Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Natio
Uploaded by
Nisar Akbar Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views16 pagesNatio
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNatio
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views16 pagesNatio
Uploaded by
Nisar Akbar KhanNatio
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
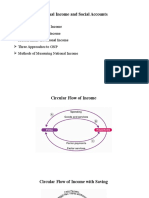
National Income
National Income is defined as the sum total
of all the goods and services produced in a
country, in a particular period of time.
Normally this period consists of one year
duration, as a year is neither too short nor
long a period. National product is usually
used synonymous with National income.
Concepts of National Income
There are different concepts of National
Income, namely; GNP, GDP, NNP, Personal
Income and Disposable Income
Gross National Product (GNP)
GNP at market price is sum total of
all the goods and services produced
in a country during a year and net
income from abroad.
Gross National Product (GNP)
While calculating GNP, the final goods and
services of the following are considered:
(a) Consumer goods and services.
(b) Gross private domestic investment.
(c) Goods and services produced by
Government.
(d) Net income from abroad
Approaches to GNP
There are three different approaches to GNP, namely income
approach, expenditure approach and product
Approach
1. Income approach
2. Expenditure approach
3. Product approach
Income approach
In income approach, we find the different categories of Income
namely;
(1) Wages and salaries
(2) Rents
(3) Interest
(4) Dividend
(5) Undistributed corporate profits
(6) Mixed incomes
(7) Direct taxes
(8) Indirect taxes
(9) Depreciation
(10) Net income from abroad.
Expenditure approach
In expenditure approach, we find the different
categories of expenditure namely,
(1) Private consumption expenditure
(2) Gross domestic private income
(3) Net foreign income
(4) Government expenditure on goods and
services.
Product approach
In product approach, we find the following categories of
output. (1) Final market value of goods and services
(2) Less cost of intermediate goods.
The following factors are to be considered while
calculating the GNP:
1. Only those goods and services which can be measured by
Money.
2. Market price of final goods and services alone will be
considered.(intermediate not included)
3. Services which are done free of cost are not considered.
4. Productions done in current year alone are considered.
5. Illegal activities are not included
GNP at Market Price
If we multiply the total output produced
in one year by their ‘Market Prices’, we
get GNP at market price
Net National Product (NNP)
In the process of production of goods and
services, there will be some depreciation of
fixed capital also called as consumption of
fixed capital, if the value of depreciation is
deducted from the value of gross national
product in a year, we obtain the value of net
national product.
National income at Factor Cost
• The National Income or national income at
factor cost is equal to net national product
minus indirect taxes plus subsidies
• NI at factor cost = NNP-Indirect Taxes + Subsidies
Personal Income
• Personal Income as “the income actually
received by persons from all sources in the
form of current transfer payments and factor
income.”
PI=national income-social security contribution –
corporate income taxes+ transfer payments
Disposable Income
• The income remaining with individuals after
deduction of all taxes levied against their
income and their property by the government.
• Disposable Income= PI- Personal Taxes
• Disposable Income= Consumption + Saving
Difficulties of measurement
• Non-monetised transactions
• Treatmentment of government activities
• Foreign firms
Difficulties of measurement in
developing counteries
• Prevalance of non monetised transactions in
under-developed countries
• No idea of quality and value of out put due to
illeteracy
• Lack of differentiation in economic functioning
• Lack of adequate statistical tools
Uses and Importance of National
Income
• Useful in measuring the standard of living of a nation through
estimating per capita income of the nation.
• Time series comparison (year to year). Measuring growth of the
economy.
• Comparison between two or more countries can be made.
• Able to know and analyze the contribution made and
performance by each production sector in the economy and
thus taken ample step for rectification
• Useful in measuring inequalities in the distribution of income.
• Useful in revealing the expenditure pattern of a country.
• Useful in measuring the level and pattern of investment.
• Balance of payments pattern.
• National income as an indicator of success or failure of national
planning.
You might also like
- Summary of David A. Moss's A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics, Second EditionFrom EverandSummary of David A. Moss's A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Nationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Document37 pagesNationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ofp 015Document51 pagesOfp 015abdul ahmad kilimaNo ratings yet
- National Income (Notes) IMBADocument27 pagesNational Income (Notes) IMBASubham .MNo ratings yet
- Economics IDocument34 pagesEconomics IKevin kayNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 National IncomeDocument65 pagesLec 9 National IncomeLakhan Subhash TrivediNo ratings yet
- 1 National IncomeDocument17 pages1 National Incomealekya.nyalapelli03No ratings yet
- Me Unit-5Document7 pagesMe Unit-5Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument24 pagesNational IncomePranay Sai Garepally100% (1)
- National Income AccountingDocument21 pagesNational Income AccountingVivek VashisthaNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Chap I National IncomeDocument34 pagesChap I National IncomeVAISALY S MBANo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument66 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeAshish Tewani100% (3)
- National IncomeDocument81 pagesNational IncomeGaurav gusaiNo ratings yet
- National Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh ChoudharyDocument18 pagesNational Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh Choudharyemin4No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument28 pagesNational Incomealexgarfield2003No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument32 pagesNational IncomeSona VermaNo ratings yet
- National Income in India, Concept and MeasurementDocument87 pagesNational Income in India, Concept and MeasurementPreeti BajajNo ratings yet
- The Concepts of National IncomeDocument22 pagesThe Concepts of National IncomeHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- National Income - ConceptsDocument21 pagesNational Income - ConceptsKunal GargNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Inter CA EconomicDocument163 pagesInter CA Economicmoceh87222No ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7.national Income Accounting 1Document23 pagesUnit 7.national Income Accounting 1RaceSome MagarNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument18 pagesNational Incomepankajpatidar7440No ratings yet
- National Income-1Document17 pagesNational Income-1Ms. Vandana MohantyNo ratings yet
- National Income Final PPT Full Including PYQDocument69 pagesNational Income Final PPT Full Including PYQSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Mod 1Document18 pagesMacroeconomics Mod 12580 Soumil SinghNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument26 pagesNational IncomerajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document10 pagesLecture Note 1mohaimenulakborNo ratings yet
- National Income: - by Shikha SinghDocument40 pagesNational Income: - by Shikha SinghPrashastiNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: National Income Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade CyclesDocument48 pagesMacro Economics: National Income Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade Cyclesusne902No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument7 pagesNational IncomeFahadNo ratings yet
- National Income PDFDocument12 pagesNational Income PDFReshma JainNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNP Concepts ExplainedDocument7 pagesGDP and GNP Concepts ExplainedAmjad KhanNo ratings yet
- Methods To Calculate National Income 64Document4 pagesMethods To Calculate National Income 64Shanmuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- National Income: Presented by Asst - Prof Nimbolkar V.R. MBA Finance (SET)Document18 pagesNational Income: Presented by Asst - Prof Nimbolkar V.R. MBA Finance (SET)Atul BorbaneNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics National Income PDFDocument9 pagesManagerial Economics National Income PDFSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationDocument15 pagesUNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationanushreeNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument4 pagesNational Incomesubbu2raj3372No ratings yet
- Understanding National IncomeDocument8 pagesUnderstanding National IncomeLaiba EqraNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument49 pagesNational IncomeStive JohnNo ratings yet
- Income CalculationDocument15 pagesIncome CalculationranjandkNo ratings yet
- Measuring National IncomeDocument19 pagesMeasuring National Incomessaeed_4No ratings yet
- National income and aggregate demand concepts explainedDocument22 pagesNational income and aggregate demand concepts explainedHarsh Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- National Income Analysis: Dr. Gopalakrishna B.VDocument29 pagesNational Income Analysis: Dr. Gopalakrishna B.Vshyam_ceeNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument18 pagesNational Income AccountingDeepikaa PoobalarajaNo ratings yet
- Eco National IncoomeDocument10 pagesEco National Incoomeanisha madhukarNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Measurement of National IncomeDocument66 pagesConcepts and Measurement of National IncomesubramanianNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document19 pagesSession 3Ramji TripathyNo ratings yet
- Measuring National Income: Concepts and MethodsDocument17 pagesMeasuring National Income: Concepts and MethodsPradeep RaviNo ratings yet
- GDP vs GNP: Understanding the Key DifferencesDocument30 pagesGDP vs GNP: Understanding the Key DifferencesHANISHA MODYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2Seamnia demoNo ratings yet
- National Income2Document44 pagesNational Income2Faith100% (1)
- Unit-V Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-V Managerial Economicsatulkumar.rise1No ratings yet
- 1 Basic Mathematics (1) 1Document6 pages1 Basic Mathematics (1) 1Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Saeed HaiderDocument2 pagesSaeed HaiderNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- 2016 FinalDocument98 pages2016 FinalNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- UBL Project ReportDocument64 pagesUBL Project ReportMuzammil_ims2507No ratings yet
- How To Succeed at TelesalesDocument22 pagesHow To Succeed at TelesalesNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- National Bank of Pakistan (HRM)Document31 pagesNational Bank of Pakistan (HRM)Waqas Aslam Khan60% (5)
- United Bank Limited (UBL) HRMDocument27 pagesUnited Bank Limited (UBL) HRMMohsin Mahmood90% (39)
- Flowchart - Grievance Level 1-3Document1 pageFlowchart - Grievance Level 1-3Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- MCB Bank Related AssignmentDocument80 pagesMCB Bank Related AssignmentNisar Akbar Khan100% (1)
- Askari Bank PRJCTDocument49 pagesAskari Bank PRJCTrehan100% (6)
- HBLDocument21 pagesHBLNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Grievance Procedure For Staff: A Guide To Handling Staff Complaints and ConcernsDocument9 pagesGrievance Procedure For Staff: A Guide To Handling Staff Complaints and ConcernsNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Wages and Employment: The Classical View:According To Pigou, TheDocument13 pagesWages and Employment: The Classical View:According To Pigou, TheNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Nation IncomeDocument11 pagesDetermination of Nation IncomeNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- 59df24f5dfe3a Tata Annual Report 2016Document76 pages59df24f5dfe3a Tata Annual Report 2016Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Etd1559 PDFDocument87 pagesEtd1559 PDFNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- AHL Annual Report 2017Document106 pagesAHL Annual Report 2017Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Defintion of EconomicsDocument10 pagesDefintion of EconomicsNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Art 60 030211Document3 pagesArt 60 030211FileuploaderNo ratings yet
- 2014 FinalDocument90 pages2014 FinalNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2017Document82 pagesAnnual Report 2017Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- 2013 FinalDocument87 pages2013 FinalNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Shezan AR 2016Document64 pagesShezan AR 2016Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- 2015 FinalDocument94 pages2015 FinalNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- 59df24f5dfe3a Tata Annual Report 2016Document76 pages59df24f5dfe3a Tata Annual Report 2016Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Annual13 PDFDocument162 pagesAnnual13 PDFNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- DOL Annual 2012Document71 pagesDOL Annual 2012Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- NIMIR Chemicals Annual Report 2016Document104 pagesNIMIR Chemicals Annual Report 2016Nisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- 2012 FinalDocument84 pages2012 FinalNisar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- MATLA PAYROLLDocument2 pagesMATLA PAYROLLTshikani JoyNo ratings yet
- Rochester MN Community ProfileDocument28 pagesRochester MN Community ProfilerebeccadriscollNo ratings yet
- Wild RiftDocument8 pagesWild RiftKomal AroraNo ratings yet
- Rich Dad Poor Dad SummaryDocument9 pagesRich Dad Poor Dad SummaryKashif KaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Investment Environment: Fundamentals of InvestingDocument14 pagesChapter 1 The Investment Environment: Fundamentals of InvestingElen LimNo ratings yet
- Significant Accounting PoliciesDocument7 pagesSignificant Accounting PoliciesMadhura Venkateswara SarmaNo ratings yet
- Basic math quiz with 21 multiple choice questionsDocument11 pagesBasic math quiz with 21 multiple choice questionsHeliosNo ratings yet
- Manning Elliott Newsletter - March 2013Document8 pagesManning Elliott Newsletter - March 2013Juan CañaSNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 MFRS 108 Changes in Acc Policies, Estimates, ErrorsDocument30 pagesTopic 6 MFRS 108 Changes in Acc Policies, Estimates, Errorsdini sofiaNo ratings yet
- Management Report On Reckitt Benckiser Bangladesh LTDDocument13 pagesManagement Report On Reckitt Benckiser Bangladesh LTDOld PagesNo ratings yet
- Money Growth and Inflation: in This Chapter, Look For The Answers To These QuestionsDocument14 pagesMoney Growth and Inflation: in This Chapter, Look For The Answers To These QuestionsPieceeNo ratings yet
- RESA TAX PreWeek (B43)Document23 pagesRESA TAX PreWeek (B43)MellaniNo ratings yet
- SMS BillDocument2 pagesSMS BillamitsbhatiNo ratings yet
- Prelude To The Awesome Power of Taxation.Document24 pagesPrelude To The Awesome Power of Taxation.Accounterist ShinangNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Cooperatives in VietnamDocument17 pagesAgricultural Cooperatives in VietnamAnonymous T4ptPKXNo ratings yet
- ACW2491 - 2018 S1 - WK 2 Lecture ExampleDocument2 pagesACW2491 - 2018 S1 - WK 2 Lecture Examplehi2joeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Regular Income Tax - Exclusion From Gross IncomeDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Regular Income Tax - Exclusion From Gross IncomeJason MablesNo ratings yet
- Completing a W-8BEN form for tax purposesDocument2 pagesCompleting a W-8BEN form for tax purposesJay100% (2)
- 252289600057294Document1 page252289600057294Pricila MercyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Capital Budgeting Defined Agency Problem in Capital BudgetingDocument107 pagesBasic Concepts Capital Budgeting Defined Agency Problem in Capital BudgetingKang JoonNo ratings yet
- Principles of Islamic Economics: © DR Muhammad Hamidullah Library, IIU, Islamabad. Http://iri - Iiu.edu - PKDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Islamic Economics: © DR Muhammad Hamidullah Library, IIU, Islamabad. Http://iri - Iiu.edu - PKHami KhaNNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument12 pagesProblemsJohn Carlo J. DominoNo ratings yet
- Less: Deduction@30%: © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument12 pagesLess: Deduction@30%: © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaAashish soniNo ratings yet
- Taxation AssignmentDocument4 pagesTaxation AssignmentSabika LindaNo ratings yet
- State of UP V Renusagar Power Co (1988)Document32 pagesState of UP V Renusagar Power Co (1988)Nishchal goelNo ratings yet
- Developer Job Offer Letter TemplateDocument5 pagesDeveloper Job Offer Letter TemplatedvvNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Housing Board, Circle - Iii, JaipurDocument1 pageRajasthan Housing Board, Circle - Iii, JaipurAshish AshishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document27 pagesChapter 07Rollon NinaNo ratings yet
- Market Value Vs Fair MV - 1Document7 pagesMarket Value Vs Fair MV - 1Jigesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Organization Structure: Sap Fi/CoDocument9 pagesOrganization Structure: Sap Fi/CoharishNo ratings yet