Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Processing Technology Hana
Uploaded by
Nabila Hana DhiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Food Processing Technology Hana
Uploaded by
Nabila Hana DhiaCopyright:
Available Formats
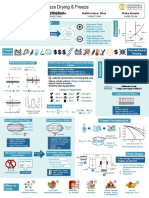
RATE OF MASS TRANSFER
PARTS OF FREEZE DRYING
When heat reaches the sublimation front, it raises the temperature and the water vapour
pressure of the ice. Vapour then moves through the dried food to a region of low vapour pressure in
the drying chamber. 1 g of ice forms 2 m3of vapour at 67 Pa and, in commercial freeze drying, it is
therefore necessary to remove several hundred cubic metres of vapour per second through the pores
in the dry food.
Water vapour pressure gradient factor control Collapse temperatures for selected foods in freeze
drying
Drying chamber pressure
Vapour condenser temperature
(should be < as possible)
Ice at the sublimation front temperature
(should be > as possible)
What happen to foods above critical collapse
temp?
Irreversible collapse of food structure
Drying operation will end
The Power of PowerPoint - thepopp.com
RATE OF MASS TRANSFER (2)
PARTS OF FREEZE DRYING
During drying, the moisture content falls from the initial
high level in the frozen zone to a lower level in the dried
layer, which depends on the water vapour pressure in
the cabinet.
kd x 2 M1 M2 s
P = P + (s i ) td =
b 8k d (s i )
Through layer NOTE
From through dry layer
Pi : partial pressure of water at s : surface temperature (oC)
sublimation front (Pa) i : temperature at sublimation
Ps : partial pressure of water at front
surface (Pa) (oC)
Kd: thermal conductivity of dry td : drying time (s)
layer (Wm-1K-1) x : thickness of food (min)
b : permeability of dry layer (kgs- : density (kg m-3)
1m-1) M1: initial moisture content
s : latent heat of sublimation (J M2: final moisture content in dry
Graph shows changes through
kg-1) layer
Generated by
each sample
The Power of PowerPoint - thepopp.com
EQUIPMENT
Contact (or conduction) freeze driers
Vacuum chamber: contains trays to hold food Food is placed onto ribbed trays which rest on heater
during drying plates.
Heaters: supply latent heat of sublimation Differences
Uneven contact
Refrigeration coils: condense vapours directly More slow than
(reduce
between drying
to ice others rates top and
heat transfer)
bottom layers
Defrosting devices: keep coils free of ice area
maximum for vapour condensation
Fine particles of
Vacuum pumps: remove non condensable Vapour velocity: 3 product may be Higher capacity
vapours m s-1 carried over in than others
Condensor efficiency =
Microprocessors: to monitor and control vapour and lost
The
Power of PowerPoint - thepopp.com
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Multiculturalism PDFDocument2 pagesMulticulturalism PDFFEBI EKA PUTRI -No ratings yet
- Ohlson VFFS ManualDocument32 pagesOhlson VFFS ManualbjpNo ratings yet
- Answer For Tutorial 5Document7 pagesAnswer For Tutorial 5Pedro DegrandiNo ratings yet
- Astm F 442-99Document7 pagesAstm F 442-99JORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTA100% (2)
- RP10Document3 pagesRP10PireyiNo ratings yet
- CIMB Niaga Master Card Payment RequestDocument2 pagesCIMB Niaga Master Card Payment RequestNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- CIMB Niaga Master Card Payment RequestDocument2 pagesCIMB Niaga Master Card Payment RequestNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- HanaDocument1 pageHanaNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Capital Estimate: - Cost Index - Capital Expenditure - BenchmarkingDocument19 pagesCapital Estimate: - Cost Index - Capital Expenditure - BenchmarkingNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- PPU AdsDocument1 pagePPU AdsNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Ip Modem:192.168.1.254 Username:support Password:theworldinyourhandDocument1 pageIp Modem:192.168.1.254 Username:support Password:theworldinyourhandNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Estimated TimelineDocument1 pageEstimated TimelineNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Adobe PO ReqDocument3 pagesAdobe PO ReqNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Kraepelin Dan Pauli TestDocument2 pagesLampiran Kraepelin Dan Pauli TestNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practice of Food Processing TechniquesDocument1 pagePrinciples and Practice of Food Processing TechniquesNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Equipment Start Up Shut Down ProcedureDocument3 pagesEquipment Start Up Shut Down ProcedureNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Bio3 Outline Assignment 3Document1 pageBio3 Outline Assignment 3Nabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Tekpang Kelompok 9Document60 pagesTekpang Kelompok 9Nabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Bio3 Outline Assignment 3Document1 pageBio3 Outline Assignment 3Nabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- DryingDocument1 pageDryingNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor and Elevator Conveyor Specs for Wood Waste TransportDocument21 pagesScrew Conveyor and Elevator Conveyor Specs for Wood Waste TransportNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Bio3 Outline Assignment 3Document1 pageBio3 Outline Assignment 3Nabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Outline Assignment 1 Technology Selection & Flowsheeting Perancangan Pabrik 2017Document1 pageOutline Assignment 1 Technology Selection & Flowsheeting Perancangan Pabrik 2017Nabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Paper UTS TekpangDocument26 pagesPaper UTS TekpangNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Dan FuelDocument18 pagesElectricity Dan FuelNabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- Chap. 22Document1 pageChap. 22Nabila Hana DhiaNo ratings yet
- AGGREGATE SURFACE COURSE SPECIFICATIONSDocument75 pagesAGGREGATE SURFACE COURSE SPECIFICATIONSShammir Tabayag MangidaNo ratings yet
- ST BFV Torque Table (Rev5.0)Document2 pagesST BFV Torque Table (Rev5.0)Anand KumarNo ratings yet
- gh10 IomDocument4 pagesgh10 IomUsman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Basic LevelDocument14 pagesHydraulics Basic LevelIndhusekaran NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Pressure testing methods for gas supply systemsDocument27 pagesPressure testing methods for gas supply systemsMatej ZirdumNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PumpsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To PumpsJaydeep TrivediNo ratings yet
- Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 26 (2015) 587-594 PDFDocument8 pagesJournal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 26 (2015) 587-594 PDFRafael CeccattoNo ratings yet
- Downhole SamplingDocument16 pagesDownhole Samplingdrojas70No ratings yet
- Pressure at The Vena Contracta With Liquid Flow in A Control ValveDocument2 pagesPressure at The Vena Contracta With Liquid Flow in A Control ValveALI5034No ratings yet
- Analytical Approach in Autofrettaged Spherical Pressure Vessels Considering The Bauschinger EffectDocument9 pagesAnalytical Approach in Autofrettaged Spherical Pressure Vessels Considering The Bauschinger EffectAnonymous UoHUagNo ratings yet
- Jan2007 Geopressure PredictionsDocument7 pagesJan2007 Geopressure Predictionsbehaki01No ratings yet
- A Text Book of Physics (C.R. Dasgupta) (Z-Library)Document760 pagesA Text Book of Physics (C.R. Dasgupta) (Z-Library)toffee9soumavaNo ratings yet
- Pumping System 28 NovDocument87 pagesPumping System 28 NovKeval ShahNo ratings yet
- Data Is Taken From Fluid PropDocument8 pagesData Is Taken From Fluid PropJofanny Ferdian Rahmansyah100% (1)
- Understanding Gas & Atmospheric PressureDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Gas & Atmospheric Pressureshazilla0% (1)
- Sylvania 6AK5 Vacuum Tube / Valve DatasheetDocument3 pagesSylvania 6AK5 Vacuum Tube / Valve DatasheetslpkthNo ratings yet
- How Pressure Sustaining Valves WorkDocument4 pagesHow Pressure Sustaining Valves WorkEverpeeNo ratings yet
- Laminating Techniques For Converters of Laminating AdhesivesDocument6 pagesLaminating Techniques For Converters of Laminating Adhesivescmmswim67No ratings yet
- FHP Series: High Pressure Fi LtersDocument19 pagesFHP Series: High Pressure Fi Ltersfrancis_15inNo ratings yet
- 6-31 Sps300a B1Document1 page6-31 Sps300a B1Ali GameelNo ratings yet
- Minivap Vpxpert: Operation Manual Of2Document63 pagesMinivap Vpxpert: Operation Manual Of2Erick Jhonhatan LimonNo ratings yet
- Study of Heat Transfer Coefficient in A Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument22 pagesStudy of Heat Transfer Coefficient in A Double Pipe Heat Exchangermahbub13320% (1)
- Pore Pressure Basic LevelDocument64 pagesPore Pressure Basic LevelAmlk MartinezNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet - Gas Blanketed Tanks - Outbreathing Process CalculationsDocument12 pagesSpreadsheet - Gas Blanketed Tanks - Outbreathing Process Calculationsselva_maniaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Lecture Notes ofDocument30 pagesFluid Mechanics: Lecture Notes ofAlsharksi AviationNo ratings yet
- Sewage Pumping HandbookDocument12 pagesSewage Pumping Handbookmfhaleem@pgesco.comNo ratings yet