Professional Documents
Culture Documents
บทที่ 3 thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Anonymous nveiFI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views11 pagesOriginal Title
บทที่ 3 thermodynamics.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views11 pagesบทที่ 3 thermodynamics
Uploaded by
Anonymous nveiFICopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Thermodynamics
Chapter 3
Properties of a Pure
Substance
367 A rigid tank initially contains 1.4-kg
saturated liquid water at 200C. At this state,
25 percent of the volume is occupied by water
and the rest by air. Now heat is supplied to the
water until the tank contains saturated vapor
only. Determine
(a) the volume of the tank,
(b) the final temperature and pressure, and
(c) the internal energy change of the water .
Answers: (a) 0.006467 m3, (b) 371.3oC, (c)
1,892 kJ
365 A rigid tank contains water
vapor at 250C and an unknown
pressure. When the tank is cooled to
150C, the vapor starts condensing.
Estimate the initial pressure in the
tank.
Answers: 0.60 MPa
364 A pistoncylinder device
contains 0.8 kg of steam at 300C
and 1 MPa. Steam is cooled at
constant pressure until one-half of
the mass condenses.
(a) Show the process on a T-v
diagram.
(b) Find the final temperature.
(c) Determine the volume change.
Answers: (b) 179.88oC, (c) -0.1282 m3
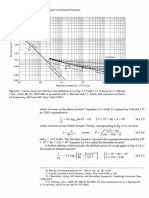
384 Determine the specific volume
of superheated water vapor at 10
MPa and 400C, using
(a) the ideal-gas equation,
(b) the generalized compressibility
chart, and
(c) the steam tables.
Also determine the error involved in
the first two cases.
Answers: (a) 0.03106 m3/kg, 17.6%;
(b) 0.02609 m3/kg, 1.2%; (c) 0.02644
m3/kg
388 Determine the specific volume
of superheated water vapor at 3.5
MPa and 450C based on
(a) the ideal-gas equation,
(b) the generalized compressibility
chart, and
(c) the steam tables.
Determine the error involved in the
first two cases.
Answers: (a) 0.09533 m3/kg, (b)
0.09161 m3/kg, (c) 0.09196 m3/kg
394 Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at
3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kg/s. CO2
is cooled at constant pressure as it flows
in the pipe and the temperature of CO2
drops to 450 K at the exit. Determine the
volume flow rate and the density of
carbon dioxide at the inlet and the
volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe
using
(a) the ideal-gas equation and
(b) the generalized compressibility chart.
Also, determine
(c) the error involved in each case.
3
3122 A 0.5-m3 rigid tank containing
hydrogen at 20C and 600 kPa is
connected by a valve to another 0.5m3 rigid tank that holds hydrogen at
30C and 150 kPa. Now the valve is
opened and the system is allowed to
reach thermal equilibrium with the
surroundings, which are at 15C.
Determine the final pressure in the
tank.
Answers: 365.8 kPa
3124 A 20-m3 tank contains nitrogen
at 23C and 600 kPa. Some nitrogen
is allowed to escape until the
pressure in the tank drops to 400 kPa.
If the temperature at this point is
20C, determine the amount of
nitrogen that has escaped.
Answers: 44.6 kg
368 A pistoncylinder device initially
contains steam at 3.5 MPa, superheated by
5C. Now, steam loses heat to the
surroundings and the piston moves down
hitting a set of stops at which point the
cylinder contains saturated liquid water. The
cooling continues until the cylinder contains
water at 200C. Determine
(a) the initial temperature,
(b) the enthalpy change per unit mass of
the steam by the time the piston first hits
the stops, and
(c) the final pressure and the quality (if
mixture).
3120 A 4-L rigid tank contains 2 kg of
saturated
liquidvapor mixture of water at 50C.
The water is now slowly heated until it
exists in a single phase. At the final
state, will the water be in the liquid
phase or the vapor phase? What would
your answer be if the volume of the
tank were 400 L instead of 4 L?
Answers: 0.002 m3/kg, 0.2 m3/kg
You might also like
- Practice Problem (Chap # 03)Document4 pagesPractice Problem (Chap # 03)nandlalwarsoorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CH2Document7 pagesTutorial CH2Paramoda TriangleNo ratings yet
- Work sheet 1Document3 pagesWork sheet 1TMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 ExamplesDocument26 pagesLecture - 5 ExamplesDimas Angga100% (7)
- Chapter 3 PBL QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 PBL QuestionsMohd Hafiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Document4 pagesNed University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Sahar Batool QaziNo ratings yet
- TH-003-Examples of Chapter ThreeDocument4 pagesTH-003-Examples of Chapter ThreeDrofer ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions 1111Document6 pagesTutorial Questions 1111Fahmy Muhd100% (1)
- Solution Manual ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesSolution Manual ThermodynamicsNur HanifahNo ratings yet
- MA2003 Thermo-Fluids Tutorial ProblemsDocument6 pagesMA2003 Thermo-Fluids Tutorial ProblemsLadnilrebNo ratings yet
- Closed System ExercisesDocument2 pagesClosed System ExercisesMareta DanarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-EntropyDocument2 pagesAssignment-Entropyme22b009No ratings yet
- ChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Document5 pagesChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Irene Kaye AceroNo ratings yet
- AssignDocument2 pagesAssignHabtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument4 pagesThermowong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics First Law Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics First Law Practice QuestionsRamis RafayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 6Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 6Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Taller 2 2023-1Document8 pagesTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4JayZx WayNo ratings yet
- ME-1100 Thermodynamics tutorial problemsDocument2 pagesME-1100 Thermodynamics tutorial problemsKethavath Sunil ch21b047No ratings yet
- Exercise PyeqDocument2 pagesExercise PyeqNaufal SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Borgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global EditionDocument168 pagesBorgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global Edition정윤서No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Document8 pagesAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Assignment 0 Revision ThermoIDocument1 pageAssignment 0 Revision ThermoIMaria SarwatNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemDocument3 pagesPractice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemNetra PujarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasNo ratings yet
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Document3 pagesChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics question bank analyzedDocument10 pagesThermodynamics question bank analyzedRaj PratyushNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2 - Pure SubstanceDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 2 - Pure SubstanceDinesh Kumar VijeyanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument6 pagesThermodynamics QuestionsRNo ratings yet
- T 2Document1 pageT 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Jamilah MrafiNo ratings yet
- INME 4045 - Chapter 3 - Suggested ProblemsDocument2 pagesINME 4045 - Chapter 3 - Suggested ProblemsAmanda SotoNo ratings yet
- Department of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #3Document4 pagesDepartment of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #3gfsfNo ratings yet
- 2018 Tutorial 5Document4 pages2018 Tutorial 5YemukelaniNo ratings yet
- MCL142 Thermal Science Tutorial - 3 Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesMCL142 Thermal Science Tutorial - 3 Key ConceptsSamarthNo ratings yet
- Tut 2Document2 pagesTut 2GUNJAN MUDGALNo ratings yet
- Guía Sesiones de Estudio TermoQDocument3 pagesGuía Sesiones de Estudio TermoQDavid Archila-PenaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionJacob Johnston100% (1)
- Tarea III: - Answer: 224 VDocument7 pagesTarea III: - Answer: 224 VANDRES FELIPE AVILA TORONo ratings yet
- AMME2200 RevisionQuestions ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesAMME2200 RevisionQuestions ThermodynamicsMatthew LinNo ratings yet
- T 5Document2 pagesT 5jfl2096No ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems StatementDocument21 pagesTutorial Problems StatementAbni AbhiNo ratings yet
- Test 1 With AnsDocument4 pagesTest 1 With AnsKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Tut 2Document2 pagesTut 2me21b105No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 PDFAnonymous hxyDxxcoJNo ratings yet
- Homework 01Document1 pageHomework 01sophixNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)Document22 pagesThermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)cwidiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Review ProblemssayanNo ratings yet
- ME 231 Montazami Whharris 10-2-18 Class Work SolutionDocument15 pagesME 231 Montazami Whharris 10-2-18 Class Work SolutionJoana ArielaNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant 134a in A Piston-Cylinder AssembliesDocument10 pagesRefrigerant 134a in A Piston-Cylinder AssembliescesardakoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (ME206)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (ME206)deshrajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 ExamplesDocument29 pagesLecture 6 ExamplesMohamed ZahranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 PDFAnonymous hxyDxxcoJNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10Document7 pagesAssignment 10Mohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsmonalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Pure Substance-AnswerDocument3 pagesTutorial-Pure Substance-Answerwanimira19No ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2015Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2015BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Pre Test: Test I. Definition of TermsDocument1 pageDay 1 Pre Test: Test I. Definition of TermsdominiqueNo ratings yet
- 2GIG ZWave CT30e Thermostat Installation GuideDocument19 pages2GIG ZWave CT30e Thermostat Installation Guideyamimaker2002No ratings yet
- ARCA SOUTH DYNAMIC DESIGNDocument26 pagesARCA SOUTH DYNAMIC DESIGNJan LhesterNo ratings yet
- AIREX Linear Motor Vacuum CompatabilityDocument3 pagesAIREX Linear Motor Vacuum Compatabilitymsahin1955No ratings yet
- Portland Cement Plaster (ACI)Document5 pagesPortland Cement Plaster (ACI)ddssssssssssssssssfNo ratings yet
- FMDS0793NDocument6 pagesFMDS0793NCHANDANNo ratings yet
- Refresher Day 10Document4 pagesRefresher Day 10Jevan A. CalaqueNo ratings yet
- ASTM E1003 13 Hydrostatic Leak Testing 1 PDFDocument3 pagesASTM E1003 13 Hydrostatic Leak Testing 1 PDFAndrea Fabiana BlaschiNo ratings yet
- Good (ELEC6089) Power Cable Insulation DesignDocument22 pagesGood (ELEC6089) Power Cable Insulation DesignvahrmNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Design GuideDocument248 pagesMachine Elements Design GuideKrishnan P MNo ratings yet
- 2014 - 004 Plumbing FixturesDocument58 pages2014 - 004 Plumbing FixturesRon Julienne Rebugio100% (2)
- Halton Vario Solution Brochure 2014Document11 pagesHalton Vario Solution Brochure 2014Marko KorenićNo ratings yet
- Practice Set - 2 (B) Young's Modulus: ElasticityDocument7 pagesPractice Set - 2 (B) Young's Modulus: ElasticityWillis ChekovNo ratings yet
- Lowara SV PDFDocument72 pagesLowara SV PDFsebastmNo ratings yet
- Item No. Qty Unit Unit Cost Total Cost Material Description: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesItem No. Qty Unit Unit Cost Total Cost Material Description: Page 1 of 2Greens Mac100% (1)
- Indian Codes - Steel Design Per IS 800:2007Document3 pagesIndian Codes - Steel Design Per IS 800:2007dineshNo ratings yet
- Fluid Properties: Dr. Akepati S. Reddy Thapar University Patiala (PUNJAB) - 147 004 IndiaDocument29 pagesFluid Properties: Dr. Akepati S. Reddy Thapar University Patiala (PUNJAB) - 147 004 IndiaDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyNo ratings yet
- Colvin T.E. Steel Boat Building - From Bare Hull To Launching Vol.2, 1986Document210 pagesColvin T.E. Steel Boat Building - From Bare Hull To Launching Vol.2, 1986VitBar100% (1)
- Structural Behaviour of Cold-Formed Steel Z Purlins With Generic Lapped ConnectionsDocument15 pagesStructural Behaviour of Cold-Formed Steel Z Purlins With Generic Lapped ConnectionsBart HoNo ratings yet
- PCM. Solar CookerDocument1 pagePCM. Solar CookerRaviranjan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - CoronaShield C - 215.55 - EN - GLDocument3 pagesDatasheet - CoronaShield C - 215.55 - EN - GLLECTORNo ratings yet
- Steam Generator Steam Generator: Quality of LifeDocument29 pagesSteam Generator Steam Generator: Quality of LifeMiguel DexsNo ratings yet
- - =-3.6 log ф ^ - J J (: 182 Chapter 6 Interphase Transport in Isothermal SystemsDocument3 pages- =-3.6 log ф ^ - J J (: 182 Chapter 6 Interphase Transport in Isothermal SystemsAndrianPratamaNo ratings yet
- Signature Plastics Packing Slip for PG Building EnvelopeDocument1 pageSignature Plastics Packing Slip for PG Building EnvelopemeghadurganNo ratings yet
- Water's Edge BrochureDocument15 pagesWater's Edge BrochureAndrew Ahmed50% (2)
- Bare Conductors PDFDocument40 pagesBare Conductors PDFGerardo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ruukki Load Bearing Sheet DrawingsDocument56 pagesRuukki Load Bearing Sheet DrawingsРостислав ВасилевNo ratings yet
- Kroma Tower Makati City Condo Preselling Alveo LandDocument30 pagesKroma Tower Makati City Condo Preselling Alveo Landpreselling0% (1)
- New Eurocode For Towers, Masts and ChimneysDocument6 pagesNew Eurocode For Towers, Masts and Chimneysbojana_246941181No ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering ADocument7 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering ALuan CaetanoNo ratings yet