority
and responsibility from the superior to his subordinates.
= Is the process of decentralizing or distributing responsibility
and authority thus preventing bottlenecks and overwork for the
administrator at the tope of hierarchy.
In every organization someone must hold authority, responsibility
and accountability for the entire organization.
The Board of Directors - representing the financiers and
stockholders , hold this authority, responsibility, and
accountability in a corporation. The board elects presidents who
is then given then authority and full responsibility to manage
the enterprise.
The Presidents
divide the functions among divisions,
departments, sections, and units, applying the principles of
division of labor and specialization.
= He must employees people whom he can rely on and hold
responsible for handling the various functions.
Authority - is the right to act or to direct other to act.
= Has the right to decide what should be done and the right
to do it or to require someone each to do it for him.
The Organization Pyramid
Chief Executive Officer
Top Management
(President or Gen. Manager)
Senior Executives (Vice Pres.)
Operating Management
Division Heads (Asst. VP)
Department Managers
Operating Supervisor
Supervisors
Foreman
Operating Personnel
Workers
Levels of Management by which Authority is Distributed
Through the Organization (Organizational Structure)
Establish Objectives
Board of
Accountable to Stockholders
Directors
Operates business makes plans
and policies
Chef Executives
Accountable to Board of Directors
(President )
Coordinates activities of
Division or department
Accountable to CEO
Operating
Supervision
WORKERS
Operating
Management
Operating
Supervision
WORKERS
Operating
Supervision
WORKERS
4. Supervision and control of workers
Accountable to operating management
5. Execute and accomplishing assignments, carry out orders.
Accountable to operating supervisors and foreman
Broad Definition of Management
Is the process of planning, organizing, staffing, leading/directing, and
controlling the efforts of organizational members and the use of other
organizational resources in order to achieved stated organizational
goals.
Organizational resources: human resources
financial resources (money)
physical/technical resources
(man)
(machineries)
Organization - grouping of people/individuals working together with
common goals.
You might also like
- Unit 1 - Nature of Organization & ManagementDocument26 pagesUnit 1 - Nature of Organization & ManagementVamsi Tarun65% (20)
- Managemant and EntreprenourshipDocument31 pagesManagemant and EntreprenourshipransdkasjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4FAIRY ZiNo ratings yet
- Reportmodule6 120508034134 Phpapp01 PDFDocument76 pagesReportmodule6 120508034134 Phpapp01 PDFdingdong magandiaNo ratings yet
- Organizing LectureDocument56 pagesOrganizing LectureSteph MarquezNo ratings yet
- Organizing I. Organizing: Module - 10: Managerial Functions: Organizing and Staffing Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesOrganizing I. Organizing: Module - 10: Managerial Functions: Organizing and Staffing Learning ObjectivesRavali AnabathulaNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational BehaviorDocument3 pagesWhat Is Organizational Behaviorjecinta wanjikuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Nine - Organizational Design and StructureDocument8 pagesChapter Nine - Organizational Design and StructureMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- 18bca35s U4Document15 pages18bca35s U4iamelynalvaro951No ratings yet
- تعديل التعديل محاضرة OrganizingDocument62 pagesتعديل التعديل محاضرة OrganizingAbdo MahfouzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Eng ManDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Eng ManJustine SabarilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 OrganizingDocument24 pagesChapter3 Organizingplatinum moviesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EditedDocument15 pagesChapter 4 EditedMuktar jiboNo ratings yet
- Akram English 2Document15 pagesAkram English 2Rose DallyNo ratings yet
- OrganisingDocument29 pagesOrganisingAnsh RawatNo ratings yet
- Intr. MGMT Chapter FourDocument15 pagesIntr. MGMT Chapter FourAYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- Unit Four Organizing FunctionDocument20 pagesUnit Four Organizing FunctionMagarsa BedasaNo ratings yet
- CH-4 MGT IntDocument11 pagesCH-4 MGT IntwubeNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionAbhishek KattaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 OrganizingDocument19 pagesWeek 4 OrganizingDona JovenNo ratings yet
- Chapter One ManagementDocument12 pagesChapter One ManagementmikialeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 OrganizingDocument22 pagesChapter 4 OrganizingRoman clashNo ratings yet
- Types of Organization Structure: Solved Assignment 2021-22 MCS-052Document23 pagesTypes of Organization Structure: Solved Assignment 2021-22 MCS-052Yash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ABM 11 - ORGMAN - Q1 - W7-8 - Mod6 EditedDocument5 pagesABM 11 - ORGMAN - Q1 - W7-8 - Mod6 EditedRenz NgohoNo ratings yet
- Ch-4-Organizing Management Functions-EditedDocument24 pagesCh-4-Organizing Management Functions-Editedanwar jemalNo ratings yet
- Nature of OrganizationDocument6 pagesNature of OrganizationShahina ParvinNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Organizational Chart: Nursing ManagementDocument14 pagesAssignment On Organizational Chart: Nursing ManagementNisha MwlzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OrganizingDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Organizingአንተነህ የእናቱNo ratings yet
- Engg MGT., Chapter 4 - Organizing Tech. Activities (Weeks 8, 9, 10)Document12 pagesEngg MGT., Chapter 4 - Organizing Tech. Activities (Weeks 8, 9, 10)Luz OcampoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Organization and ManagementDocument7 pagesLesson 7 - Organization and ManagementDeshanNo ratings yet
- History: Organizing of Information WriteDocument5 pagesHistory: Organizing of Information WriteJohn MoralesNo ratings yet
- ABM G11 Chap 4 Org MGTDocument15 pagesABM G11 Chap 4 Org MGTEljey Eushe F. SorianoNo ratings yet
- 18ME51 Notes-PDF 1Vb23Document16 pages18ME51 Notes-PDF 1Vb23thiruma k dNo ratings yet
- Items Description of ModuleDocument12 pagesItems Description of Modulekhushboo rajputNo ratings yet
- Shipon IpeDocument9 pagesShipon Iperobin KhanNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management ReviewerDocument13 pagesOrganization and Management ReviewerSunghoon ParkNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument18 pagesOrganizingIGA ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Pom - Organisation NotesDocument5 pagesPom - Organisation NotesShodan IddyaNo ratings yet
- Educational Management and Leadership - CoordinatingDocument31 pagesEducational Management and Leadership - CoordinatingConnie LopicoNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument25 pagesOrganizingCiara ManangoNo ratings yet
- Types of Organization Structure: Solved Assignment 2021-22 MCS-052Document23 pagesTypes of Organization Structure: Solved Assignment 2021-22 MCS-052Yash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document82 pagesUnit 4Shweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ans: The Characteristics of Management AreDocument11 pagesAns: The Characteristics of Management AreLendle ThokchomNo ratings yet
- Functions of ManagementDocument5 pagesFunctions of ManagementPETER OTIENONo ratings yet
- Engineering ManagementDocument10 pagesEngineering Managementapahh100% (1)
- ORGANIZINGDocument18 pagesORGANIZINGBai Jamellah KasuyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: OrganizingDocument19 pagesChapter 4: OrganizingCath Domingo - LacisteNo ratings yet
- Fom Unit 3Document48 pagesFom Unit 3tarunNo ratings yet
- Organising: Building A Dyanamic OrganisationDocument18 pagesOrganising: Building A Dyanamic OrganisationYUSHA-U YAKUBUNo ratings yet
- Management Theory and Practice 1Document7 pagesManagement Theory and Practice 1Yogesh BhapkarNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Process of OrganizingDocument21 pagesMeaning and Process of OrganizingSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem AssignmentDocument158 pages1st Sem AssignmentWasim_Siddiqui_31100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Managers in OrganizationDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Managers in OrganizationJia wei SohNo ratings yet
- Nature and Structures of OrganizationDocument35 pagesNature and Structures of OrganizationJennifer SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - OrganizingDocument41 pagesChapter 5 - OrganizingbvinothhhNo ratings yet
- Mob MidDocument14 pagesMob MidgoodboyNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument17 pagesOrganizingAsif Shah50% (2)
- OrgMan - Organizational TheoriesDocument18 pagesOrgMan - Organizational TheoriesDIVINA GRACE RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 New Syllabus Notes (With Watermark and Corrected Notes and Checked)Document7 pagesChapter 2 New Syllabus Notes (With Watermark and Corrected Notes and Checked)shaunelcasimiro74No ratings yet
- Human Resources Management: A Guide on How to Implement HR Best Practices Includes Ready Structured Procedures and FormsFrom EverandHuman Resources Management: A Guide on How to Implement HR Best Practices Includes Ready Structured Procedures and FormsNo ratings yet
- Paalam Kay LeonorDocument4 pagesPaalam Kay Leonorjf katigbac100% (1)
- Paalam Kay LeonorDocument4 pagesPaalam Kay Leonorjf katigbac100% (1)
- MGNT 7Document37 pagesMGNT 7jf katigbacNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Purpose of PlanningDocument7 pagesThe Nature and Purpose of Planningjf katigbacNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Social Development 2nd Edition by Clarke Stewart ParkeDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Social Development 2nd Edition by Clarke Stewart Parkekellywalkerdasbgefrwx100% (41)
- Tefl01 - t6 - Act (1) Error AnalysisDocument3 pagesTefl01 - t6 - Act (1) Error AnalysisVania AndreaNo ratings yet
- Nurisng Management ReportDocument7 pagesNurisng Management ReportjudssalangsangNo ratings yet
- Princeton University Press: Physics & Astrophysics 2012Document32 pagesPrinceton University Press: Physics & Astrophysics 2012Princeton University Press60% (5)
- Nina Holzer: ProfileDocument3 pagesNina Holzer: ProfileninaholzerNo ratings yet
- Aue@chem - Ucsb.edu: Instructor Code For Aue's 109A: MCAUE06615)Document4 pagesAue@chem - Ucsb.edu: Instructor Code For Aue's 109A: MCAUE06615)Allison ChangNo ratings yet
- Catanduanes Is An IslandDocument8 pagesCatanduanes Is An Islandsaintjames2No ratings yet
- Best Home Learning SpaceDocument23 pagesBest Home Learning Spacema. belinda borborNo ratings yet
- Multicultural Diversity:: A Challenge To Global TeachersDocument14 pagesMulticultural Diversity:: A Challenge To Global Teachersjessalyn ilada100% (1)
- Description: Tags: Sar45Document27 pagesDescription: Tags: Sar45anon-131556No ratings yet
- English: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesEnglish: ObjectivesJessi HerediaNo ratings yet
- HW 0Document1 pageHW 0Kumar RajputNo ratings yet
- Englis Discoveries NIVEL 4Document55 pagesEnglis Discoveries NIVEL 4sandra garciaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesAP Physics Problems and SolutionsYash UpasaniNo ratings yet
- Surgical Tech HomeworkDocument8 pagesSurgical Tech Homeworkafnofjmzeldfie100% (1)
- Soc 2510-Summer ' 19 Tues1Document9 pagesSoc 2510-Summer ' 19 Tues1Noah CanalesNo ratings yet
- Intention-Based Models of Entrepreneurship Education: January 2004Document31 pagesIntention-Based Models of Entrepreneurship Education: January 2004RennyBintoroNo ratings yet
- Final Copy of IBR Guideline Preliminary 30102014Document11 pagesFinal Copy of IBR Guideline Preliminary 30102014Babatunde AbayomiNo ratings yet
- Addition - CorrectedDocument4 pagesAddition - CorrectedMailyn M. PermiNo ratings yet
- Week4 PE DLPDocument8 pagesWeek4 PE DLPMica DuhinaNo ratings yet
- High School CarpentryDocument4 pagesHigh School CarpentryFlyEngineerNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Aptitudes PDFDocument92 pagesUnderstanding Your Aptitudes PDFstutikapoorNo ratings yet
- Rubric Speaking TestDocument7 pagesRubric Speaking TestKurikulum PerpustakaanSMKLNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chapter 1 Significance of The StudyDocument7 pagesThesis Chapter 1 Significance of The Studymyelramosnorthlasvegas100% (2)
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument15 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyRushil ShahNo ratings yet
- Rackham Dissertation Committee GuidelinesDocument4 pagesRackham Dissertation Committee GuidelinesPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperForMeCanada100% (1)
- Shooq Ali 201600097Document4 pagesShooq Ali 201600097api-413391021No ratings yet
- Reading and Writing 3 Outline Q: Skills For SuccessDocument2 pagesReading and Writing 3 Outline Q: Skills For SuccessĐạt LêNo ratings yet
- KDP Mentor Training Course SummaryDocument2 pagesKDP Mentor Training Course SummaryJohnNo ratings yet
- PromoDocument40 pagesPromoEno PraiseNo ratings yet