Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 - Group Behavior
Uploaded by
Megz OkadaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 - Group Behavior
Uploaded by
Megz OkadaCopyright:
Available Formats
10th Edition
Managing Organizational Behavior
Moorhead & Griffin
Chapter 9
Group and Interpersonal
Behavior
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning Prepared by Charlie Cook
All rights reserved. The University of West Alabama
Chapter Learning Objectives
After studying this chapter you should be able to:
Discuss the interpersonal nature of organizations.
Define a group and illustrate their importance in
organizations.
Identify and discuss the types of groups commonly
found in organizations.
Describe the general stages of group development.
Discuss the major group performance factors.
Discuss intergroup dynamics.
Describe group decision making in organizations.
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 92
The Interpersonal Nature of Organizations
Interpersonal relations and group processes
pervade all organizations and are vital in
managerial activities
Interpersonal dynamicstypes of interactions
Between individuals
Between groups
Between individuals and groups
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 93
Outcomes of Interpersonal Behaviors
Results
Resultsofof
Interpersonal
Interpersonal Relations
Relations
Need
Need Social
Social Synergy
Synergy Conflict
Conflict
Satisfaction
Satisfaction Support
Support
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 94
The Nature of Groups
Group Defined
Two or more people who interact with one another
such that each person influences and is influenced by
each other person
Categorization of Groups
By degrees of formalization
Formal groupsestablished by organization
Informal groupsself-created by members
By degrees of permanence
Permanent
Temporary
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 95
Characteristics of Groups
Members may identify a little or not at all with the groups
goal
Members may satisfy needs just by being members
Behavior of individuals both affects and is affected by the
group
Accomplishments of groups are strongly influenced by the
behavior of their individual members
The work group is the primary means by which managers
coordinate individuals' behavior to achieve organizational
goals
The behavior of individuals is key to the groups success or
failure
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 96
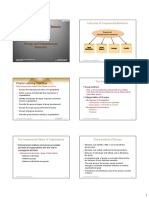
9.1
A General Model
of Group Dynamics
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 97
Types of Groups
Categorization
Categorization of
of
Groups
Groups
Formal
FormalGroups
Groups Informal
InformalGroups
Groups
Command
Command Friendship
Friendship
Task
Task Interest
Interest
Affinity
Affinity
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 98
9.1 Classification Scheme for Types of Groups
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 99
Stages of Group Development
Four-Stage Development Process of Groups
1. Mutual acceptance
2. Communication and decision making
3. Motivation and productivity
4. Control and organization
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 910
9.2 Stages of Group Development
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 911
Group Performance
Factors
FactorsAffecting
Affecting
Group
GroupPerformance
Performance
Composition
Composition Size
Size Norms
Norms Cohesiveness
Cohesiveness
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 912
Group Performance Factors
Group Composition
The degree of similarity or difference among group
members on factors important to the groups work
Homogeneity
Degree to which members are similar in one or several
ways that are critical to the groups work
Heterogeneity
Degree to which members differ in one or more ways that
are critical to the groups work
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 913
Group Performance Factors (contd)
Group Composition (contd)
Variables relating to group composition
Productivity
Type of task
Organizational diversity
Cultural traits: distrust, stereotyping, and communication
Effects of diversity on cooperation and understanding in
organizational alliances across country and culture
boundaries
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 914
Group Performance Factors (contd)
Group Size
Is the number of members of the group
Affects resources available to perform the task
Affects degree of formalization of interactions,
communication, and participation
Can increase the degree of social loafing
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 915
Group Performance Factors (contd)
Factors that Determine Ideal Group Size
Group members ability to interact and influence each
other (maturity of the group)
Maturity of individual group members
Group tasks
Ability of the group leader
to deal with communication,
conflict, task activities
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 916
Group Performance Factors (contd)
Group Norms
Are the standards against which the appropriateness
of the behaviors of members are judged
Determine behavior expected in a certain situation
Result from:
Personality characteristics of members
The situation
The historical traditions of the group
Are enforced only for actions that are important to
group members
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 917
Group Performance Factors (contd)
Purposes of Norms
Help the group survive
Simplify and increase predictability of expected
behaviors of group members
Help the group to avoid embarrassing situations
Express the groups central values for membership
identification and identify the group to others
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 918
Group Performance Factors (contd)
Group Cohesiveness
Is the extent to which a group is committed to staying
together
Results from forces acting on the members
Attraction to the group
Resistance to leaving the group
Motivation to remain a member of the group
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 919
9.3 Factors That Affect Group Cohesiveness and
Consequences of Group Cohesiveness
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 920
9.4 Group Cohesiveness, Goals, and Productivity
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 921
Intergroup Dynamics
Primary
PrimaryFactors
FactorsInfluencing
Influencing
Intergroup
IntergroupInteractions
Interactions
Task
Taskand
and
Characteristics
Characteristics Organizational
Organizational situational
situational
of
ofeach
eachof
ofthe
the setting
settingin
inwhich
which bases
basesofof
groups
groups groups
groupsinteract
interact interaction
interaction
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 922
9.5
Factors That
Influence Intergroup
Interactions
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 923
Group Decision Making
Factors
FactorsAffecting
Affecting
Group
GroupDecision
DecisionMaking
Making
Group
Group
Group
Group Groupthink
Groupthink Problem
Problem
Polarization
Polarization Solving
Solving
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 924
Group Decision Making (contd)
Group Polarization
The tendency for a groups average post-discussion
attitudes to be more extreme than its average pre-
discussion attitudes (risky shift or toward a more
conservative view)
Why Polarization Occurs
Increasing confidence from shared opinions
Persuasive arguments convincing weaker supporters
Individuals substituting group responsibility for
individual responsibility for the decision
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 925
Group Decision Making (contd)
Groupthink
A mode of thinking that occurs when members of a group
are deeply involved in a cohesive in-group and the desire
for unanimity offsets their motivation to appraise
alternative courses of action
Effects of Groupthink
Consideration of and focus on fewer alternatives
Failure to perceive non-obvious risks and drawbacks of
an alternative
Rejection of expert opinions
Ignoring potential for setbacks or actions of competitors
in not developing contingency plans
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 926
Groupthink
Conditions
ConditionsFavoring
Favoringthe
the
Development
Development of
of Groupthink
Groupthink
Leaders
Leaders Insulation
Insulationof
of
Strong
Stronggroup
group promotion
promotionof of the
thegroup
group
cohesiveness
cohesiveness aapreferred
preferred from
fromexperts
experts
solution
solution opinions
opinions
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 927
9.6 The Groupthink Process
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 928
Symptoms of Groupthink
Illusion of invulnerability
Collective efforts to rationalize/discount warnings
Unquestioned belief in the groups inherent morality
Stereotyped views of enemy leaders
Direct pressure on a member
Self-censorship of deviations
Shared illusion of unanimity
Emergence of self-appointed mind-guards
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 929
9.2 Prescriptions for Preventing Groupthink
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 930
Group Decision Making (contd)
Participation
Is the degree to which employees should be involved
in decision process
Benefits of Participation
Helps in judgmental problem-solving situations
Produces more and better decisions
Helps in solving complex problems
Creates a greater interest in the task
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 931
Group Decision Making (contd)
Group Problem Solving Difficulties
Factors limiting the generation-of-alternatives phase
Immediate reactions to alternatives discourages further
proposals of alternatives
Experience, status, and power of some members intimidates
less confident members
Limitations on idea generation imposed by the group leader
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 932
Group Decision Making (contd)
Group
GroupProblem
ProblemSolving
Solving
Techniques
Techniques
Nominal
Nominal
Brain-
Brain- Delphi
Delphi
Group
Group
storming
storming Technique
Technique
Techniques
Techniques
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 933
Organizational Behavior in Action
After reading the chapter:
Which interpersonal behaviors have you seen at work
or in classes that suggest that people have social
needs?
Which of the groups to which students commonly
belong could be defined as command groups?
What conflicts could occur when informal and formal
groups overlap in an organization?
2012 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 934
You might also like
- Stages of Group Development - 10-21-14 Extension PresentationDocument6 pagesStages of Group Development - 10-21-14 Extension PresentationshalinaNo ratings yet
- CH.3 DR - MahmoodDocument30 pagesCH.3 DR - MahmoodMarwa HassanNo ratings yet
- CasveDocument10 pagesCasveapi-299080505No ratings yet
- Olivia Millsop - Case Study Docx 1202Document11 pagesOlivia Millsop - Case Study Docx 1202api-345759649No ratings yet
- Group & Team Behaviour: By: Name - Pulkit Gupta Enrollment No. - 1011001112Document57 pagesGroup & Team Behaviour: By: Name - Pulkit Gupta Enrollment No. - 1011001112Muktak GoyalNo ratings yet
- Topic 12.contingency Theories & Situational LeadershipDocument43 pagesTopic 12.contingency Theories & Situational Leadershipmurti51No ratings yet
- Work and Social Adjustment Scale (W&sas)Document1 pageWork and Social Adjustment Scale (W&sas)Najia ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Industrial PsychologyDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Industrial PsychologyRuth Irene EstevesNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Human Behavior01Document14 pagesFoundations of Human Behavior01Candido PerezNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument8 pagesStress ManagementSanthoshi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Humor As A Moderator of Leadership Style EffectsDocument18 pagesHumor As A Moderator of Leadership Style EffectsAhmed TaherNo ratings yet
- Group Behavior, Teams and ConflictDocument78 pagesGroup Behavior, Teams and ConflictEhla Silverio-Vito100% (1)
- Foundation of Individual BehaviorDocument19 pagesFoundation of Individual Behaviorfeya ayef100% (1)
- Fiedler's Contingency Model of Leadership EffectivenessDocument23 pagesFiedler's Contingency Model of Leadership EffectivenessDiego MendozaNo ratings yet
- Session - Group BehaviorDocument23 pagesSession - Group BehaviorvasundhraNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - Mind Map On Traditional Functions of HRMDocument14 pagesHuman Resource Management - Mind Map On Traditional Functions of HRMZamzam Abdelazim100% (1)
- CHCGRP002 Plan and Conduct Group Activities 1Document5 pagesCHCGRP002 Plan and Conduct Group Activities 1Tonnie KiamaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Eighteenth EditionDocument37 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Eighteenth EditionPrashant Kumar100% (1)
- Foundations of Individual BehaviorDocument18 pagesFoundations of Individual BehaviorSahil67% (3)
- Project - Group DynamicsDocument45 pagesProject - Group Dynamicsmonzyans100% (1)
- Listening To Out-Group MembersDocument26 pagesListening To Out-Group MembersNgoc LeeNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument24 pagesPerformance AppraisalSalil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organizational BehaviourDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Organizational BehaviourDumitru ErhanNo ratings yet
- Group & Group Dynamics Assignment-HRMDocument18 pagesGroup & Group Dynamics Assignment-HRMsushilyer100% (3)
- Objective: The Learners Identify The Personal Factors Influencing Career ChoicesDocument22 pagesObjective: The Learners Identify The Personal Factors Influencing Career ChoicesebgambaNo ratings yet
- How To Choose The Correct Statistical TestDocument51 pagesHow To Choose The Correct Statistical TestTheGimhan123No ratings yet
- Component BDocument17 pagesComponent BSakshi Ranabhat100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Power, Politics and Organizational JusticeDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Power, Politics and Organizational JusticeThisisfor TiktokNo ratings yet
- QNST 3RDocument20 pagesQNST 3RLaibaSadafNo ratings yet
- Chap-01 Management and OrganizationsDocument36 pagesChap-01 Management and OrganizationsGamer nckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Power and PoliticsDocument23 pagesChapter 13: Power and PoliticsWan Na PrommanopNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting TheoryDocument2 pagesGoal Setting TheoryNajam ZameerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 PDFDocument19 pagesChapter 1.3 PDFmahesh_khebadeNo ratings yet
- Change Mgt Intro Forces Resistance ModelsDocument8 pagesChange Mgt Intro Forces Resistance ModelssaurabhNo ratings yet
- "Leadership: Instructor: Sheena PitafiDocument46 pages"Leadership: Instructor: Sheena Pitafiami iNo ratings yet
- The Five Practices of Exemplary LeadershipDocument2 pagesThe Five Practices of Exemplary Leadershipapi-361590674No ratings yet
- APJ5Feb17 4247 1Document21 pagesAPJ5Feb17 4247 1Allan Angelo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Day (2002) School Reform and Transition in Teacher Professionalism and IdentityDocument16 pagesDay (2002) School Reform and Transition in Teacher Professionalism and Identitykano73100% (1)
- Types of Counselling and Essential Counselling SkillsDocument12 pagesTypes of Counselling and Essential Counselling SkillsLorna Dollisen Labrada - MiguelaNo ratings yet
- Parenting styles and their effectsDocument1 pageParenting styles and their effectsIsabel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Group DynamicsDocument25 pagesGroup DynamicsporseenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - LeadingDocument31 pagesChapter 6 - LeadingNaaim AzmiNo ratings yet
- CH4-E3-E4 Management-Conflict Management PDFDocument29 pagesCH4-E3-E4 Management-Conflict Management PDFsantosh usendiNo ratings yet
- Organisational BehaviorDocument6 pagesOrganisational BehaviorIlamurugu PorchelvanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of TeamsDocument2 pagesThe Importance of TeamssymhoutNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing AttitudeDocument3 pagesFactors Influencing AttitudeJoshua PasionNo ratings yet
- Contingency TheoryDocument26 pagesContingency TheoryNeha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology-SLM2Document12 pagesIndustrial and Organizational Psychology-SLM2CHESSCA ERA100% (2)
- Managing Stress and The WorkLife BalanceDocument32 pagesManaging Stress and The WorkLife Balancezz030No ratings yet
- 3 - Power in OrganisationsDocument14 pages3 - Power in OrganisationsChau ToNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Culture and LeadershipDocument24 pagesTopic 4 Culture and LeadershipCARLVETT ELLENNE JUNNENo ratings yet
- Alban Metcalfe 2013Document18 pagesAlban Metcalfe 2013Musadaq HanandiNo ratings yet
- Teams vs Groups Benefits Costs Types Implementing TeamsDocument22 pagesTeams vs Groups Benefits Costs Types Implementing TeamsRaymond AlhambraNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics Concepts, Formation, and Impact on OrganizationsDocument26 pagesGroup Dynamics Concepts, Formation, and Impact on OrganizationsMathangiNo ratings yet
- Affective AssessmentDocument34 pagesAffective AssessmentEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Human Relations Approach - Focus on Individual Needs & MotivationDocument1 pageHuman Relations Approach - Focus on Individual Needs & MotivationArun SastryNo ratings yet
- The Application of Motivation Theory in Manufacturing CompanyDocument6 pagesThe Application of Motivation Theory in Manufacturing Companyblurking2002No ratings yet
- Career SuccessDocument15 pagesCareer SuccessNnamdi EzeNo ratings yet
- HBO Group PDFDocument6 pagesHBO Group PDFMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- HBO GroupDocument6 pagesHBO GroupMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Nonverbal Communication CodesDocument20 pagesNonverbal Communication CodesMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- SmokingDocument14 pagesSmokingMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Finish The Pattern 2Document1 pageFinish The Pattern 2Megz OkadaNo ratings yet
- MacroDocument3 pagesMacroMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- HBO Group PDFDocument6 pagesHBO Group PDFMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Stages of The Listening ProcessDocument1 pageStages of The Listening ProcessMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Kelloggs Edition 13 Full PDFDocument4 pagesKelloggs Edition 13 Full PDFMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- 7890136791431Document21 pages7890136791431YahiMicuaVillandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To OBDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To OBMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Multidimensional Nature of PovertyDocument6 pagesMultidimensional Nature of PovertyVasu KodagantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 DevGdGovDocument18 pagesChapter2 DevGdGovMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- HBO GroupDocument6 pagesHBO GroupMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- National Anti-Poverty Program Part2Document34 pagesNational Anti-Poverty Program Part2Melba TutorNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 DevGdGovDocument6 pagesChapter1 DevGdGovMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Solidfiles Links Post2-20Document35 pagesSolidfiles Links Post2-20Megz Okada0% (2)
- Documents - Tips Pricing Strategy of Nokia 560d8a2b0d1ebDocument42 pagesDocuments - Tips Pricing Strategy of Nokia 560d8a2b0d1ebMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Prof Interview on Legal WritingDocument2 pagesProf Interview on Legal WritingTanyaNo ratings yet
- Volleyball Terminology Guide Under 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesVolleyball Terminology Guide Under 40 CharactersMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - Chap 28Document5 pagesSample Questions - Chap 28Megz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Vocabulary TermsDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Vocabulary TermsMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Ob13 10Document17 pagesOb13 10Nazish Afzal Sohail BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillDocument8 pagesListening SkillAyu Puspita IndahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Work TeamsDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Work TeamsNaitik Shah100% (1)
- Listening ProcessDocument1 pageListening ProcessMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Answers Eoc Odd QuestionsDocument52 pagesAnswers Eoc Odd QuestionsMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- ReviewQA 3Document7 pagesReviewQA 3Megz OkadaNo ratings yet
- MGMT1135 Final Exam NotesDocument10 pagesMGMT1135 Final Exam NotesMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument33 pagesPDFMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Kwan Leadership ReflectionDocument7 pagesKwan Leadership ReflectionMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- A Tribute To Frank Lloyd WrightDocument3 pagesA Tribute To Frank Lloyd WrightJuan C. OrtizNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry FunctionsDocument14 pagesTrigonometry FunctionsKeri-ann Millar50% (2)
- Immigrant Women and Domestic Violence Common Experiences in Different CountriesDocument24 pagesImmigrant Women and Domestic Violence Common Experiences in Different Countriesapi-283710903100% (1)
- Data Statistik F TestDocument2 pagesData Statistik F TestDwiNo ratings yet
- Exploring Filipino TraditionsDocument6 pagesExploring Filipino TraditionsAshley TañamorNo ratings yet
- 2012 PhenomenaDocument17 pages2012 PhenomenaInderdip ShereNo ratings yet
- Revisied Final Ecs 2040 ManualDocument113 pagesRevisied Final Ecs 2040 Manualapi-346209737No ratings yet
- TCM Points TableDocument5 pagesTCM Points TableSkorman7No ratings yet
- HAT 2007 Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesHAT 2007 Marking SchemerusteeeeNo ratings yet
- DLL Philo Week 1Document5 pagesDLL Philo Week 1GABRIEL CABANSAGNo ratings yet
- Sage Publications, Inc. Political Theory: This Content Downloaded From 160.39.204.152 On Thu, 22 Dec 2016 06:41:54 UTCDocument37 pagesSage Publications, Inc. Political Theory: This Content Downloaded From 160.39.204.152 On Thu, 22 Dec 2016 06:41:54 UTCa24dkNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument15 pagesPhilosophyArnab Kumar MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- High school years shape our futureDocument2 pagesHigh school years shape our futureSilva SharphyNo ratings yet
- Translations of Persian LiteratureDocument18 pagesTranslations of Persian LiteratureAfshin IraniNo ratings yet
- LM 1002 Integrated English II PDFDocument13 pagesLM 1002 Integrated English II PDFLuzviminda A. TajosNo ratings yet
- Ethics of Spying A Reader For The Intelligence Professional PDFDocument2 pagesEthics of Spying A Reader For The Intelligence Professional PDFAmosNo ratings yet
- TridentDocument9 pagesTridentShikha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Allen NTSE Statewise Sample Paper With Solution-14Document8 pagesAllen NTSE Statewise Sample Paper With Solution-14ASDF100% (1)
- Group5 Affective Social Experiences PrintDocument11 pagesGroup5 Affective Social Experiences PrintshrutiNo ratings yet
- ERP Implementation and Upgrade in KenyaDocument288 pagesERP Implementation and Upgrade in Kenyasanyal2323No ratings yet
- Sirdamma TheroDocument15 pagesSirdamma TheroSiri Sadaham MonastryNo ratings yet
- EnglishElective SQPDocument11 pagesEnglishElective SQPmansoorbariNo ratings yet
- DO - PERDEV 11 - Q1 - Mod2Document10 pagesDO - PERDEV 11 - Q1 - Mod2RubenNo ratings yet
- Intro Design Thinking ProcessDocument34 pagesIntro Design Thinking ProcessDanijelBaraNo ratings yet
- Deep Ecology Debate on Humans' Environmental RoleDocument8 pagesDeep Ecology Debate on Humans' Environmental RoleVidushi ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- The Dangers of Emotional AttachmentDocument2 pagesThe Dangers of Emotional AttachmentMatthew JosephNo ratings yet
- Guide To SimulationDocument399 pagesGuide To Simulationvivipauf100% (1)
- Safety Induction Post Test Answer Sheet: Name: Nexus: Score: Instructor: DateDocument1 pageSafety Induction Post Test Answer Sheet: Name: Nexus: Score: Instructor: DateJunard Lu HapNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric HX Taking and MSEDocument45 pagesPsychiatric HX Taking and MSERhomizal Mazali100% (2)
- ZerotoThree Guidelines PDFDocument34 pagesZerotoThree Guidelines PDFwolfdare11No ratings yet