Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Consumer Motivation
Uploaded by
Karan KhuranaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Consumer Motivation
Uploaded by
Karan KhuranaCopyright:
Available Formats
CONSUMER
MOTIVATION
PRESENTED TO :OMESH CHADDHA
PRESENTED BY:
KARAN KHURANA
KUSHAL ARORA
SUSHMIL SAHAI
NIKHIL SAINI
Motivation Definition
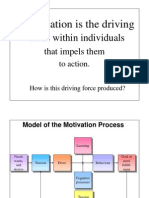
Motivation is the driving force within
individuals that impels them to action.
Motivation may be rooted in the basic need to
minimize physical pain and maximize
pleasure, or it may include specific needs such
as eating and resting, or a desired object,
hobby, goal, state of being, ideal, or it may be
attributed to less-apparent reasons such as
altruism, morality, or avoiding mortality.
Model of Motivational Process
Needs
Innate Needs (Biogenic or Primary)
Physiological needs
Acquired Needs (Psychological or Secondary)
Learned from culture or environment.
Extrinsic Needs Motivates an individual to
achieve end results.
Intrinsic Needs His/ her own comfort.
MOTIVES Positive and Negative
Positive Shaping up the body
Negative To avoid health problems
GOALS
Generic Goals
Product Specific Goals
The selection of Goals
Personal experiences
Physical capacity
Prevailing cultural norms & values
Goals accessibility in the physical and social
environment
Individuals characteristics
Positive and Negative Goal
Promotion and Prevention Focus
Positive Goal( Approach Object) towards which
behavior is directed.
Negative Goal ( Avoidance Object) behavior
which is directed away.
Promotion growth and development.
Prevention safety and security.
Utilitarian and Hedonic
Utilitarian Utility
Hedonic feelings, to enhance satisfaction
Interdependence Of Needs And Goals
Needs and goals are interdependent; neither
exists without the other.
Individuals are more aware of their
physiological needs than are of their
psychological needs.
Rational Vs Emotional Motives
Rational people choose product which gives
most utility (size, weight, price and miles)
Emotional people select goals according to
personal or subjective ( eg: pride, fear,
affection or status)
Dynamics of Motivation
Needs are never fully satisfied
Needs emerge as old needs are satisfied
Success and failure influence goals:
Substitute Goals
Frustration
Defense Mechanism
Aggression express anger.
Rationalization they say the goal is worthless.
Regression childish behavior.
Withdrawal
Projection blaming others
Daydreaming / fantasizing.
Identification solving the issue by comparing with others.
Repression or suppression, Sublimation avoid thinking about the goal
itself.
Arousal of Motives
Physiological Arousal
Emotional Arousal
Cognitive Arousal
Types and systems of Needs
Segmentation and promotional
applications
A trio of needs
Power :- individuals desire to control environment
e.g. ego needs
Affiliation :- need for friendship, acceptance, and
belonging
e.g. groups
Achievement :- need for personal
accomplishment , closely related to egoistic and
self-actualization needs , e.g. self confident
MOTIVATION AND GOALS
Negative
Positive
Motivation
A driving force
toward some object
or condition
Approach Goal
A positive goal
toward which
behavior is directed
Motivation
A driving force away
from some object or
condition
Avoidance Goal
A negative goal from
which behavior is
directed away
The Dynamic Nature of Motivation
Needs are never fully satisfied
New needs emerge as old needs are satisfied
People who achieve their goals set new and
higher goals for themselves
Goals
The sought-after results of motivated behavior
Generic goals are general categories of goals
that consumers see as a way to fulfill their
needs
Product-specific goals are specifically branded
products or services that consumers select as
their goals
The Selection of Goals
The goals selected by an individual depend on
their:
Personal experiences
Physical capacity
Prevailing cultural norms and values
Goals accessibility in the physical and social
environment
Philosophies Concerned with Arousal of
Motives
Behaviorist
Behavior is response to stimulus
Elements of conscious thoughts are to be
ignored
Consumer does not act, but reacts
Cognitive
School
School
Behavior is directed at goal achievement
Needs and past experiences are reasoned,
categorized, and transformed into attitudes
and beliefs
Motivational Research
Qualitative research designed to uncover
consumers subconscious or hidden
motivations
Attempts to discover underlying feelings,
attitudes, and emotions
Qualitative Motivational Research
Metaphor analysis
Storytelling
Word association and sentence completion
Thematic apperception test
Drawing pictures and photo-sorts
Many Companies Specialize in Motivational
Research
weblink
we blink
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Consumer Motivation: by Balachandar K Reference Book: Consumer Behavior, Schiffman & KanukDocument14 pagesConsumer Motivation: by Balachandar K Reference Book: Consumer Behavior, Schiffman & KanukarashpreetNo ratings yet
- Motivation Is The Driving: Force Within IndividualsDocument17 pagesMotivation Is The Driving: Force Within Individualsrishu31789No ratings yet
- Motivation in CBDocument25 pagesMotivation in CBaaryanNo ratings yet
- Consumer MotivationDocument18 pagesConsumer MotivationChintan MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Consumer As An IndividualDocument31 pagesThe Consumer As An IndividualSumedh BodadeNo ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation: Understanding Motivation Understanding Goals & NeedsDocument20 pagesConsumer Motivation: Understanding Motivation Understanding Goals & NeedsVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motivation As A Psychological ForceDocument42 pagesMotivation As A Psychological ForceTia MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outline: - Model of The Motivation Process - Goals - Motives - Needs - Motivational ResearchDocument70 pagesChapter Outline: - Model of The Motivation Process - Goals - Motives - Needs - Motivational ResearchpradeepNo ratings yet
- Need, Motivation and EmotionsDocument37 pagesNeed, Motivation and EmotionsAvani PatilNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document4 pagesNotes 2Sharavanan MNo ratings yet
- Motivation and PersonalityDocument6 pagesMotivation and PersonalityAsmath ShaikNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour MotivationDocument25 pagesConsumer Behaviour MotivationmansinancyNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 1 1Document11 pagesLecture1 1 1yeteday615No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Individual Influences On Consumer Behavior (PU DS) 565963786Document80 pagesChapter 5 Individual Influences On Consumer Behavior (PU DS) 565963786Vivek Lal KarnaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation & NeedsDocument6 pagesConsumer Motivation & NeedsChaitanya YskNo ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation and PersonalityDocument5 pagesConsumer Motivation and PersonalityParth DhingraNo ratings yet
- Personal Development ReviewerDocument1 pagePersonal Development ReviewerJohn Lloyd GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Motivation Process & Theories: Goal or An IncentiveDocument27 pagesMotivation Process & Theories: Goal or An IncentiveKipkorir KisorioNo ratings yet
- Consumer As An Individual & MotivationsDocument14 pagesConsumer As An Individual & MotivationsZeelkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Notes Consumer BehaviourSidra KhanNo ratings yet
- Motivation Proces1Document28 pagesMotivation Proces1Anonymous sZLcBAgNo ratings yet
- 3 Consumer MotivationDocument23 pages3 Consumer MotivationSaini JasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document4 pagesLecture 3Zuhair RiazNo ratings yet
- Module-3 INdividual Influences On Consumer BehaviourDocument132 pagesModule-3 INdividual Influences On Consumer BehaviourAnonymous YweU6CNo ratings yet
- CCB LeadershipDocument36 pagesCCB LeadershiprajavikramarkaNo ratings yet
- Adjustment & Adaptation To Illness & DisabilityDocument48 pagesAdjustment & Adaptation To Illness & Disabilityandrew_tam0319No ratings yet
- MotivationDocument28 pagesMotivationAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Session 8, MotivationDocument26 pagesSession 8, MotivationYash Aggarwal BD20073No ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation: Major-MFM IIDocument37 pagesConsumer Motivation: Major-MFM IIAbhigna DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Why Are My Students Misbehaving and What Can IDo About ItDocument3 pagesWhy Are My Students Misbehaving and What Can IDo About ItMarcia CamposNo ratings yet
- Motivation, Emotion, and Stress and CopingDocument109 pagesMotivation, Emotion, and Stress and CopingeyobNo ratings yet
- FOME Unit 3Document28 pagesFOME Unit 3Shubham RajNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 18 NOLA PENDERDocument2 pagesReviewer 18 NOLA PENDERClaireNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1 Understanding Consumer MotivationDocument2 pagesLesson-1 Understanding Consumer MotivationKristine Angela RanotNo ratings yet
- As A Psychological ForceDocument3 pagesAs A Psychological ForceKristine Angela RanotNo ratings yet
- Motivation 104Document78 pagesMotivation 104Rakesh Mohan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Needs and MotivationDocument37 pagesConsumer Needs and MotivationPreeti KumariNo ratings yet
- Motivation and EmotionDocument12 pagesMotivation and EmotionSristi RayNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument28 pagesMotivationRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Individual Determinants in Consumer BehaviourDocument24 pagesIndividual Determinants in Consumer BehaviouritzmeaneeshNo ratings yet
- Racquel F. Castañeda & Shirley E. Balajadia: ReportersDocument17 pagesRacquel F. Castañeda & Shirley E. Balajadia: Reportersjonathan0marianoNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument34 pagesMotivationrahul240486No ratings yet
- 1 - MotivationDocument24 pages1 - MotivationSabhaya Chirag100% (1)
- Consumer Needs & Motivation: Meaning, Classification and Theories of MotivationDocument41 pagesConsumer Needs & Motivation: Meaning, Classification and Theories of Motivationbanti022No ratings yet
- Reality TherapyDocument18 pagesReality Therapyhundredwaters7387100% (2)
- Consumer Needs & Motivation: Meaning, Classification and Theories of MotivationDocument41 pagesConsumer Needs & Motivation: Meaning, Classification and Theories of MotivationpremjsNo ratings yet
- CB Unit 3Document90 pagesCB Unit 3manjunathNo ratings yet
- Motivation LecturesDocument77 pagesMotivation LecturesVani ToshaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation SlidsDocument14 pagesConsumer Motivation SlidsKashi MalikNo ratings yet
- Reality Therapy For Web 11-23-05Document16 pagesReality Therapy For Web 11-23-05Joy Q. LimNo ratings yet
- Marife Reyes (Report)Document8 pagesMarife Reyes (Report)Francis AjeroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology (4) : Kate Tackie B. Pharm Pharmacy. Mphil Clinical PsychologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Psychology (4) : Kate Tackie B. Pharm Pharmacy. Mphil Clinical Psychologyoscar3spurgeonNo ratings yet
- Motivation Resources and ActivitiesDocument18 pagesMotivation Resources and ActivitiesMaria Felisadae Lorenzo-RomanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Motivation: Inter-Departmental Minor-UGDocument46 pagesConsumer Motivation: Inter-Departmental Minor-UGMard GeerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Abby NavarroNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument5 pagesMotivationBilal MalikNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 Midterms PDFDocument9 pagesCHN 2 Midterms PDFStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Gate LessonDocument5 pagesGate Lessonapi-283979987No ratings yet
- Unit 3 How Children Learn Mathematics: StructureDocument24 pagesUnit 3 How Children Learn Mathematics: StructurekarmaNo ratings yet
- InnaPeace GuidelinesDocument26 pagesInnaPeace GuidelinesJim Dandy50% (2)
- Lesson Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson Activity 1Mariel Suaiso Angeles0% (1)
- Principles For Teaching Speaking SkillsDocument2 pagesPrinciples For Teaching Speaking SkillsSymr MhzzbNo ratings yet
- Science 3 DLP 1 - Sense Organs and Their FunctionsDocument16 pagesScience 3 DLP 1 - Sense Organs and Their FunctionsRussel Jane Sumonod - Maraguinot100% (3)
- Making Inferences 'Night' Elie WieselDocument3 pagesMaking Inferences 'Night' Elie WieselalyssaeislerNo ratings yet
- Tip Sheet: Phonological Awareness Lessons & Read-Aloud BooksDocument4 pagesTip Sheet: Phonological Awareness Lessons & Read-Aloud BooksABTNNo ratings yet
- Panduan Penskoran: Pentaksiran Tingkatan 3Document8 pagesPanduan Penskoran: Pentaksiran Tingkatan 3Nurul KhusnaNo ratings yet
- THE Powers of The MindDocument24 pagesTHE Powers of The MindEunice C. LoyolaNo ratings yet
- DLP 2nd QurterDocument5 pagesDLP 2nd QurterRizel FerrerNo ratings yet
- English 3 LampDocument145 pagesEnglish 3 Lampkarlene viejoNo ratings yet
- Questions For The Revised Bloom TaxonomyDocument2 pagesQuestions For The Revised Bloom Taxonomyapi-360025326No ratings yet
- TEXT ANALYSIS Chapter 8 SummaryDocument4 pagesTEXT ANALYSIS Chapter 8 SummaryOriianaa AcoostaNo ratings yet
- SystemsThinking Transcript 2Document4 pagesSystemsThinking Transcript 2Bara DanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1 FinalDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 1 Finalapi-279400741100% (2)
- Bilingualism in Children - WMDocument3 pagesBilingualism in Children - WMhhos619No ratings yet
- Reading DifficultiesDocument7 pagesReading DifficultiesFailan MendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Thinking, Language, and IntelligenceDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Thinking, Language, and IntelligenceRose100% (1)
- Management - Learning Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesManagement - Learning Lecture NotesweirdwolfvortexNo ratings yet
- Test Items - Cognitive DomainDocument2 pagesTest Items - Cognitive DomainRommel RoyceNo ratings yet
- Surell John Lery ED 33 Assignment 1 Foundation For Special Inclusive EducationDocument6 pagesSurell John Lery ED 33 Assignment 1 Foundation For Special Inclusive EducationJohn Lery SurellNo ratings yet
- White Wind Zen Community - The Forms of Attention - 2013-09-21Document5 pagesWhite Wind Zen Community - The Forms of Attention - 2013-09-21SantiagoNo ratings yet
- North Carolina 6-Point Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesNorth Carolina 6-Point Lesson Planabc abcNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation: Far Eastern University General EducationDocument2 pagesArt Appreciation: Far Eastern University General EducationSam MichaelNo ratings yet
- Analysis of High School Students Critical Thinking Ability To Solve Social Science ProblemsDocument13 pagesAnalysis of High School Students Critical Thinking Ability To Solve Social Science ProblemsGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Challenges Faced by Teachers and Young Learners in Early Literacy Reading and Writing in EFL ContextDocument10 pagesTeaching and Learning Challenges Faced by Teachers and Young Learners in Early Literacy Reading and Writing in EFL ContextAnisa KurniadhaniNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 2Document29 pages08 Chapter 2Jason LimNo ratings yet
- Training Program For Kindergarten TeachersDocument2 pagesTraining Program For Kindergarten TeachersJanice Gentile Alison100% (1)
- Lesson Reflection 3Document3 pagesLesson Reflection 3Fatima ObaidNo ratings yet
- The Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismFrom EverandThe Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesFrom EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1635)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionFrom EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2475)
- Master Your Emotions: Develop Emotional Intelligence and Discover the Essential Rules of When and How to Control Your FeelingsFrom EverandMaster Your Emotions: Develop Emotional Intelligence and Discover the Essential Rules of When and How to Control Your FeelingsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (321)
- Indistractable: How to Control Your Attention and Choose Your LifeFrom EverandIndistractable: How to Control Your Attention and Choose Your LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- The Power of Now: A Guide to Spiritual EnlightenmentFrom EverandThe Power of Now: A Guide to Spiritual EnlightenmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4125)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsFrom EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (709)
- Summary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Summary: The Gap and the Gain: The High Achievers' Guide to Happiness, Confidence, and Success by Dan Sullivan and Dr. Benjamin Hardy: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Gap and the Gain: The High Achievers' Guide to Happiness, Confidence, and Success by Dan Sullivan and Dr. Benjamin Hardy: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonFrom EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1479)
- The War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesFrom EverandThe War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- The 16 Undeniable Laws of Communication: Apply Them and Make the Most of Your MessageFrom EverandThe 16 Undeniable Laws of Communication: Apply Them and Make the Most of Your MessageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (73)
- The 5 Second Rule: Transform your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageFrom EverandThe 5 Second Rule: Transform your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Silva Mind Method: for Getting Help from the Other SideFrom EverandThe Silva Mind Method: for Getting Help from the Other SideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (51)
- Uptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingFrom EverandUptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingNo ratings yet
- Own Your Past Change Your Future: A Not-So-Complicated Approach to Relationships, Mental Health & WellnessFrom EverandOwn Your Past Change Your Future: A Not-So-Complicated Approach to Relationships, Mental Health & WellnessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (85)
- Mastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationFrom EverandMastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Quantum Success: 7 Essential Laws for a Thriving, Joyful, and Prosperous Relationship with Work and MoneyFrom EverandQuantum Success: 7 Essential Laws for a Thriving, Joyful, and Prosperous Relationship with Work and MoneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (38)
- Speaking Effective English!: Your Guide to Acquiring New Confidence In Personal and Professional CommunicationFrom EverandSpeaking Effective English!: Your Guide to Acquiring New Confidence In Personal and Professional CommunicationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (74)
- The Science of Self Discipline: How Daily Self-Discipline, Everyday Habits and an Optimised Belief System will Help You Beat Procrastination + Why Discipline Equals True FreedomFrom EverandThe Science of Self Discipline: How Daily Self-Discipline, Everyday Habits and an Optimised Belief System will Help You Beat Procrastination + Why Discipline Equals True FreedomRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (866)
- The Motive: Why So Many Leaders Abdicate Their Most Important ResponsibilitiesFrom EverandThe Motive: Why So Many Leaders Abdicate Their Most Important ResponsibilitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (224)
- The Slight Edge: Turning Simple Disciplines into Massive Success and HappinessFrom EverandThe Slight Edge: Turning Simple Disciplines into Massive Success and HappinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (117)
- Summary of The Art of Seduction by Robert GreeneFrom EverandSummary of The Art of Seduction by Robert GreeneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- How To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryFrom EverandHow To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (556)
- The Science of Deliberate Creation - A Quarterly Journal and Catalog Addendum - Jul, Aug, Sept, 2003 - Single Issue Pamphlet – 2003From EverandThe Science of Deliberate Creation - A Quarterly Journal and Catalog Addendum - Jul, Aug, Sept, 2003 - Single Issue Pamphlet – 2003Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (179)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxFrom EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (155)