Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resource Based by Navneet S55
Uploaded by
Ritesh Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views8 pagesThe resource-based theory of the firm proposed by Peteraf focuses on a firm's resources and capabilities. For a firm to have a sustainable competitive advantage according to this theory, it requires: (1) heterogeneity between firms in their resource bundles, (2) ex-ante limits to competition for resources, and (3) imperfect mobility of resources. This allows the firm to achieve rents, sustain those rents against imitation, and capture the value of the rents internally.
Original Description:
Marketing Research
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe resource-based theory of the firm proposed by Peteraf focuses on a firm's resources and capabilities. For a firm to have a sustainable competitive advantage according to this theory, it requires: (1) heterogeneity between firms in their resource bundles, (2) ex-ante limits to competition for resources, and (3) imperfect mobility of resources. This allows the firm to achieve rents, sustain those rents against imitation, and capture the value of the rents internally.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views8 pagesResource Based by Navneet S55
Uploaded by
Ritesh KumarThe resource-based theory of the firm proposed by Peteraf focuses on a firm's resources and capabilities. For a firm to have a sustainable competitive advantage according to this theory, it requires: (1) heterogeneity between firms in their resource bundles, (2) ex-ante limits to competition for resources, and (3) imperfect mobility of resources. This allows the firm to achieve rents, sustain those rents against imitation, and capture the value of the rents internally.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Resource Based
Strategy View
Narinder jeet kaur
S 55
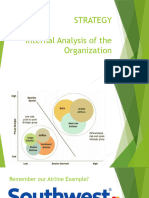
PART 3: RESOURCE BASED ‘THEORY’ OF
THE FIRM
• The “resource-based” approach is concerned with the
nature of the firm’s resources and how these resources
are combined into capabilities.
• This is proposed by Peteraf (1993). Her approach is
outlined below and summed up the figure below-
Peteraf’s model - Linn Products
Ex-post limits to
Heterogeneity
competition
The industry is made of firms
Specialist knowledge
with access to different
and reputation
resources and skills. Linn has
particular distinctive Competitive
competencies.
Advantage
Imperfect Ex-ante limits to
Mobility competition
Shared specialist knowledge Linn has demonstrated an
and reputation ability to leverage the
potential of existing
technologies
ALL THESE LEAD TO SUSTAINABLE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
THROUGH DIFFERENTATION
Competitive Advantage Peteraf
A firm is said to have a competitive advantage when it can:
• achieve rents: which requires resource heterogeneity
between firms (some better bundles than others).
• enjoy rents that are not offset by the costs of achieving a
superior set of resources: which requires ex ante limits to
competition for those resources.
• appropriate those rents for the firm: which requires
imperfect resource mobility.
• sustain those rents: which requires ex-post limits to
competition.
Heterogeneity:
• Bundles of resources and capabilities are heterogeneous
across firms. Heterogeneity implies that firms with
superior resources/ capabilities will earn superior returns.
• An important class of resources are those which are
limited in the short run but may be renewed and
expanded within firms that use them. Prahalad and Hamel
(1990) argue that core competencies - particularly
knowledge-based resources - are enhanced as they are
used because of learning.
Ex-post limits to competition
Forces which limit competition from imitators.
These arise from sources already discussed:
Imperfect imitability, replicability, and
substitutability of resources/ capabilities isolating
the firm from challengers.
Ex ante limits to competition
• The source of a firm’s rents is a superior resource position.
• But imagine the situation before any firm has achieved
this position.
• If many firms recognised its potential, a competitive
struggle would ensue to obtain the resources and build
the capabilities to occupy that position.
• This process would compete away all rents that could be
obtained from occupying the position. For example,
• (a)National Lottery licence.
• (b)Sony licence for transistor.
Imperfect resource mobility
• This refers to the marketability or otherwise
of the underlying resources and capabilities.
• Thus good high street locations are important
for retailers but competition means the rental
costs reflect this fact. The value of the
location is captured by the property owner
not the retailer per se.
You might also like
- Reading 1 - Science - BIOL105 - Disease - ResponseDocument9 pagesReading 1 - Science - BIOL105 - Disease - ResponsemykrohNo ratings yet
- Antenna Seatel Series 94 Troubleshooting GuideDocument248 pagesAntenna Seatel Series 94 Troubleshooting GuideDo0k13100% (3)
- Ladd CC 1964 - Stress-Strain Behavior of Saturated Clay and Basic Strength Principles PDFDocument125 pagesLadd CC 1964 - Stress-Strain Behavior of Saturated Clay and Basic Strength Principles PDFSaraswati NoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 STRAT InternalScanning T.NeparidzeDocument28 pagesLecture5 STRAT InternalScanning T.NeparidzeDemonSideNo ratings yet
- Chapter4. Internal AnalysisDocument25 pagesChapter4. Internal AnalysisBùi HiềnNo ratings yet
- STRM 04Document13 pagesSTRM 04Professor Dr. Md. Atiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document40 pagesChapter 03Mohamed WDNo ratings yet
- Evaluating A Firm's Internal CapabilitiesDocument21 pagesEvaluating A Firm's Internal Capabilitiessweta_kakati100% (26)
- 5 InternalAnalysis-1Document32 pages5 InternalAnalysis-1gre.gomez426No ratings yet
- Chapter 4, Evaluating Internal EnvironmentDocument12 pagesChapter 4, Evaluating Internal EnvironmentStuti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 CompleteDocument27 pagesChapter 4 CompleteHamza GoherNo ratings yet
- The VRIO FrameworkDocument3 pagesThe VRIO Frameworklgn70No ratings yet
- Vrio TruefanDocument21 pagesVrio TruefanJoseph NaderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document22 pagesLecture 4Phu Thien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage (CA) : Ch-3 of SalonerDocument35 pagesCompetitive Advantage (CA) : Ch-3 of SalonerMahnoor AmjadNo ratings yet
- Presented To: Dr. Ashraf Labib: Implemented by Group 5Document15 pagesPresented To: Dr. Ashraf Labib: Implemented by Group 5eslamNo ratings yet
- The Internal Environment - Resources - Capabilities - and Core CompetenciesDocument40 pagesThe Internal Environment - Resources - Capabilities - and Core CompetenciesBirungi TinishaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Sihwan A - Executive Summary of Competing On ResourcesDocument4 pagesMuhammad Sihwan A - Executive Summary of Competing On ResourcesmsihwanaNo ratings yet
- BPS CHP 03Document42 pagesBPS CHP 03Mimi mariyamNo ratings yet
- MGT4001 Internal Organisation Competitive Advantage For StudentsDocument31 pagesMGT4001 Internal Organisation Competitive Advantage For Studentss225830No ratings yet
- Analisis Internal JatmikoDocument13 pagesAnalisis Internal Jatmikosoo nginNo ratings yet
- Internal Scanning: Organizational AnalysisDocument31 pagesInternal Scanning: Organizational AnalysisARLENE GARCIANo ratings yet
- Inrtoduction To Strategic ManagementDocument45 pagesInrtoduction To Strategic ManagementGhost RiderNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Company Resourece Competitive CapabilityDocument57 pagesEvaluating Company Resourece Competitive CapabilityharithasahuNo ratings yet
- Mib (PPT) PTDocument17 pagesMib (PPT) PTdeepali sharmaNo ratings yet
- ch5 Internal AnalysisDocument45 pagesch5 Internal AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1semahegn amareNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument20 pagesStrategic ManagementATI BUDGETNo ratings yet
- Im 2Document5 pagesIm 2Tanya MarwahNo ratings yet
- IMGT490 Ch3Document40 pagesIMGT490 Ch3Zeina HassaneinNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Presentation Resources and Capabilities 2022 11-18-14!42!28Document51 pagesCH 5 Presentation Resources and Capabilities 2022 11-18-14!42!28SOFIA TERESA MURUA BENITEZNo ratings yet
- Internal Environment and Core CompetencyDocument35 pagesInternal Environment and Core CompetencymussaiyibNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing Management-: The Competitive Advantage & Value CreationDocument29 pagesStrategic Marketing Management-: The Competitive Advantage & Value Creationnaveen jaffriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cbmec 2Document52 pagesChapter 5 Cbmec 2Virlaine JameroNo ratings yet
- Competing On Resources: A Comprehensive Study of Article by David J. Collis and Cynthia A. MontgomeryDocument13 pagesCompeting On Resources: A Comprehensive Study of Article by David J. Collis and Cynthia A. MontgomeryEkansh VashisthaNo ratings yet
- VRIO FrameworkDocument14 pagesVRIO FrameworkaditiNo ratings yet
- CH 6 AMS - Understanding The Organizational Resource BaseDocument39 pagesCH 6 AMS - Understanding The Organizational Resource BaseAde TenyomNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Chapter 01 Part 2Document31 pagesStrategic Management Chapter 01 Part 2Hiwot GebreEgziabherNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management & Theory - The Internal EnvironmentDocument27 pagesStrategic Management & Theory - The Internal EnvironmentDarshan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 & 5: Internal Analysis & Strategy DevelopmentDocument63 pagesLecture 4 & 5: Internal Analysis & Strategy DevelopmentApostol BoujevNo ratings yet
- Internal AnalysisDocument24 pagesInternal AnalysisRa JaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: Internal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, and Core CompetenciesDocument18 pagesStrategic Marketing: Internal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, and Core CompetenciesShamol EuNo ratings yet
- Cornerstones of Competitive Advantage: A Resource Based ModelDocument27 pagesCornerstones of Competitive Advantage: A Resource Based ModelhhaiderNo ratings yet
- Resources and CapabilitiesDocument13 pagesResources and CapabilitiesRayNo ratings yet
- Part I - Internal Situation AnalysisDocument38 pagesPart I - Internal Situation Analysistranvuhoaan31No ratings yet
- pp04Document38 pagespp04Aaya BougrineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Core Competencies, Resources, & Capabilities)Document4 pagesChapter 4 (Core Competencies, Resources, & Capabilities)Sagita RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- ADMS 1000 - Session 4 SlidesDocument35 pagesADMS 1000 - Session 4 Slidespeggysun1023No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Internal AnalysisDocument53 pagesLecture 4 Internal AnalysisAyushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Marketing - HighTech - 3e - ch02 Strategic Marketing PlanningDocument48 pagesMarketing - HighTech - 3e - ch02 Strategic Marketing PlanningSudipto MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Creating Competitive AdvantageDocument18 pagesCreating Competitive AdvantageAli RAZANo ratings yet
- CH 5Document32 pagesCH 5Mohammed AttaNo ratings yet
- Resouce Based ViewDocument17 pagesResouce Based ViewpisupativkNo ratings yet
- Internal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, and Core CompetenciesDocument44 pagesInternal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, and Core Competenciesjunaid_256No ratings yet
- Introduction 1Document68 pagesIntroduction 1Chaudhary Ahmad100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - Internal AnalysisDocument9 pagesLesson 3 - Internal AnalysissurangauorNo ratings yet
- 2 - Evaluating Internal EnvironmentDocument28 pages2 - Evaluating Internal EnvironmentAayushya ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- SM - Internal Analysis & Competitive AdvantageDocument13 pagesSM - Internal Analysis & Competitive AdvantageAkshat TiwariNo ratings yet
- ch5 (Organizational Analysis IndustryDocument47 pagesch5 (Organizational Analysis IndustryPavithra TamilNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Presenter: Ismatullah Butt PHD (Candidate)Document24 pagesOperations Management: Presenter: Ismatullah Butt PHD (Candidate)Ismatullah ButtNo ratings yet
- EVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESFrom EverandEVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESNo ratings yet
- Investing with Intelligent ETFs: Strategies for Profiting from the New Breed of SecuritiesFrom EverandInvesting with Intelligent ETFs: Strategies for Profiting from the New Breed of SecuritiesNo ratings yet
- MIS: Web 2.0 & Web 3.0: By: Somnath MitraDocument11 pagesMIS: Web 2.0 & Web 3.0: By: Somnath MitraRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Mis - Gds Session - 10: by Somnath MitraDocument14 pagesMis - Gds Session - 10: by Somnath MitraRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- GRP 6fenesta - Storyline v4Document15 pagesGRP 6fenesta - Storyline v4Ritesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Allotment Letter - OCPKDocument18 pagesAllotment Letter - OCPKRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Writing ProposalsDocument100 pagesWriting ProposalsSaad Motawéa50% (2)
- Fmparente Erftc Porto 20090605Document78 pagesFmparente Erftc Porto 20090605ChiefpereraNo ratings yet
- A словаDocument297 pagesA словаailisha libraNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 20 Paper (01-05-2023)Document30 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 20 Paper (01-05-2023)vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
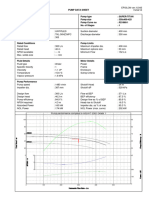
- Goulds Pumps: WE SeriesDocument4 pagesGoulds Pumps: WE SeriesJorge ManobandaNo ratings yet
- Who Am I MemoDocument2 pagesWho Am I Memoapi-652685391No ratings yet
- 7.proceeding Snib-Eng Dept, Pnp-IndonesiaDocument11 pages7.proceeding Snib-Eng Dept, Pnp-IndonesiamissfifitNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Topic1 Digital Logic IntroductionDocument33 pagesUnit1 Topic1 Digital Logic IntroductionHari Kumar N CNo ratings yet
- Layout Proposal CSD 17 5613Document1 pageLayout Proposal CSD 17 5613Cesar Garay RangelNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Axiom Control BoardDocument15 pagesDatasheet Axiom Control BoardZEN ONENo ratings yet
- STPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 Sem 2Document8 pagesSTPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 Sem 2vtdvkkjbf100% (2)
- Watson 2015Document5 pagesWatson 2015Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- TKL Pump - Data - SheetDocument1 pageTKL Pump - Data - Sheetธนาชัย เต็งจิรธนาภาNo ratings yet
- BBA LLB Global I Semester Statitics Unit IDocument22 pagesBBA LLB Global I Semester Statitics Unit IPragyan BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- HS527 SilvanChipDocument3 pagesHS527 SilvanChipBouhafs AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Program in Less Than 24 MonthsDocument2 pagesProgram in Less Than 24 MonthsHermi BurquesNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S223878542300652X MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S223878542300652X MainFahra Aqilla AzzurahNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document42 pagesCH 15mah b0% (1)
- PDF Prop Trading GuidelineDocument16 pagesPDF Prop Trading GuidelineMuhammad ZeeharzNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Insulation & RefractoriesDocument9 pages2.5 Insulation & Refractoriesriyazcomm_257961932No ratings yet
- Njagi Substructures Boq 2020Document76 pagesNjagi Substructures Boq 2020michaelNo ratings yet
- Experion MX MD Controls R700.1 Traditional Control: Configuration and System Build ManualDocument62 pagesExperion MX MD Controls R700.1 Traditional Control: Configuration and System Build Manualdesaivilas60No ratings yet
- 2010 Summer SchoolDocument31 pages2010 Summer SchoolAlbanita MendesNo ratings yet
- Exam2SampleProblems SP17 - 1507832832437Document5 pagesExam2SampleProblems SP17 - 1507832832437rohitrgt4uNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Manager ConceptDocument9 pagesConcurrent Manager Conceptnikhil_cs_08No ratings yet
- DR TahaniCV 2012Document5 pagesDR TahaniCV 2012Yousif_AbdalhalimNo ratings yet
- My Intro To ChatGPT SlideshowDocument38 pagesMy Intro To ChatGPT SlideshowKamelia SavovaNo ratings yet