Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wireshark: Presented By: Hiral Chhaya, Anvita Priyam
Uploaded by
Naponee Nap-shot Evans0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views24 pagesOriginal Title
Wire Shark
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views24 pagesWireshark: Presented By: Hiral Chhaya, Anvita Priyam
Uploaded by
Naponee Nap-shot EvansCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
Wireshark
Presented By: Hiral Chhaya, Anvita Priyam
Network Protocol Analyzer
Computer s/w or h/w, intercepts & logs traffic passing over the
network
Captures packets, decodes & analyzes contents
A network Analyzer is used for
Troubleshooting problems on the network
Analyzing the performance of a network to discover bottlenecks
Network intrusion detection
Analyzing the operations of applications
Overview
Introduction to Wireshark
Features
Uses
> detecting VOIP problems
> downloading FLV files
What it can’t do
Conclusion
About Wireshark
It is a packet sniffer Computer application
Functionality is very similar to tcpdump
Has a GUI front-end and many more
information sorting and filtering options
“eWeek” Labs named Wireshark one of "The
Most Important Open-Source Apps of All
Time" as of May 2, 2007
Background
Initiated by Gerald Combs under the name
Ethereal
First version was released in 1998
The name Wireshark was adopted in June
2006
Features
“Understands" the structure of different
network protocols.
Displays encapsulation and single fields and
interprets their meaning.
It can only capture on networks supported by
pcap.
It is cross-platform running on various OS
(Linux, Mac OS X, Microsoft windows)
WinP Cap
Industries –standard tool for link layer network
access in windows environment
Allows application to capture and transmit network
packets by passing the protocol stack
Consists of a driver-extends OS to provide low level
network access
Consists of library for easy access to low level
network layers
Also contains windows version of libPCap Unix API
Example
Applications of Wireshark
Exposing VOIP problems
Supports Malware Detection
Helps recognize DOS attack
Downloading FLV files
Exposing VoIP Problems Using Wireshark
VoIP –Protocol Optimized for
transmission of voice through
Internet(IP telephoning)
VOIP is affected by Latency,
Jitter and Packet Loss
Troubleshooting VoIP network
with other protocol analyzer
software is costly
VoIP involves complex setup
protocols that wireshark can
decode and relate
It provides excellent tools to
interpret the data
Exposing VOIP problems
VOIP suffers from three common problems
> when a number is dialed, phone idles & no
ringing is heard
> only one party hears audio
> missing conversation due to packet loss
No Ringing
When wireshark is launched we must ensure that
correct interface is being used
Phone SIP INVITE PBX
host PROXY Authentication required
host
ACK
Wrong user name & password
Capture Options
Capture of ipphone Traffic
One sided Audio
Uses advanced analysis tools
When capture is loaded, select
Statistics->VOIP calls
Click on the call and Graph button- summary
of SIP calls
Stream is set up between two end points by
SIP using SDP
Decodes the protocol contained within
currently selected packet
Graphical Interpretation
SIP packet Containing SDP
Session Description Protocol
Type: 3 (destination unreachable)
Code: 1 (host unreachable)
Checksum: 0x7a2
Problem
Given IP address is private and unreachable
So when remote host sends packets, they are
lost as no such route exists
Partially audible conversation
Out of order packets are lost
Wireshark uses decoded packets to provide a list of all
audio conversations
Stream Analysis
Select Problematic stream-> Click Find Reverse button-> Click
Analyze to provided packet by packet look at the stream
Lost packets will show up as having the wrong sequence
number
Also Displays current bandwith,latency and jitter
Audio replay
We can also listen to the content of the voice
call
Select Save Payload button-> Select the .au
file format-> press the OK button
The voice call is saved to your hard drive
Can be played by audio program like XMMS
What it Cannot Do….
It cannot be used to map out a network
It does not generate network data-Passive
tool
Only shows detail information about protocols
it understand
It can only capture data as well as the
OS\Interface\Interface driver supports.
An example of this is capturing data over
wireless networks.
Conclusion
Wireshark's wireless analysis features have grown to
be a very powerful tool for troubleshooting and
analyzing wireless networks.
With Wireshark's display filters and powerful
protocol dissector features, you can sift through large
quantities of wireless traffic
Without a doubt, Wireshark is a powerful assessment
and analysis tool for wireless networks that should be
a part of every auditor, engineer, and consultant
toolkit.
You might also like
- Cisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandCisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Profile PDFDocument16 pagesMikroTik Profile PDFlayalyalNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik Routeros Configuration Bandwidth Management For GamesDocument26 pagesMikrotik Routeros Configuration Bandwidth Management For GamesdudyNo ratings yet
- Basic Mistakes by ISP's On Network Setup & BGPDocument27 pagesBasic Mistakes by ISP's On Network Setup & BGPHightech ITNo ratings yet
- Basic & Advanced Syllabus of MikrotikDocument3 pagesBasic & Advanced Syllabus of Mikrotikabhi281100% (1)
- Verifying NAT Operation and Basic NAT TroubleshootingDocument10 pagesVerifying NAT Operation and Basic NAT TroubleshootingcsystemsNo ratings yet
- MPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesFrom EverandMPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Nat For Ipv4: Faculty of Technology University of Sri Jayewardenepura 2020Document40 pagesNat For Ipv4: Faculty of Technology University of Sri Jayewardenepura 2020Yeaseen ArafatNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik IpsecDocument13 pagesMikrotik IpsecMertol SerbanNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik-Part3 - Managment Manual IPDocument269 pagesMikrotik-Part3 - Managment Manual IPYmiuchinNo ratings yet
- GBSS13.0 Troubleshooting Guide 01 (PDF) - enDocument381 pagesGBSS13.0 Troubleshooting Guide 01 (PDF) - enAriv LorensNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 - TSHOOT - Lab4 2 - Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity - StudentDocument13 pagesCCNPv7 - TSHOOT - Lab4 2 - Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity - StudentfranzeskaNo ratings yet
- Manual - OSPF Forwarding Address - MikroTik WikiDocument3 pagesManual - OSPF Forwarding Address - MikroTik WikiGeny MamaniNo ratings yet
- OSPF in MikroTik RouterOS V6: The Basics by InquirinityDocument4 pagesOSPF in MikroTik RouterOS V6: The Basics by InquirinityUxville UnabiaNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik Security: Built-In Default Configuration: Erick Setiawan - 2019Document25 pagesMikrotik Security: Built-In Default Configuration: Erick Setiawan - 2019Samsul MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Melimit Download Per Ip ClientDocument3 pagesMelimit Download Per Ip ClientAbdul GeaNo ratings yet
- Eoip Tunnel in MikrotikDocument4 pagesEoip Tunnel in MikrotikmargubupolNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Web-Proxy Rev1.2 PDFDocument24 pagesMikroTik Web-Proxy Rev1.2 PDFRony Dettmar Celis ReateguiNo ratings yet
- L2TP VPN Troubleshooting FAQDocument3 pagesL2TP VPN Troubleshooting FAQAjitNo ratings yet
- Setting Up Internet Access Server On Basis of Mikrotik Routeros and Isp Billing System Netup Utm5Document9 pagesSetting Up Internet Access Server On Basis of Mikrotik Routeros and Isp Billing System Netup Utm5Vijay Kumar TitarmareNo ratings yet
- 10-Troubleshooting OSPF Routing IDocument8 pages10-Troubleshooting OSPF Routing Imansoorali_afNo ratings yet
- Manual - IP - DNS - MikroTik WikiDocument5 pagesManual - IP - DNS - MikroTik Wikimona_mi8202No ratings yet
- Manual Configuration Management MikrotikDocument6 pagesManual Configuration Management MikrotikEdu EdyNo ratings yet
- Zubair Khan - It Network EngineerDocument3 pagesZubair Khan - It Network EngineercdeekyNo ratings yet
- CCIE Routing & Switching Version 5.0 - VPNDocument6 pagesCCIE Routing & Switching Version 5.0 - VPNbomoarebunNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik Queues To Limit The Video Streaming ProtocolsDocument1 pageMikrotik Queues To Limit The Video Streaming ProtocolsitsmenowNo ratings yet
- Understanding Carrier Grade NATDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Carrier Grade NATSkdead SkdeadNo ratings yet
- Port GameDocument8 pagesPort GameRahmat Jaya TeknologiNo ratings yet
- Uso de Layer 7 ProtocolsDocument7 pagesUso de Layer 7 ProtocolsJose Hidalgo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Manual IP Firewall Mangle - MikroTik WikiDocument10 pagesManual IP Firewall Mangle - MikroTik WikiachainyaNo ratings yet
- FTP Server ConfigurationDocument16 pagesFTP Server ConfigurationbharatNo ratings yet
- Transparently Bridge Two Networks MikrotikDocument7 pagesTransparently Bridge Two Networks Mikrotiksergiov8No ratings yet
- PPTP VPN Troubleshooting FAQDocument3 pagesPPTP VPN Troubleshooting FAQAjitNo ratings yet
- Script Up Down MikrotikDocument1 pageScript Up Down Mikrotikangelo68000No ratings yet
- Configure Verify and Troubleshoot LACPDocument4 pagesConfigure Verify and Troubleshoot LACPMohammed HazzaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The World of Network Analysis .................................................................. 1Document20 pagesChapter 1: The World of Network Analysis .................................................................. 1johnbohnNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik - IPv6Document45 pagesMikrotik - IPv6Musyaffak SNo ratings yet
- GregSowell Mikrotik SecurityDocument22 pagesGregSowell Mikrotik SecurityMarco Vinicio Rojas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik - Part1Document154 pagesMikrotik - Part1ebilma2No ratings yet
- Mikrotik External SquidDocument5 pagesMikrotik External SquidDavid CastroNo ratings yet
- Eoip MikrotikDocument16 pagesEoip MikrotikFernandez EkoNo ratings yet
- Lab - Use Wireshark To View Network TrafficDocument6 pagesLab - Use Wireshark To View Network TrafficAyeyi Mills-RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)Document18 pagesLink Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)Wewe SlmNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.2 - Introduction To WiresharkDocument20 pagesLab 4.2 - Introduction To Wiresharkminhnhse183751No ratings yet
- Manual - The Dude v6 - Dude Telegram Example - MikroTik WikiDocument2 pagesManual - The Dude v6 - Dude Telegram Example - MikroTik WikiCarlos Henrique TrentiniNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik - Firewall - RawDocument3 pagesMikrotik - Firewall - Rawmauro lipisNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik Snffer ToolsDocument2 pagesMikrotik Snffer ToolsitsmenowNo ratings yet
- Mplement Ontent Iltering: Lay Minh (Makito)Document27 pagesMplement Ontent Iltering: Lay Minh (Makito)NaingWinOoNo ratings yet
- MikroTik SwOSDocument4 pagesMikroTik SwOSNoc PlbNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting SwitchDocument56 pagesTroubleshooting SwitchJaime Andres NiñoNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument9 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- MikRoTik VPN ConfigurationDocument5 pagesMikRoTik VPN ConfigurationShah ParanNo ratings yet
- Mtcna 05 2012Document398 pagesMtcna 05 2012wahyuningastuti_82No ratings yet
- EIGRP AdvancesDocument96 pagesEIGRP Advancesnenad20090% (1)
- Q in Q TunnelingDocument17 pagesQ in Q TunnelingNabeel SalmanNo ratings yet
- 3.7.10 Lab - Use Wireshark To View Network TrafficDocument6 pages3.7.10 Lab - Use Wireshark To View Network TrafficDeglad UataakeNo ratings yet
- Effect of Mobile Marketing On YoungstersDocument33 pagesEffect of Mobile Marketing On Youngsterssaloni singhNo ratings yet
- Electromach EX Poster2016 PDFDocument1 pageElectromach EX Poster2016 PDFphilippe69No ratings yet
- 1B30 07Document542 pages1B30 07saNo ratings yet
- UNLV PHD InformaticsDocument3 pagesUNLV PHD InformaticsAnonymous gzESmV9No ratings yet
- Pacific General ManualDocument53 pagesPacific General Manualroi_marketingNo ratings yet
- HCD RG221Document64 pagesHCD RG221Berenice LopezNo ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS Idle Mode and Channel Behavior Feature Guide U9.2Document102 pagesZTE UMTS Idle Mode and Channel Behavior Feature Guide U9.2Pushp SharmaNo ratings yet
- Excel ExerciseDocument296 pagesExcel ExerciseshubhamNo ratings yet
- Matlab 5Document38 pagesMatlab 5Shruti YashNo ratings yet
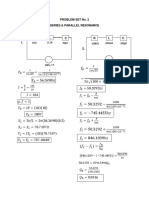
- Problem Set No.2 SolutionDocument9 pagesProblem Set No.2 SolutionAshley Quinn MorganNo ratings yet
- Duckademy LFI-RFI How LFI and RFI WorkDocument42 pagesDuckademy LFI-RFI How LFI and RFI WorkKlentiB.ÇukariNo ratings yet
- C++ ProgramsDocument145 pagesC++ ProgramsRinky SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Find The Coordinates of Every Square: Naval Grid CalculatorDocument2 pagesFind The Coordinates of Every Square: Naval Grid CalculatorMarie MythosNo ratings yet
- AlfrescoDocument10 pagesAlfrescoanangsaNo ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Pi Home ServerDocument16 pagesPi Home ServerKhedotGloryaNo ratings yet
- Cgaxis Models Volume 118Document26 pagesCgaxis Models Volume 118AntezanaFernandoNo ratings yet
- Guidely Age Set 1 PDFDocument5 pagesGuidely Age Set 1 PDFPriya KumariNo ratings yet
- Online Consumer Complaint Filing: E-Filing of Complaints at Consumer Forums of IndiaDocument13 pagesOnline Consumer Complaint Filing: E-Filing of Complaints at Consumer Forums of IndiaLAVANYA SAMPATHNo ratings yet
- Free PDF Reader Sony Ericsson w595Document2 pagesFree PDF Reader Sony Ericsson w595AdamNo ratings yet
- OQLDocument16 pagesOQLVikram KarkiNo ratings yet
- CLUSTER 1-Magsaysay-WSPPRDocument18 pagesCLUSTER 1-Magsaysay-WSPPRJopheth RelucioNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Technical InformationDocument11 pagesAppendix B: Technical InformationOnTa OnTa60% (5)
- Projection of Points &lineDocument25 pagesProjection of Points &lineSai Radha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 2 2 2 2 "Enter The Elements of 1st Matrix/n": Int Float IntDocument12 pages2 2 2 2 2 2 "Enter The Elements of 1st Matrix/n": Int Float IntSagar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents For Computer Architecture: A Minimalist PerspectiveDocument6 pagesTable of Contents For Computer Architecture: A Minimalist PerspectiveWilliam GilreathNo ratings yet
- AI-powered Technology To Health-Check Soil and Water: Contact: Mathias SteinerDocument22 pagesAI-powered Technology To Health-Check Soil and Water: Contact: Mathias SteinerLucasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Skull - Terraria WikiDocument1 pageMechanical Skull - Terraria WikiEduard NagyNo ratings yet
- Annex 4 (Word Format)Document1 pageAnnex 4 (Word Format)Amores, ArmandoNo ratings yet
- SHA MAN 0052 Ver4 WebDocument96 pagesSHA MAN 0052 Ver4 WebGreed CssNo ratings yet