Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 WCDMA RNP CW Test and Propagation Model Tuning
Uploaded by
mamangmoriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 WCDMA RNP CW Test and Propagation Model Tuning
Uploaded by
mamangmoriCopyright:
Available Formats
Internal
WCDMA RNP CW Test
and Propagation Model
Tuning
www.huawei.com
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 1
Introduction
CW test (Continuous Wave test) is an
important step of Propagation Model Tuning.
According to the CW test data (including
latitude/longitude and received level) and
corresponding Digital maps, we can get the
accurate Propagation Model through tuning.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 2
CONTENT
Chapter 1 Principle of Radio Propagation
and CW Test
Chapter 2 CW Test Flow
Chapter 3 Analysis of CW Test Data
Chapter 4 Propagation Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 3
Principle of Radio Propagation and CW Test
Section 1 Basic Principle of Radio
Propagation
Section 2 Principle of
Propagation Model Tuning
Section 3 Purpose of CW Test
Section 4 Basic Principle of CW
Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 4
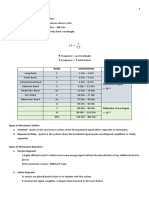
Radio Waveband Classification
Frequency Classification Designation
3-30Hz
30-300Hz Extremely Low ELF
Frequency
300-3000Hz Voice Frequency VF
3-30KHz Very-low Frequency VLF
30-300KHz Low Frequency LF
300-3000KHz Medium Frequency MF
3-30MHz High Frequency HF
30-300MHz Very High Frequency VHF
300-3000MHz Ultra High Frequency UHF
3-30GHz Super High Frequency SHF
30-300GHz Extremely High EHF
Frequency
300-3000GHz
Frequencies in different bands have different propagation characteristics.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 5
Generation of Electromagnetic Wave
Based on Maxwell equations set:
The variable magnetic field can excite eddy electric field and variable electric field can also
excite eddy magnetic field.
Continuous electromagnetic oscillation (electromagnetic wave) forms due to mutual
excitation of alternating electric and magnetic field.
The speed of electromagnetic wave only varies with electric and magnetic characteristics of
medium. The propagation speed of electric microwave in vacuum equals that of light in
vacuum.
Light and electromagnetic wave are essentially the same. Light is electromagnetic wave of a
certain wavelength.
Oscillator
Magnetic field
Magnetic field
Electric field Electric field Electric field
Transmission direction of electric wave
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 6
Propagation Path
Perpendicular incidence wave Troposphere reflection wave
and ground reflection wave (the propagation is very random)
(most common propagation modes)
Ionosphere refraction wave
Mountain diffraction wave (beyond-the-horizon communication path)
(shadow area signal source)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 7
Propagation of Electromagnetic Wave
Ripple in the pond: Energy is propagated around from the source point and
gradually weakens.
Electromagnetic wave is similarly propagated except that (when the radiation source
is isotropically effective ideal point source):
It is propagated in the form of spherical wave in three-dimension space.
The propagation media are different, including air, obstacle and reflector.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 8
Characteristics of Radio Propagation
Electric wave propagation system LOS and NLOS
of Land Mobile Communications
Radio propagation
in actual
Reflected wave of building
environment Diffracted wave
Direct wave
Reflected wave on the ground
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 9
Characteristics of Radio Channels
Pr (dBm) Fast fading
Radio channels vary with
users position and time. Slow fading
-20
Multipath scattering and
obstruction result in
acute changes to -40
received power.
Slow fading
-60
Attenuation: Pr is in direct
proportion to 1/dn.
Shadow: obstructed by barriers
Fast fading 10 20 30 d (m)
Multipath effect
Fast changes to signal
strength at small distance
and time interval
Doppler frequency shift
Delay spread
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 10
Diversity Technology
Measures against fast fading- diversity technologies
Explicit diversity
Space diversity
Polarization diversity
Frequency diversityGSM-frequency hopping; WCDMA-spread
spectrum
Implicit diversity
Implicit diversity uses signal processing technologies to hide
diversity functions into signals under transmission, such as RAKE
reception technology, interleaving and error code correction.
Regarded as time diversity
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 11
Delay Spread
Multipath propagation: Signals on different paths reach the receiver at
different time.
When the receiver fails to distinguish multipath signals, co-channel
interference (CCI) occurs. In the WCDMA system, only the multipath
delay larger than one chip period (0.26s) can be recognized.
Typical value (s): Open < 0.2, Suburban = 0.5, Urban = 3
Solutions Equalization and RAKE technology
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 12
Doppler Frequency Shift
Example of Doppler effect: A train is passing by you.
Doppler frequency shift in Mobile Communications
f1
f3
f2
V(km/h)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 13
Loss
Diffraction loss Penetration loss
T
R
R
Clutter loss
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 14
Penetration Loss
Indoor signals depend on penetration loss of building.
Signals are different at the indoor window and in the middle of room.
Building materials have great effect on penetration loss.
The reference angle of electromagnetic wave have great effect
on penetration loss.
d
w1 D w2
0 0
E2
0 0
E1
WdBm XdBm
Penetration loss=X-W=B dB Reflection and refraction of
electromagnetic wave through the
wall
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 15
Penetration Loss
Obstacle/penetration loss is:
Partition obstruction: 520dB
Floor obstruction: 20dB
Obstruction of furniture and other barriers: 215dB
Thick glass: 610dB
Penetration loss of the carriage of the train: 1530dB
Penetration loss of lift: 30dB or so
Loss of thick leaves: 10dB
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 16
Reflection Loss
Paddy City, mountain
Ground type Water Field
field and forest
Equivalent ground
0.91 0.60.8 0.30.5 0.10.2
reflection coefficient
Reflection loss (dB) 01 24 610 1420
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 17
Radio Propagation Environment
Radio propagation environment determines the propagation
models directly. And propagation environment is impacted by the
following factors:
Landform: mountain, hill, plain, waters, and vegetation
Clutter: building, road and bridge
Noise: natural noise and artificial noise
Climate: rain, snow and ice (tiny effect on UHF band)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 18
Radio Propagation Environment
Type of radio environment
Radio environment is classified as follows, according to ITU-R P.1411-1
and specific conditions in China.
Propagation
Description
environment
Many tall buildings, signals fail to diffract from the roof of
Dense urban
building .
Signals can diffract from the roof due to low buildings and wide
Urban
streets.
Suburban Low and sparse buildings
Rural Low and sparse buildings, but with lots of vegetation
Mountainous areas
Road
Indoor
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 19
Radio Propagation Environment
Type of propagation environment
The corresponding cell type is as follows:
Cell type Cell type Typical antenna installation
Installed outdoors, higher than average height of
Macro-cell >500 m
surrounding roofs
Installed outdoors, lower than average height of
Micro-cell 100~500m
surrounding roofs
Installed outdoors or indoors, lower than height of all
Pico-cell <100m
roofs
Type of other new cells, such as Mini-cell
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 20
Principle of Radio Propagation and CW Test
Section 1 Basic Principle of
Radio Propagation
Section 2 Theory of Propagation
Model Tuning
Section 3 Purpose of CW Test
Section 4 Basic Principle of CW
Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 21
Radio Propagation Model
Propagation model is used to predict the
effect of terrain,
obstacle and artificial environment on the
path loss.
WCDMA common propagation models
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 22
Radio Propagation Model
Common propagation models
Okumura/Hata model
For: 900M2000MHz
COST231-Hata model
For: 1500-2000MHz
COST231 Walfish-Ikegami model
For: 800M-2000MHz
Keenan-Motley model
For indoor propagation
Propagation model in UNET
For macro cell on 300M2000M
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 23
Radio Propagation Model
Model in UNET:
L=K1 + K2log(d) + K3log(HTxeff) + K4Diffraction
+ K5log(d)log(HTxeff) + K6(HRxeff) + Kclutterf(clutter)
K1: constant (dB)
K2: multiplier factor of log(d)
d: distance between Tx antenna and Rx antenna (m)
K3: multiplier factor of log(HTxeff)
HTxeff: effective height of Tx antenna (m)
K4: multiplier factor of diffraction loss, which must be a positive value
Diffraction loss: diffraction loss through the path with barriers (dB)
K5: multiplier factor of log(HTxeff)log(d)
K6: multiplier factor of HRxeff
HRxeff : effective height of Rx antenna (m)
Kclutter: multiplier factor of for f(clutter)
f(clutter): average weighted loss caused by clutter
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 24
Principle of Radio Propagation and CW Test
Section 1 Basic Principle of
Radio Propagation
Section 2 Theory of
Propagation Model Tuning
Section 3 Purpose of CW Test
Section 4 Basic Principle of
CW Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 25
Purpose of CW Test
GPS
Compare CW test data
with prediction results,
and then tune the
propagation parameters
to improve the accuracy
of coverage prediction.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 26
Principle of Radio Propagation and CW Test
Section 1 Basic Principle of
Radio Propagation
Section 2 Theory of
Propagation Model Tuning
Section 3 Purpose of CW Test
Section 4 Basic Principle of CW
Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 27
Basic Principle of CW Test
Typification
The CW test data must represent the characteristic of
electromagnetic wave in this area.
Balance
The CW test data must represent the characteristic of
electromagnetic wave by the proportion of different clutters
in this area.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 28
CONTENT
Chapter 1 Principle of Radio Propagation
and CW Test
Chapter 2 CW Test Flow
Chapter 3 Analysis of CW Test Data
Chapter 4 Propagation Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 29
CW Test Flow
Section 1 Site Selection
Section 2 Building Test
Platform in Networking
Section 3 Drive Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 30
Site Selection
Principles of site selection
Number of sites: It is usually agreed that a minimum of 5 sites should be
tested in large and dense city, but one site is enough in the city, which
mainly depends on antenna height and EIRP.
Representation: Site selection should aim to cover all types of clutter
(from the digital map) in the coverage zone.
Multiple models: Define the corresponding zone of each model if the test
environment requires multiple models to describe its propagation
characteristics.
Overlap: Increase measurement overlap area between each site as
much as possible. But reasonable inter-site distance should be ensured.
Obstacle: The data should be filtered in the subsequent processing if
obvious obstacle exists.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 31
Site Selection
Standards of site selection
a. Antenna height should be greater than 20m.
b. The antenna should be 5m higher than the nearest
obstacle.
c. The obstacle mainly refers to the highest building on the
roof where the antenna is installed. The building where the
site is located should be higher than average height of
surrounding buildings.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. Page 32
5m
HUAWEI Confidential
CW Test Flow
Section 1 Site Selection
Section 2 Building Test
Platform in Networking
Section 3 Drive Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 33
Building Test Platform in Networking
Tx subsystem: Tx antenna, feeder, high-frequency signal source and
antenna holder
Rx subsystem: test receiver, GPS receiver, test software and laptop
Tx antenna
Signal source TMA
RF cable 1 RF cable 2
Rx antenna Drive test
instrument Laptop
Power supply Build-in GPS
High frequency signal
source
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 34
Building Test Platform in Networking
Record the gain of the following parts on signals
during networking:
Tx power of signal source
Loss of RF cable
Gain of Tx antenna
Gain of Rx antenna
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 35
CW Test Flow
Section 1 Site Selection
Section 2 Building Test
Platform in Networking
Section 3 Drive Test
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 36
Drive Test
Keep to the following standards to select a test path
Landform: The test route must cover all main landforms in the area.
Height: The test route must cover landforms with different height in this area
if the landforms are up-and-down.
Distance: The test route must cover different positions from the site in the
area.
Direction: The test points must be consistent on the horizontal and vertical
route.
LengthThe total distance of one CW test should be longer than 60km.
Number of test points: The more, the better.
Overlap: Overlap the test route in different sites as much as possible to
improve the reliability of models.
Obstacle: Shadow areas behind this wall should be avoided when antenna
signals are obstructed by the wall at a side.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 37
Drive Test
Lee criteria for sampling: 50 samples by 40
The maximum vehicle speed: Vmax=0.8/Tsample
Delete test results from the sampled data under abnormal
conditions:
Fading over 15~30db without reasonable
causes
In tunnels
Under the viaducts
Select test routes from the main lobe coverage area if directional
antennas are adopted for a CW test.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 38
CONTENT
Chapter 1 Principle of Radio Propagation
and CW Test
Chapter 2 CW Test Flow
Chapter 3 Analysis of CW Test Data
Chapter 4 Propagation Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 39
Analysis of Test Data
Section 1 Data Filtering
Section 2 Data Dispersion
Section 3 Data Binning
Section 4 Format Conversion
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 40
Data Filtering
Data to be filtered is as follows:
1. Data tested in the places where
GPS is unable to locate accurately
(such as under the overhead rack,
in the tunnel).
2. Data obtained when the distance
to antenna is too near or far.
3. Data obtained with too weak
signals.
4. Error data caused by inexact AP
(antenna pattern).
5. Other data inconsistent with the
requirements during the route
design of CW test.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 41
Analysis of Test Data
Section 1 Data Filtering
Section 2 Data Dispersion
Section 3 Data Binning
Section 4 Format Conversion
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 42
Data Dispersion
Propagation in mobile communications can be indicated as
follows:
x L
1
r(x) = m(x)r0(x) m( x)
2L xL
r ( y)dy
X: distance
r(x): received signals
r0(x): Raileigh Fading
m(x): local mean value, the combination of long-term fading
and space propagation loss
2L: average length between sampling areas, also called
intrinsic length
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 43
Data Dispersion
The CW test is to obtain the local mean value of each geography
location in some areas as far as possible, i.e. the difference of r(x) and
m(x) should be the minimum value. In this sense, effect of Raileigh
Fading should be excluded.
When the intrinsic length equals 40 wavelength and the number of
sampling points is 50, the difference of test data and actual local mean
value can be less than 1dB according to Lee criteria.
Intrinsic length is average length for binning (2G band is 6 m long,
namely, 40 wavelength)
Since the locating speed of GPS is far lower than the receiving
speed of the receiver, the dispersion processing is required before the
binning.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 44
Data Dispersion
The principle of dispersion processing is as follows:
Conditions:
There are many test records arranged under each locating
point in time sequence because the receiving speed of the
receiver is far higher than the locating speed of GPS.
The vehicle speed between two locating points is uniform.
The time interval between every two measurement records is
the same.
Processing:
Equally distribute these records to the route section between
two points in time sequence so that there will be sufficient
points in every 6m range on test route.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 45
Analysis of Test Data
Section 1 Data filtering
Section 2 Data Dispersion
Section 3 Data Binning
Section 4 Format Conversion
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 46
Data Binning
Objectives:
Reserve the impact of slow fading but eliminate the fast
fading
Methods:
Method 1: make grids for the whole area with 6m side,
perform the arithmetic average for the data located in each
grid, and then take the grid center as the new location.
Method 2: divide the path into sections in equal interval
with 6m for each, and perform the arithmetic binning for the
data in each section to select some point for the location of
mean value.
Tool: CW Data Editor
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 47
Analysis of Test Data
Section 1 Data Filtering
Section 2 Data Dispersion
Section 3 Data Binning
Section 4 Format Conversion
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 48
Format Conversion
The data format exported by Agilent E74xx Series is
X Y CW_Power_List__ CW_Power_List__A Time Date
Freq__Hz mpl__dBm
Data format imported to UNET is
X Y CW_Power_List__Ampl__dBm
Format conversion can be implemented manually (saved
as .dat file)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 49
CONTENT
Chapter 1 Principle of Radio Propagation
and CW Test
Chapter 2 CW Test Flow
Chapter 3 Analysis of CW Test Data
Chapter 4 Propagation Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 50
Propagation Model Tuning
Section 1 Preparation
Section 2 Propagation Model
Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 51
Preparations
Installing network planning software:
UNET is powerful planning and optimization
software and model tuning is only one of its
functional modules.
Creating a project
In UNET, perform planning and optimization
model tuning based on each project.
Importing antenna pattern file
Correctly import the antenna pattern varying
with different manufacturers
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 52
Propagation Model Tuning
Section 1 Preparations
Section 2 Propagation
Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 53
Propagation Model Tuning Flow
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 54
Propagation Model Tuning
Establishing a model
Establish a standard macrocell model to be
tuned.
Select the effective antenna height.
Select a calculation method of diffraction
loss.
Importing data
Import CW test data file into the project.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 55
Propagation Model Tuning
Map correction
GPS locating in CW test usually adopts WGS84 and UTM
projection. However, digital maps in China do not use such
projections and reference plane. Correct digital maps if CW
test data does not correspond to them.
Correction method:
Correct four parameters on rectangular coordinates
in a digital map to realize the optimal match with the
test data.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 56
Propagation Model Tuning
Setting Filtering
Distance filtering:
Filter the data of which r is less than
150m or r is greater than 3000m.
Signal strength filtering:
Filter the data of which Signal is greater
than -40dBm or Signal is less than -
121dB.
Clutter filtering
Filter the Clutter in which sampling
points are less than 300.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 57
Propagation Model Tuning
Parameter tuning
L=K1 + K2log(d) + K3log(Heff) + 4Diffraction
+ K5log(d)log(HTxeff) + K6(HRxeff)
+ Kclutterf(clutter)
Tune such parameters as log(d), log(Heff),
Diff, log(d)log(Heff), Hmeff and Klutter to
finally tune SPM propagation model.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 58
Propagation Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 59
Propagation Model Tuning
ERROR (measurement prediction)
Regression line
calculated
values for the
variable
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 60
Propagation Model Tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 61
Propagation Model Tuning
Correction of propagation model parameters in a city
Parameter K Reference value
K1 23.2
K2 44.90
K3 5.83
K4 0.5
K5 -6.55
K6 0
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 62
Propagation Model Tuning
Analysis of correction results
Analyze correctness of the acquired model after
correction.
Evaluate the correctness of the model with Std Dev, which
refer to the binding degree of the acquired model and actual
test environment.
Make Std Dev less than 8 as much as possible in actual
model tuning, which indicates that the tuned model and
actual test environment are well bound.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 63
Summary
After completing this course, you should be able
to master:
Principle and purpose of CW test
Process of CW test
Process of propagation model tuning
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 64
Thank you
www.huawei.com
You might also like
- Frequency Modulation Theory: Application to Microwave LinksFrom EverandFrequency Modulation Theory: Application to Microwave LinksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 03 WCDMA RNP CW Test and Propagation Model TuningDocument65 pages03 WCDMA RNP CW Test and Propagation Model TuningBruno AndradeNo ratings yet
- 02 WCDMA RNP CW Test and Propagation Model TuningDocument64 pages02 WCDMA RNP CW Test and Propagation Model TuningGudang MiloNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation Theory PDFDocument36 pagesRadio Propagation Theory PDFrasyidiNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Radio Propagation and Basic RF KnowledgeDocument83 pagesBasic Principles of Radio Propagation and Basic RF KnowledgeChristian ZapataNo ratings yet
- MW TXN and RTNDocument105 pagesMW TXN and RTNHAWLITUNo ratings yet
- Fun Intro To EMS WorksheetDocument6 pagesFun Intro To EMS WorksheetgraceNo ratings yet
- MW TXN and RTNDocument102 pagesMW TXN and RTNgemedachikakoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Physical LayerDocument38 pagesLecture 3 Physical LayerBatool SajidaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Physical LayerDocument38 pagesLecture 3 - Physical LayerMuhammad Noman JavidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microwave Circuits & SystemsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Microwave Circuits & Systemsgetahun fentawNo ratings yet
- Mw&oce Mid-1Document119 pagesMw&oce Mid-1S K N JAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Radio Transmission Systems - Common - 11.9.5 - f2 - QUIZDocument72 pages01 Intro To Radio Transmission Systems - Common - 11.9.5 - f2 - QUIZMoctar MoumouniNo ratings yet
- Antenna and Wave Propagation: Prof. Pushpendra Singh BIT DurgDocument46 pagesAntenna and Wave Propagation: Prof. Pushpendra Singh BIT DurgDhiman DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 4 Part2Document61 pagesLecture Notes 4 Part2Huseyin OztoprakNo ratings yet
- Frequency Range ZyyadDocument33 pagesFrequency Range ZyyadsabirNo ratings yet
- Channel Models and Mitigation PDFDocument73 pagesChannel Models and Mitigation PDFkiraethio21No ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument86 pagesMicrowaveNathan KemboNo ratings yet
- The Principle of English)Document55 pagesThe Principle of English)sal_owudaNo ratings yet
- Digital Microwave Radios TUTORIALDocument43 pagesDigital Microwave Radios TUTORIALDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation Theory & Model TuningDocument28 pagesRadio Propagation Theory & Model TuningJesus Eduardo Flores100% (1)
- Transmissionmedia 140116100825 Phpapp01Document21 pagesTransmissionmedia 140116100825 Phpapp01Jyoti LakhaniNo ratings yet
- What Are Radio Frequency WavesDocument11 pagesWhat Are Radio Frequency WavesjackNo ratings yet
- 03 Wave PropagationDocument34 pages03 Wave Propagationwayneseal1No ratings yet
- Microwave Engg Notes-Unit 1Document14 pagesMicrowave Engg Notes-Unit 1devanga10% (2)
- RectangularWaveGuides by H V K KUMARDocument88 pagesRectangularWaveGuides by H V K KUMARkisu12No ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Radio Systems v4 - 0316 - T8.3Document45 pages01 Intro To Radio Systems v4 - 0316 - T8.3sunilpanda08No ratings yet
- Microwave Principles: Knowledge Service Dept. Microwave TeamDocument48 pagesMicrowave Principles: Knowledge Service Dept. Microwave TeamMoe Thet HninNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Introduction To Channel ModelingDocument7 pagesChapter Two: Introduction To Channel Modelinggashawbeza tayeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microwave & Satellite Technologies-1Document55 pagesFundamentals of Microwave & Satellite Technologies-1Rodric PeterNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line TheoryDocument50 pagesTransmission Line Theorykhusnul khotimah100% (2)
- Microwave Engineering: S.Prabhu Das Associate Professor ECE DepartmentDocument196 pagesMicrowave Engineering: S.Prabhu Das Associate Professor ECE Departmentprabhudas ceccNo ratings yet
- 102 L4 PropDocument40 pages102 L4 PropB.R.J TestNo ratings yet
- Wave GuidesDocument33 pagesWave GuidesJoshua RefeNo ratings yet
- Photonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesDocument19 pagesPhotonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesSenjuti KhanraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Chapter 5 - Overview of Wireless Communication PDFDocument56 pagesLecture 5 - Chapter 5 - Overview of Wireless Communication PDFKeyNo ratings yet
- Pre-Dissertation On Analysis of Microwave Component (Waveguides) Using Available SoftwareDocument34 pagesPre-Dissertation On Analysis of Microwave Component (Waveguides) Using Available SoftwareApurva ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chap1 MicrowaveDocument17 pagesChap1 MicrowaveVamsi Krishna Dokku100% (1)
- Muhammad Umer Shehzad - Jawad FakhirDocument74 pagesMuhammad Umer Shehzad - Jawad Fakhirmohamed bilhageNo ratings yet
- Notes MSDocument16 pagesNotes MSPatricia SayamanNo ratings yet
- RAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010Document45 pagesRAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010zulianaNo ratings yet
- Notes-Radio Systems and Personal Communication Networks PDFDocument27 pagesNotes-Radio Systems and Personal Communication Networks PDFHaris HasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document40 pagesChapter 3 Part 1Behailu AsmareNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering - WaveguidesDocument1 pageMicrowave Engineering - Waveguideskozsef ebenNo ratings yet
- MW TransmissionDocument23 pagesMW Transmissionbonsatilahun1992No ratings yet
- Basic Propagation Principles of Radio Waves and Basic RF KnowledgeDocument83 pagesBasic Propagation Principles of Radio Waves and Basic RF Knowledgenarges5058100% (6)
- LF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Document29 pagesLF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Camilo Bazan HerediaNo ratings yet
- 4c4 Propagation ModelsDocument56 pages4c4 Propagation ModelsMelania DîmbeanuNo ratings yet
- Antenna & Propagation: by Nor Hadzfizah Binti Mohd Radi Faculty of Electric & Electronics EngineeringDocument17 pagesAntenna & Propagation: by Nor Hadzfizah Binti Mohd Radi Faculty of Electric & Electronics EngineeringDr-Ahmed ElkoranyNo ratings yet
- 1a. Review Radio TheoryDocument46 pages1a. Review Radio TheoryRhonny AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Urkund Report - Thesis (4) .Docx (D49086685)Document22 pagesUrkund Report - Thesis (4) .Docx (D49086685)pooja singhNo ratings yet
- MW Communication System in UMTS NetworksDocument84 pagesMW Communication System in UMTS NetworksshripalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 CDocument29 pagesLecture 1 CLohith NNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER Four: Wireless Networks PrinciplesDocument50 pagesCHAPTER Four: Wireless Networks Principlesachut achutNo ratings yet
- Question 5Document7 pagesQuestion 5nkugwa6brianNo ratings yet
- To Microwaves: TopicDocument43 pagesTo Microwaves: TopicBasavaraj ShellikeriNo ratings yet
- Page 1Document2 pagesPage 1krupa23No ratings yet
- Overview of Waveguides: Asmita Singhal Su/PdicDocument28 pagesOverview of Waveguides: Asmita Singhal Su/PdicAsmitaSinghalBairathiNo ratings yet
- Atoll 3 2 1 Model Calibration Guide PDFDocument96 pagesAtoll 3 2 1 Model Calibration Guide PDFmamangmoriNo ratings yet
- Wireless Network Engineering Software: Prediction and Measurement-Based Planning and OptimisationDocument8 pagesWireless Network Engineering Software: Prediction and Measurement-Based Planning and Optimisationtgstelecom100% (2)
- Mentum Planet LTE Plan For RFDocument12 pagesMentum Planet LTE Plan For RFHogr RgohNo ratings yet
- Wcdma RNP CW Test and Propagation Model Tuning: InternalDocument65 pagesWcdma RNP CW Test and Propagation Model Tuning: InternalmamangmoriNo ratings yet
- Atoll CDMA PlanningDocument14 pagesAtoll CDMA PlanningMoayed YagoutNo ratings yet
- Atoll 3 1 0 Umts GSM Multi-Rat AcpDocument21 pagesAtoll 3 1 0 Umts GSM Multi-Rat AcpPhạm Thái SơnNo ratings yet
- ATOLL Planning - by DEV - 16MARCH09Document24 pagesATOLL Planning - by DEV - 16MARCH09deovrat_dubey100% (1)
- ZTE GUL900 Site Trial - 3.0Document5 pagesZTE GUL900 Site Trial - 3.0mamangmoriNo ratings yet
- Atoll LTE Planning PDFDocument88 pagesAtoll LTE Planning PDFmamangmoriNo ratings yet
- Apxv86 909014 CDocument2 pagesApxv86 909014 CmamangmoriNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFmamangmoriNo ratings yet
- T 121102Document2 pagesT 121102mamangmoriNo ratings yet
- T 121102Document8 pagesT 121102Ayman ElnasharNo ratings yet
- Legend 2G3G4G - 121017Document1 pageLegend 2G3G4G - 121017mamangmoriNo ratings yet
- Android App Development NotesDocument6 pagesAndroid App Development NotesTony Jiang0% (1)
- BS en 918 PDFDocument15 pagesBS en 918 PDFcenkunalNo ratings yet
- bp2331 PDFDocument8 pagesbp2331 PDFAhmed BaheiNo ratings yet
- Underground Enclosures SpecificationsDocument3 pagesUnderground Enclosures SpecificationsJose Antonio Sanchez MarquezNo ratings yet
- 47LX6500 Specifications PDFDocument2 pages47LX6500 Specifications PDFtemporalNo ratings yet
- Standart 0508Document3 pagesStandart 0508carlosNo ratings yet
- Folder Drenos PDFDocument6 pagesFolder Drenos PDFbiomedical_com_brNo ratings yet
- Vishay 4N35 DatasheetDocument10 pagesVishay 4N35 DatasheetMohamed NaserNo ratings yet
- Get Current Location From Best Available Provider - Stack OverflowDocument4 pagesGet Current Location From Best Available Provider - Stack Overflowjayanth3dNo ratings yet
- Atm ProjectDocument18 pagesAtm Projectsujit_ranjanNo ratings yet
- As 2359.9-2006 Powered Industrial Trucks Overhead Guards - Specification and Testing (ISO 6055-2004 MOD)Document8 pagesAs 2359.9-2006 Powered Industrial Trucks Overhead Guards - Specification and Testing (ISO 6055-2004 MOD)SAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- DataSheet of CH341Document14 pagesDataSheet of CH341scribdatyopmailNo ratings yet
- Turbo C LectureDocument14 pagesTurbo C LecturebanglecowboyNo ratings yet
- Filtre TV EpcosDocument13 pagesFiltre TV Epcosparvalhao_No ratings yet
- CUSM BK SF31C8B0 00 Socialminer-User-GuideDocument92 pagesCUSM BK SF31C8B0 00 Socialminer-User-GuideAnonymous IU9mn1No ratings yet
- Dutro Hybrid PDFDocument169 pagesDutro Hybrid PDFDaniel Farfan100% (2)
- 3406Document4 pages3406Ivan Morel100% (2)
- Biréli LagrèneDocument17 pagesBiréli LagrèneMarcos Faustino0% (1)
- Catalogue Siemens Built-In Brochure 2015 PDFDocument108 pagesCatalogue Siemens Built-In Brochure 2015 PDFFirdaus PanthakyNo ratings yet
- Kato SR 700L PDFDocument10 pagesKato SR 700L PDFejazNo ratings yet
- Amberjet1200 PDFDocument3 pagesAmberjet1200 PDFKamilaRiquelmeVidalNo ratings yet
- Pcie Intel SpecificationDocument9 pagesPcie Intel Specificationdipin555No ratings yet
- Basic Control Valve and Sizing and SelectionDocument38 pagesBasic Control Valve and Sizing and SelectionNguyen Anh Tung50% (2)
- Additional Communication System TD Canrig.Document5 pagesAdditional Communication System TD Canrig.Abdelghani ZitouniNo ratings yet
- 2019 11 20 23 41 26Document227 pages2019 11 20 23 41 26Aqua Galon0% (1)
- Module 6 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS OF QUALITY MANAGEMENTDocument5 pagesModule 6 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS OF QUALITY MANAGEMENTjennie kimNo ratings yet
- PZ4 BrochureDocument6 pagesPZ4 BrochureMohamed SamyNo ratings yet