Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Read Diode
Uploaded by
Anonymous jiembd100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
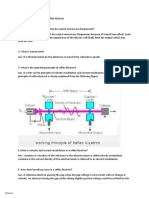
2K views14 pages1) Gunn diodes have two regions - a thin p-type region where avalanche multiplication occurs under a high electric field, and an intrinsic drift region where generated holes must travel to the p+ contact.
2) When reverse biased above the breakdown voltage, the space charge region extends through the p and intrinsic regions, creating a high electric field near the n+-p junction where electron-hole pairs are generated through avalanche multiplication.
3) The carrier current generated by avalanche multiplication is pulsed and delayed relative to the applied voltage, while the external current induced in the external circuit by moving holes is delayed by 90 degrees, resulting in negative conductance that allows the diode to oscillate at microwave
Original Description:
Read Diode
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Gunn diodes have two regions - a thin p-type region where avalanche multiplication occurs under a high electric field, and an intrinsic drift region where generated holes must travel to the p+ contact.
2) When reverse biased above the breakdown voltage, the space charge region extends through the p and intrinsic regions, creating a high electric field near the n+-p junction where electron-hole pairs are generated through avalanche multiplication.
3) The carrier current generated by avalanche multiplication is pulsed and delayed relative to the applied voltage, while the external current induced in the external circuit by moving holes is delayed by 90 degrees, resulting in negative conductance that allows the diode to oscillate at microwave
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views14 pagesRead Diode
Uploaded by
Anonymous jiembd1) Gunn diodes have two regions - a thin p-type region where avalanche multiplication occurs under a high electric field, and an intrinsic drift region where generated holes must travel to the p+ contact.
2) When reverse biased above the breakdown voltage, the space charge region extends through the p and intrinsic regions, creating a high electric field near the n+-p junction where electron-hole pairs are generated through avalanche multiplication.
3) The carrier current generated by avalanche multiplication is pulsed and delayed relative to the applied voltage, while the external current induced in the external circuit by moving holes is delayed by 90 degrees, resulting in negative conductance that allows the diode to oscillate at microwave
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
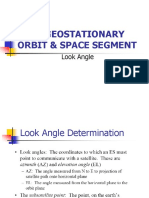
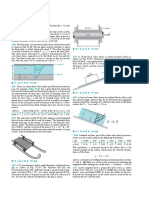
Physical Description
PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION
+ very high doping
i or v intrinsic material
Two regions
1) Thin p region (High field/Avalanche region)
avalanche multiplication occurs
2) Intrinsic region (Drift region) generated holes
must drift towards the p+ contact
The space between n+ -p junction and the i p+
junction is called the space charge region.
The diode is reverse biased and mounted in a
microwave cavity.
The impedance of the cavity is mainly inductive
which is matched with the capacitive impedance of
the diode to form a resonant circuit.
Such device can produce a negative ac resistance
that in turns delivers power from the dc bias to the
oscillation.
AVALANCHE MULTIPLICATION
When the reverse bias voltage is above the
breakdown voltage, the space charge region always
extends from n+ -p junction to the i-p+ junction
through the p and the i regions.
The fixed charges are shown in the figure.
A positive charge moves from left to right and
gives a rising field. The maximum field which is at
the n+ -p junction is about several hundred
kilovolt/cm.
Carriers (holes) in the high field region near the
n+ -p junction acquire energy to knock down the
valence electrons in the conduction band and
hence electron hole pairs are generated. This is
avalanche multiplication.
The electrons move into the n+ region and the
holes drift through the space charge region to the
p+ region with a constant velocity vd.
The field throughout the space charge is about 5
kV/cm.
The transit time of a hole across the drift i-region L
is given by
And the avalanche multiplication factor is
The breakdown voltage for a silicon p+ -n junction
can be expressed as
Carrier Current Io(t) and External
Current Ie(t)
The diode can be mounted in a microwave
resonant circuit.
An ac voltage can be maintained at a given
frequency in the circuit, and the total field across
the diode is the sum of ac and dc fields which
causes breakdown at the n+ -p junction during the
positive half cycle of the ac voltage cycle if the field
is above the breakdown voltage.
The carrier current (hole current in this case) Io(t)
generated at the n+ -p junction by the avalanche
multiplication grows exponentially with time while
the field is above critical voltage.
During the negative half cycle, when the field is
below breakdown voltage, the carrier current
decays exponentially.
Io(t) is in the form a pulse of very short duration
and it reaches its maximum in the middle of the ac
voltage cycle or one quarter of the cycle later than
the voltage.
Under the influence of electric field the generated
holes are injected into the space region towards the
negative terminal.
As the injected holes traverse the drift space,
1) they induce a current Ie(t) in the external circuit.
2) Cause a reduction of the field
Since the velocity of the holes in the space charge is
constant
The external current Ie(t) because of the moving
holes is delayed by 90 relative to the pulsed Io(t).
Since the carrier current Io(t) is delayed by one
quarter cycle or 90 relative to the ac voltage, Ie(t) is
then delayed by 180 relative to the voltage.
Hence negative conductance occurs and the diode
can be used for microwave oscillation and
amplification.
Applications
Excellent signal sources for RFmicrowave
applications.
Alarms.
Radar.
Detectors using RF technology.
You might also like
- Star-Delta TransformationDocument7 pagesStar-Delta TransformationAbhijit Kar Gupta80% (5)
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT THEORY MCQs PDFDocument9 pagesELECTRICAL CIRCUIT THEORY MCQs PDFYashNo ratings yet
- Amw MCQDocument150 pagesAmw MCQSanthosh PaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: 1. Derive The Fundamental Equation For Free Space Propagation? AnsDocument11 pagesUnit 8: 1. Derive The Fundamental Equation For Free Space Propagation? AnsRamya RammiNo ratings yet
- Sun spot cycle effects on ionosphere frequenciesDocument11 pagesSun spot cycle effects on ionosphere frequenciesburni50% (2)
- EC 442 CH-8 Finite Length Linear DipoleDocument114 pagesEC 442 CH-8 Finite Length Linear DipoleDonna NobartNo ratings yet
- Precision Rectifier Circuits ExplainedDocument14 pagesPrecision Rectifier Circuits ExplainedKedar Patil0% (1)
- Wave Propagation (Unit VI)Document65 pagesWave Propagation (Unit VI)Nuzhath FathimaNo ratings yet
- Merz Price Differential Protection For TransformerDocument2 pagesMerz Price Differential Protection For TransformerapjbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Characteristics & Microwave DevicesDocument165 pagesTransmission Line Characteristics & Microwave DevicesAnonymous JnvCyu85100% (2)
- GUNN DiodeDocument29 pagesGUNN DiodePriyanka DasNo ratings yet
- UNIT5-Ground Wave Propagation PDFDocument44 pagesUNIT5-Ground Wave Propagation PDFRameshbabu SadineniNo ratings yet
- Assignments - NOC - Semiconductor Devices and CircuitsDocument48 pagesAssignments - NOC - Semiconductor Devices and CircuitsPraghashraja100% (2)
- Transistor Switching Times ExplainedDocument6 pagesTransistor Switching Times ExplainedManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electrical Machines Chapter One: Electromagnetic PrinciplesDocument286 pagesIntroduction to Electrical Machines Chapter One: Electromagnetic Principlestesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- UNIT 1 PPT Satellite CommunicationDocument34 pagesUNIT 1 PPT Satellite Communicationselvi100% (1)
- Gateforum EE GATE-2018 SolutionsDocument46 pagesGateforum EE GATE-2018 SolutionsDeepu SinghNo ratings yet
- Low Pass Sampling TheoremDocument24 pagesLow Pass Sampling TheoremLavanya RajuNo ratings yet
- Edc Quiz 2Document2 pagesEdc Quiz 2Tilottama DeoreNo ratings yet
- New Active FiltersDocument73 pagesNew Active FiltersPradip GhorpadeNo ratings yet
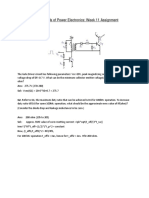
- Fundamentals of Power Electronics: Week 11 AssignmentDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Power Electronics: Week 11 AssignmentDeep GandhiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication - Lab - ManualDocument53 pagesMobile Communication - Lab - ManualRutuja KurkelliNo ratings yet
- EMF - 2 Mark & 16 MarksDocument26 pagesEMF - 2 Mark & 16 MarksKALAIMATHINo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of Two Stage RC Coupled AmplifierDocument38 pagesFrequency Response of Two Stage RC Coupled AmplifierAyesha Gupta100% (2)
- Gate Question LICDocument46 pagesGate Question LICnaveeth11No ratings yet
- Microwave Introduction Objective QuestionsDocument4 pagesMicrowave Introduction Objective Questionsganesh4u_p0% (1)
- Ect401 M2Document15 pagesEct401 M2hrithikNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions With Answers On Power Electronics and DrivesDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions With Answers On Power Electronics and DrivesRaees AslamNo ratings yet
- IC 723 Voltage RegulatorsDocument16 pagesIC 723 Voltage RegulatorsAtheessh .B0% (1)
- Transferred Electron DevicesDocument42 pagesTransferred Electron DevicesSubrahmanyam GrandhiNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering MCQ Questions PDFDocument31 pagesPower Plant Engineering MCQ Questions PDFMzna AlshehhiNo ratings yet
- Velammal EC8701 MCQ Questions on Antenna and Microwave EngineeringDocument29 pagesVelammal EC8701 MCQ Questions on Antenna and Microwave EngineeringAhamedNo ratings yet
- Interfacing DAC with 89C51Document6 pagesInterfacing DAC with 89C51Girish ChapleNo ratings yet
- Ed & I Lab 18ecl37 ManualDocument29 pagesEd & I Lab 18ecl37 Manualcharan mNo ratings yet
- Detect Cell Phone RF Signals Circuit Components ListDocument5 pagesDetect Cell Phone RF Signals Circuit Components ListAntus Alok SahuNo ratings yet
- Antenna Design Concepts Explained with Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument26 pagesAntenna Design Concepts Explained with Multiple Choice QuestionskolisettyvsureshNo ratings yet
- Gunn DiodeDocument80 pagesGunn DiodeBindu Narayanan Nampoothiri100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Power Electronics Assignment SolutionsDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Power Electronics Assignment SolutionsDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- Circuitrix EventDocument6 pagesCircuitrix EventNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Radar Systems Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesRadar Systems Important QuestionsJanardhan Ch100% (1)
- Vi Characteristics of PN Junction DiodeDocument17 pagesVi Characteristics of PN Junction DiodePranay PathadeNo ratings yet
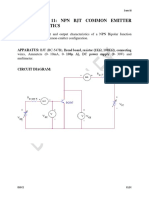
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2005 With SolutionsDocument53 pagesGATE EE 2005 With SolutionsAbhishek Mohan50% (2)
- Analog Electronics Circuits (Semester V - EEE) : Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnalog Electronics Circuits (Semester V - EEE) : Important QuestionsHadush KingNo ratings yet
- Questionnaires Antennas CH 1 & 2Document5 pagesQuestionnaires Antennas CH 1 & 2Joshua CarrionNo ratings yet
- SATELLITE LINK DESIGNDocument123 pagesSATELLITE LINK DESIGNvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Op-Amp (Operational Amplifier) - Electronics PostDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Op-Amp (Operational Amplifier) - Electronics PostDurga Devi100% (1)
- Op-Amp MCQDocument13 pagesOp-Amp MCQAbhisek Gautam BTNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 7: FIR Filter Design: Dr. Manjunatha. P Professor Dept. of ECEDocument94 pagesUNIT - 7: FIR Filter Design: Dr. Manjunatha. P Professor Dept. of ECEBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8 PDFDocument9 pagesAssignment 8 PDFvidhya dsNo ratings yet
- Network SolDocument189 pagesNetwork Solsandeep12911050% (2)
- Important Question and Answers On Reflex KlystronDocument2 pagesImportant Question and Answers On Reflex KlystronAtanuGoraiNo ratings yet
- Lab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument5 pagesLab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterHemanth GedelaNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller Module 5 NotesDocument27 pages8051 Microcontroller Module 5 Notesrakesh rakiNo ratings yet
- Impatt DiodeDocument12 pagesImpatt DiodeKathy Palmer56% (9)
- Optical SourcesDocument89 pagesOptical Sourcessambasivarao racakonda100% (2)
- Newton's RingDocument5 pagesNewton's Ringprateekjain01100% (1)
- IMPATT Diode Transit Time DevicesDocument21 pagesIMPATT Diode Transit Time DevicesRandomNo ratings yet
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Source Publication List For Web of Science: Science Citation Index ExpandedDocument143 pagesSource Publication List For Web of Science: Science Citation Index ExpandedGarima GuptaNo ratings yet
- Source Publication List For Web of Science: Science Citation Index ExpandedDocument143 pagesSource Publication List For Web of Science: Science Citation Index ExpandedGarima GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6 Optical DetectorsDocument26 pages6 Optical DetectorsAbdelaziz MahmoudNo ratings yet
- LTspice ManualDocument206 pagesLTspice ManualGhiles Khelil100% (1)
- List of Journals - SCI and SSCIDocument69 pagesList of Journals - SCI and SSCIRahul RajNo ratings yet
- Ec1269 - Microprocessors ApplicationsDocument31 pagesEc1269 - Microprocessors ApplicationsNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- List of SCOPUS Indexed Engineering JournalsDocument1 pageList of SCOPUS Indexed Engineering JournalsAnonymous jiembdNo ratings yet
- Freq Response of BJT AmplifierDocument6 pagesFreq Response of BJT AmplifierAnonymous jiembdNo ratings yet
- Schottky DiodeDocument4 pagesSchottky DiodeAnonymous jiembdNo ratings yet
- Journals With Low RatingDocument70 pagesJournals With Low Ratingferdad4realNo ratings yet
- Journals With Low RatingDocument70 pagesJournals With Low Ratingferdad4realNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Tutorial Reciprocating CompressorsDocument2 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Tutorial Reciprocating CompressorsChris ZiyuenNo ratings yet
- Ch. 15 - Science Notebook Sec. 1Document4 pagesCh. 15 - Science Notebook Sec. 1Savannah MontelongoNo ratings yet
- SSP Tut and Ia QaDocument36 pagesSSP Tut and Ia QaHarsh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Phreatic Line PDFDocument21 pagesPhreatic Line PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Applications Using The Partial Differential Equation ToolboxDocument11 pagesApplications Using The Partial Differential Equation ToolboxIgor WosniakNo ratings yet
- Papagiannakis Solutions For Text BookDocument112 pagesPapagiannakis Solutions For Text BookRishiKaithala100% (2)
- Quantum Physics Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuantum Physics Practice QuestionsKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- G1 Group 1CDocument72 pagesG1 Group 1CNH SyzlnNo ratings yet
- Constraint PDFDocument12 pagesConstraint PDFNeelesh BenaraNo ratings yet
- New Regulations For Geotech GermanyDocument10 pagesNew Regulations For Geotech GermanySâu HeoNo ratings yet
- Course Structure and Detailed Syllabus For 1st Year B.tech Admission Batch 2023-24Document27 pagesCourse Structure and Detailed Syllabus For 1st Year B.tech Admission Batch 2023-24nabajyotimajhi2000No ratings yet
- Dowel Bar-Tie Bar-IRC-58-2015Document3 pagesDowel Bar-Tie Bar-IRC-58-2015SONU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Lateral Electromagnetic Waves Theory and Applications To Communications, Geophysical Exploration, and Remote SensingDocument770 pagesLateral Electromagnetic Waves Theory and Applications To Communications, Geophysical Exploration, and Remote SensingBélaid Hocine AnisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RRLDocument9 pagesChapter 2 RRLpans pansNo ratings yet
- 3-7 Fluids in Rigid-Body Motion: - We ObtainedDocument6 pages3-7 Fluids in Rigid-Body Motion: - We ObtainedAsmaa Ali El-AwadyNo ratings yet
- Lectu 14Document4 pagesLectu 14YeviraArinDiyanaNo ratings yet
- Download Physics Formula ListDocument19 pagesDownload Physics Formula Listanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Tarea 1 MunsonDocument4 pagesTarea 1 MunsonAlexander JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cosmos 2007Document38 pagesCosmos 2007Oswaldo NeaveNo ratings yet
- Vpvs AplicatiponsDocument6 pagesVpvs Aplicatiponspetro AliNo ratings yet
- Thesis ReportDocument132 pagesThesis ReportOana UdreaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Test ReviewDocument9 pagesProperties of Matter Test ReviewAngel PeayNo ratings yet
- JNTU World Geotech Engineering ExamDocument4 pagesJNTU World Geotech Engineering ExamDp VisheshNo ratings yet
- MRAM: Magnetic Random Access MemoryDocument15 pagesMRAM: Magnetic Random Access MemoryJoyitaNo ratings yet
- Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields W BlanksDocument4 pagesMotion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields W BlanksAshir50% (2)
- Resume AyanchattopadhyayDocument2 pagesResume Ayanchattopadhyayapi-163237383No ratings yet
- Shiv Chhatrapati Shikshan Sanstha, Latur Syllabus For Main Screening Test - 2021 1 MotionDocument2 pagesShiv Chhatrapati Shikshan Sanstha, Latur Syllabus For Main Screening Test - 2021 1 MotionDinesh PavanNo ratings yet
- Structural Control System for Water TankDocument4 pagesStructural Control System for Water TankJOSMRIVERCNo ratings yet
- ABB Motors Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageABB Motors Technical Data SheetAgung AfrizalNo ratings yet
- APEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalDocument22 pagesAPEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalbaljinderNo ratings yet