Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 3
Uploaded by
Jared Bressler0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
79 views25 pagesOriginal Title
Week 3.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
79 views25 pagesWeek 3
Uploaded by
Jared BresslerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Non Binding Price celling
Effects of price ceilings
persistent shortage of the good/inefficiently low quantity produced
Inefficient allocation of the good to consumers,
resources wasted in searching for the good
inefficiently low quality of the good offered for sale
the emergence of illegal, black market activity
a persistent surplus of the good/inefficiently low quantity consumed
inefficient allocation of sales among sellers
wasted resources
an inefficiently high level of quality offered by suppliers
the temptation to engage in illegal activity, particularly bribery and corruption of
government official
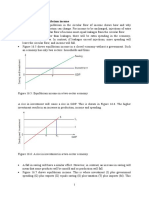
a. What are the equilibrium wage and quantity of workers in
this market?
b. For it to be effective, where would the government have to
set a minimum wage?
c. If the government set a minimum wage at $8 per our
i. how many workers would supply their labor?
ii. how many workers would be hired?
iii. how many workers would want to work that did not want to
work for the equilibrium wage?
iv. how many previously employed workers would no longer
have a job?
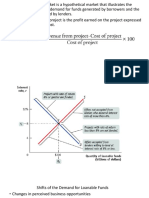
The Wedge=Quota Rent
supply price of a given quantity is the price at
which producers will supply that quantity.
Suppose that the quota is 8 million rides and that demand decreases
due to a decline in tourism. Show on your graph the smallest parallel
leftward shift in demand that would result in the quota no longer
having an effect on the market.
5. Which of the following would decrease the effect of a quota on a market? A(n)
a. decrease in demand
b. b. increase in supply
c. increase in demand
d. price ceiling above the equilibrium price
e. none of the above
Draw a correctly labeled graph illustrating hypothetical supply and demand
curves for the U.S. automobile market. Label the equilibrium price and quantity.
Suppose the government institutes a quota to limit automobile production. Draw
a vertical line labeled Qineffective to show the level of a quota that would have
no effect on the market. Draw a vertical line labeled Qeffective to show the
level of a quota that would have an effect on the market. Shade in and label the
deadweight loss resulting from the effective quota. Label the demand price, the
supply price, and the quota rent. Caculate the size of the deadweight loss.
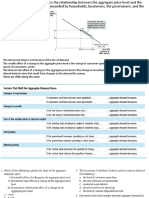
A household is a person or group of people
who share income. A firm is an organization
that produces goods and services for sale.
Product markets are where goods and
services are bought and sold.
Factor markets are where resources,
especially capital and labor, are bought and
sold.
Consumer spending is household spending
on goods and services.
Government transfers are payments that the government makes to individuals without expecting a good or service in
return.
Disposable income= Total income+government transfers-taxes,
Private savings= disposable income-consumer spending, is disposable income that is not spent on consumption. The
financial markets: channel private savings and foreign lending into investment spending, government borrowing, and foreign
borrowing
A stock is a share in the ownership of a company held by a shareholder.
A bond is a loan in the form of an IOU that pays interest.
Government borrowing: The amount of funds borrowed by the government in the financial markets.
Government purchases: total expenditures on goods and services by federal, state, and local governments.
Exports: Goods and services sold to other countries
Imports: Goods and services we buy from other countries
Inventories are stocks of goods and raw materials held to facilitate business operations.
Investment spending: spending on new capital, such as machinery and structures, and on changes in inventories
National income and product accounts, or national accounts, keep track of the
flows of money between different sectors of the economy.
Gross domestic product, or GDP, is the total value of all final goods and services produced in the economy during
a given year.
Final goods and services v Intimidate goods and services
Three ways to calculate
Survey firms to calculate the value of all their final goods and services produced
Add up the factor income earned by households in the economy
Aggregate spending: Add up spending on goods and services produced in the United States
GDP=C+I+G+(X-IM)
(X-IM)=Net Exports
The value added of a producer is the value of its sales minus
the value of its purchases of inputs
You might also like
- Summary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleFrom EverandSummary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleNo ratings yet
- CFA QUANT LVL 1 TESTDocument8 pagesCFA QUANT LVL 1 TESTTùng Dương ThanhNo ratings yet
- Economic Efficiency: Read About Consumer Surplus, Producer Surplus, and Deadweight LossDocument7 pagesEconomic Efficiency: Read About Consumer Surplus, Producer Surplus, and Deadweight LossNgọc Minh Đỗ ChâuNo ratings yet
- Total Revenue Is Defined AsDocument12 pagesTotal Revenue Is Defined AsRia BarisoNo ratings yet
- Economics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics GlossaryDocument7 pagesEconomics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics Glossarymarcodl18No ratings yet
- Economics PRICE CHANGE TESTDocument10 pagesEconomics PRICE CHANGE TESTyiNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Ch.2.2024Document4 pagesPublic Finance Ch.2.2024Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 NotesHuong GiangNo ratings yet
- UOP E Tutors - ECO 365 Final Exam Answers FreeDocument12 pagesUOP E Tutors - ECO 365 Final Exam Answers FreeUOP E TutorsNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizDocument28 pagesMicroeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizSuleyman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch10solution ManualDocument31 pagesCh10solution ManualStoneCold Alex Mochan100% (5)
- Transweb E Tutors - ECO 365 Final Exam, ECO 365 Week 5 Final ExamDocument8 pagesTransweb E Tutors - ECO 365 Final Exam, ECO 365 Week 5 Final Examtranswebetutors3100% (1)
- Tariff 3Document27 pagesTariff 30703055No ratings yet
- Econ Analysis of ProjectsDocument91 pagesEcon Analysis of ProjectsBarkhad MohamedNo ratings yet
- UOP E Assignments - ECO 365 & ECO 365 Final Exam Answers FreeDocument12 pagesUOP E Assignments - ECO 365 & ECO 365 Final Exam Answers FreeuopeassignmentsNo ratings yet
- Task 16 Ch.l.sri KariDocument41 pagesTask 16 Ch.l.sri KariEswar Sai VenkatNo ratings yet
- Factors Shifting Demand CurveDocument5 pagesFactors Shifting Demand CurveAiswarya ManojNo ratings yet
- MPSTME Notes 2Document38 pagesMPSTME Notes 2Ayush VikheNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics ExamDocument8 pagesMicroeconomics ExamBraceley & CoNo ratings yet
- Economics Assignment 2Document9 pagesEconomics Assignment 2EDWINNo ratings yet
- QUESTION: Explain How Elasticity of Demand Concept May Be Used by Government andDocument5 pagesQUESTION: Explain How Elasticity of Demand Concept May Be Used by Government andChitepo Itayi StephenNo ratings yet
- National Income StatisticsDocument5 pagesNational Income StatisticsShingirayi MazingaizoNo ratings yet
- B. The Value of Final SalesDocument9 pagesB. The Value of Final SalesJules AntenorNo ratings yet
- IIM Trichy PI Kit 2023Document69 pagesIIM Trichy PI Kit 2023Glen DsouzaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument5 pagesFormulasraj_mishra_17No ratings yet
- Export Marketing Imports and Exports What Are Imports and Exports?Document71 pagesExport Marketing Imports and Exports What Are Imports and Exports?MonashreeNo ratings yet
- ME NotesDocument6 pagesME NotesArka BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Def For EconsDocument12 pagesDef For EconsSockYii ChuaNo ratings yet
- Trade & DevelopmentDocument4 pagesTrade & DevelopmentAli HasnainNo ratings yet
- Eco402 Final Term Quiz FileDocument30 pagesEco402 Final Term Quiz FileYounas MujahidNo ratings yet
- Final Exam TermsDocument5 pagesFinal Exam TermsJessica KhouryNo ratings yet
- Economics Notes - 2Document17 pagesEconomics Notes - 2sindhu pNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesASSIGNMENTAteeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurs in A Market EconomyDocument46 pagesEntrepreneurs in A Market EconomyRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- WGU FPC1 MicroEconomics - Most RecentDocument81 pagesWGU FPC1 MicroEconomics - Most RecentsdwewNo ratings yet
- AP Macroeconomics Study GuideDocument39 pagesAP Macroeconomics Study GuideAustin Chungsta100% (1)
- Economics PRICE CHANGE TEST 2Document10 pagesEconomics PRICE CHANGE TEST 2yiNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document14 pagesChap 12Syed HamdanNo ratings yet
- Module 10 QuestionsDocument3 pagesModule 10 QuestionsRishi BhagatNo ratings yet
- ECO1101 Economic Concepts, Issues and ToolsDocument30 pagesECO1101 Economic Concepts, Issues and ToolsChris TengNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Mr. AllicockDocument60 pagesLecture 2. Mr. AllicockPrecious MarksNo ratings yet
- AP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1Document20 pagesAP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1KayNo ratings yet
- AP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1Document20 pagesAP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1KayNo ratings yet
- Economic AssignmentDocument5 pagesEconomic AssignmentAlbamiish Ibnu MohamedNo ratings yet
- EconomicDocument25 pagesEconomicmanulaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets in SS12Document11 pagesProblem Sets in SS12Johnoricks Ace Camarillo Catling0% (1)
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Exam 1Document12 pagesAP Macroeconomics Practice Exam 1Nguyễn Phương LiênNo ratings yet
- Economics Definition SummaryDocument16 pagesEconomics Definition Summarybloober blooberNo ratings yet
- Understanding Aggregate DemandDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Aggregate DemandKawsar WaraabeNo ratings yet
- SuggestionDocument8 pagesSuggestionanupareek1301No ratings yet
- GE Chapter 04 Solutions - FMTDocument14 pagesGE Chapter 04 Solutions - FMTAli RazaNo ratings yet
- International Trade TerminologyDocument10 pagesInternational Trade Terminologynimitjain10No ratings yet
- CH 7 Measuring GrowthDocument15 pagesCH 7 Measuring GrowthAdam XuNo ratings yet
- Interview Kit by IIM Tiruchirappalli - Page - 3Document18 pagesInterview Kit by IIM Tiruchirappalli - Page - 3Arisha AliNo ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument6 pagesEconomics Assignmentsolo_sudhanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MacroeconomicsDocument12 pagesModule 1 MacroeconomicsGagan H PNo ratings yet
- Glossary - BusinessDocument10 pagesGlossary - BusinesssaipraneethNo ratings yet
- ECO-501 All Question Ans For Mid Term Exam: Q. Define The Direct Tax and Indirect Tax & Give The Proper ExampleDocument7 pagesECO-501 All Question Ans For Mid Term Exam: Q. Define The Direct Tax and Indirect Tax & Give The Proper ExampleAsim HowladerNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment 1Document4 pagesWritten Assignment 1ahmed almhjaniNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument6 pagesManagerial EconomicsMilan Shah100% (1)
- Every K Ever Is ShitDocument1,481 pagesEvery K Ever Is ShitJared Bressler100% (1)
- Week 1Document41 pagesWeek 1Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document26 pagesWeek 2Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document24 pagesWeek 6Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document21 pagesWeek 8Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document25 pagesWeek 7Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 9Document32 pagesWeek 9Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document29 pagesWeek 4Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document20 pagesWeek 5Jared BresslerNo ratings yet
- 3-ABC Design-PeriodicDocument2 pages3-ABC Design-PeriodicFroilan RolaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Statements AuditDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Financial Statements AuditDemafilasan, Khyro Paul G.No ratings yet
- FFBL's Financial Management and OperationsDocument20 pagesFFBL's Financial Management and OperationsSunny KhanNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: f6198 - 1999Document1 pageUS Internal Revenue Service: f6198 - 1999IRSNo ratings yet
- ACC421 Chapter 18 Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesACC421 Chapter 18 Questions and AnswersNhel AlvaroNo ratings yet
- MA Florian Gronde Flashloans-Ohne AppendixDocument75 pagesMA Florian Gronde Flashloans-Ohne AppendixCollors TPLNo ratings yet
- Financing Health Care: Concepts, Challenges and Practices: April 28 - May 9, 2014Document2 pagesFinancing Health Care: Concepts, Challenges and Practices: April 28 - May 9, 2014J.V. Siritt ChangNo ratings yet
- NTS - Candidate (Portal)Document3 pagesNTS - Candidate (Portal)MUHAMMAD FAIZAANNo ratings yet
- Journal LedgerDocument50 pagesJournal LedgerShevina Maghari shsnohsNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Week 1 & 2Document38 pagesBusiness Finance Week 1 & 2Myka Zoldyck100% (6)
- Working Capital Managmnet - Pune University - MBA Project Report - Set2Document48 pagesWorking Capital Managmnet - Pune University - MBA Project Report - Set2amol.naleNo ratings yet
- NRI Document Checklist - Merchant NavyDocument2 pagesNRI Document Checklist - Merchant NavyAvinash ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Prince Bhai Legal NoticeDocument3 pagesPrince Bhai Legal Noticepradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Book 5Document174 pagesBook 5Anonymous hsZanpCNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument3 pagesCasesouzheshiNo ratings yet
- Micro and Small Enterprises in India PDFDocument23 pagesMicro and Small Enterprises in India PDFSuryamaniNo ratings yet
- WGU C 213 Accounting Terms - Most RecentDocument13 pagesWGU C 213 Accounting Terms - Most Recentsdwew0% (1)
- Unit 3-Time Value of MoneyDocument12 pagesUnit 3-Time Value of MoneyGizaw BelayNo ratings yet
- NANDIVARAM BRANCH AUCTIONDocument3 pagesNANDIVARAM BRANCH AUCTIONRaghavendra RaoNo ratings yet
- Supporting References in Oracle Ebs r12Document65 pagesSupporting References in Oracle Ebs r12AbbasNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document6 pagesQuiz 1jojojepNo ratings yet
- Accounting CycleDocument10 pagesAccounting CycleJane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Acme Shoe Rubber V Court of AppealsDocument3 pagesAcme Shoe Rubber V Court of AppealsPaolo BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Profit and Loss Week 8 - Break-Even Point: Business Math Leap - W7 & W8Document23 pagesWeek 7 - Profit and Loss Week 8 - Break-Even Point: Business Math Leap - W7 & W8david austriaNo ratings yet
- Og 23 1701 1802 00242559Document7 pagesOg 23 1701 1802 00242559tushar gargNo ratings yet
- Harvard Professor Benjamin Esty CVDocument8 pagesHarvard Professor Benjamin Esty CVadi2005No ratings yet
- Understanding Tax Credit CommunitiesDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Tax Credit CommunitiesJosh KwonNo ratings yet
- Capital GainsDocument25 pagesCapital GainsanonymousNo ratings yet
- Home Depot ROE decomposition 1986-1999Document11 pagesHome Depot ROE decomposition 1986-1999agnarNo ratings yet
- BFI Topic 1 2 3Document17 pagesBFI Topic 1 2 3Arnold LuayonNo ratings yet