Professional Documents
Culture Documents
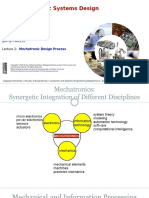
Key Elements of Mechatronics
Uploaded by
matininamdar50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views14 pagesOriginal Title
KEY ELEMENTS OF MECHATRONICS.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views14 pagesKey Elements of Mechatronics
Uploaded by
matininamdarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
OVERVIEW
Impact of Modelling and simulation in Mechatronics system
Mechatronic system components
Phases of Mechatonics system
Types of Design
Integrated product Design
Traditional Vs Mechatronics Approach
Mechatronics Key Elements
MODELLING & SIMULATION
Modelling is the process of representing the behaviour of a real system by a
collection of mathematical equations and logic.
Physical-mathematical description of a technical component,
subassembly or a complex system.
Simulation is the process of solving the same model on computer.
Calculation of the behavior of a system model in dependence on time,
and the state of a system and environment. The simulation provides projections
about the behavior of the real system with the aid of a model, which can be
executed in a computer.
Simulation process has the three basic steps:
Initialization
Iteration
Termination
AUTOMATIC CONTROL
System control is achieved by sensors,
actuators and embedded microcontrollers.
A system in which, the output has an effect
upon the input quantity, in such a manner
to maintain the desired output value is
automatic control system.
OPTIMIZATION
In Mechatronics, optimization is primarily used to establish the optimal
system configuration. It solves the problem of distributing limiting resources
throughout a system such that the pre-specified aspects of its behavior is
satisfied.
Here, resources are referred to as design variables, aspects of system
behaviour as objectives, and system governing relationships (equations and
logic) as constraints.
Example - for a box-shaped luggage to maximise volume:
Design variables : L (length), W (width), H (height)
Objective : Maximise V = V(L,W,H)
Constraints : System relationship V = LHW
Key elements of Mechatronic systems can be classified under following categories
1. Information systems
2. Mechanical systems
3. Electrical systems
4. Computer system
5. Sensors and actuators
6. Real time interfacing
Integration of Components (Hardware Integration)
Embedded with sensors, actuators and microcomputers
Designing the mechatronics system which integrating the
sensors, actuators and computers into the mechanical process and
can be arranged at several places.
Integration of Information Processing (Software Integration)
Embedded with advanced control functions
Besides a Feed forward and feed back control, an additional
influence may take place through the process knowledge and
corresponding online information processing. This means processing
of available signals at higher levels using fault diagnosis and
optimization
Classification of Mechatronics system
Phases of Mechatronics design process
Modeling : Systems are represented by a suitable model for evaluating the
behavior characteristics using simulation methods.
Prototyping : Sensors and actuators are interfaced with i/p and o/p signals with the
trial models, resulting in partial mathematical and real models. Here
real part provides real-time analysis and mathematical part provides
simulated time-based response. We can synchronized to understand
and validate the design
Deployment : Associated with the final product, embedded software deployment and
lifecycle.
Steps involved in modeling and simulation
Need : Adaptive market research and knowledge must be
accumulator to achieve a clear picture of what the
customer wants.
Feasibility : Examine the commercial as well as technical aspects
of the proposed product such as Warranty and future
maintenance cost which will influence the profitability.
Specifications : It encompasses the weight, payload and interfaces,etc.
Conceptual design : Generate six possible solution.
Embodiment & : Once optimal solution has been identified, we move to
Optimization detailed design phase and the production of
manufacturing drawings
Integrated Design Approach
MCT consists of several interconnected subsystem and components
TYPES OF DESIGN
[
Design for strength or stiffness
Design for reliability
Design for maintainability - Features such as repair on replacement
Design for manufacture - Concerned for Automatic assembly. Here the machine
capability must be taken into account for the
rationalisation of component, fixture & fitting between
between similar product & process.
Traditional Approach Mechatronics Approach
Original and operating characteristics
will changes due to the actual loading System is reliable due the
and dynamic interactions. integrated system design.
Perfect impedance matching of the
two designed system is quite difficult
Traditional Approach Mechatronic Approach
Bulky system Compact
Complex mechanism Simplified mechanism
Rigid heavy structures Lighter structures
Manual control Automatic and programmable control
Non adjustable movement cycle Programmable movements.
Accuracy is less Good accuracy due to feedback
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Stage in design process
a) Production of a detailed design
b) More flexible
c) Dead time
d) None of the above
2. The first stage in developing the design
a) Solving the problem
b) true nature of the problem
c) Temperature control
d ) none of the above.
3. Need in design for
a)Intelligent control
b)Defined control
c)Both a and b
d)None of the above.
You might also like
- Design of Mechatronics SystemDocument28 pagesDesign of Mechatronics SystemMamo ZelalemNo ratings yet
- MT6603 DMS Unt 3 PDFDocument39 pagesMT6603 DMS Unt 3 PDFKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Transducers and Sensors ReviewDocument113 pagesTransducers and Sensors ReviewSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics SyllabusDocument2 pagesHydraulics and Pneumatics SyllabusMulu Girmay67% (3)
- CNC Technology 2 MarksDocument10 pagesCNC Technology 2 Markssivaeinfo0% (1)
- Timers and Counters Instruction PLC TutorialDocument26 pagesTimers and Counters Instruction PLC TutorialAlpha75% (4)
- Unit 1 Steady & Variable Stresses in Machine Members: Design of Machine ElementsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 Steady & Variable Stresses in Machine Members: Design of Machine ElementsPrasanth YuviNo ratings yet
- CIM-2 MarksDocument18 pagesCIM-2 MarksHod MechNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Control SystemDocument86 pagesUnit 1 Control SystemVijay Ct67% (3)
- UNIT 2 MechatronicsDocument35 pagesUNIT 2 MechatronicsMuthuvel M91% (11)
- Chapter 2 - Robot KinematicsDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - Robot KinematicsShitnu SuwanNo ratings yet
- Robotic SensorsDocument30 pagesRobotic Sensorsmanoj50% (4)
- NC & CNC MachinesDocument12 pagesNC & CNC MachinesRenjith RajendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Automation in ManufacturingDocument41 pagesAutomation in ManufacturingOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- CIM Wheel: A Concise Guide to Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument43 pagesCIM Wheel: A Concise Guide to Computer Integrated ManufacturingNathanael Aklilu Ejersa100% (2)
- Detroit Type of AutomationDocument73 pagesDetroit Type of Automationvinay846458% (12)
- Maintenance of Machinery Course Code: Mceng 5142 Instructor: Mesfin S. (PH.D.)Document30 pagesMaintenance of Machinery Course Code: Mceng 5142 Instructor: Mesfin S. (PH.D.)Mikias Tefera100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Robot KinematicsDocument38 pagesChapter 4 - Robot KinematicsteamehadushNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power Principles and Hydraulic PumpsDocument12 pagesFluid Power Principles and Hydraulic PumpsDr. Manikandan.G MECH0702100% (4)
- Machine Drawing Two Mark QuestionsDocument13 pagesMachine Drawing Two Mark QuestionsHimanshuSisodiyaNo ratings yet
- RoboticsDocument41 pagesRoboticsMark Jason100% (3)
- Design of Transmission System Question BankDocument18 pagesDesign of Transmission System Question BankAravind50% (2)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B.Tech IV-I Sem Automation and Robotics NotesDocument75 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B.Tech IV-I Sem Automation and Robotics NotesG.Harivasu HarivasuNo ratings yet
- Model-based monitoring system block diagramDocument2 pagesModel-based monitoring system block diagram9740177035No ratings yet
- Pictorial Drawing TechniquesDocument41 pagesPictorial Drawing Techniquesamdeva100% (1)
- UNIT 1 MechatronicsDocument15 pagesUNIT 1 MechatronicsMuthuvel M82% (17)
- UNIT 3 MechatronicsDocument38 pagesUNIT 3 MechatronicsMuthuvel M67% (6)
- Cme347 Lean Manufacturing Question Bank in PDFDocument18 pagesCme347 Lean Manufacturing Question Bank in PDFTHIRUMALAI0% (1)
- DOCUMENT - Mechanical Engineering MCQ TestDocument3 pagesDOCUMENT - Mechanical Engineering MCQ TestNitesh Asthana75% (4)
- Classification of NCDocument9 pagesClassification of NCAmarnadh60% (5)
- Engineering Metrology and Measurement - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocument21 pagesEngineering Metrology and Measurement - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M92% (13)
- Chapter 8: Fluid Basic Electrical and Logic Control SystemDocument34 pagesChapter 8: Fluid Basic Electrical and Logic Control SystemSiraj BusseNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Assignment 1 & 3Document2 pagesMechatronics Assignment 1 & 3Dinesh MechNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine Unit 1Document122 pagesTheory of Machine Unit 1Deepak PrajapatNo ratings yet
- BASIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN COUPLINGS, CLUTCHES AND BRAKESDocument41 pagesBASIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN COUPLINGS, CLUTCHES AND BRAKESKadiyam VijayNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CNC Machine Tools: StructureDocument17 pagesUnit 3 CNC Machine Tools: StructureRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Direct Energy ConversionDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Direct Energy ConversionHuzaifa Wasim100% (2)
- Dynamics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument14 pagesDynamics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDHINAKARANVEEMAN100% (2)
- Objective Questions - Group Technology & RoboticsDocument1 pageObjective Questions - Group Technology & RoboticsAnonymous YkDJkSqNo ratings yet
- Applied ElectronicsDocument37 pagesApplied ElectronicsGuruKPO100% (2)
- Engineering Metrology 2 MarksDocument13 pagesEngineering Metrology 2 MarksRavi SivaprakashNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 MechatronicsDocument16 pagesUNIT 5 MechatronicsMuthuvel M85% (27)
- UNIT - 3-Sensors and Machine VisionDocument19 pagesUNIT - 3-Sensors and Machine VisionM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENo ratings yet
- CAD/CAM Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesCAD/CAM Important Questionsivs yeswanthNo ratings yet
- 12ed11 - Advanced Machine Tool DesignDocument15 pages12ed11 - Advanced Machine Tool DesignBradeesh MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Questions Mechatronics (MH1031) Unit - 1Document12 pagesTwo Marks Questions Mechatronics (MH1031) Unit - 1cakejhNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety FundamentalsDocument17 pagesIndustrial Safety FundamentalsPrasanna GNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Automated Flow LinesDocument94 pagesUnit Ii Automated Flow LinesRajesh Shah100% (1)
- Manufacturing Processes Lab ManualDocument46 pagesManufacturing Processes Lab ManualAnas AminNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical Micro Machining Assignment-Week 8Document7 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical Micro Machining Assignment-Week 8PranjalGuptaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Test AnswersDocument5 pagesPneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Test AnswersZuhaila MohammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 C DH Representation For Robotic ManipulatorsDocument88 pagesChapter 3 C DH Representation For Robotic ManipulatorsCharlton S.Inao100% (1)
- Mechatronics MCQDocument14 pagesMechatronics MCQNandakrishnan S L71% (7)
- Chapter 7 Numerical Control and Industrial RoboticsDocument53 pagesChapter 7 Numerical Control and Industrial RoboticsYousab CreatorNo ratings yet
- Metrology and MeasurementsDocument140 pagesMetrology and MeasurementsVallik Tad0% (1)
- PLC & Scada Lab Manual (Part-1)Document33 pagesPLC & Scada Lab Manual (Part-1)Pavan Deshpande70% (10)
- LEC 08-10 - Mechatronics Systems and ApplicationsDocument29 pagesLEC 08-10 - Mechatronics Systems and ApplicationsAakash ParmarNo ratings yet
- Mechatronic Systems Design: Mohammed AhmedDocument54 pagesMechatronic Systems Design: Mohammed AhmedShivam Kumar ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics: by Ajay Kumar VermaDocument17 pagesMechatronics: by Ajay Kumar VermaAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Mechatronic System Design Course OverviewDocument21 pagesMechatronic System Design Course OverviewSaravanakumardevarajNo ratings yet
- IntegrityDocument5 pagesIntegrityPritam Kumar100% (1)
- Case Study On Maruti 800Document4 pagesCase Study On Maruti 800Nizar MesaniNo ratings yet
- Osprey, Men-At-Arms #008 The Black Watch (1971) (-) OCR 8.12Document48 pagesOsprey, Men-At-Arms #008 The Black Watch (1971) (-) OCR 8.12mancini100% (4)
- PSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipDocument4 pagesPSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipAfees OlajideNo ratings yet
- Solwezi General Mental Health TeamDocument35 pagesSolwezi General Mental Health TeamHumphreyNo ratings yet
- Resp Part 4Document95 pagesResp Part 4Kristian CadaNo ratings yet
- Sample ResumeDocument3 pagesSample Resumeapi-380209683% (6)
- ZJJ 3Document23 pagesZJJ 3jananiwimukthiNo ratings yet
- Joy Difuntorum-Ramirez CVDocument2 pagesJoy Difuntorum-Ramirez CVJojoi N JecahNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.7Document2 pagesAssignment No.7queen estevesNo ratings yet
- Principles of CHN New UpdatedDocument4 pagesPrinciples of CHN New Updatediheart musicNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Constitution SyllabusDocument7 pagesPhilippine Politics and Constitution SyllabusIvy Karen C. Prado100% (1)
- ccpc15 Supportive and Preventive WorkbookDocument30 pagesccpc15 Supportive and Preventive WorkbookJeremy HamptonNo ratings yet
- English A June 2008 p2Document9 pagesEnglish A June 2008 p2LilyNo ratings yet
- Optimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining EquipmentDocument9 pagesOptimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining EquipmentLucia QuispeNo ratings yet
- Biology GCE 2010 June Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument10 pagesBiology GCE 2010 June Paper 1 Mark SchemeRicky MartinNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Contemporary Project Management 4th EditionDocument15 pagesSolution Manual For Contemporary Project Management 4th EditionDanaAllendzcfa100% (77)
- Differentiation SS2Document88 pagesDifferentiation SS2merezemenike272No ratings yet
- Auerbach Slideshow How To Write A ParagraphDocument22 pagesAuerbach Slideshow How To Write A ParagraphFreakmaggotNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Pregnancy Shady' With YouDocument48 pagesI Am Sharing 'Pregnancy Shady' With YouNouran AlaaNo ratings yet
- Analogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiDocument235 pagesAnalogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiAl-FarabiNo ratings yet
- Article 106899Document6 pagesArticle 106899Abhinave SNo ratings yet
- Anticipate Problems Before They Emerge: White PaperDocument7 pagesAnticipate Problems Before They Emerge: White PaperYotsapol KantaratNo ratings yet
- PMMC ExperimentDocument2 pagesPMMC ExperimentShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Educating The PosthumanDocument50 pagesEducating The PosthumanCatherine BrugelNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019Document4 pagesQuantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019SANAMGI BHAVYANo ratings yet
- Berger Paints (India) Limited 21 QuarterUpdateDocument7 pagesBerger Paints (India) Limited 21 QuarterUpdatevikasaggarwal01No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (MGT 4320) : Kulliyyah of Economics and Management SciencesDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Management (MGT 4320) : Kulliyyah of Economics and Management SciencesAbuzafar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assessing Khazaria-Serpent PeopleDocument1 pageAssessing Khazaria-Serpent PeopleJoao JoseNo ratings yet
- Fancy YarnsDocument7 pagesFancy Yarnsiriarn100% (1)