Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasound-Guided Invasive Procedures in Obstetrics
Uploaded by
ari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views18 pagesusg
Original Title
Ultrasound-guided Invasive Procedures in Obstetrics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentusg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views18 pagesUltrasound-Guided Invasive Procedures in Obstetrics
Uploaded by
ariusg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Ultrasound-guided Invasive
procedures in obstetrics
dr. Hariyasa Sanjaya, SpOG(K) MARS
Division of Maternal and Fetal
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Sanglah Hospital
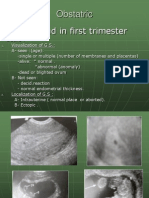
Diagnostic Procedures in the
1st Trimester
CVS : under continuous sonographic visualization of
the catheter in which chorionic villi are aspirated from the
developing placenta.
Early Amniocentesis : an aspiration needle is
guided into the amniotic fluid under continuous
sonographic guidance. It is sometimes difficult to
puncture both chorion and amnion in 13 16 W
pregnancies
Retrieval of tissue for karyotyping
(Arthur C. Fleischer, 2004)
Chorionic Villous Sampling
Major Indications :
1. Maternal age : 35 years at delivery
2. Previous child with non-disjunction
chromosome abnormality
3. Parent is carrier of balanced translocation or
other chromosome disorder
4. Both parents are carriers of a sex-linked
disease
5. Positive 1st trimester screen for trisomy-21 or
18
CVS : the procedure
Procedure related anatomy
Sampling technique
Transcervical sampling
Transabdominal CVS
Confirmation of adequate tissue
retrieval : visual inspection of the
syringe contents or by dissecting
microscope
Risk Associated with CVS
Bleeding : 7-10% transcervically
Infection : 0.3% of pregnancy loss
Ruptured membranes : very rare
Elevated MSAFP : transient
Rh Isoimmunization : Rh (-) women should
receive Rho (D) immunoglobulin
Pregnancy loss : 2-3%
Risk of fetal abnormalities after CVS : limb
deformities
Perinatal risks and impact on long-term
development of the infant
Amniocentesis
Indications of amniocentesis
Late 1st and 2nd trimester diagnosis :
cytogenetic diagnosis, diagnosis of NTD, diagnosis
of metabolic disorders
Late 2nd and 3rd trimester : evaluation of the
severity of isoimmunization, fetal lung maturity,
diagnosis of intra amniotic infection, confirmation of
ruptured membranes
Therapeutic : drainage of polyhydramnios, medical
treatment of fetal disorders
Technical aspects of the
procedure
Gestational age : 15 18 W
Needle selection : 20 22 G
Ultrasound
Operative technique : insertion of the
transducer into a sterile glove
Volume of amniotic fluid : 8 45 cc (20
25 cc)
Intraoperative complications
Membrane tenting : separation of the
chorioamniotic membrane from the anterior
uterine wall during needle insertion
Multiple needle insertions
Bloody taps
Fetomaternal transfusion : Kleihauer-Betke
test
Discolored amniotic fliod : brown, green
FETAL BLOOD SAMPLING
Indications of FBS
Cytogenetic diagnosis
Congenital infections : TORCH, parvovirus
Preterm labor and premature rupture of
membranes
Congenital immunodeficiency
Coagulopathy : hemophylia A and B
Platelet disorders
Hemoglobinopathies
IUGR
Fetal therapy
Techniques of Fetal Blood
Sampling
Cordocentesis
Intrahepatic FBS
Cardiocentesis
Quality control of the specimen
Duration of the procedure
Training
Normal value for fetal blood :
erythroblast count
Complications of FBS
Fetal losses : 1.4%
Hemorrhage : bleeding from the puncture site
: 41 53%, with a mean duration of 35 second
Cord hematoma : 17%
Bradicardia : transient (12%)
Fetomaternal hemorrhage
Abruptio placentae
Preterm delivery : 7%
Fetal resuscitation
Ultrasound-Guided Fetal
Invasive Therapy
Fetal uropathy : obstructive uropathy
Fetal surgery : pulmonary hypoplasia,
diaphragmatic hernia
Evaluation of renal function
Hydrocephalus
Isolated pleural effusions : fetal
pleuroamniotic shunting
Bronchogenic cyst
Invasive therapy for NTD
You might also like
- DR Robert Malone Speaks OutDocument40 pagesDR Robert Malone Speaks OutB100% (2)
- Exposing The Myth of The Germ TheoryDocument10 pagesExposing The Myth of The Germ Theoryziotibia100% (14)
- Ultrasound in 1st, 2nd & 3rd trimester د.رامز الأسوديDocument13 pagesUltrasound in 1st, 2nd & 3rd trimester د.رامز الأسوديMohammad BelbahaithNo ratings yet
- Transabdominal and Transvaginal Ultrasound of the UterusDocument68 pagesTransabdominal and Transvaginal Ultrasound of the UterusEsraa AlmassriNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy: Management ChallengesDocument35 pagesCardiac Disease in Pregnancy: Management ChallengesMannat ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Management of Fungal Infections in MCS and Cardiothoracic Organ Transplant Recipients: ISHLT Monograph Series (Volume 12)From EverandManagement of Fungal Infections in MCS and Cardiothoracic Organ Transplant Recipients: ISHLT Monograph Series (Volume 12)No ratings yet
- An Atlas of Three - and Four-Dimensional Sonography in Obstetrics and Gynecology by Kurjak, Asim Jackson, David (2004)Document227 pagesAn Atlas of Three - and Four-Dimensional Sonography in Obstetrics and Gynecology by Kurjak, Asim Jackson, David (2004)Guilherme ChavesNo ratings yet
- Benign Gynecologic Lesions: Urethral Caruncle, Cyst, Nevus, Hemangioma, Fibroma, Lipoma, Endometriosis, Urethral DiverticulumDocument158 pagesBenign Gynecologic Lesions: Urethral Caruncle, Cyst, Nevus, Hemangioma, Fibroma, Lipoma, Endometriosis, Urethral DiverticulumArianne Joy C. TamarayNo ratings yet
- Clinical Doppler Ultrasound 2nd EditionDocument384 pagesClinical Doppler Ultrasound 2nd EditionDenis PogoreviciNo ratings yet
- ULTRASOUND Fetal AnomaliesdocxDocument86 pagesULTRASOUND Fetal AnomaliesdocxAlexandra MateiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Obstetric and Gynecologic PDFDocument190 pagesUltrasound Obstetric and Gynecologic PDFAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Detected Ovarian Cysts For Nuh Gynaecology TeamsDocument11 pagesUltrasound Detected Ovarian Cysts For Nuh Gynaecology TeamsDirga Rasyidin LNo ratings yet
- Micropara Lab NotesDocument34 pagesMicropara Lab NotesShyenNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder Cancer Treatment and PrognosisDocument61 pagesGallbladder Cancer Treatment and PrognosisZaki DhiifNo ratings yet
- Normal Fetal Anatomy2Document26 pagesNormal Fetal Anatomy2swati100% (1)
- First Aid LeafletDocument11 pagesFirst Aid LeafletshahnawazNo ratings yet
- Echocardiographic Anatomy in The FetusDocument14 pagesEchocardiographic Anatomy in The FetusAnonymous hOHi6TZTnNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Right Side Foetal Myocardial Performance Index in Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Right Side Foetal Myocardial Performance Index in Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes MellitusGabyliz Gonzalez CastilloNo ratings yet
- DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN PREGNANCYDocument64 pagesDOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN PREGNANCYHerry SasukeNo ratings yet
- Green Top Guidelines 7Document34 pagesGreen Top Guidelines 7garfield1No ratings yet
- Fetal Biometry and Growth ChartsDocument27 pagesFetal Biometry and Growth ChartsnellieauthorNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Versus Abdominal Radical HysterectomyDocument10 pagesMinimally Invasive Versus Abdominal Radical HysterectomyClinton Franda Markus SitanggangNo ratings yet
- 62 Colposcopy StandardsDocument73 pages62 Colposcopy Standardsrijal mahdiy pNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis - Morphology Scan, Invasive Methods - R. Choy, Et. Al., (Intech, 2012) WW PDFDocument219 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis - Morphology Scan, Invasive Methods - R. Choy, Et. Al., (Intech, 2012) WW PDFFlavius YoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Differential Diagnosis For The Breast Mass in An Adolescent?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Differential Diagnosis For The Breast Mass in An Adolescent?theodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis and Management of The Acute Abdomen in Pregnancy-Greenspan, Peter, Springer Verlag (2017)Document284 pagesThe Diagnosis and Management of The Acute Abdomen in Pregnancy-Greenspan, Peter, Springer Verlag (2017)AndreaAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging TechniquesDocument96 pagesMedical Imaging TechniquesNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- Routine Mid Trimester Fetal UltrasoundDocument17 pagesRoutine Mid Trimester Fetal UltrasoundCharlotte QuintanaNo ratings yet
- GTG 55 Late Intrauterine Fetal Death and Stillbirth 10 11 10-2Document33 pagesGTG 55 Late Intrauterine Fetal Death and Stillbirth 10 11 10-2fahlevyNo ratings yet
- 03-First Trimester UsgDocument103 pages03-First Trimester UsgBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis With Salpingitis Simulating Acute AppendicitisDocument20 pagesEndometriosis With Salpingitis Simulating Acute AppendicitisWyendae CliquersNo ratings yet
- Doppler in ObstetricsDocument13 pagesDoppler in ObstetricsPrajakta TumbareNo ratings yet
- 2023 - Acute Abdomen During Pregnancy (Goran Augustin)Document1,050 pages2023 - Acute Abdomen During Pregnancy (Goran Augustin)César EscobarNo ratings yet
- WeBSurg Winners 42 1Document129 pagesWeBSurg Winners 42 1Ana Adam100% (1)
- SmartXide DOT - Clinical User Manual v.2.2 PDFDocument44 pagesSmartXide DOT - Clinical User Manual v.2.2 PDFAlfredo Altamirano Linares100% (5)
- 1 First Trimester UltrasonographyDocument17 pages1 First Trimester UltrasonographyClaudia Paola Salazar SanchezNo ratings yet
- Diabetic FootDocument22 pagesDiabetic FootNaikko80100% (1)
- Anomalies of Fetal Cardiac SystemDocument42 pagesAnomalies of Fetal Cardiac SystemNishant RajNo ratings yet
- Pop, RevDocument139 pagesPop, RevYusof AndreiNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Vault ProlapseDocument9 pagesVaginal Vault ProlapseOanaNo ratings yet
- Radiation TherapyDocument9 pagesRadiation TherapyNica PinedaNo ratings yet
- Control of Insects and RodentsDocument21 pagesControl of Insects and RodentsZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Approach To An Unconscious PatientDocument62 pagesApproach To An Unconscious Patientangiolikkia80% (5)
- Urodynamics: Committee 7Document56 pagesUrodynamics: Committee 7Coral Garcia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Class XI Biology Support MaterialDocument248 pagesClass XI Biology Support MaterialPranav Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Queenan's Management of High-Risk Pregnancy: An Evidence-Based ApproachFrom EverandQueenan's Management of High-Risk Pregnancy: An Evidence-Based ApproachNo ratings yet
- Surgery For Male InfertilityDocument8 pagesSurgery For Male InfertilityAkhmad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction System 1Document48 pagesReproduction System 1SITI AISYAHNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityFrom EverandHandbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityMichael H. DahanNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial AbnormalitiesDocument12 pagesCraniofacial Abnormalitiesnpr00No ratings yet
- Vascular Disorders StudentsDocument70 pagesVascular Disorders StudentsedwinNo ratings yet
- Sof MarkersDocument21 pagesSof MarkersHari NairNo ratings yet
- IPD Patient History ChecklistDocument2 pagesIPD Patient History ChecklistdrjriNo ratings yet
- Ad en Om Yo SisDocument6 pagesAd en Om Yo SisMariaa EndahhNo ratings yet
- E.O 51Document7 pagesE.O 51Lezirk SuercNo ratings yet
- Placenta Iugr PDFDocument298 pagesPlacenta Iugr PDFM Iqbal EffendiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nephrology and Urology DR Samed AlsalmiDocument268 pagesPediatric Nephrology and Urology DR Samed AlsalmitemisedwinNo ratings yet
- Sonography of GITDocument11 pagesSonography of GITsononik1674100% (1)
- Use of Anticoagulants During Pregnancy and Postpartum - UpToDateDocument38 pagesUse of Anticoagulants During Pregnancy and Postpartum - UpToDateCristinaCaprosNo ratings yet
- SkeletaxrayDocument144 pagesSkeletaxrayradiologgNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury (OASIS) - UpToDateDocument39 pagesObstetric Anal Sphincter Injury (OASIS) - UpToDateErickNo ratings yet
- Bosniak ClassificationDocument19 pagesBosniak ClassificationGirish Kumar100% (1)
- 2018 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Cardiovascular Disease in PregnancyDocument84 pages2018 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancyasm obginNo ratings yet
- Twins Discharge SummaryDocument3 pagesTwins Discharge Summarynandipati ramnadhNo ratings yet
- Management of Monochorionic Twin Pregnancy: Green-Top Guideline No. 51Document13 pagesManagement of Monochorionic Twin Pregnancy: Green-Top Guideline No. 51indra_strongNo ratings yet
- Germ Cell TumoursDocument32 pagesGerm Cell Tumoursapi-3705046No ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Management of Endometrioma: Tarek A Gelbaya, Luciano G NardoDocument10 pagesEvidence-Based Management of Endometrioma: Tarek A Gelbaya, Luciano G NardofebrianoramadhanaNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Risk of Malignancy in Adnexal Masses Based On IOTA AJOG 2016Document14 pagesPredicting The Risk of Malignancy in Adnexal Masses Based On IOTA AJOG 2016Fernando Suarez ChumaceroNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tools in ObgynDocument27 pagesDiagnostic Tools in ObgynHenok Y KebedeNo ratings yet
- Cheng-Taiwan NHI at TwentyDocument9 pagesCheng-Taiwan NHI at TwentyariNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument71 pagesAcute AbdomenariNo ratings yet
- Syok Dalam KebidananDocument32 pagesSyok Dalam KebidananariNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument71 pagesAcute AbdomenariNo ratings yet
- 1st AffirDocument2 pages1st AffirariNo ratings yet
- My Good Boy (Hentai Manga) AnthologyDocument92 pagesMy Good Boy (Hentai Manga) AnthologyariNo ratings yet
- Nyx, A Noctournal - 8: SkinDocument158 pagesNyx, A Noctournal - 8: SkinNyx, a noctournalNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Intoxication and ToxicoinfectionsDocument73 pagesFoodborne Intoxication and ToxicoinfectionsAyuIrhoniRosadiNo ratings yet
- Health 8: Learning Activity SheetsDocument16 pagesHealth 8: Learning Activity SheetsDonalyn Veruela AbonNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Filarial Worms (PG 30-38)Document38 pages2.4 Filarial Worms (PG 30-38)Rj RiveraNo ratings yet
- HerpanginaDocument8 pagesHerpanginaWendy Nadya Vitasani HalohoNo ratings yet
- Lec 7proteus SPPDocument22 pagesLec 7proteus SPPbujalkanNo ratings yet
- TAREA 13 Safety Data Sheet For Quality SpecimensDocument5 pagesTAREA 13 Safety Data Sheet For Quality SpecimensRosa CanahuiNo ratings yet
- Vetcare Kenya - Tylo - Doxy 200WSPDocument2 pagesVetcare Kenya - Tylo - Doxy 200WSPHerman NdauNo ratings yet
- CH. 26 Microbial Diseases of The Urinary and Reproductive SystemsDocument3 pagesCH. 26 Microbial Diseases of The Urinary and Reproductive SystemstkanesNo ratings yet
- INTEGMED1Document17 pagesINTEGMED1Nica RTNo ratings yet
- Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences: Bacterial Contamination of Personal Mobile Phones in IraqDocument1 pageJournal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences: Bacterial Contamination of Personal Mobile Phones in IraqarialNo ratings yet
- 6-Moehring-SPICE-Antibiotic-use-2019 ANTIBIOTICS HAIS 2020Document67 pages6-Moehring-SPICE-Antibiotic-use-2019 ANTIBIOTICS HAIS 2020SIUSANTO HadiNo ratings yet
- Fever and Rash in The Immunocompetent PatientDocument62 pagesFever and Rash in The Immunocompetent PatientsunilchhajwaniNo ratings yet
- Pityrosporum FolliculitisDocument3 pagesPityrosporum Folliculitisshivam18No ratings yet
- Susceptible Exposed Infected Recovery (SEIR) Model With Immigration: Equilibria Points and Its ApplicationDocument8 pagesSusceptible Exposed Infected Recovery (SEIR) Model With Immigration: Equilibria Points and Its ApplicationAkhmad Riki FadilahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Module1 SDLDocument88 pagesModule1 SDLbillboggins100% (1)
- PHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesDocument89 pagesPHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesLina RamojNo ratings yet
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument6 pagesChronic PyelonephritisKaustav JainNo ratings yet
- SANGUINARIA Polygonum AviculareDocument7 pagesSANGUINARIA Polygonum AviculareBiol. Miguel Angel Gutiérrez DomínguezNo ratings yet