Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amity Business School: MBA Class of 2014, Semester II
Uploaded by
Mobashir MahmoodOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amity Business School: MBA Class of 2014, Semester II
Uploaded by
Mobashir MahmoodCopyright:
Available Formats
Amity Business School
Amity Business School
MBA Class of 2014, Semester II
Consumer Behavior
Ms.Vandana Gupta
Amity Business School
Opinion
Leadership
The process by which
one person (the
opinion leader)
informally influences
the consumption
actions or attitudes of
others who may be
opinion seekers or
opinion recipients.
Amity Business School
What Is Opinion Leadership?
Opinion
Leader
Opinion
Receiver
Opinion
Seeker
Amity Business School
Word of Mouth in Action
Figure 15-1
Amity Business School
Dynamics of the Opinion Leadership Process
Credibility
Positive and Negative Product Information
Information and Advice
Opinion Leadership Is Category-Specific
Opinion Leadership Is a Two-way Street
Amity Business School
Many not-forprofit
organizations
that hope to
change
behavior, count
on opinion
leaders.
Amity Business School
Motivations Behind Opinion
Leadership
Issues
The Needs of
Opinion Leaders
The Needs of
Opinion Receivers
Purchase Pals
Surrogate Buyers
versus Opinion
Leaders
Self-involvement
Social involvement
Product involvement
Message involvement
Amity Business School
Motivations Behind Opinion
Leadership
Issues
The Needs of
Opinion Leaders
The Needs of
Opinion Receivers
Purchase Pals
Surrogate Buyers
versus Opinion
Leaders
New product or new usage
information
Reduction of perceived
risk
Reduction of search time
Receiving the approval of
the opinion leader
Amity Business School
Motivations Behind Opinion
Leadership
Issues
The Needs of
Opinion Leaders
The Needs of
Opinion Receivers
Purchase Pals
Surrogate Buyers
versus Opinion
Leaders
Actually accompany
consumers on
shopping trips
Used 25 percent of
the time for purchases
of electronic
equipment
Amity Business School
Motivations Behind Opinion
Leadership
Issues
The Needs of
Opinion Leaders
The Needs of
Opinion Receivers
Purchase Pals
Surrogate Buyers
versus Opinion
Leaders
Surrogate buyers may
replace opinion
leaders
An example is a
wardrobe consultant
who helps in the
purchase of business
clothes
Key Differences Between Opinion Leaders and
Amity Business School
Surrogate Buyers
Part I: Opinion Leaders
OPINION LEADER
1. Informal relationship with end users
2. Information exchange occurs in the context of a casual interaction
3. Homophilous (to a certain extent) to end users
4. Does not get paid for advice
5. Usually socially more active than end users
6. Accountability limited regarding the outcome of advice
7. As accountability limited, rigor in search and screening of alternatives
low
8. Likely to have used the product personally
9. More than one can be consulted before making a final decision
10. Same person can be an opinion leader for a variety of related product
categories
Key Differences Between Opinion Leaders and
Amity Business School
Surrogate Buyers
Part II: Surrogate Buyers
SURROGATE BUYER
1. Formal relationship; occupation-related status
2. Information exchange in the form of formal instructions/advice
3. Heterophilus to end users (that is, is the source of power)
4. Usually hired, therefore gets paid
5. Not necessarily socially more active than end-users
6. High level of accountability
7. Search and screening of alternatives more rigorous
8. May not have used the product for personal consumption
9. Second opinion taken on rare occasions
10. Usually specializes for a specific product/service category
Amity Business School
Measurement of Opinion Leadership
Self-Designating Method
Sociometric Method
Key Informant Method
Objective Method
Measuring Opinion Leadership
Amity Business School
OPINION LEADERSHIP
MEASUREMENT
METHOD
DESCRIPTION OF METHOD
SAMPLE
QUESTIONS ASKED
SELF-DESIGNATING
METHOD
Each respondent is asked a
series of questions to determine
the degree to which he or she
perceives himself or herself to
be an opinion leader.
Do you influence
other people in their
selection of
products?
SOCIOMETRIC
METHOD
Members of a social system are
asked to identify to whom they
give advice and to whom they
go for advice.
Whom do you
ask?Who asks you
for info about that
product category?
Amity Business School
OPINION
LEADERSHIP
MEASUREMENT
METHOD
DESCRIPTION OF METHOD
SAMPLE
QUESTIONS ASKED
KEY INFORMANT
METHOD
Carefully selected key informants in Who are the most
a social system are asked to
influential people in
designate opinion leaders.
the group?
OBJECTIVE
METHOD
Artificially places individuals in a
Have you tried the
position to act as opinion leaders
product?
and measures results of their efforts.
Amity Business School
Profile of Opinion Leaders
GENERALIZED
ATTRIBUTES ACROSS
PRODUCT CATEGORIES
Innovativeness
Willingness to talk
Self-confidence
Gregariousness
Cognitive differentiation
CATEGORY-SPECIFIC
ATTRIBUTES
Interest
Knowledge
Special-interest media exposure
Same age
Same social status
Social exposure outside group
Amity Business School
Market
Maven
Individuals whose
influence stems from a
general knowledge or
market expertise that
leads to an early
awareness of new
products and services.
Amity Business School
The Interpersonal Flow of Communication
Two-Step Flow
A communication model that portrays opinion
leaders as direct receivers of information from
mass media sources who, in turn, interpret
and transmit this information
Multistep Flow
A revision of the traditional two-step theory
that shows multiple communication flows
Amity Business School
Two-Step Flow of Communication
Theory
Amity Business School
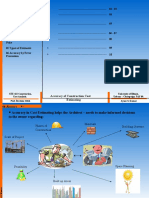
Multistep Flow of
Communication Theory
Amity Business School
Issues in Opinion Leadership and Marketing
Strategy
Advertisements Stimulating Opinion
Leadership
Word of Mouth May Be Uncontrollable
Amity Business School
Marketers Seek to Take Control of the Opinion
Leadership Process
Creating products with built-in buzz
potential
Strategy designed to stimulate buzz
Viral marketing
Weblogs
You might also like
- Ks School of MGMT: MBA Class of 2018, Semester III ConsumerDocument63 pagesKs School of MGMT: MBA Class of 2018, Semester III ConsumerpradeepNo ratings yet
- Brand Research & Analysis: Understand Its Importance & ApplicationFrom EverandBrand Research & Analysis: Understand Its Importance & ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Opinion LeadershipDocument22 pagesOpinion LeadershipZayed KhanNo ratings yet
- Handbook for Strategic HR - Section 3: Use of Self as an Instrument of ChangeFrom EverandHandbook for Strategic HR - Section 3: Use of Self as an Instrument of ChangeNo ratings yet
- Opinion LeadershipDocument48 pagesOpinion LeadershipZoheb Ali K100% (1)
- The 5 Paths to Persuasion (Review and Analysis of Miller and Williams' Book)From EverandThe 5 Paths to Persuasion (Review and Analysis of Miller and Williams' Book)No ratings yet
- CB Notes - Unit 6Document21 pagesCB Notes - Unit 6Arjun NayakNo ratings yet
- CB - OpinionL & InnovationDocument34 pagesCB - OpinionL & InnovationDeepika SinghNo ratings yet
- Consumer Influence and Diffusion of InnovationsDocument29 pagesConsumer Influence and Diffusion of InnovationsGagan BhallaNo ratings yet
- The Consumer's Decision-Making Process: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionDocument48 pagesThe Consumer's Decision-Making Process: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionShashank SNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior - Module 7Document7 pagesConsumer Behavior - Module 7Dr VIRUPAKSHA GOUD GNo ratings yet
- Consumer Influence and The Diffusion of InnovationsDocument42 pagesConsumer Influence and The Diffusion of InnovationsManju B GowdaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Influence and The Diffusion of InnovationsDocument6 pagesConsumer Influence and The Diffusion of InnovationsMachoNo ratings yet
- Module 7-38 PDFDocument29 pagesModule 7-38 PDFRahul NeelakantanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Influence and The Diffusion of InnovationsDocument64 pagesConsumer Influence and The Diffusion of Innovationsmanjit tewaryNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior at Retail StoresDocument39 pagesConsumer Behavior at Retail StoresKajal V100% (1)
- UCB Lec 10Document23 pagesUCB Lec 10Priyadarshini TripathiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: Definition of Opinion LeadershipDocument4 pagesConsumer Behaviour: Definition of Opinion Leadershiptayaisgreat75% (4)
- Session 6 - Opinion LeadershipDocument21 pagesSession 6 - Opinion LeadershipAparna Sachin KanchanNo ratings yet
- The Consumer's Decision-Making Process: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionDocument52 pagesThe Consumer's Decision-Making Process: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionPranesh SanthamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Characteristics of Opinion LeaderDocument17 pagesMeasurement and Characteristics of Opinion LeaderAnurag Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Opinion LeadershipDocument37 pagesOpinion LeadershipCruciferNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document41 pagesCH 5Wondwosen TilahunNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Tata Motors Cars (Osmania Format)Document51 pagesA Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Tata Motors Cars (Osmania Format)Satya Kumar75% (12)
- Consumer BehaviorDocument14 pagesConsumer BehaviorJORDI MASFERRERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 CBDocument4 pagesChapter 15 CBKazi Rakibur Rahman0% (1)
- Introuction of The Study - (The Problem)Document13 pagesIntrouction of The Study - (The Problem)viral whatsapp statusNo ratings yet
- Opinion LeadershipDocument9 pagesOpinion LeadershipShalu KumariNo ratings yet
- Communication Within Groups andDocument17 pagesCommunication Within Groups andTarun PandeyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception Towards Tata MotorsDocument51 pagesConsumer Perception Towards Tata Motorsarjunmba11962486% (7)
- Factors Affecting Brand Choice of Mobile Phone HandsetsDocument54 pagesFactors Affecting Brand Choice of Mobile Phone HandsetsSiddhant JoshiNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument11 pagesConsumer BehaviourSania MerchantNo ratings yet
- BC AssignmentDocument5 pagesBC Assignmentmukeremm25No ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument7 pagesMarketing ManagementYe Naing ZawNo ratings yet
- Schiffman Cb09 PPT 15Document44 pagesSchiffman Cb09 PPT 15Swadha Singh BNo ratings yet
- Why Did You Choose That Study/ Title?Document6 pagesWhy Did You Choose That Study/ Title?Jubeleen DolosaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Survey On Britannia BiscuitsDocument33 pagesMarketing Survey On Britannia Biscuitsanon-80031369% (29)
- Consumer and Business Buyer Behavior: Nathan GeorgeDocument32 pagesConsumer and Business Buyer Behavior: Nathan GeorgeAjay Roshan P100% (1)
- Buying MotivesDocument17 pagesBuying MotivesJigyasa Sharma100% (1)
- CB Chapter 11 Group Influence and Social Media Sixth EditionDocument16 pagesCB Chapter 11 Group Influence and Social Media Sixth EditionMike CloryNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Reference GroupsDocument12 pagesChapter-5 Reference Groupsmushtaq765No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour at Shopping Malls'Document53 pagesConsumer Behaviour at Shopping Malls'Nagireddy KalluriNo ratings yet
- Role of Research in Understanding Consumer BehaviourDocument50 pagesRole of Research in Understanding Consumer Behaviouraqib_khan55No ratings yet
- MKTG 3 Cons Buying BehDocument55 pagesMKTG 3 Cons Buying BehSanket GangalNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards Organic India of Gproducts in Lucknow City GeetikaDocument89 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards Organic India of Gproducts in Lucknow City GeetikaRishabh DhawanNo ratings yet
- CBNotesDocument54 pagesCBNotesShifaNo ratings yet
- For The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement of The Degree of Master of Management Study (MMS)Document30 pagesFor The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement of The Degree of Master of Management Study (MMS)Sammi ShahuNo ratings yet
- WEEK 12-Pengaruh Grup Dan Media SosialDocument35 pagesWEEK 12-Pengaruh Grup Dan Media SosialKASIH PILIANG SEJATINo ratings yet
- Course AimsDocument115 pagesCourse Aimsmaryam keddisNo ratings yet
- Unit2 161017112537 PDFDocument194 pagesUnit2 161017112537 PDFFahad BataviaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Brand Switching Factors of Millennial Customers On ToiletriesDocument43 pagesA Study On Brand Switching Factors of Millennial Customers On ToiletriesNandhaGopal RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Consumer Behaviour: Consumer Behavior Is The Process Involved WhenDocument54 pagesModule-1: Consumer Behaviour: Consumer Behavior Is The Process Involved WhenlicopodicumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 5 & 6 SummarySenorita ,No ratings yet
- Marketing Management Module 4Document109 pagesMarketing Management Module 4sebastianNo ratings yet
- Mba 3Document8 pagesMba 3KurikuriNo ratings yet
- Marketing OrientationDocument6 pagesMarketing OrientationSarfraz ArbaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing Survey On Britannia BiscuitsDocument31 pagesMarketing Survey On Britannia BiscuitsAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Opinion LeadershipDocument3 pagesOpinion LeadershipSanaul Haque SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Buyer Decision ProcessDocument83 pagesBuyer Decision ProcessSunil JoshiNo ratings yet
- DATE: 08/04/2020: SL No Name Designation Ph. No. Salary League Name Match DateDocument14 pagesDATE: 08/04/2020: SL No Name Designation Ph. No. Salary League Name Match DateMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- App Banner PDFDocument1 pageApp Banner PDFMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- SR - No Remarks Name Match Date Designation Ph. No. Salary Disb TimeDocument8 pagesSR - No Remarks Name Match Date Designation Ph. No. Salary Disb TimeMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- QSL DISB 20.05.2020: Remarks Remarks Name Match Date Designation Ph. No. Salary EMP SIGNDocument14 pagesQSL DISB 20.05.2020: Remarks Remarks Name Match Date Designation Ph. No. Salary EMP SIGNMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 21 MayDocument7 pages21 MayMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Total Result 165Document13 pagesTotal Result 165Mobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- SL No League Name Name Match Datedesignation Ph. No. SalaryDocument14 pagesSL No League Name Name Match Datedesignation Ph. No. SalaryMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- QSL DISB 20.05.2020: Remarks Remarks Name Match Date Designation Ph. No. Salary EMP SIGNDocument14 pagesQSL DISB 20.05.2020: Remarks Remarks Name Match Date Designation Ph. No. Salary EMP SIGNMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements TemplateDocument19 pagesFinancial Statements TemplateAbdullahTufailNo ratings yet
- Restaurant Feasibility Study Boston Restaurant Group 170314 FINAL PDFDocument33 pagesRestaurant Feasibility Study Boston Restaurant Group 170314 FINAL PDFRex LibiadoNo ratings yet
- TF00000053Document4 pagesTF00000053Mobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Indg345 PDFDocument6 pagesIndg345 PDFeastNo ratings yet
- TF00000053Document4 pagesTF00000053Mobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Excavation Work CoPDocument46 pagesExcavation Work CoPAndre MarsNo ratings yet
- Tool Box Talk - Working in Hot WeatherDocument1 pageTool Box Talk - Working in Hot WeatherMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Pre-Feasibility Study: Salt Products Manufacturing UnitDocument19 pagesPre-Feasibility Study: Salt Products Manufacturing UnitMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Igc1 Sample QP 2019 v1Document4 pagesIgc1 Sample QP 2019 v1khalid100% (1)
- Contrato Qatar - ENG - tcm30-43525 PDFDocument2 pagesContrato Qatar - ENG - tcm30-43525 PDFMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument60 pagesStrategic ManagementVamsiReddyNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCCION ING1 tcm30-34709 PDFDocument48 pagesCONSTRUCCION ING1 tcm30-34709 PDFMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- RV MeasuringROI WP PDFDocument10 pagesRV MeasuringROI WP PDFMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Nebosh IGC Element 1. Foundations in Health and Safety (Notes)Document7 pagesNebosh IGC Element 1. Foundations in Health and Safety (Notes)kkalvi92% (204)
- Tool Box Talk: How Can Heat Related Illnesses Be Prevented?Document1 pageTool Box Talk: How Can Heat Related Illnesses Be Prevented?Mobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements TemplateDocument19 pagesFinancial Statements TemplateAbdullahTufailNo ratings yet
- Eplc Staffing Management Practices GuideDocument2 pagesEplc Staffing Management Practices GuideMuhammad Tahir NawazNo ratings yet
- Competencies and Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCompetencies and Learning Objectivesramyresdavid100% (1)
- Ibm Assignment Question NewDocument61 pagesIbm Assignment Question NewMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Notes PDFDocument68 pagesStrategic Management Notes PDFMobashir Mahmood100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Project Evaluation CriteriaDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Project Evaluation CriteriaMobashir Mahmood100% (1)
- 1234Document7 pages1234Mobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The National Academies Press: Autonomy Research For Civil Aviation: Toward A New Era of Flight (2014)Document91 pagesThe National Academies Press: Autonomy Research For Civil Aviation: Toward A New Era of Flight (2014)ERRAMESH1989No ratings yet
- Learning Styles of Social Studies 4th YearDocument14 pagesLearning Styles of Social Studies 4th YearChristian AlfornonNo ratings yet
- Modularly Harmonized BSC Post Basic Medical Radiologic Technology CurriculumDocument262 pagesModularly Harmonized BSC Post Basic Medical Radiologic Technology CurriculumNigusse Obse100% (1)
- The-Space-Traders Derrick Bell PDFDocument13 pagesThe-Space-Traders Derrick Bell PDFOya Soulosophy100% (3)
- Ra 8545Document6 pagesRa 8545KFNo ratings yet
- Nagbalayong National High School: Department of EducationDocument2 pagesNagbalayong National High School: Department of EducationvernaNo ratings yet
- Application of Building Information Modeling (BIM) To Civil Engineering ProjectsDocument3 pagesApplication of Building Information Modeling (BIM) To Civil Engineering ProjectsChuan Sin PanNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management On McdonaldsDocument4 pagesInventory Management On McdonaldsGaffur Boliya80% (5)
- 21st Century - Impre DemoDocument2 pages21st Century - Impre DemoWilliam RanaraNo ratings yet
- Sample Works CitedDocument2 pagesSample Works CitedmrtalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Entrepeneurship Week 1: Identifying Market ProblemsDocument11 pagesEntrepeneurship Week 1: Identifying Market ProblemsJoi BarlisNo ratings yet
- Accuracy of Construction Cost EstimatingDocument11 pagesAccuracy of Construction Cost EstimatingRandy PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- PBJ March 23, 2018 Failed Startup PDFDocument36 pagesPBJ March 23, 2018 Failed Startup PDFSuzanne StevensNo ratings yet
- Firearms Training AssociatesDocument4 pagesFirearms Training Associatesdominique babisNo ratings yet
- Teacher and Student Perceptions of The Methods Used in Teaching and Learning English Secondary Writing SkillsDocument2 pagesTeacher and Student Perceptions of The Methods Used in Teaching and Learning English Secondary Writing SkillsMiftahul HusnaNo ratings yet
- CV of Shouvik Biswas 8.8.2021Document3 pagesCV of Shouvik Biswas 8.8.2021Avisheak PalNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 - Blog On Sources of Finance FinalDocument2 pagesAssessment 2 - Blog On Sources of Finance FinalSatyam AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Call For Paper 2020Document3 pagesCall For Paper 2020aquino de la peña100% (1)
- CBC Mechanical Drafting NC IDocument49 pagesCBC Mechanical Drafting NC ICharo GironellaNo ratings yet
- Telephones Past and Present STEMDocument2 pagesTelephones Past and Present STEMSUDAE A/P SENASENDRAM MoeNo ratings yet
- ASA (American Sociological Association) Format: in Text CitationsDocument5 pagesASA (American Sociological Association) Format: in Text CitationsEmily NgNo ratings yet
- Aristotle and PersuasionDocument3 pagesAristotle and PersuasionTibor SpiegelNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Liquids: Lesson-For-Kids - HTML 6288367Document4 pagesCharacteristics of Liquids: Lesson-For-Kids - HTML 6288367Myla Ricamara100% (5)
- Pragmatics and LanguageDocument15 pagesPragmatics and LanguageAbdullah Naeem100% (1)
- The Philippine Bangsamoro ConflictDocument20 pagesThe Philippine Bangsamoro Conflictmindanaopeace100% (1)
- Resume For Aldine IsdDocument2 pagesResume For Aldine Isdapi-601237277No ratings yet
- Activity#2 - Gardigo, Ray Iverson D.Document3 pagesActivity#2 - Gardigo, Ray Iverson D.ray gardigoNo ratings yet
- NDA TemplateDocument7 pagesNDA Templatecrosalejos100% (1)
- Operator Guide - Nozzles - ENDocument16 pagesOperator Guide - Nozzles - ENAlexander SimanovskyNo ratings yet
- Thematic Exploration of Obtala Music in OyoManuscript 2018 JonathanDocument16 pagesThematic Exploration of Obtala Music in OyoManuscript 2018 JonathanJonathan OlapadeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsFrom EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOFrom EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEORating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobFrom EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeFrom EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Summary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendFrom EverandSummary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverFrom EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- How to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersFrom EverandHow to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (95)
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingFrom EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (210)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxFrom EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (155)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekFrom EverandSummary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (142)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersFrom EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (150)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleFrom EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2565)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceFrom EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceNo ratings yet
- Entreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesFrom EverandEntreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldFrom Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (20)
- Everyone Communicates, Few Connect: What the Most Effective People Do DifferentlyFrom EverandEveryone Communicates, Few Connect: What the Most Effective People Do DifferentlyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (346)
- Follow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipFrom EverandFollow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (122)
- Spark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessFrom EverandSpark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindFrom EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- Optimal: How to Sustain Personal and Organizational Excellence Every DayFrom EverandOptimal: How to Sustain Personal and Organizational Excellence Every DayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Soundtracks: The Surprising Solution to OverthinkingFrom EverandSoundtracks: The Surprising Solution to OverthinkingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Cultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams, and OrganizationsFrom EverandCultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams, and OrganizationsNo ratings yet
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsFrom EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- The Most Powerful Woman in the Room Is You: Command an Audience and Sell Your Way to SuccessFrom EverandThe Most Powerful Woman in the Room Is You: Command an Audience and Sell Your Way to SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)