Professional Documents
Culture Documents
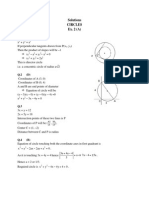
Circle
Uploaded by
Maliney PohsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circle
Uploaded by
Maliney PohsCopyright:
Available Formats
TOPIC 1
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
CONIC SECTIONS
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
1.2 Circle
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the lesson, you should be able to :
a) Define a circle
b) Determine the equations of a circle with radius, r and centre, C at
(0,0) and (h,k)
c) Determine the centre and radius of a circle by completing the
squares
d) To find the equation a a circle
i. Passing through three points
ii. Passing through two points where the equation of the diameter given
e) To find the points of intersections of two circles
f) To solve application problems :
i. Find the equations on tangents and normals to a circles
ii. Find the length of a tangent from a point to a circle
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Circle
(h,k)
A circle is a set of all points in a plane
equidistant from a given fixed point
called
the centre.
A line segment determined by the
centre and
any point on the circle is called a
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
(a) If r represents the radius of a circle and
y C(h,k) represents the centre, then
P(x,y)
C(h,k)
Phytagoras
Theorem
CQ2 + PQ2 =
PC2
The equation of the circle in standard form
is given by
x h
y k
r2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
(b) If r represents the radius of the circle and
(0,0) represents the centre at the origin, then
the equation of the circle is
x y r
2
Standard form of the
equation of a circle
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 1:
Determine the centre, radius and
draw the circle represented by the
following equation;
x 4
y 3 5
2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Solution :
Since the equation is in the standard form, the
centre is at (4,-3) and the radius is 5
.
0
5
(4,-3)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 2 :
Determine the equation of a circle whose centre
is at (-2,3) and whose radius is 4.
Solution :
Substitute h = -2 , k = 3 and r = 4 into the
standard form of the equation of a circle.
x h y k 2 r 2
2
2
2
x 2 y 3 4
2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 3 :
Determine the equation of a circle having its centre at
(3,-1) and passing through the point (-1,2) .
Solution :
We determine the radius as the distance from the
centre of the circle to any point on the circle, thus :
So the equation is r
3 1 2 1 2 2
25 5
x 3
y 1 25
2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
General form of the equation of a circle
The equation of a circle with centre (h,k) and radius, r is :
Consider the equation x h 2 y k 2 r 2
x h 2 y k 2 r 2
2
standard form
2 xh h 2 y 2 2 yk k 2 r 2
x 2 2 xh y 2 2 yk h2 k 2 r 2 0
Where , the centre ( h,k ) = (- g,- f )
x 2 2 x ( g ) y 2 2 y ( f ) ( g ) 2 ( f )2 r 2 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
x 2 2 x ( g ) y 2 2 y ( f ) ( g )2 ( f )2 r 2 0
x 2 2 xg y 2 2 yf r 2 g 2 f 2 0
Let c r g f
2
General form of the equation of a circle
x 2 y 2 2 gx 2 fy c 0
The radius, r =
g2 f 2 c
general form
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 4 :
Find the centre and radius of a circle
given the equation of circle is
x y 2x 6 y 6 0
2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Solution:
x y 2x 6 y 6 0
2
x y 2x 6 y 6
2
By completing the
square;
2
2
( x 2 x 1) ( y 6 y 9) 6 1 9
Simplify
the result,
2
x 1 y 3 2 4
x 1 2 y 3 2
22
Centre: (1,3)
Radius = 2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Alternative Method :
x2 y 2 2x 6 y 6 0
Comparing with ;
x y 2 gx 2 fy c 0
2
( h,k ) = ( - g,- f ) = (1,3)
r g2 f 2 c
1 2 3 2 6 2
and
2g = - 2 , g = -1
2f = - 6 , f = - 3
-g=1,-f=3
Centre: (1,3)
Radius = 2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Circle passing
passing through
through three
three given
given
Circle
points
points
A
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 1
Find the equation of the circle passing
through the points (3,0) , (3,2) and (-1,2).
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Solution
Let
perpendicular
bisector
Q (3,2)
chord
R
(-1,2)
C
chord
perpendicular
bisector
P (3,0)
The perpendicular bisectors of the chords
PR and QR meet at the centre of the circle, C.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
First, find the equation of the perpendicular
bisectors of PR and QR.
2
1
4
2
1
1
2
1
m PR
2
20
m PR
1 3
m PR
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
mid point of PR =
3 1 0 2
,
2
2
= (1,1)
Thus, the equation of the perpendicular
bisector of PR is
y - 1 = 2 (x -1)
y 2x + 1 = 0
... (1)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
22
0
m QR
0
1 3
4
1
m QR
m PR
a vertical
line
is undefined
mid point of QR =(1,2)
Thus, the equation of perpendicular bisector of QR
is
x=1
... (2)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
By solving these equations simultaneously ,
we will get the centre of the circle.
y 2x + 1 = 0
... (1)
x=1
... (2)
y 2(1) +1 = 0
y=1
The centre of the circle is (1,1).
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
CP is the radius of the circle,
r (1 0) 2 (1 3) 2
Thus, the equation of the circle is
(x -1)2 + ( y 1)2 = 5
x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y - 3 = 0
OR
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
An Alternative Method
The general equation of the circle is
x2+ y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
Substitute each point into the equation.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
At point (3,0),
(3)2 + 0 + 2g(3) + 2f(0) + c = 0
9 + 6g + c = 0 ... (1)
At point (3,2),
(3)2 + (2)2 + 2g(3) + 2f(2) + c = 0
13 + 6g + 4f + c = 0 ... (2)
At point (-1,2),
(-1)2 + (2)2 + 2g(-1) + 2f(2) + c = 0
5 - 2g + 4f + c = 0 ... (3)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Then, solve these equations simultaneously to get the
values of g, f and c.
(2)-(1)
13 + 6g + 4f + c = 0 ... (2)
9 + 6g + 0f + c = 0 ... (1)
4 + 4f = 0
f = -1
(2)-(3)
13 + 6g + 4f + c = 0 ... (2)
5 - 2g + 4f + c = 0 ... (3)
8 + 8g = 0
g = -1
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Substitute g = -1 into (1)
9 + 6(-1) + c = 0
c = -3
We have c = -3, g = -1 and f = -1
Thus, the equation of the circle is
x2 + y2 2x 2y - 3 = 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Circle passing through two points with
the equation of the diameter given.
P
C (-g,-f)
Q
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 2
Find the equation of the circle passing
through the points (0,0) and (4,2) with its
diameter is x + y = 1.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Solution
perpendicular
bisector
Let
P
chord
C
diameter
The perpendicular bisector of the chord
PQ intersects with the diameter at the
centre of the circle, C.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
First, find the equation of the perpendicular
bisector of PQ.
m PQ
20
40
1
m PQ
m PQ
=-2
midpoint of PQ = (2,1)
Thus, the equation of the perpendicular
bisector of PQ is
y - 1 = - 2 (x -2)
y + 2x - 5 = 0
...(1)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Then, solve these equations simultaneously to get the
centre of the circle.
y +2x - 5 = 0 ...(1)
y + x -1 = 0 ...(2)
equation of the
diameter
(1)-(2)
x=4
y=-3
The centre of the circle is (4, - 3).
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
The radius is the distance of the two points (0,0) and
(4, - 3).
r (4 0) 2 (3 0) 2
25 5
Thus, the equation of the circle is
(x - 4)2 + ( y + 3)2 = 25
x2 + y2 8x + 6y = 0
OR
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
An Alternative Method
The general equation of the circle is
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
Substitute each point given into the equation.
At point (0,0),
c = 0 ... (1)
At point (4,2), 20 + 8g + 4f + c = 0 ... (2)
(2)-(1)
20 + 8g + 4f = 0
5 + 2g + f = 0 ... (3)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Substitute (-g,-f) into the equation of the
diameter
x +y=1
-g -f=1
f = - g 1 ...(4)
Substitute (4) into (3)
5 + 2g + f = 0 ...(3)
5 + 2g + (-g 1) = 0
g=-4
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Substitute g = - 4 into (4)
f = - g - 1 ...(4)
= - (- 4) -1
=3
We have c = 0, g = - 4 and f = 3
Thus, the equation of the circle is
x2 + y2 8x + 6y = 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 3
Find the equation of the circle having AB as
its diameter where A (1,5) and B (-2,3).
Solution
the centre of the circle is
C
B the mid point of AB and
the radius is AB.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
centre =
3
1
2 2
1
,4
2
1
r ( 1 ( 2 ))2 ( 5 3 )2
2
1
13
2
The equation of the circle is
13
(x +) + ( y - 4) = 4
2
x2 + y2 + x 8y + 13 = 0
OR
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
An Alternative Method
If P is any point on the
circle and AB is the
diameter, then
mAP mPB = -1
y 5 y 3
1
So,
x 1 x 2
(y - 5)(y - 3) = - (x - 1)(x +2)
y2 - 8y + 15 = - ( x2 + x - 2)
x2+y2+ x 8y +13 = 0
P(x,y)
B
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
A tangent to a circle is a line that touches the circle
at a point.
A normal to a circle is a line that is perpendicular to
the tangent and passing through the centre.
C
normal
tangent
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Intersection of two circles
Consider two circles C1 and C2 whose equation are ;
x 2 y 2 2 g1 x 2 f1 y c1 0
.(1)
x 2 y 2 2 g2 x 2 f 2 y c2 0
.(2)
Any point on both circles must have
coordinates (x,y) which satisfies the above equations.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Intersection of two circles
P
C2
C1
Q
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 4
Find the points of intersection of the
circles with equation ;
x y 2x 8 y 7 0
2
x y 8 x 2 y 13 0
2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
Solution
MATHEMATICS UNIT
x y 2x 8 y 7 0
2
x 2 y 2 8 x 2 y 13 0
(i) - (ii)
(i)
(ii)
6x 6 y 6 0
The two circles will meet at the line :
6x-6y -6 = 0 or y = x 1.
Substitute y = x 1 into the equation of the first circle to
find the points of intersection.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
x 2 x 1 2 x 8 x 1 7 0
2
2 x 2 12 x 16 0
x2 6x 8
x 2 x 4
0
0
x 2 or x 4
When
x 2 , y 1
x 4 , y 3
So the intersection points of the two circles
are (2,1) and (4,3).
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Theorem
If the equation of a circle is
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0,
then the equation of a tangent to a circle
at the point P(x1,y1) is given by
xx1 + yy1+ g( x + x1) + f ( y + y1) + c = 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 5
Find the tangent and normal line to a circle
x2 + y2 - 6x 10y -82 = 0
at the point K(-1,-5).
Solution
x2 + y2 - 6x 10y - 82 = 0
We have g = -3, f = -5 and c = -82
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
The equation of the tangent at K(-1,-5) is
xx1+ yy1+ g(x + x1) + f(y + y1) +c = 0
x(-1) + y(-5) + (-3)(x -1) +(-5)(y - 5) +(-82) = 0
-x - 5y - 3x + 3 - 5y + 25 82 = 0
- 4x - 10y 54 = 0
2x + 5y + 27 = 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
2x + 5y + 27 = 0
The gradient of the normal is
1
5
mn
2
2
5
Thus, the equation of the
normal at the point P(-1,-5) is
5
y 5 ( x 1)
2
2y + 10 = 5x + 5
5x - 2y 5 = 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
An Alternative Method
x2 + y2 - 6x 10y -82 = 0
We have g = -3 and f = -5
So, the centre = (-g,-f)
= (3,5)
The gradient of the normal is
5 (5) 10 5
4 2
3 (1)
C(-g,-f)
(-1,-5)
Thus, the equation of the normal is
5
y 5 (x 1)
2
2y 10 5x 5
5x 2y 5 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
The gradient of the tangent is
1
2
5
5
2
Thus, the equation of the tangent is
2
y 5 (x 1)
5
5y 25 2x 2
2x 5y 27 0
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
The Length of the Tangent to a Circle from a Fixed Point
N(a,b)
The length of the tangent from a
fixed point N(a,b) to a circle with
equation
x2 + y2 +2gx + 2fy +c = 0 is given by
d a 2 b 2 2ga 2fb c
M
C(-g,-f)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 6
Find the length of the tangent from the point K(4,6) to the
circle x2 + y2 - 4x 2y - 6 = 0
Solution
We have a = 4, b = 6, g = -2, f =-1 and c = -6
The length of the tangent from K(4,6) to the circle is
d a b 2 ga 2 fb c
2
4 2 6 2 2(2)(4) 2(1)(6) (6)
18 3 2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
An Alternative Method
K(4,6 )
h
d
M
Given x2 + y2 - 4x 2y - 6 = 0
So, g = -2, f = -1 and c = -6
The centre = (2,1)
(2) 2 (1) 2 (6)
r g2 f 2 c
11
C(2,1)
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
h (4 2) 2 (6 1) 2
29
By using Pythagoras Theorem, the length of the
tangent from a fixed point K(4,6) to the circle is
d h r
29 11
18 3 2
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Example 7
Show that the circles x2 + y2 10x 8y + 8 = 0 and
x2 + y2 8x 4y + 14 = 0 do not intersect each
other.
Solution
C1 : x 2 y 2 10 x 8 y 8 0
x 2 10 x y 2 8 y 8 0
( x 5)2 25 ( y 4)2 16 8 0
( x 5)2 ( y 4)2 33
The centre ,
P1 (5,4)
The radius ,
r1 33
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
C 2 : x 2 y 2 8 x 4 y 14 0
x2 8 x y2 4 y 8 0
( x 4)2 16 ( y 2) 2 4 14 0
( x 4)2 ( y 2)2 6
The centre ,
P2 (4, 2)
The radius ,
r2 6
The distance between P1 and P2 :
P1 P2 (5 4)2 (4 2)2
1 4 5
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
P1 P2 r2 5 6
2.2361 2.4495
4.6856 33
P1 P2 r2 33
Since
therefore these two circle intersect each other.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
To find the equation of a circle passing
through
i.
three points
ii.
two points and whose equation of
the diameter is given,
substitute each point given into the
general equation. Then, solve these
equations simultaneously.
PENANG MATRICULATION COLLEGE
MATHEMATICS UNIT
the equation of a tangent to a circle at the point
P(x1,y1) is given by
xx1 + yy1+ g( x + x1) + f ( y + y1) + c = 0
The length of the tangent from a fixed
point N(a,b) to a circle with equation
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is given by
a 2 b 2 2ga 2fb c
You might also like
- CPTR-5 Class-2Document18 pagesCPTR-5 Class-2Kiran SuryaNo ratings yet
- EQUATION OF THE CIRCLEDocument33 pagesEQUATION OF THE CIRCLEPatrick Rómulo CabilingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The CircleDocument21 pagesChapter 12 The CircleGaziisrarNo ratings yet
- EM-II Text BookDocument76 pagesEM-II Text BookViswanadhapalli RajuNo ratings yet
- CH 08 RevisedDocument22 pagesCH 08 RevisedFaisal MughalNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument3 pagesCircles PDFChong Xue ErNo ratings yet
- Mat049 Module 1Document28 pagesMat049 Module 1Rasheda SingkalaNo ratings yet
- Equation of A CircleDocument27 pagesEquation of A CircleMl Phil100% (1)
- Stem 1 - Pre Calculus: Lesson 2 - CirclesDocument10 pagesStem 1 - Pre Calculus: Lesson 2 - CirclesMary Jasmine AzulNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Circles HWT - 1Document6 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Circles HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Circles ImpDocument9 pagesCircles ImpSyed SalmanNo ratings yet
- Circle SolutionDocument18 pagesCircle SolutionSushil MeshramNo ratings yet
- Math 10 - Q2 - Week 8 - Module 8 - The Equation of A Circle - For ReproductionDocument20 pagesMath 10 - Q2 - Week 8 - Module 8 - The Equation of A Circle - For ReproductionJohn Clifford Ambaic Jayoma100% (2)
- Mahesh Tutorials ScienceDocument40 pagesMahesh Tutorials ScienceJobert Sardoma GargolesNo ratings yet
- Circle Theory EDocument18 pagesCircle Theory EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument5 pagesCircleRon HartNo ratings yet
- 46 THE POINT DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDocument22 pages46 THE POINT DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDVishal VjNo ratings yet
- Xii STD Mathematics Chapter-5Document17 pagesXii STD Mathematics Chapter-5Kiran SuryaNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument14 pagesAnalytical GeometryjonnelNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 W8 QADocument28 pagesMath10 Q2 W8 QASheila Mauricio GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Analytic Geometry Lesson on CirclesDocument6 pagesPre-Calculus Analytic Geometry Lesson on CirclesEriel MagramoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsAik0% (1)
- Lecture - Circles - Problem Solving - ExamplesDocument3 pagesLecture - Circles - Problem Solving - ExamplesMaryNo ratings yet
- Teel Stem Pre Cal ModuleDocument64 pagesTeel Stem Pre Cal ModuleemNo ratings yet
- COORDINATE GEOMETRY Part2 The CircleDocument6 pagesCOORDINATE GEOMETRY Part2 The CircleMartha K TrinashaNo ratings yet
- MAT 112 Trigonometry Analytic Geometry CirclesDocument15 pagesMAT 112 Trigonometry Analytic Geometry CirclesBABATIMILEYIN OLLANo ratings yet
- Mathematics10 Quarter2 Week9Document6 pagesMathematics10 Quarter2 Week9Jaymar AbetoNo ratings yet
- Focus On Exam 5: Chapter 5 Analytic GeometryDocument8 pagesFocus On Exam 5: Chapter 5 Analytic GeometryShinyi GanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document55 pagesChapter 11tirumalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Conic Sections and CirclesDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Conic Sections and CirclesAngelo ResuelloNo ratings yet
- MC Ty Circles 2009 1Document10 pagesMC Ty Circles 2009 1mirelaasmanNo ratings yet
- AnGeom Bridging 1Document10 pagesAnGeom Bridging 1blackmasqueNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) - Radius Form of The Equation of A Circle - Iih-1Document3 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) - Radius Form of The Equation of A Circle - Iih-1Chiara Paulin100% (1)
- Q2 WK No.6 LAS Math10 Finalcopy1Document8 pagesQ2 WK No.6 LAS Math10 Finalcopy1Ramil J. MerculioNo ratings yet
- Equation of a CircleDocument21 pagesEquation of a CircleitsmohanecomNo ratings yet
- Writing The Equation of A Circle and Determining The Center and Radius of A CircleDocument18 pagesWriting The Equation of A Circle and Determining The Center and Radius of A CircleJulie Arne EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Aims Tutorial 2B Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesAims Tutorial 2B Important QuestionsSyed Salman100% (3)
- (Session: 2021-22) Subject: Mathematics Class: Xi Topic: Conic SectionDocument2 pages(Session: 2021-22) Subject: Mathematics Class: Xi Topic: Conic SectionShivankur GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 StraightDocument22 pages1 StraightPraveen Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Equations of CirclesDocument13 pagesEquations of CirclesmengleeNo ratings yet
- Circles Module Lesson Intro to Conic SectionsDocument5 pagesCircles Module Lesson Intro to Conic SectionsShiela Mae Sotto UcangNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Sample Paper CBSE 2015 XDocument12 pagesMathematics Sample Paper CBSE 2015 Xvv1234567No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Section 2-6: CirclesDocument27 pagesAnalytic Geometry Section 2-6: CirclesenggNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument70 pagesCircleArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Modul 4 CircleDocument14 pagesModul 4 CircleRudi BerlianNo ratings yet
- ACT Coordinate GeometryDocument25 pagesACT Coordinate GeometryaftabNo ratings yet
- 2b Maths ImportantDocument5 pages2b Maths ImportantSyed Salman62% (13)
- Latihan Coordinate Geometry Form 4Document26 pagesLatihan Coordinate Geometry Form 4Nur Saida Syamim FauziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Problem Solving in MathematicsDocument17 pagesMathematics: Problem Solving in MathematicsRedzuan SaidiNo ratings yet
- 6 Coordinate GeometryDocument18 pages6 Coordinate Geometryawsk129No ratings yet
- Equations of Circles: Skills AssessmentDocument29 pagesEquations of Circles: Skills AssessmentLyy ChloéNo ratings yet
- The Circle PDFDocument16 pagesThe Circle PDFEbookcrazeNo ratings yet
- Parabola Circle Ellipse HyperbolaDocument18 pagesParabola Circle Ellipse HyperbolaSaptarshi DasNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoryDocument8 pagesCircle Theoryapi-278074538100% (3)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- IIMC-2022 Keystage-2 Individual.x17381Document5 pagesIIMC-2022 Keystage-2 Individual.x17381Mas SatriaNo ratings yet
- Cones and CylindersDocument14 pagesCones and CylindersFaye Nathalie MontesNo ratings yet
- Maureen Darcy ResumeDocument2 pagesMaureen Darcy ResumeMaureen K. DarcyNo ratings yet
- Vector and ODEsDocument23 pagesVector and ODEsChengeto MajoniNo ratings yet
- CvsDocument2 pagesCvsapi-490520214No ratings yet
- 3B07 Exercise E Full SolutionDocument29 pages3B07 Exercise E Full SolutionAnswermanNo ratings yet
- Daniel Sitaru, Claudia N Anut I - RomaniaDocument4 pagesDaniel Sitaru, Claudia N Anut I - RomaniaPerepePereNo ratings yet
- 2 CH 6-1 Sum of Interior and Exterior Angles in PolygonsDocument31 pages2 CH 6-1 Sum of Interior and Exterior Angles in PolygonshinitahNo ratings yet
- External Template UG-29 UG-80 - 81 Calculation - Rev.0Document5 pagesExternal Template UG-29 UG-80 - 81 Calculation - Rev.0souren1975100% (1)
- Vectors and The Geometry of Space: 1.1 3D Coordinate SystemsDocument9 pagesVectors and The Geometry of Space: 1.1 3D Coordinate SystemsAshish DeekondaNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document11 pagesMath 2Turjo KSNo ratings yet
- Katie Miller TCNJ ResumeDocument3 pagesKatie Miller TCNJ Resumeapi-284814564No ratings yet
- SPS OrgChart AllDocument8 pagesSPS OrgChart AllJulian A.No ratings yet
- Essay Topic 2Document2 pagesEssay Topic 2Elson ShaanikaNo ratings yet
- Profile CalculationDocument13 pagesProfile CalculationAtsis PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- Planes and Lines in R3Document21 pagesPlanes and Lines in R3Mary Dianneil MandinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-SPUR GEARS AND GEAR TRAINSDocument64 pagesChapter 9-SPUR GEARS AND GEAR TRAINSMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Romero L Otl505 Module 3Document4 pagesRomero L Otl505 Module 3api-255720288No ratings yet
- Amc Senior 7 PDFDocument2 pagesAmc Senior 7 PDFRUSDIN, S.Si100% (2)
- Mathematics (Class-Vii) Major Test # 01: Section-ADocument4 pagesMathematics (Class-Vii) Major Test # 01: Section-ASandeep SomaiyaNo ratings yet
- Professional ResumeDocument2 pagesProfessional Resumeapi-311120158No ratings yet
- Mock-Set-7 1MA1 1H Question-PaperDocument20 pagesMock-Set-7 1MA1 1H Question-PaperKingCrimsonNo ratings yet
- 2014 VJC JC1 H2 MYE Solutions (Modified)Document11 pages2014 VJC JC1 H2 MYE Solutions (Modified)Yeehui LivelaughloveNo ratings yet
- Mock 02 Maths B Paper 01Document16 pagesMock 02 Maths B Paper 01Raiyan AlamNo ratings yet
- Properties of Equality and CongruenceDocument7 pagesProperties of Equality and CongruenceJhofran HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Group Tuition with Mr Arthur Lee APGP WS2 - GPDocument22 pagesGroup Tuition with Mr Arthur Lee APGP WS2 - GPMichelle LouNo ratings yet
- Projection of LineDocument3 pagesProjection of LineSuyog ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Calculus WorkbookDocument114 pagesCalculus WorkbookrandonamNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Thực HànhDocument15 pagesBài Tập Thực HànhĐặng Thị Trúc LinhNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide fp1 PDFDocument163 pagesRevision Guide fp1 PDFDanDezideriuIacobNo ratings yet