Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and Applications
Uploaded by
jesus MaldonadoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and Applications
Uploaded by
jesus MaldonadoCopyright:
Available Formats
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline
Engineering Thermoplastics
Materials, properties and applications.
Prepared by the IAPD Education Committee (Module 4)
Presented courtesy of Modern Plastics Inc.
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
AMORPHOUS HIGH PERFORMANCE PLASTICS
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Key Characteristics Materials:
High Cost Polysulfone
High Temperature Polyetherimide
High Strength & Good Stiffness Polyethersulfone
Good Chemical Resistance Polyarylsulfone
Transparency
AMORPHOUS PLASTICS
Hot Water & Steam Resistance
AMORPHOUS ENGINEERING PLASTICS
Key Characteristics: Materials:
Moderate Cost Polycarbonate
Moderate Temperature Resistance Modified PPO
Moderate Strength Modified PPE
Good Impact Resistance Thermoplastic Urethane
Translucency
Good Dimensional Stability
Good Optical Qualities
AMORPHOUS COMMODITY PLASTICS
Key Characteristics: Materials:
Low Cost Acrylic
Low Temperature Resistance] Polystyrene
Low Strength ABS
Good Dimensional Stability PVC
Bond Well PETG
Typically Transparent CAB
AMORPHOUS PLASTICS KEY CHARACTERISTICS:
Soften Over a Broad Range Of Temperatures
Easy to Thermoform
Tend to Be Transparent
Bond Well Using Adhesives and Solvents
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module Prone
4 To Stress Cracking
Poor Fatigue Resistance
Stuctural Applications Only (Not for Bearing & Wear)
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Amorphous Engineering Thermoplastics
Key Characteristics
• Moderate cost, strength and temperature resistance
• Good impact resistance
• Translucency
• Good dimensional stability
• Excellent optical qualities
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Amorphous Engineering Thermoplastics
Materials
• Polycarbonate (PC)
• Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
• Polyphenelyne Ether (PPE)
• Thermoplastic Urethane (TPU)
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Polycarbonate (PC)
Strengths
Excellent clarity
Excellent toughness
Good heat resistance
Excellent electrical properties
Intrinsic flame-retardancy
Excellent strength
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Polycarbonate (PC)
Limitations
• Continual exposure to hot water causes gradual
embitterment
• Most aromatic solvents, esters and ketones can
cause crazing and cracking
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Polycarbonate (PC)
Applications
• Vandal resistant windows
• Machine guards
• Outdoor signs
• Sky lights
• Backboards
• Bike, roller blading protective
wear
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Modified Polyphenylene Oxide (Mod PPO)
Modified Polyphenylene Ether (Mod PPE)
Key Characteristics
• High dielectric strength
• Available in FDA compliant grades
• Less expensive than polycarbonate (PC)
• Good chemical resistance to strong acids,
bases and water
• Wide range of processing
• Good creep resistance
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Modified Polyphenylene Oxide (Mod PPO)
Modified Polyphenylene Ether (Mod PPE)
Applications
• Electrical housings in appliance, computers, business
equipment, etc.
• Water purification equipment parts
• Insulators
• Gears
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Key Characteristics
• Wide range of service temperatures
• Wide range of harness options
• Excellent tear resistance
• Excellent compression strength
• Excellent resistance to non polar solvents
• Excellent electrical properties
• Excellent abrasion resistance
• High tensile strength
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Applications
• Impact resistant housings
• Valves
• Water filter caps
• Geophysical cable spacer
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE HIGH PERFORMACE PLASTICS
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Key Characteristics: Materials:
High Cost PVDF
High Temperature PTFE
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE PLASTICS
High Strength ECTFE
Good Electrical Properties FEP
Outstanding Chemical Resistance PFA
Low Coefficient of Friction PPS
Good Toughness PEEK
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE ENGINEERING PLASTICS
Key Characteristics: Materials:
Moderate Cost Nylon
Moderate Temperature Resistance Acetal
Moderate Strength PET
Good Chemical Resistance PBT
Good Bearing and W ear Properties UHMW-PE
Low Coefficient of Friction
Difficult to Bond
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE COMMODITY PLASTICS
Key Characteristics: Materials:
Low Cost Polyethylene
Low Temperature Resistance Polypropylene
Low Strength Polymetnylpentene(TPX)
Excellent Chemical Resistance
Low Coefficient of Friction
Near Zero Moisture Absorption
Very Good Electrical Properties
Good Toughness
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE PLASTICS KEY CHARACTERISTICS:
Sharp Melting Point
Difficult to Thermoform
Tend to Be Opaque
Difficult To Bond Using Adhesives and Solvents
Good Resistance To Stress Cracking
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module Good
4 Fatigue Resistance
Good For Bearing and Wear, As Well As Structural Applications
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Semi-Crystalline Engineering
Thermoplastics
Key Characteristics
• Moderate cost, strength
• Moderate temperature resistance
• Good chemical resistance
• Good bearing and wear properties
• Low COF
• Difficult to bond
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Semi-Crystalline Engineering
Thermoplastics
Materials
• Polyamide (PA) — Nylon
• Polyoxymethylene (POM) — Acetal
• Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
• Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
• Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene
(UHMW-PE)
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Nylon (PA)
Strengths
• Good strength
• Good toughness
• Fair heat resistance
• Good chemical resistance
• Low COF
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Nylon (PA)
Limitations
Strong acidic environments
Areas where moisture absorption is of
concern
Areas experiencing high operating
temperatures
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Nylon (PA)
Applications
• Film
• Automotive
• Electrical/electronics
• Consumer goods
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Cast PA vs. Extruded PA
• Extruded nylon can be produced in almost any grade
• Cast nylon grades are limited to Type 6, Type 6 1/2 and some
Type 12
• Generally Nylon 6/6 and Nylon 6 (cast or extruded) are
interchangeable in most applications (physical property
differences are minor)
• Nylon 6/6 is stronger and stiffer than Nylon 6, and has more
resistance to compression
• Nylon 6 has better elongation values than Nylon 6/6, providing
better ductility
• Cast Nylon can be produced in large profiles and custom shapes,
and is generally less expensive than extruded grades
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Acetal (POM)
Strengths
• Good dimensional stability
• Good wear resistance
• Excellent strength
• Excellent stiffness
• Good rigidity
• Low moisture absorption
• Low COF
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Acetal (POM)
Limitations
• Centerline porosity in copolymers
• Using copolymer in hot water environments
(boiling/steam)
• Strong acidic environments
• Strong alkali environments
• Areas experiencing high operating
temperatures
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Acetal (POM)
Applications
• Bearings
• Bushings
• Valve seats
• Washers
• Nozzles
• Spools
• Cams
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Thermoplastic Polyesters
Key Characteristics
Good range of mechanical properties
Good dimensional stability
Superior chemical resistance
Good electrical properties
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Thermoplastic Polyesters
Materials
• Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
• Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Key Characteristics
• High dimensional stability under heat
• High stiffness and hardness
• Good bearing strength
• Good electrical properties
• Good resistance to chemicals
• Good stress-cracking resistance
• Excellent flow characteristics
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Thermoplastic Polyesters
Applications
• Pump components
• Automotive components
• Food packaging components
• Insulators
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Thermoplastic Polyesters
Caution!
Watch high temperature environments!
Use caution when recommending thermoplastic
polyesters in applications requiring high temperature
resistance, above 93-121oC/200-250oF.
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Ultra High Molecular Weight PE
(UHMW-PE)
Strengths
• Highest abrasion resistance and impact strength of
any plastic
• Very low COF
• Excellent cryogenic (low temperature) material
• Self-lubricating
• FDA/USDA compliant
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Ultra High Molecular Weight PE
(UHMW-PE)
Limitations
• Only good until 82oC/180oF
• Not a self-supporting material
• High cost for tooling for custom extrusion and
custom parts
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Ultra High Molecular Weight PE
(UHMW-PE)
Applications
• Guides
• Wear strips
• Liners
The IAPD Plastics Primer, Module 4
IMIDE MATERIALS
The International Association of Plastics Distributors
Key Characteristics: Materials:
Very High Cost Per Pound PI
Excellent Properties Above 400°F PAI
Excellent Electrical Properties PBI
Excellent Dimensional Stability
Low Coefficient of Friction
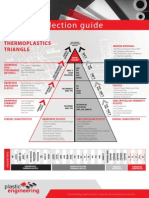
AMORPHOUS HIGH PERFORMANCE PLASTICS SEMI-CRYSTALLINE HIGH PERFORMACE PLASTICS
Key Characteristics Materials: Key Characteristics: Materials:
High Cost Polysulfone High Cost PVDF
High Temperature Polyetherimide High Temperature PTFE
SEMI-CRYSTALLINE PLASTICS
High Strength & Good Stiffness Polyethersulfone High Strength ECTFE
Good Chemical Resistance Polyarylsulfone Good Electrical Properties FEP
Transparency Outstanding Chemical Resistance PFA
AMORPHOUS PLASTICS
Hot Water & Steam Resistance Low Coefficient of Friction PPS
Good Toughness PEEK
AMORPHOUS ENGINEERING PLASTICS SEMI-CRYSTALLINE ENGINEERING PLASTICS
Key Characteristics: Materials: Key Characteristics: Materials:
Moderate Cost Polycarbonate Moderate Cost Nylon
Moderate Temperature Resistance Modified PPO Moderate Temperature Resistance Acetal
Moderate Strength Modified PPE Moderate Strength PET
Good Impact Resistance Thermoplastic Urethane Good Chemical Resistance PBT
Translucency Good Bearing and Wear Properties UHMW-PE
Good Dimensional Stability Low Coefficient of Friction
Good Optical Qualities Difficult to Bond
AMORPHOUS COMMODITY PLASTICS SEMI-CRYSTALLINE COMMODITY PLASTICS
Key Characteristics: Materials: Key Characteristics: Materials:
Low Cost Acrylic Low Cost Polyethylene
Low Temperature Resistance] Polystyrene Low Temperature Resistance Polypropylene
Low Strength ABS Low Strength Polymetnylpentene(TPX)
Good Dimensional Stability PVC Excellent Chemical Resistance
Bond Well PETG Low Coefficient of Friction
Typically Transparent CAB Near Zero Moisture Absorption
Very Good Electrical Properties
Good Toughness
AMORPHOUS PLASTICS KEY CHARACTERISTICS: SEMI-CRYSTALLINE PLASTICS KEY CHARACTERISTICS:
Soften Over a Broad Range Of Temperatures Sharp Melting Point
Easy to Thermoform Difficult to Thermoform
Tend to Be Transparent Tend to Be Opaque
Bond Well Using Adhesives and Solvents Difficult To Bond Using Adhesives and Solvents
Prone To Stress Cracking Good Resistance To Stress Cracking
The IAPD Plastics Primer,
Poor FatigueModule
Resistance4 Good Fatigue Resistance
Stuctural Applications Only (Not for Bearing & Wear) Good For Bearing and Wear, As Well As Structural Applications
You might also like
- Cube Tetris AssembleDocument8 pagesCube Tetris AssembleLolo VingtcinqNo ratings yet
- Engineering Plastics Properties and ApplicationsDocument28 pagesEngineering Plastics Properties and ApplicationsApoorva MNNo ratings yet
- IAPD Thermoplastics Module on Imidized Plastics Properties and ApplicationsDocument40 pagesIAPD Thermoplastics Module on Imidized Plastics Properties and ApplicationsbrotherNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Commodity Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsDocument35 pagesAmorphous and Semi-Crystalline Commodity Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsrajkalmekarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Basics of Plastic Materials and The IAPD Thermoplastics RectangleDocument20 pagesUnderstanding The Basics of Plastic Materials and The IAPD Thermoplastics RectangleMiranda BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsDocument29 pagesAmorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsabhidssNo ratings yet
- IAPD Guide to Engineering ThermoplasticsDocument29 pagesIAPD Guide to Engineering ThermoplasticsFranzMigNo ratings yet
- Fisicoquímica de Los Polímeros 1Document29 pagesFisicoquímica de Los Polímeros 1Kevin Alvarado GómezNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV-Non MetallicDocument112 pagesUNIT-IV-Non MetallicSethu ramNo ratings yet
- Week-10 PolymersDocument40 pagesWeek-10 PolymersMoey RenNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Civil Engineering ApplicationsDocument33 pagesPolymers in Civil Engineering Applicationslimbong budimanNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Civil Engineering: Properties and ApplicationsDocument34 pagesPolymers in Civil Engineering: Properties and ApplicationsSiriluck NevestNo ratings yet
- Ens TecDocument28 pagesEns TecBorja CanalsNo ratings yet
- Technical Yarns: Nahida Akter Ela Assistant Professor, AUSTDocument30 pagesTechnical Yarns: Nahida Akter Ela Assistant Professor, AUSTimranNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics: Submitted By:)Document15 pagesThermoplastics: Submitted By:)Nikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE336 12 Polymer CompositesDocument34 pagesCE336 12 Polymer CompositesAmit karNo ratings yet
- Ghid Mase PlasticeDocument3 pagesGhid Mase PlasticeLavinia CalinNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor Dept of Mechanical & Design Program IIT Kanpur, IndiaDocument27 pagesMatrices: Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor Dept of Mechanical & Design Program IIT Kanpur, IndiaMahesh RajaNo ratings yet
- Polyplastics General Plastics InfoDocument56 pagesPolyplastics General Plastics InfoSARAI MARINNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Engineering Materials Topic: Engineering Thermoplastics-PolycarbonateDocument33 pagesUnit Iii Engineering Materials Topic: Engineering Thermoplastics-PolycarbonateArchies ParabNo ratings yet
- ThermoplasticsDocument11 pagesThermoplasticsஞான கிங்ஸ்பர்No ratings yet
- PolyethyleneDocument51 pagesPolyethyleneiiphyd2403No ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Resins: PE & PP GuideDocument8 pagesThermoplastic Resins: PE & PP GuideRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor Dept of Mechanical & Design Program IIT Kanpur, IndiaDocument27 pagesMatrices: Dr. J. Ramkumar Professor Dept of Mechanical & Design Program IIT Kanpur, Indiadavid josephNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics: by Kenneth Chaw (A13KM0053)Document7 pagesThermoplastics: by Kenneth Chaw (A13KM0053)Kenneth ChawNo ratings yet
- 15-Ktp PRR PipesDocument46 pages15-Ktp PRR PipesmohammedNo ratings yet
- V4.0 Common Polymers Selection and PropertiesDocument1 pageV4.0 Common Polymers Selection and PropertiesКрасимир ГеоргиNo ratings yet
- HPPs: Properties and ApplicationsDocument57 pagesHPPs: Properties and ApplicationsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Denure Base ResinDocument94 pagesDenure Base ResinVishnu S Pattath100% (1)
- POLYMERSDocument17 pagesPOLYMERSNur Nabila HudaNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics - Properties and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesThermoplastics - Properties and Applicationslenojerin3486No ratings yet
- Overview of Composite Materials & the Autoclave MethodDocument12 pagesOverview of Composite Materials & the Autoclave MethodAnishok MishraNo ratings yet
- 11-Almunaif Prr-Pipes and FittingsDocument44 pages11-Almunaif Prr-Pipes and FittingsmohammedNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Molding EDocument9 pagesPlastic Injection Molding Egopal06No ratings yet
- Polymers in Civil EngineeringDocument33 pagesPolymers in Civil EngineeringMayank MishraNo ratings yet
- Extra Notes For PolymerDocument8 pagesExtra Notes For PolymerNHNo ratings yet
- Research Article 1Document31 pagesResearch Article 1Rohit SachdevNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics Selection GuideDocument1 pageThermoplastics Selection GuidelokomundoNo ratings yet
- The Thermoset Difference: Thermoset vs. Thermoplastic: © 2014 Davies Molding LLCDocument4 pagesThe Thermoset Difference: Thermoset vs. Thermoplastic: © 2014 Davies Molding LLCshafiraNo ratings yet
- PPO SlideDocument29 pagesPPO SlideRadhashyam GiriNo ratings yet
- PolyimidesDocument2 pagesPolyimidesthinnnhNo ratings yet
- Design Guide: Injection MoldingDocument17 pagesDesign Guide: Injection MoldingVictor Villouta LunaNo ratings yet
- A1120897415 23418 4 2018 PolymersDocument43 pagesA1120897415 23418 4 2018 PolymersKushNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Plastic Parts For Car Interior: Project TitleDocument56 pagesDesign and Development of Plastic Parts For Car Interior: Project TitleJyoti KaleNo ratings yet
- Materials GuideDocument1 pageMaterials GuideggudayakumarNo ratings yet
- ElastomersDocument42 pagesElastomersAkash YadavNo ratings yet
- Polymer Preparation:: 1.basic SynthesisDocument20 pagesPolymer Preparation:: 1.basic Synthesiswaqar_baloch_07No ratings yet
- Flexible Plastic Film Laminates SeminarDocument58 pagesFlexible Plastic Film Laminates SeminarEtHical EmoTionNo ratings yet
- Polymer'S: Ashok Awinash Dulip - 1106105316 ANTONIUS IVAN - 1106071776Document39 pagesPolymer'S: Ashok Awinash Dulip - 1106105316 ANTONIUS IVAN - 1106071776John William HorasiaNo ratings yet
- Polypropylene (PP)Document8 pagesPolypropylene (PP)julioNo ratings yet
- Material Science ContentDocument23 pagesMaterial Science ContentHoongNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument20 pagesPolymerslakshay ManglaNo ratings yet
- Plastics Material For DPT Iv SemDocument49 pagesPlastics Material For DPT Iv SemMohsin Alam100% (2)
- Design For Plastic Processing: Group 1 Faisal Bin Abd. Nasir Gan Yin Ting Habibah Binti Abd. MutallibDocument24 pagesDesign For Plastic Processing: Group 1 Faisal Bin Abd. Nasir Gan Yin Ting Habibah Binti Abd. MutallibKelly GanNo ratings yet
- CEM-001 CelaneseQuickRefTrifold AM 0913Document3 pagesCEM-001 CelaneseQuickRefTrifold AM 0913cesaroleinikNo ratings yet
- Engineering Plastic Products: Established 1980Document8 pagesEngineering Plastic Products: Established 1980ananduesi3276No ratings yet
- Fiber and TextileDocument43 pagesFiber and Textileinfo.akira.ictNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Santa Rosa Junior College Spring 2009 Engr 45 - Materials ScienceDocument23 pagesPolymers: Santa Rosa Junior College Spring 2009 Engr 45 - Materials ScienceAnish SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Polycarbonate: Experiment and Modeling for Aeronautical and Aerospace ApplicationsFrom EverandMechanical Properties of Polycarbonate: Experiment and Modeling for Aeronautical and Aerospace ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Drugs Pharmacy BooksList2011 UBPStDocument10 pagesDrugs Pharmacy BooksList2011 UBPStdepardieu1973No ratings yet
- Patent for Fired Heater with Radiant and Convection SectionsDocument11 pagesPatent for Fired Heater with Radiant and Convection Sectionsxyz7890No ratings yet
- A Compilation of Thread Size InformationDocument9 pagesA Compilation of Thread Size Informationdim059100% (2)
- Tutorial On The ITU GDocument7 pagesTutorial On The ITU GCh RambabuNo ratings yet
- Aortic Stenosis, Mitral Regurgitation, Pulmonary Stenosis, and Tricuspid Regurgitation: Causes, Symptoms, Signs, and TreatmentDocument7 pagesAortic Stenosis, Mitral Regurgitation, Pulmonary Stenosis, and Tricuspid Regurgitation: Causes, Symptoms, Signs, and TreatmentChuu Suen TayNo ratings yet
- 1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFDocument4 pages1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFIan WoodsNo ratings yet
- CAT Ground Engaging ToolsDocument35 pagesCAT Ground Engaging ToolsJimmy Nuñez VarasNo ratings yet
- Sto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of SpecializationDocument2 pagesSto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of Specializationinah jessica valerianoNo ratings yet
- Is.4162.1.1985 Graduated PipettesDocument23 pagesIs.4162.1.1985 Graduated PipettesBala MuruNo ratings yet
- Problem SolutionsDocument5 pagesProblem SolutionskkappaNo ratings yet
- Sayre Materia Medica-3Document87 pagesSayre Materia Medica-3ven_bams5840No ratings yet
- The CongoDocument3 pagesThe CongoJoseph SuperableNo ratings yet
- Project Binder 2Document23 pagesProject Binder 2Singh DhirendraNo ratings yet
- JUPITER 9000K H1PreliminaryDocument1 pageJUPITER 9000K H1PreliminaryMarian FlorescuNo ratings yet
- CP 343-1Document23 pagesCP 343-1Yahya AdamNo ratings yet
- VA TearDownDocument5 pagesVA TearDownfaj_larcfave5149No ratings yet
- Railway Airport Docks and HarbourDocument21 pagesRailway Airport Docks and HarbourvalarmathibalanNo ratings yet
- Product ListDocument4 pagesProduct ListyuvashreeNo ratings yet
- 1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDDocument81 pages1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDJerome Samuel100% (1)
- Antennas Since Hertz and MarconiDocument7 pagesAntennas Since Hertz and MarconiTaiwo Ayodeji100% (1)
- Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesNickel-Metal Hydride Battery Safety Data SheetYeong WheeNo ratings yet
- Who will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisDocument12 pagesWho will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisbhasker sharmaNo ratings yet
- DR-M260 User Manual ENDocument87 pagesDR-M260 User Manual ENMasa NourNo ratings yet
- Sattvik Brochure - Web VersionDocument4 pagesSattvik Brochure - Web Versionudiptya_papai2007No ratings yet
- Math 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionDocument2 pagesMath 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionNyannue FlomoNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Ep15krtDocument37 pagesCaterpillar Ep15krtIvan MajikNo ratings yet
- DNB Paper - IDocument7 pagesDNB Paper - Isushil chaudhari100% (7)
- Reiki BrochureDocument2 pagesReiki BrochureShikha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Young Women's Sexuality in Perrault and CarterDocument4 pagesYoung Women's Sexuality in Perrault and CarterOuki MilestoneNo ratings yet