Professional Documents
Culture Documents
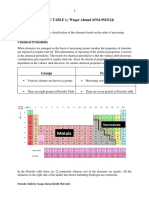
The Alkali Metals v1.0
Uploaded by
Anna Corti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views39 pagesm
Original Title
12. the Alkali Metals v1.0
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views39 pagesThe Alkali Metals v1.0
Uploaded by
Anna Cortim
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 39
1 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
2 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Where are the alkali metals?
The elements in group 1, on the left of the periodic table,
are called the alkali metals.
lithium Li
sodium Na
potassium K
rubidium Rb
caesium Cs
francium Fr
These metals are all very reactive and are rarely found in
nature in their elemental form.
3 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the alkali metals?
4 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Why are they called the alkali metals?
The alkali metals are so
reactive that, as elements,
they have to be stored in
oil. This stops them reacting
with oxygen in the air.
The alkali metals are unlike
most other metals, which
are usually hard and dense.
Alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife, and the
most common alkali metals, lithium, sodium and potassium,
all float on water.
The elements in group 1 also react with water and form
alkaline compounds. This is why they are called alkali metals.
5 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is the electron structure of alkali metals?
The alkali metals all have one electron in their outer shell.
This means that:
lithium
They are found in group 1 2,1
of the periodic table.
They have similar
physical and chemical sodium
properties. 2,8,1
They can readily lose
the outer shell electron
to form positive ions potassium
with a +1 charge and a 2,8,8,1
full outer shell.
6 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do you identify alkali metals?
7 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
8 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the properties of the alkali metals?
The characteristic properties of the alkali metals are:
They are soft and can be cut by a knife.
Softness increases going down the group.
They have a low density.
Lithium, sodium and potassium float on water.
They have low melting and boiling points.
These properties mean that the alkali metals are different to
typical metals. However, alkali metals do also share some
properties with typical metals:
They are good conductors of
heat and electricity.
They are shiny. This is only seen
when alkali metals are freshly cut.
9 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is the trend in density?
The alkali metals generally become more dense going down
the group, but the trend is not perfect because potassium is
less dense than sodium.
Element Density (g/dm3)
lithium 0.53
sodium 0.97
potassium 0.86
rubidium 1.53
caesium 1.87
Water has a density of 1 g/dm3.
Which elements in group 1 will float on water?
10 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the trends in density?
11 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is the trend in melting and boiling point?
The melting points and boiling points of alkali metals
decrease going down the group.
Element Melting point (C) Boiling point (C)
lithium 181 1342
sodium 98 883
potassium 64 760
rubidium 39 686
caesium 28 671
The melting and boiling points decrease going down group 1
because the atoms get larger. In each metallic structure, the
attraction between the positive metal ions and the delocalized
sea of electrons gets weaker and so they become easier to
melt, and to boil.
12 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the trends in melting point?
13 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the trends in boiling point?
14 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Properties of alkali metals quiz
15 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
16 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do the alkali metals react with oxygen?
All alkali metals react with oxygen in the
air to form metal oxides. This produces
a layer of dull oxide on the surface of the
metal, called tarnish.
The speed with which alkali metals react
with oxygen in the air increases going
down the group:
lithium tarnishes slowly
sodium tarnishes quickly
potassium tarnishes very quickly.
Why are alkali metals stored in oil?
The oil prevents them from reacting with
oxygen and tarnishing.
17 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is the equation for the reaction with oxygen?
The reaction between an alkali metal and oxygen is an
example of an oxidation reaction:
alkali metal + oxygen alkali metal oxide
The word and chemical equations for the reaction between
lithium and oxygen are:
lithium + oxygen lithium oxide
4Li (s) + O2 (g) 2Li2O (s)
What are the word and chemical equations for the reaction
that causes sodium to tarnish?
sodium + oxygen sodium oxide
4Na (s) + O2 (g) 2Na2O (s)
18 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do the alkali metals react with water?
19 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What does the reaction with water produce?
All the alkali metals react vigorously with water.
The reaction with water becomes more vigorous as you go
down the group.
It is an exothermic reaction as it releases a lot of heat.
The reaction produces a gas that ignites a lighted splint with
a squeaky pop. What is this gas?
When green universal indicator
is added to the reaction mixture,
it turns purple.
What does this tell you about
the products of this reaction?
20 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is the equation for the reaction with water?
This reaction creates alkaline hydroxide ions.
This is why the group 1 elements are called the alkali metals.
The general equation for the reaction between an alkali
metal reacting with water is:
alkali metal + water alkali metal + hydrogen
hydroxide
2M(s) + 2H2O(l) 2MOH (aq) + H2(g)
21 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How does lithium react with water?
Lithium is the least reactive of
the alkali metals.
When added to water, it fizzes
and moves around slowly
across the surface of the water.
What is the equation for
this reaction?
lithium + water lithium + hydrogen
hydroxide
2Li (s) + 2H2O (l) 2LiOH (aq) + H2 (g)
22 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How does sodium react with water?
When added to water, sodium fizzes more than lithium, and
moves quickly across the surface of the water.
The sodium melts as it
reacts, and it becomes
spherical and shiny, like
a ball bearing.
The hydrogen sometimes
catches fire because of
the heat from the reaction.
What is the equation for this reaction?
sodium + water sodium + hydrogen
hydroxide
2Na (s) + 2H2O (l) 2NaOH (aq) + H2 (g)
23 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How does potassium react with water?
When added to water, the
potassium moves across the
surface of the water very quickly.
The reaction produces so much
heat that the hydrogen given off
catches alight.
What colour would the flame be?
Like sodium, it melts with the heat of the reaction.
What is the equation for this reaction?
potassium + water potassium + hydrogen
hydroxide
2K (s) + 2H2O (l) 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
24 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do alkali metals react with water?
Which of the alkali metals will react most strongly with water?
25 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How does electron structure affect reactivity?
The reactivity of alkali metals increases going down the
group. What is the reason for this?
The atoms of each element get larger
Li going down the group.
increase in reactivity
This means that the outer shell electron
gets further away from the nucleus and
Na is shielded by more electron shells.
The further an electron is from the
positive nucleus, the easier it can be
lost in reactions.
K This is why the reactivity of the alkali
metals increases going down group 1.
26 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is the order of reactivity?
27 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do alkali metals react with chlorine?
Alkali metals burst into flames when heated and added to
chlorine. They form metal chlorides.
alkali metal + chlorine alkali metal chloride
The word and chemical equations for the reaction between
lithium and chlorine are:
lithium + chlorine lithium chloride
2Li (s) + Cl2 (g) 2LiCl (s)
What are the word and chemical equations for the reaction
that produces sodium chloride?
sodium + chlorine sodium chloride
2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) 2NaCl (s)
28 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
True or false?
29 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
30 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the uses of alkali metals?
How many uses of alkali metals can you see below?
31 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the uses of alkali metals?
32 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are the uses of alkali metals?
33 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
34 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Glossary
alkali metal An element that belongs to group 1 of the
periodic table.
exothermic A reaction that releases heat into its
surroundings.
metal chloride The type of solid produced when an
alkali metal is burned in chlorine gas.
metal hydroxide The type of alkali produced by the
reaction between an alkali metal and water.
metal oxide The type of solid produced when an alkali
metal reacts with oxygen.
oxidation The process by which a substance reacts and
combines with oxygen.
tarnish The discolouration of metal after exposure to air
caused by the formation of an oxide on the metals surface.
35 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Anagrams
36 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Completing alkali metal equations
37 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Comparing reactivity with water
38 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Multiple-choice quiz
39 of 39 Boardworks Ltd 2007
You might also like
- Alkali MetalsDocument32 pagesAlkali MetalsGhana Cintai DiaNo ratings yet
- Alkali MetalsDocument31 pagesAlkali Metalsromiifree100% (1)
- The Reactivity Series PDFDocument33 pagesThe Reactivity Series PDFSandipan Chakraborty100% (1)
- The Halogens v1.0Document37 pagesThe Halogens v1.0Supadi Rahdi100% (1)
- © Boardworks LTD 2006 1 of 37Document37 pages© Boardworks LTD 2006 1 of 37Kate ParanaNo ratings yet
- © Boardworks LTD 2008 1 of 35Document35 pages© Boardworks LTD 2008 1 of 35xatolom719No ratings yet
- 5 ElectricalSignalsDocument42 pages5 ElectricalSignalsIsabel Iglesias QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Classification - 2015Document22 pagesClassification - 2015randyhmthsNo ratings yet
- KS4 Biology: AdaptationDocument21 pagesKS4 Biology: AdaptationHanifa Uly AmrinaNo ratings yet
- 2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Document84 pages2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Listiyaning TiasNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument33 pagesEquilibriumGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity BoardworksDocument27 pagesElasticity BoardworksMurugan.SubramaniNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument34 pagesOpticsdiane hoylesNo ratings yet
- Are Very Large Molecules Made When Hundreds of Join Together To Form Long ChainsDocument23 pagesAre Very Large Molecules Made When Hundreds of Join Together To Form Long ChainsAlaa Al HamedNo ratings yet
- The Halogens v1.0Document37 pagesThe Halogens v1.0asdfghjNo ratings yet
- Heating and CoolingDocument45 pagesHeating and CoolingGillianne AndradeNo ratings yet
- KS4 Transition MetalsDocument16 pagesKS4 Transition MetalsIsabel Iglesias QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Boardworks Earth and Its Resources W8Document7 pagesBoardworks Earth and Its Resources W823_11_1993No ratings yet
- Making Polymers v2.0Document43 pagesMaking Polymers v2.0Ricki HanNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Shapes of Molecules and IonsDocument33 pages2.3 Shapes of Molecules and IonsjtNo ratings yet
- PolymerisationDocument9 pagesPolymerisationeeenusNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ChemistryDocument56 pagesQuantitative ChemistryMuddamsetty ArunkalyanNo ratings yet
- GCSE Active TransportDocument10 pagesGCSE Active TransportNoel Johansen-BergNo ratings yet
- The KidneysDocument27 pagesThe KidneysleanneNo ratings yet
- 8K LightDocument47 pages8K Lightraba10067% (3)
- Forces - Speed and AccelerationDocument32 pagesForces - Speed and Accelerationrobin biswasNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science Exam Revision Answers - Sets 1-5Document33 pagesYear 9 Science Exam Revision Answers - Sets 1-5KassyKasNo ratings yet
- Pressure and MomentsDocument48 pagesPressure and MomentsDessy Norma JuitaNo ratings yet
- 9l Pressure and MomentsDocument37 pages9l Pressure and Momentsyara aliNo ratings yet
- KS3 Physics: Electromagnets ExplainedDocument29 pagesKS3 Physics: Electromagnets ExplainedPoornimaNo ratings yet
- KS4 Radioactive DecayDocument31 pagesKS4 Radioactive DecayJaleel James100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Part 1 - Enthalpy ChangesDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Part 1 - Enthalpy ChangesYacineNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument50 pagesNutrientsThomas YeNo ratings yet
- How leaves and roots help photosynthesisDocument16 pagesHow leaves and roots help photosynthesisfarahNo ratings yet
- 2.12 Mass Spectra and IRDocument30 pages2.12 Mass Spectra and IRSandyDavidNo ratings yet
- 4.4 How Far - EntropyDocument43 pages4.4 How Far - EntropyMehreenSaeedNo ratings yet
- Halogen Oal KanesDocument31 pagesHalogen Oal KanesEhab MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Organic-Synthesis & ChiralityDocument34 pagesOrganic-Synthesis & ChiralityAlaa Al HamedNo ratings yet
- KS4 Metallic BondingDocument17 pagesKS4 Metallic BondingGian CarloNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures: Diamond, Graphite, SilicaDocument6 pagesGiant Covalent Structures: Diamond, Graphite, Silicadhshah281100% (1)
- Biotechnology - FermentationDocument17 pagesBiotechnology - FermentationsilNo ratings yet
- Reactions of AcidsDocument47 pagesReactions of AcidsjtNo ratings yet
- Space (Part 1)Document33 pagesSpace (Part 1)Murugan.SubramaniNo ratings yet
- 1 of 9 © Boardworks LTD 2015Document9 pages1 of 9 © Boardworks LTD 2015Ajay PawarNo ratings yet
- Resistance and ResistivityDocument31 pagesResistance and Resistivityapi-247243068No ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument30 pagesAnalytical ChemistrySakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2.11 MechanismDocument38 pages2.11 MechanismAmber Michaels100% (1)
- Acids and AlkalisDocument17 pagesAcids and AlkalisSumi VjNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument39 pagesReversible ReactionsjtNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion RotDocument53 pagesLaws of Motion RotGyrot Gan100% (1)
- DynamicsDocument28 pagesDynamicsChaiseNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic ScreeningDocument49 pagesGas Exchange Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic Screeningmlk100% (1)
- Theories About The UniverseDocument8 pagesTheories About The UniverseAllan Jay DaligdigNo ratings yet
- Covalent StructuresDocument11 pagesCovalent StructuresjtNo ratings yet
- Lenses 1Document13 pagesLenses 1Yuni MuliaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 7 Alkali MetalsDocument24 pagesForm 2 7 Alkali MetalsHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- The Alkali Metals: © Boardworks LTD 2005Document25 pagesThe Alkali Metals: © Boardworks LTD 2005MuflihunNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument9 pagesPeriodic TableXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Elements in Group 1Document7 pagesElements in Group 1winkeugingieNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Coronation Egg 1897Document2 pagesCoronation Egg 1897Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Final Timetable 2018 v5Document1 pageYear 11 Final Timetable 2018 v5Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- 0620 s17 Ms 42Document9 pages0620 s17 Ms 42Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- Cheesecakes Pavlovas Trifles by The Australian Women S Weekly PDFDocument35 pagesCheesecakes Pavlovas Trifles by The Australian Women S Weekly PDFAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- 0620 s17 Ms 41Document7 pages0620 s17 Ms 41Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- Hint: Think Whether The Collision Is Inelastic or ElasticDocument1 pageHint: Think Whether The Collision Is Inelastic or ElasticAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- Basic Radiographic PrinciplesDocument93 pagesBasic Radiographic PrinciplesOdalis Lizeth Zamora100% (2)
- 0620 s17 Ms 41Document7 pages0620 s17 Ms 41Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- Classified Chemistry CombinedDocument130 pagesClassified Chemistry CombinedMaaz Rashid87% (15)
- 0610 s07 QP 6 PDFDocument12 pages0610 s07 QP 6 PDFAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- Maths Question Paper Winter: 0580 - w02 - QP - 4Document8 pagesMaths Question Paper Winter: 0580 - w02 - QP - 4petal100% (1)
- Vectors Additional Maths Oxford Textbook 2Document14 pagesVectors Additional Maths Oxford Textbook 2Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- Matrices Additional Maths Oxford Textbook 2Document17 pagesMatrices Additional Maths Oxford Textbook 2Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- Classified Chemistry CombinedDocument130 pagesClassified Chemistry CombinedMaaz Rashid87% (15)
- Chapter 2Document16 pagesChapter 2Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- GP Micro MCQ PDFDocument8 pagesGP Micro MCQ PDFAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Micro 07 AnsDocument7 pagesExam 1 Micro 07 AnsAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) Paper 2Document35 pages(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) Paper 2Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- 9H Using Chemistry SATS QDocument15 pages9H Using Chemistry SATS QAnna CortiNo ratings yet
- 02 - Extracellular Matrix - Proteoglycans - Glycosaminoglycans and Structural Glycoproteins 2Document67 pages02 - Extracellular Matrix - Proteoglycans - Glycosaminoglycans and Structural Glycoproteins 2Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- KS4 FR Grammar Worksheets - 2Document52 pagesKS4 FR Grammar Worksheets - 2Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- Solcart B PDFDocument8 pagesSolcart B PDFMohammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric Acid MSDSDocument1 pageSulphuric Acid MSDSGermán Cárdenas AlvarezNo ratings yet
- MADE EASY ONLINE TEST SERIES SOLUTIONSDocument26 pagesMADE EASY ONLINE TEST SERIES SOLUTIONSvenkateshNo ratings yet
- BLOCK DATA AlloycraftDocument104 pagesBLOCK DATA Alloycraftv2vcoderNo ratings yet
- Creep Damage and Expected Creep LifeDocument9 pagesCreep Damage and Expected Creep LifeTrương Ngọc SơnNo ratings yet
- CNG Tank DevelopmentDocument98 pagesCNG Tank Developmentjunrey paracuellesNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopDocument30 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopJeannie UyNo ratings yet
- Upvc SWR Pipes PDFDocument7 pagesUpvc SWR Pipes PDFalmig200No ratings yet
- Fisa Tehnica PVC OptimaDocument2 pagesFisa Tehnica PVC OptimaIon SaispeNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodeDocument8 pagesSemiconductor DiodeAshvani ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Determination of AshDocument7 pagesExperiment 7: Determination of AshhasifahNo ratings yet
- Pemisahan Katoda AnodaDocument11 pagesPemisahan Katoda AnodaHamdi Zae malikNo ratings yet
- Oxidations With Cerium Sulphate SolutionsDocument4 pagesOxidations With Cerium Sulphate Solutionsliz_hobbs79No ratings yet
- Aroclor 1232Document48 pagesAroclor 1232mcreadmailNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Lesson 2:mineralsDocument55 pagesEarth and Life Science Lesson 2:mineralsRoldan Bibat BoresNo ratings yet
- Comparative study of concrete mix design by adding various types of admixturesDocument6 pagesComparative study of concrete mix design by adding various types of admixturesSagarNo ratings yet
- Fiche Technique Joint SpiraleDocument1 pageFiche Technique Joint SpiraleHakima DermecheNo ratings yet
- Stack: Prof. Osama El MasryDocument28 pagesStack: Prof. Osama El MasryRyanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Stage 3 Exam 2012Document40 pagesChemistry Stage 3 Exam 2012Naomi David NewNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fly Ash On Engineering Properties of Expansive SoilsDocument4 pagesEffect of Fly Ash On Engineering Properties of Expansive SoilsBasha FayissaNo ratings yet
- Production Report November 2021Document9 pagesProduction Report November 2021nasir ahmedNo ratings yet
- Tablet and Capsule ManufacturingDocument28 pagesTablet and Capsule ManufacturingShibaprasad DandapatNo ratings yet
- Thesis FulltextDocument472 pagesThesis FulltextBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mastertop 564Document2 pagesMastertop 564Doby YuniardiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Total AlkalinityDocument4 pagesLab Manual-Total AlkalinitySuvanka DuttaNo ratings yet
- 2 KV AL Cable Datasheet - Priority CablesDocument1 page2 KV AL Cable Datasheet - Priority CablesVipin KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Module I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Document9 pagesModule I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Suriati Bt A RashidNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 NeutralizationDocument32 pagesLec 8 Neutralizationhaseeb tahirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry o Level NotesDocument11 pagesChemistry o Level NotesThaboooNo ratings yet
- EPS 2011 - 04. Overview of NCHRP Design Guideline For EPS Block Geofoam in Slope Stabilization and RepairDocument46 pagesEPS 2011 - 04. Overview of NCHRP Design Guideline For EPS Block Geofoam in Slope Stabilization and RepairSaid SaGaNo ratings yet