Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - Intro To Chemistry: by Kendon Smith - Columbia Central HS - Brooklyn, MI
Uploaded by
Mehak Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views15 pagesThis document provides an overview of introductory chemistry concepts. It defines chemistry as the study of matter and its changes. It outlines the five major branches of chemistry as organic, inorganic, biochemistry, analytical, and physical chemistry. Applied chemistry focuses on directed research with goals and applications, while pure chemistry pursues knowledge for its own sake. Chemistry is studied to explain the natural world, prepare for careers, and become informed citizens. Chemistry impacts materials, energy, medicine, agriculture, and the environment. The scientific method is introduced as the logical approach used to solve problems.
Original Description:
muet
Original Title
chap1notes-130214141338-phpapp02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of introductory chemistry concepts. It defines chemistry as the study of matter and its changes. It outlines the five major branches of chemistry as organic, inorganic, biochemistry, analytical, and physical chemistry. Applied chemistry focuses on directed research with goals and applications, while pure chemistry pursues knowledge for its own sake. Chemistry is studied to explain the natural world, prepare for careers, and become informed citizens. Chemistry impacts materials, energy, medicine, agriculture, and the environment. The scientific method is introduced as the logical approach used to solve problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views15 pagesChapter 1 - Intro To Chemistry: by Kendon Smith - Columbia Central HS - Brooklyn, MI
Uploaded by
Mehak KhanThis document provides an overview of introductory chemistry concepts. It defines chemistry as the study of matter and its changes. It outlines the five major branches of chemistry as organic, inorganic, biochemistry, analytical, and physical chemistry. Applied chemistry focuses on directed research with goals and applications, while pure chemistry pursues knowledge for its own sake. Chemistry is studied to explain the natural world, prepare for careers, and become informed citizens. Chemistry impacts materials, energy, medicine, agriculture, and the environment. The scientific method is introduced as the logical approach used to solve problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Chapter 1 Intro to Chemistry
By Kendon Smith Columbia Central HS Brooklyn, MI
Chapter 1 Notes: Introduction to Chemistry
I. What is Chemistry?
Chemistry is the study of matter and the
changes that matter undergoes.
Matter = Anything that has mass
and occupies space.
Examples of Matter?
Air, Water, A desk, YOU!
Examples of Non-matter?
Heat, Light, Sound, Energy
II. Five Major Branches of Chemistry
1. Organic Chemistry study of essentially all
chemicals containing carbon
2. Inorganic Chemistry study of chemicals, in
general, that do NOT contain carbon
3. Biochemistry study of chemical processes
that occur in living things
4. Analytical chemistry are of study that focuses
on the composition of matter.
II. Five Major Branches of Chemistry
5. Physical Chemistry deals with the
mechanism, the rate, and the energy transfer
that occurs when matter undergoes a change.
* Investigates underlying scientific principles
behind changes.
Chemical change = chemical reaction!
II. Pure and Applied Chemistry
1. Pure Chemistry pursuing of knowledge
simply for the sake of knowing it or to satisfy
mans natural curiosity about the world.
2. Applied Chemistry research that is directed
toward a goal or application in order to solve
a problem.
3. Technology the means by which society
provides its members with the things they need
or desire.
III. Why study Chemistry?
1. In order to explain the natural world.
2. To help you prepare for a career.
3. To become an informed citizen.
IV. Chemistry Far and Wide
1. Materials Chemists design materials to fit
specific needs in the world.
a. Macroscopic the world in which objects
are large enough to see.
b. Microscopic the world in which objects can
only be seen under magnification
2. Energy Chemists play an essential role in
finding ways to conserve, produce, and store
energy.
IV. Chemistry Far and Wide
3. Medicine Chemistry supplies the medicines,
materials, and technology that doctors use to
treat their patients.
- Biotechnology applies science to produce
biological products and processes
IV. Chemistry Far and Wide
4. Agriculture Chemists help develop more
productive crops and safer, more effective ways
to protect crops.
i. Soil quality testing to improve soil
ii. Adding fertilizers to the soil
iii. Developing herbicides to prevent weeds
iv. Developing insecticides to kill pests
v. Developing other chemicals to prevent plant diseases
vi. Biochemists modify the genes of plants
IV. Chemistry Far and Wide
5. The Environment Chemists identify
pollutants and prevent pollution
V. The Scientific Method
Def A logical, systematic approach to solving
problems.
1. Problem a question to be answered, usually
stated as a question.
2. Observations Using your senses to obtain
information about the problem.
3. Hypothesis A proposed explanation for an
observation.
V. The Scientific Method
4. Experiment A procedure used to test your
hypothesis.
a. Manipulated or independent variable a
variable you change.
b. Responding or dependent variable a
variable you observe.
V. The Scientific Method
5. Conclusion Analyze experimental results to
form theories or laws.
a. Theory a well tested explanation for a set
of observations.
- Tries to explain why, but can never be
proven
b. Law a concise statement that summarizes
results of many observations.
- A law is simply a statement of fact that does
not try to explain.
End of Chapter 1
Read and study the rest of the
chapter on your own for the test.
Pay attention to vocabulary!
Start off the year with a good test
grade! Dont underestimate this test!
You might also like
- Gen ChemDocument226 pagesGen ChemKemal PujabNo ratings yet
- Conversion Table: Distance PressureDocument2 pagesConversion Table: Distance Pressurerizkboss8312No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam CMTDocument13 pagesMidterm Exam CMTLester CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Iron - The Repair of Wrought & Cast IronDocument58 pagesIron - The Repair of Wrought & Cast Ironsaravanan_c1100% (2)
- CATALOG Blind and Solid RivetsDocument58 pagesCATALOG Blind and Solid Rivetsjhos douglasNo ratings yet
- Oil Free Process Gas Screw CompressorsDocument16 pagesOil Free Process Gas Screw CompressorsAndresoMartinecNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumDocument105 pages1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumJohn Cedrick Coronel RafananNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 3Document17 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 3bonnniii100% (1)
- 34 Samss 711Document26 pages34 Samss 711ShojikuriakoseTNo ratings yet
- Module 1 OrgchemDocument7 pagesModule 1 OrgchemJHUNNTY LOZANO100% (1)
- INORGANIC AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY GDocument25 pagesINORGANIC AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY GMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- G. Biology PPT Chapter 1-6new1Document238 pagesG. Biology PPT Chapter 1-6new1Alemayehu MelkamuuNo ratings yet
- (Introduction To Chemistry) : General Engineering DepartmentDocument5 pages(Introduction To Chemistry) : General Engineering DepartmentDanny Riel BarachinaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Chapter 1A WEEK 2 - October 12-16, 2020 Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Chapter 1A WEEK 2 - October 12-16, 2020 Learning ObjectivesReygemae Quitoras-ObsidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry"Document41 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry"Judy Ann CastorNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Environmental Science 15th Edition by Miller Spoolman ISBN 1305090446 9781305090446Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Environmental Science 15th Edition by Miller Spoolman ISBN 1305090446 9781305090446stevenedwardsgjfdctxork100% (23)
- Chem Int CC CH 01 - Introduction To Chemistry - Answers (09.15)Document12 pagesChem Int CC CH 01 - Introduction To Chemistry - Answers (09.15)JhonNo ratings yet
- Somaville University Semester: I Lecture: Chemistry Topic: AssignmentDocument3 pagesSomaville University Semester: I Lecture: Chemistry Topic: AssignmentnuurNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFdanagarzad90y100% (11)
- Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesLiving in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manualjerrybriggs7d5t0v100% (20)
- Chapter IntroDocument12 pagesChapter IntroVideo TimeNo ratings yet
- Chem 205 Week 1 To 3Document24 pagesChem 205 Week 1 To 3REAN KEM CUTAMORANo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manualbombyciddispelidok100% (22)
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFemicant.pintosfe9soe100% (13)
- Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesLiving in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualJonathanSwansonbwyi100% (63)
- Solution Manual For Environmental Science 14th Edition by Miller Spoolman ISBN 9781111988937Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Environmental Science 14th Edition by Miller Spoolman ISBN 9781111988937stevenedwardsgjfdctxork100% (23)
- Week 1 Module 1 LectDocument8 pagesWeek 1 Module 1 LectAtilano RenzNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFserenadinhmzi100% (10)
- Full Download Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manualdisroot.predecayhq0u6s100% (35)
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions ManualMorganLoganposxg100% (56)
- Dwnload Full Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFserenadinhmzi100% (11)
- Full Download Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manualdisroot.predecayhq0u6s100% (35)
- Lectures 1ST 4THDocument78 pagesLectures 1ST 4THNorie Castillo Santos AmadorNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesEssentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions ManualJohnCraiggmyrp100% (58)
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1Nataniel DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumDocument105 pages1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumJohn Cedrick Coronel RafananNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Concepts of Biology 3rd Edition by Mader ISBN 0073525537 9780073525532Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Concepts of Biology 3rd Edition by Mader ISBN 0073525537 9780073525532benjaminwolfprdiyajkcz100% (28)
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFcryer.westing.44mwoe100% (10)
- Full Download Essentials of Biology 4th Edition Mader Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Biology 4th Edition Mader Solutions Manualscantletdecumanszfdq100% (38)
- Full Download Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions Manualfannerbarogram.ywlkl100% (33)
- Chemistry Ss11sttermDocument80 pagesChemistry Ss11sttermDidimako GodstimeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Is Called Central ScienceDocument3 pagesChemistry - Is Called Central Scienceinah_30No ratings yet
- Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions ManualJeremyJonesjkfe100% (50)
- Prelims EnviSci Chapter2Document3 pagesPrelims EnviSci Chapter2Ramona RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Branches of BiologyDocument3 pagesBranches of BiologyDith JarillaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions ManualCassieTurnerqszj100% (53)
- Unit 1 TahsiliDocument7 pagesUnit 1 Tahsilieducationpurpuses111No ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 Week5 6 MELC03 Module3 Serna RhealynneDocument19 pagesScience 10 Q4 Week5 6 MELC03 Module3 Serna Rhealynnevincent alejandroNo ratings yet
- Lim - Assignment #1Document3 pagesLim - Assignment #1Mhich GeyrozagaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY f4 Chapter1Document21 pagesBIOLOGY f4 Chapter1Kar KuanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Biologyrommel benamirNo ratings yet
- Las - Science7 Q1 M1Document8 pagesLas - Science7 Q1 M1JAYME JOSWANo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument46 pages1 Introduction To ChemistryMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- 01 The Chemical WorldDocument1 page01 The Chemical WorldTewodirosNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Organic Chem PrelimsDocument28 pagesInorganic and Organic Chem PrelimsAlly WelchNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To ChemisrtyDocument24 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To ChemisrtyBainun DaliNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction Lecture Notes PDFDocument18 pages01 Introduction Lecture Notes PDFMaryrose Martinez Goloran0% (1)
- Full f1Document18 pagesFull f1Dalxe WadaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Jr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Biology M1 Nature of BiologyDocument25 pagesBiology M1 Nature of BiologyDansNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1020 Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesBIOL 1020 Lecture NotesMalik ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Physics Basic ScienceDocument23 pagesModule 1 Physics Basic SciencejudyaralarNo ratings yet
- Biology: What Is The Study of Life?Document13 pagesBiology: What Is The Study of Life?Bio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Bridging Program: Balian Community CollegeDocument12 pagesBridging Program: Balian Community CollegePinky SubionNo ratings yet
- Survey of Progress in Chemistry: Volume 2From EverandSurvey of Progress in Chemistry: Volume 2Arthur F. ScottNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Physical Changes of Organic CompoundsDocument34 pagesChemical and Physical Changes of Organic CompoundsMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- Organic and Inorganic Chemistry: Presented By: Memoona Memon AND Fazila KanwalDocument19 pagesOrganic and Inorganic Chemistry: Presented By: Memoona Memon AND Fazila KanwalMehak KhanNo ratings yet
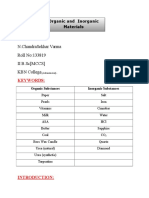
- N.Chandrasekhar Varma Roll No:133819 Ii B.SC (MCCS) KBN CollegeDocument6 pagesN.Chandrasekhar Varma Roll No:133819 Ii B.SC (MCCS) KBN CollegeMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing (Theory) : Mehran University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument1 pageEngineering Drawing (Theory) : Mehran University of Engineering and TechnologyMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- Cure Matters - Epo-TekDocument4 pagesCure Matters - Epo-TekCelia ThomasNo ratings yet
- Antiproliferative Effect of Synadenium Grantii Hook FDocument6 pagesAntiproliferative Effect of Synadenium Grantii Hook FCesar Alberto Verastegui ZapataNo ratings yet
- Weightage Analysis For IIT JEE 2011Document3 pagesWeightage Analysis For IIT JEE 2011Resonance KotaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Beuchat Caca 2008Document36 pagesCatalogo Beuchat Caca 2008alexpt2000No ratings yet
- 1 Theory2Document16 pages1 Theory2Tushar RajNo ratings yet
- 1251 Weighing On An Analytical BalanceDocument6 pages1251 Weighing On An Analytical Balancenonick18No ratings yet
- Soal Pas Genap - Big Xi - k13 - Revisi2Document16 pagesSoal Pas Genap - Big Xi - k13 - Revisi2citraNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin CalciumDocument4 pagesAtorvastatin Calciumehsan050628No ratings yet
- Aluminium WindowDocument1 pageAluminium WindowArshad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 2006, Fluent 6.3 Fuel Cell Modules Manual PDFDocument85 pages2006, Fluent 6.3 Fuel Cell Modules Manual PDFEd SilvaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Chemical EquationsDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Chemical EquationsAndreNo ratings yet
- SG1001 ChemlokAdhesivesDocument6 pagesSG1001 ChemlokAdhesivesAnonymous e0kwBYSaNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and Plant Nutrition: Rogelio R. Picart JR., Lic. AgrDocument14 pagesSoil Fertility and Plant Nutrition: Rogelio R. Picart JR., Lic. AgrJevelyn Mendoza FarroNo ratings yet
- IPC-TK34XT Spec SheetDocument1 pageIPC-TK34XT Spec SheetRahesa Wahyu NalendraNo ratings yet
- Polishing Pad Selection GuideDocument2 pagesPolishing Pad Selection GuidegaborodcNo ratings yet
- New Energy Efficient Car Built With 3d PrintingDocument3 pagesNew Energy Efficient Car Built With 3d PrintingKarthi KNo ratings yet
- Ti O2Document4 pagesTi O2Muhamad Fahmi Dermawan EndonesyNo ratings yet
- Practical ReportDocument3 pagesPractical ReportpuitengggNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument24 pagesElectrochemistryZainul AbedeenNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of A Hermetic Reciprocating CompressorDocument10 pagesPerformance Analysis of A Hermetic Reciprocating Compressorhermit44535No ratings yet
- ch03 PDFDocument11 pagesch03 PDFFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- cUSTOMS tARIFF OF mYANMARDocument729 pagescUSTOMS tARIFF OF mYANMARsoewinaung100% (1)
- Unit10 - Phan111 RedoxDocument57 pagesUnit10 - Phan111 RedoxAyille Dorado ArcigalNo ratings yet