Professional Documents
Culture Documents
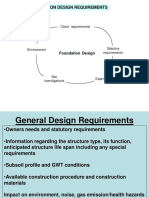
Factors To Consider in Foundation Design
Uploaded by
emmanuelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors To Consider in Foundation Design
Uploaded by
emmanuelCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors To Consider
In Foundation
Design
Notes These notes are prepared with the help of books
written by Braja M. Das, Craig, Joseph e. Bowles, Wayne
C. Teng, class notes and other relevant materials
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design
1. Footing Depth and Spacing
2. Location consideration for Spread footings
3. Displaced Soil Effect
4. Net versus Gross Soil Pressure
5. Erosion Problems for structures adjacent to flowing water
6. Corrosion Protections
7. Water Table fluctuation
8. Foundation Sand and Silt
9. Foundation on Clays and Clayey Silt
10.Foundations On Loess And Other Collapsible Soils
11.Foundations On Clays and Clayey Silts.
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design - Footing Depth and Spacing
1. Footing Depth and Spacing
The frost line
Zones of high volume change due to moisture fluctuations
Topsoil or organic material
Peat and muck
Unconsolidated material such as abandoned (or closed) garbage
dumps and similar filled in areas.
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design -Location consideration for Spread
footings
b) Location consideration for Spread footings
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design -Location consideration for Spread
footings
) Location consideration for Spread footings
If the new footing is lower than the existing footing
1 zf + q0 ---(01)
3= 0 = 1 K - 2c K ---(02)
= zf K+ q0 - 2c K --- (03)
Solving for excavation depth zf
(and using Safety Factor), we obtained
Zf = {2c / [(SF) K]} {q0 / (SF) }
--- (04)
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design -Location consideration for Spread
footings
the new footing is adjacent to the existing footing
Potential settlement or instability from loss of overburden pressure .
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design - Net
versus Gross Soil Pressure (Design soil pressures)
Net versus Gross Soil Pressure (Design soil pressures)
The bearing capacity equations are based on gross soil pressure
qult, which is everything above the foundation level. If the
allowable pressure is based on the bearing capacity equations,
the pressure is a gross pressure.
Settlements are caused only by net increase in pressure over
the existing overburden pressure. If the allowable pressure is
based on settlement consideration, it is a net pressure.
NOTE :- YOU CAN ADD DERIVATION OF NET / GROSS PRESSURES
B4 MIDTERM
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design -Erosion /
Scouring Problems for structures adjacent to flowing
water
Erosion / Scouring Problems for structures adjacent
to flowing water
Bridge piers, abutments, bases for retaining walls and footings for other
structures adjacent to or located in flowing water must be located at a depth
such that erosion or scour does not undercut the soil and cause a failure
An accurate prediction of scour depth is necessary so as to use the shortest
possible pile lengths
proaches to avoid Scouring
Scour is accelerated if the foundation creates channel obstruction; To
reduce scour the foundation should create a minimum obstruction to
normal stream flow patterns
Determine the foundation types
Estimate the probable depth of scour ,effects, etc.
Estimate the cost of foundations for normal and various scour
conditions
Determine the cost versus risk and revise the design accordingly
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design Corrosion
Protections
Corrosion Protections
In polluted ground areas such as old sanitary
landfills, shorelines, near sewer outfalls line from
older industrial plants, or backwater areas where
water stands over dead vegetation, there can be
corrosion problems with metal foundation members
as well as concrete. Concrete is normally resistant
to corrosion;
However, if sulfates are present, it may
necessary to use sulfate-resistant concrete.
It may occasionally be necessary to use airentrained concrete for foundation members.
Use of treated timber piling instead of metal piling
be
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design Water
Table Fluctuations
Water Table fluctuation
A lowered water table increases the effective pressure and may cause additional
settlements. A raised water table may create problems for the owner from the following;
Floating the structure ( making it unstable or tilting it)
Reducing the effective pressure (causing excessive settlement)
Creating a wet basement if the basement walls are not watertight.
proaches to Water Table Fluctuations
By introducing some type of drainage (water does not accumulate
around the building walls or produce hydrostatic uplift beneath the
basement).
Use of drain tile around the basement perimeter (common for residential
dwellings and some larger buildings).
A sloping basement excavation that is backfilled with granular materials
to the required horizontal level in combination with a well (called a sump
pit) at the low point that is fitted with a pump (a sump pump system) can
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design Sand and
Silt Deposits
Just Discussion. Details from the notes already
given
Bearing capacity.
Densification of loose deposits to control settlement.
Placing the footing at a sufficient depth that the soil beneath the footing is
confined. If silt or sand is not confined, it will roll out from the footing
perimeter with a loss of density and bearing capacity. Wind and water may
erode sand or silt from beneath a footing that is too near the ground
surface.
Uncontaminated glacial silt deposits can have a large capillary rise because
of the small particle sizes.
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design FOUNDATIONS
ON LOESS AND OTHER
COLLAPSIBLE SOILS
Just Discussion in Class . Details from the
notes given
Collapsible soils are generally wind-blown (aeolian) deposits of silts, dune sands, and
volcanic ash. Typically they are loose but stable, with contact points well-cemented with a
water soluble bonding agent, so that certain conditions of load + wetting produce a collapse
of the soil structure with a resulting large settlement.
Loess is the predominating collapsible soil that engineers are confronted with.
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design FOUNDATIONS
ON EXPANSIVE SOILS
Just Discussion in Class . Details from the
notes given
Expansive soils undergo volume changes upon wetting and drying.
In general, all clayey soils tend to shrink on drying and
expand when the degree of saturation S increases.
Usually, the lower the shrinkage limit and the wider
the range of the plasticity index Ip, the more likely is
volume change to occur
Factors To Consider In Foundation Design - Foundations
on Clays and Clayey Silts
Just Discussion in Class . Details from the
notes given
Clays and clayey silts may range from very soft, normally
consolidated, to very stiff, highly over-consolidated deposits.
Major problems are often associated with the very soft to
soft, deposits from both bearing-capacity considerations and
consolidation settlements.
You might also like
- Complete Hemi Sync Gateway Experience ManualDocument43 pagesComplete Hemi Sync Gateway Experience Manualapi-385433292% (92)
- 2 Principles of Roof Truss DesignDocument10 pages2 Principles of Roof Truss Designabhi aroteNo ratings yet
- Hotel Design Planning and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesHotel Design Planning and DevelopmentTio Yogatma Yudha14% (7)
- How To Design A Flat Roof PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Design A Flat Roof PDFMaria Rose Giltendez - BartianaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDocument123 pagesBearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationEngineer fozeb ali100% (3)
- Doors, Windows, PaintDocument64 pagesDoors, Windows, PaintArchana AcchuNo ratings yet
- Construction of Raft Foundation in Deep Sandy Beds For Major Bridges Across Perennial RiversDocument36 pagesConstruction of Raft Foundation in Deep Sandy Beds For Major Bridges Across Perennial RiversAfzal Ahmad100% (2)
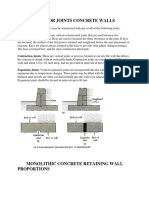
- Provision For JointDocument3 pagesProvision For Jointfazle rabbiNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity - 1Document57 pagesBearing Capacity - 1Wamanga David60% (5)
- 4 Bedroom BungalowDocument17 pages4 Bedroom Bungalowemmanuel100% (5)
- Strip FoundationDocument64 pagesStrip FoundationRuss Pope67% (6)
- Shallow Foundations in SoilDocument45 pagesShallow Foundations in SoilAizat HermanNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY EV103 CHAP 5 FOUNDATIONSDocument47 pagesCONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY EV103 CHAP 5 FOUNDATIONSLi Jun ChuaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Foundation Damage in Black Cotton SoilDocument23 pagesCauses of Foundation Damage in Black Cotton SoilAbhishek Mishra67% (3)
- Bs Steel CodeDocument14 pagesBs Steel CodeA.K.A. HajiNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Failure of Retaining WallDocument31 pagesCase Study of Failure of Retaining WallRahul Ramesh88% (8)
- Homo Sapiens ActivityDocument8 pagesHomo Sapiens ActivityJhon Leamarch BaliguatNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Telecommunications Structures v1.0 - NSW GovernmentDocument29 pagesGuidelines For Telecommunications Structures v1.0 - NSW GovernmentruayoNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Lecture Note .2Document198 pagesBuilding Construction Lecture Note .2amu aytuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Flexible and Composite Pavements Final (Individual Narrative Reports)Document30 pagesChapter 5 - Flexible and Composite Pavements Final (Individual Narrative Reports)Frederick AgliamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Substructure Foundation WorksDocument90 pagesChapter 3 - Substructure Foundation WorksPhillip Mendez100% (2)
- Isolated Footing PDFDocument21 pagesIsolated Footing PDFNupur Bhadra100% (2)
- C ClutchesDocument131 pagesC ClutchesjonarosNo ratings yet
- Types of FoundationDocument23 pagesTypes of FoundationemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Soil Compaction: A. General PrinciplesDocument6 pagesSoil Compaction: A. General PrinciplesIcha EstradaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines on Telecom Mast InstallationDocument39 pagesGuidelines on Telecom Mast InstallationOkpara Chibuike James100% (1)
- Shimano Brakes ManualDocument36 pagesShimano Brakes ManualKon Arva100% (1)
- Unit 4 (ROAD CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND TESTING)Document19 pagesUnit 4 (ROAD CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND TESTING)Zara Nabilah100% (1)
- Raft Foundations - Design & Analysis With A Practical Approach PDFDocument140 pagesRaft Foundations - Design & Analysis With A Practical Approach PDFemmanuel83% (6)
- Palgrave Handbook of Research in Historical Culture and EducationDocument847 pagesPalgrave Handbook of Research in Historical Culture and EducationGonzalo Garcia100% (1)
- Unbound Aggregates in RoadsFrom EverandUnbound Aggregates in RoadsR.H. JonesNo ratings yet
- CM Lecture - Bill of QuantityDocument14 pagesCM Lecture - Bill of QuantityAbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics I.handoutDocument114 pagesSoil Mechanics I.handoutZeleke Taimu100% (1)
- 2 - Compressibility of SoilsDocument34 pages2 - Compressibility of SoilsKatherine Shayne YeeNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument7 pagesRetaining WallEdward SmithNo ratings yet
- Manual of Specs & Standards For Power Transmission Systems - IndiaDocument45 pagesManual of Specs & Standards For Power Transmission Systems - IndiaemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Material Schedule Breakdown for Proposed Residential DevelopmentDocument13 pagesMaterial Schedule Breakdown for Proposed Residential Developmentemmanuel100% (1)
- Shallow Foundations ExplainedDocument14 pagesShallow Foundations Explainededmond100% (3)
- FOUNDATION DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL STABILITYDocument18 pagesFOUNDATION DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL STABILITYDanyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mba Project GuidelinesDocument8 pagesMba Project GuidelinesKrishnamohan VaddadiNo ratings yet
- Soil CompactionDocument30 pagesSoil CompactionJherome ManuelNo ratings yet
- FOUNDATION TYPES FOR BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONDocument34 pagesFOUNDATION TYPES FOR BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONashenafi.aNo ratings yet
- Foundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of ADocument12 pagesFoundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of Ahabtamu abateNo ratings yet
- 2 - Types of Stone, Brick and Block Masonry-2000Document70 pages2 - Types of Stone, Brick and Block Masonry-2000asadNo ratings yet
- Staircase Design and Load DistributionDocument9 pagesStaircase Design and Load DistributionRuzengulalebih ZEta's-ListikNo ratings yet
- Structural LayoutDocument6 pagesStructural Layoutkhan khan100% (1)
- Chapter 4.1.2018 - Pad FoundationDocument45 pagesChapter 4.1.2018 - Pad FoundationHawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering: Meaning and Types of FoundationDocument29 pagesFoundation Engineering: Meaning and Types of FoundationNasr UllahNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Materials PDFDocument10 pagesMiscellaneous Materials PDFPriyanka BasuNo ratings yet
- Compressibility of SoilDocument7 pagesCompressibility of SoiljuryNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering-Foundation: Mr.B.RameshDocument35 pagesBasic Civil Engineering-Foundation: Mr.B.RameshacroxmassNo ratings yet
- Standard Proctor Compaction Test ResultsDocument12 pagesStandard Proctor Compaction Test Resultsaidil adhaNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage Limit ExperimentDocument10 pagesShrinkage Limit ExperimentMuhammad Ilyas LanjarNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 RoofDocument20 pagesTopic 2 RoofChee HernNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth Pressures and Retaining Wall TypesDocument20 pagesLateral Earth Pressures and Retaining Wall Typessalt2009No ratings yet
- Compensated FoundationDocument12 pagesCompensated FoundationekaciptaNo ratings yet
- SOIL MECHANICS Chapter 1Document20 pagesSOIL MECHANICS Chapter 1Lawrence Omai100% (1)
- Excavation ToolsDocument41 pagesExcavation ToolsTejas Eknath PawarNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 7 - Lateral Earth Pressure-MDocument62 pages06 Chapter 7 - Lateral Earth Pressure-Mthuaiyaalhinai100% (1)
- Compaction Equipments FinalDocument37 pagesCompaction Equipments FinalVageesha Shantha Veerabhadra Swamy100% (1)
- Effect of Water Table On Allowable Bearing CapacityDocument4 pagesEffect of Water Table On Allowable Bearing Capacitykalpanaadhi100% (1)
- SubstructureDocument35 pagesSubstructureMeghna AshokNo ratings yet
- Floor Finishes: Chitkara School of Planning & Architecture, Chitkara UniversityDocument36 pagesFloor Finishes: Chitkara School of Planning & Architecture, Chitkara UniversityArsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- #1 What Are The Typical Characterstics Black Cotton Soil?Document16 pages#1 What Are The Typical Characterstics Black Cotton Soil?yeshi janexoNo ratings yet
- Vertical Stress in The GroundDocument12 pagesVertical Stress in The GroundRabindraSubediNo ratings yet
- Braced CutDocument14 pagesBraced CutAnikNo ratings yet
- SHORINGDocument10 pagesSHORINGIzzuddin ShahidanNo ratings yet
- Installation Method of Auto Cad 2007Document1 pageInstallation Method of Auto Cad 2007Samma Noor GujjarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.0.2018 - Retaining WallDocument36 pagesChapter 5.0.2018 - Retaining WallHawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5.2 Floor SystemDocument68 pagesChapter-5.2 Floor SystemFikaduKitessa67% (3)
- Design of Retaining WallDocument35 pagesDesign of Retaining WalluviNo ratings yet
- 5 Factors To Consider in Foundation DesignDocument25 pages5 Factors To Consider in Foundation DesignMotamed Ben TaherNo ratings yet
- Assignment No-11 P&F (CT-F16-42)Document3 pagesAssignment No-11 P&F (CT-F16-42)Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Labc NHW Ground Workers Pocket Book (Foundations and Substructures)Document44 pagesLabc NHW Ground Workers Pocket Book (Foundations and Substructures)kjm73No ratings yet
- Building Materials List and QuantitiesDocument2 pagesBuilding Materials List and QuantitiesemmanuelNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Communication Towers and AntennasDocument11 pagesCommunication Towers and AntennasemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematical Economics: January 2007Document16 pagesIntroduction To Mathematical Economics: January 2007emmanuelNo ratings yet
- MTN Job SummaryDocument3 pagesMTN Job SummaryemmanuelNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Admin - HR Officer at BIRC LimitedDocument3 pagesAdmin - HR Officer at BIRC LimitedemmanuelNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Foundation Shweta MishraDocument16 pagesFoundation Shweta MishraemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Revit Tutorial PDFDocument48 pagesRevit Tutorial PDFemmanuelNo ratings yet
- 12 Abeykoon, UOP PDFDocument4 pages12 Abeykoon, UOP PDFjesusgameboyNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel StructuresDocument26 pagesDesign of Steel StructuresMfon UdoitaNo ratings yet
- MTN Job Summary1Document1 pageMTN Job Summary1emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Base Transceiver Station: Trans-Receiving Antenna For Communication PurposeDocument1 pageBase Transceiver Station: Trans-Receiving Antenna For Communication PurposeemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Communication Towers and AntennasDocument11 pagesCommunication Towers and AntennasemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Technical Specifications - NIMET 1Document70 pagesGuidelines On Technical Specifications - NIMET 1emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Ma TANK PDFDocument1 pageMa TANK PDFemmanuelNo ratings yet
- 8Document7 pages8emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Communication Tower Foundation Selection CriteriaDocument6 pagesCommunication Tower Foundation Selection CriteriaSara RamliNo ratings yet
- MK TANKDocument1 pageMK TANKemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Structural Control System for Water TankDocument4 pagesStructural Control System for Water TankJOSMRIVERCNo ratings yet
- Tugas B InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas B Inggrisiqbal baleNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Truemax Concrete Pump Truck Mounted TP25M4Document16 pagesBrochure - Truemax Concrete Pump Truck Mounted TP25M4RizkiRamadhanNo ratings yet
- 3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFDocument6 pages3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFPablo MatrakaNo ratings yet
- Tupperware India's Perception StudyDocument10 pagesTupperware India's Perception StudyAnmol RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- Manju Philip CVDocument2 pagesManju Philip CVManju PhilipNo ratings yet
- EPF Passbook Details for Member ID RJRAJ19545850000014181Document3 pagesEPF Passbook Details for Member ID RJRAJ19545850000014181Parveen SainiNo ratings yet
- DNT Audit Cash CountDocument2 pagesDNT Audit Cash CountAnonymous Pu7TnbCFC0No ratings yet
- SIM5320 - EVB Kit - User Guide - V1.01 PDFDocument24 pagesSIM5320 - EVB Kit - User Guide - V1.01 PDFmarkissmuzzoNo ratings yet
- Front Cover Short Report BDA27501Document1 pageFront Cover Short Report BDA27501saperuddinNo ratings yet
- EE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument23 pagesEE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherMirza Azhar HaseebNo ratings yet
- STEM Spring 2023 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSTEM Spring 2023 SyllabusRollins MAKUWANo ratings yet
- AIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - SolutionsDocument34 pagesAIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - Solutionsbhavyakavya mehta100% (1)
- Manual Bombas CHWDocument16 pagesManual Bombas CHWFred GarciaNo ratings yet
- Policies and Regulations On EV Charging in India PPT KrishnaDocument9 pagesPolicies and Regulations On EV Charging in India PPT KrishnaSonal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToDocument79 pagesPresentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToVidyaNo ratings yet
- CHEM206 Answers 1Document3 pagesCHEM206 Answers 1Shiro UchihaNo ratings yet
- Digital Citizenship Initiative To Better Support The 21 Century Needs of StudentsDocument3 pagesDigital Citizenship Initiative To Better Support The 21 Century Needs of StudentsElewanya UnoguNo ratings yet
- Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsDocument8 pagesAddition and Subtraction of PolynomialsPearl AdamosNo ratings yet
- January 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Document2 pagesJanuary 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Rizwanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- PowerhouseDocument10 pagesPowerhouseRanjan DhungelNo ratings yet
- Practical LPM-122Document31 pagesPractical LPM-122anon_251667476No ratings yet
- Done by Akansha Bharti Harshitha K.N. Ishika Sunil Rajput Rashmi NaikDocument12 pagesDone by Akansha Bharti Harshitha K.N. Ishika Sunil Rajput Rashmi NaikRamya BalanNo ratings yet
- Hencher - Interpretation of Direct Shear Tests On Rock JointsDocument8 pagesHencher - Interpretation of Direct Shear Tests On Rock JointsMark2123100% (1)