Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometric Steering
Uploaded by
Rems RMCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometric Steering
Uploaded by
Rems RMCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometrical Steering
Like a driver steers the car, the directional driller
steers the well to its final destination. Involves using
only survey and toolface data to adjust theposition
of the well bore.
During kick off stage in the drilling of directional well
survey is necessary to ensure the well path is
following the intended trajectory.
If not the bent sub has to be re-oriented to bring the
deviated well bore on track.
- The well bore is surveyed continuously while being
drilled with mud motor by running an instrument in
the BHA.
- These surveying tools are known as Steering
tools.
Steering tool - MWD
- The sensors used in steering tools and MWD
tools are solid state electronic devices known
as magnetometer and accelerometer which
responds to the earths magnetic field and
gravitational field respectively.
Since the magnetometer reading is affected
by steel collars/drill pipe the devices are
seated inside non-magnetic drill collars.
- Gives real time survey for directional
control: wellbore geometry (inclination,
azimuth), drilling system orientation (tool
face),
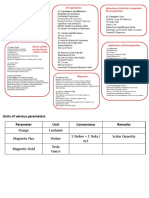
Magnetometer
Magnetometer is an instrument used for
determining the strength and direction of the
magnetic field in the vicinity of the instrument.
Magnetometers are sensitive to the earths
magnetic field; each magnetometer has two
primary coils and a pick up secondary coil
surrounds the primary coils.
An alternating current passes through the two primary coils; symmetrical voltage pulses are then
generated in the secondary coil each time the AC current changes direction. However, if an
external magnetic field exists, it can distort the voltage pulses in the secondary coil. The
magnetometer reacts by supplying a buckling current through the second coil to drive the voltage
pulses back to their symmetric state. The magnitude of the buckling current is proportional to the
earths magnetic field strength and aligned to the axis of the magnetometers.
Fluxgate Magnetometer
https://www.youtube.com/watc
h?
v=eqZgxR6eRjo&list=PLQIJDd
O1_LCN1GS6qxeaME14NXx0X
yTCA
Accelerometer
They are used to measure the earths local
gravitational field.
Each accelerometer consists of a magnetic
mass (pendulum) suspended in an
electromagnetic field. Gravity deflects the
mass from its null position.
Sufficientcurrent is applied to the sensor
to return the mass to the null position. This
current is directly proportional to the
gravitational force acting on the mass. The
gravitational readings are used to calculate
the hole inclination, toolface, and the
vertical reference used to determine dip
angle.
Basics : Inclination
Inclination is the angle between a
vertical line and the path of the
well bore at that point.
An inclination of 0 is a vertical
hole and 90is a horizontal hole.
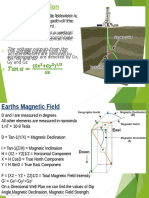
Earths Magnetic Field
Electrically charged molten magma flowing around a solid iron core.
The earths field is similar to the field generated around a very large bar magnet as
if it were located at the center of the earth.
The lines of magnetic flux are drawn exiting
from the north end of the bar magnet, looping
around the earth, and entering at the south end
of the magnet.
The north end of the bar magnet points towards
the earths Magnetic South Pole (Antarctic) and the
South end of the bar magnet points towards the
earths Magnetic North Pole (Arctic).
Magnetic Declination
Magnetic Declination: Magnetic north and true
north do not coincide. The divergence between
true north and magnetic north is different for
most points on the earths surface, and in
addition to this the magnetic north pole changes
its position very slightly each year.
The angle in degrees between true and magnetic
north is called the declination angle.
West Declination is always Subtracted and East
Declination is always Added. i.e.,
TRUE NORTH = MAGNETIC NORTH
(DECLINATION)
You might also like
- TWT Twta HandbookDocument133 pagesTWT Twta HandbookMudassar RafiqNo ratings yet
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Rigging Guide 2008Document222 pagesRigging Guide 2008Alex1No ratings yet
- PW5 Basic Double Busbar Dis 20Document12 pagesPW5 Basic Double Busbar Dis 20Shanthiyaah ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Geophysics Presentation MagnetometerDocument17 pagesGeophysics Presentation MagnetometerSoliman El KalashyNo ratings yet
- Barath Physics ProjectDocument21 pagesBarath Physics ProjectAkash SNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lecture-2Document28 pagesSurveying Lecture-2Bittu BittuNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument1 pagePhysicsDinesh DoraNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Projectpromptfaker0% (2)
- Arthanarieswaran ProjectDocument22 pagesArthanarieswaran Projecthi broNo ratings yet
- Modul 5. Instrumentasi Dan EksplorasiDocument15 pagesModul 5. Instrumentasi Dan EksplorasiRafi RiloNo ratings yet
- Physics Project by Krishna Hirenoor For Sri Chaitnaya StudentsDocument19 pagesPhysics Project by Krishna Hirenoor For Sri Chaitnaya Studentskrishnapanduranga75No ratings yet
- Fi 3Document17 pagesFi 3shankar sachinNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 2 SensorDocument4 pagesDigital Assignment 2 SensorSoumyajyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Lim, Jac Angelo T. (Assessment No.4)Document2 pagesLim, Jac Angelo T. (Assessment No.4)jac angeloNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Report 12th PhysicssDocument13 pagesInvestigatory Report 12th PhysicssserehabilitationgwlNo ratings yet
- 03 Page 10 11 12Document4 pages03 Page 10 11 12ayushtripathi8081No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics ProjectABINAYA ARIVAZHAGAN 11 C-3670No ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields: Asst. Prof. Dr. Gülnihal MuratoğluDocument33 pagesMagnetic Fields: Asst. Prof. Dr. Gülnihal MuratoğluKarim SharafNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Magnetic Field - Basics PDFDocument15 pagesThe Earth's Magnetic Field - Basics PDFAntonio Jose da CostaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument23 pagesPhysics Projectaryan sharrmaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument25 pagesPhysics Projectaryan sharrma100% (1)
- To Study The Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument14 pagesTo Study The Moving Coil GalvanometerLohitthaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Magnetism&Electricity - Rev-3 22-Jun-2019Document170 pagesNotes - Magnetism&Electricity - Rev-3 22-Jun-2019krishnamurthy69No ratings yet
- Physics Project FileDocument29 pagesPhysics Project Filerishabhand50No ratings yet
- Yug Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesYug Physics Investigatory ProjectyugpalsanawalaNo ratings yet
- Jmfguy, KuDocument15 pagesJmfguy, KuCoReDevNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 TDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12 TZackNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Dec-2022Document13 pagesAdobe Scan 07-Dec-2022Anirudh PratapNo ratings yet
- Wa0003. 1Document11 pagesWa0003. 1tejashjaiswal7878No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 TPDFDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12 TPDFAjeet KUMAR MEENANo ratings yet
- Jigar's Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesJigar's Physics ProjectDugcc DurdydNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument10 pagesPhysicsGyan BardeNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectNaveen ShrawanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric CurrentKamesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectNigel LoboNo ratings yet
- UDIT SINGH SHEKHAWAT - Tangent GalvanometerDocument14 pagesUDIT SINGH SHEKHAWAT - Tangent GalvanometerDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics1ist Year Practical FilDocument27 pagesPhysics1ist Year Practical FilManish GoyalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Project Class 12Document16 pagesPHYSICS Project Class 12mihir khabiya100% (1)
- Physics XII PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics XII PDFNobisuke NobiNo ratings yet
- Project PhyDocument18 pagesProject PhySrinivasSeenuNo ratings yet
- Tangent Galvanometr 3Document13 pagesTangent Galvanometr 3HOD HONOURSNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 TDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12 TFaraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Surveyors Magnetic Locator Theory of OperationDocument1 pageSurveyors Magnetic Locator Theory of OperationlakisNo ratings yet
- PDF Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 T CompressDocument18 pagesPDF Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 T CompressSatyam GamingNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectaadya bhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document17 pagesPhy 1rk.rethish.2006No ratings yet
- Syed Phy ProjectDocument18 pagesSyed Phy Projectayansyed2901No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectmangroliyajenil0No ratings yet
- GalvanometerDocument5 pagesGalvanometerStanley TimotiusNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument22 pagesMagnetismWalaa MajeedNo ratings yet
- Altimeter: List of Flight InstrumentsDocument7 pagesAltimeter: List of Flight InstrumentsNima NiassatiNo ratings yet
- Basic InstrumentDocument7 pagesBasic InstrumentOscar KobagauNo ratings yet
- Circular Field:: Circular and Longitudinal Magnetic FieldsDocument1 pageCircular Field:: Circular and Longitudinal Magnetic FieldsRajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Electric Machines: Practical No: 01Document6 pagesElectric Machines: Practical No: 01Rajesh RamwaniNo ratings yet
- Galvanometer: Navigation SearchDocument12 pagesGalvanometer: Navigation SearchmusmanafzalNo ratings yet
- Inductive & Magnetic Type Electrical Speed Sensor Complete ConceptDocument3 pagesInductive & Magnetic Type Electrical Speed Sensor Complete ConceptПетр СотниковNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument29 pagesChapter - 4 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDevika TannaNo ratings yet
- Project PhysicsDocument12 pagesProject PhysicsCoReDevNo ratings yet
- NBVBVVDocument15 pagesNBVBVVtanmaygrover69No ratings yet
- Physics Asl Project (Rayan Shapheer)Document15 pagesPhysics Asl Project (Rayan Shapheer)Rayan ShapheerNo ratings yet
- AZIMUTHDocument3 pagesAZIMUTHRems RMNo ratings yet
- AbrasiveDocument7 pagesAbrasiveRems RMNo ratings yet
- Rack To Store PartsDocument8 pagesRack To Store PartsRems RMNo ratings yet
- Tool FaceDocument8 pagesTool FaceRems RMNo ratings yet
- Everyone Is Born With A Purpose It Just Needs The Time and Effort To Look Into Yourself and Search The Very Reason of Your ExistenceDocument1 pageEveryone Is Born With A Purpose It Just Needs The Time and Effort To Look Into Yourself and Search The Very Reason of Your ExistenceRems RMNo ratings yet
- Success PDFDocument1 pageSuccess PDFRems RMNo ratings yet
- Success PDFDocument1 pageSuccess PDFRems RMNo ratings yet
- I Am Never Gonna Let The Faith Fade I Will Nurture My Beliefs That I Have Learnt Through The Journey of LifeDocument1 pageI Am Never Gonna Let The Faith Fade I Will Nurture My Beliefs That I Have Learnt Through The Journey of LifeRems RMNo ratings yet
- Life Is A Journey To Explore The TruthDocument1 pageLife Is A Journey To Explore The TruthRems RMNo ratings yet
- More TextDocument1 pageMore TextRems RMNo ratings yet
- More TextDocument1 pageMore TextRems RMNo ratings yet
- MouldsDocument1 pageMouldsRems RMNo ratings yet
- MouldDocument1 pageMouldRems RMNo ratings yet
- General InstallationE Instructions For Peikko Transport AnchorsDocument10 pagesGeneral InstallationE Instructions For Peikko Transport AnchorsMarko ŠimićNo ratings yet
- Emergency Access ManagementDocument5 pagesEmergency Access ManagementPabitraKumarNo ratings yet
- Thomson Chasis ICC17Document52 pagesThomson Chasis ICC17videosonNo ratings yet
- JUMONG General (JMPS) Installation Manual - en - CMP200 - 20181129Document44 pagesJUMONG General (JMPS) Installation Manual - en - CMP200 - 20181129Juan Alberto RomeroNo ratings yet
- Power Xpert Power Quality Meters: Product FocusDocument20 pagesPower Xpert Power Quality Meters: Product FocusMike MendozaNo ratings yet
- Boss Ve-20 ManualDocument144 pagesBoss Ve-20 ManualCarlo Mauricio González Parra100% (1)
- Metallographic Sample Preparation Techniques: BackgroundDocument8 pagesMetallographic Sample Preparation Techniques: BackgroundQA LAB ISMNo ratings yet
- NEMA Enclosure TypeDocument6 pagesNEMA Enclosure TypeKumar MadhuNo ratings yet
- RF Single Site Verification Methodology: Test Tools DescriptionDocument11 pagesRF Single Site Verification Methodology: Test Tools DescriptionroniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Product RecoveryDocument2 pagesChapter 17 Product RecoveryCarlos Miguel DacaimatNo ratings yet
- Draft SOP For Usage of Tree PrunerDocument2 pagesDraft SOP For Usage of Tree PrunerAkhilesh Kumar Singh100% (1)
- C - Prog AssDocument29 pagesC - Prog Assgal_farsyNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language 8086 Exercise Solution (Marut) PDFDocument58 pagesAssembly Language 8086 Exercise Solution (Marut) PDFShaibal Ahmed56% (9)
- Wood AshDocument5 pagesWood AshJohn loyd hernandezNo ratings yet
- Francis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesDocument5 pagesFrancis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesfahadNo ratings yet
- Gardner Denver S.R.L. Spare Parts Price List Gds 10Document140 pagesGardner Denver S.R.L. Spare Parts Price List Gds 10Tina Manousi100% (2)
- BlastingDocument31 pagesBlastingTamerGalhoum100% (1)
- EIA/TIA 568A Wiring Standard EIA/TIA 568B Wiring StandardDocument3 pagesEIA/TIA 568A Wiring Standard EIA/TIA 568B Wiring Standardavnish100No ratings yet
- 2N Lift1: Brief ManualDocument12 pages2N Lift1: Brief ManualMartijnMartensNo ratings yet
- Infineon Bar64series Ds v01 01 enDocument15 pagesInfineon Bar64series Ds v01 01 enAbohicham AbhNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Standards ListDocument45 pagesInstrumentation Standards ListRajeevNo ratings yet
- Loctite Instant Adhesives: Instant Solutions in Every DropDocument9 pagesLoctite Instant Adhesives: Instant Solutions in Every DroptejassidhpuraNo ratings yet
- The CPL Exams: CHUF - CPL Human Factors ExaminationDocument5 pagesThe CPL Exams: CHUF - CPL Human Factors Examinationgreg mNo ratings yet
- RBC NiceDocument56 pagesRBC NiceTIOCA01No ratings yet
- SCB - 9003.a.e Surge ArrestorDocument4 pagesSCB - 9003.a.e Surge ArrestorMichelle WebsterNo ratings yet
- Dental Clinic - ResearchDocument10 pagesDental Clinic - ResearchAmorphus ViNo ratings yet
- Dubai Municipality RequirementsDocument1 pageDubai Municipality RequirementsmaheshbandhamNo ratings yet