Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 Combustion II
Uploaded by
raja.mt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views16 pagesThe document discusses fluidized bed combustion, which involves passing air or gas through a bed of solid particles like sand at high velocities until the bed behaves like a fluid, allowing efficient combustion of fuels like coal. It explains the mechanisms, types like atmospheric and pressurized fluidized beds, fuel and sorbent requirements, advantages of reduced emissions and ability to burn different fuels, and disadvantages like high dust loads and limited maximum operating temperatures.
Original Description:
6 Combustion II
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses fluidized bed combustion, which involves passing air or gas through a bed of solid particles like sand at high velocities until the bed behaves like a fluid, allowing efficient combustion of fuels like coal. It explains the mechanisms, types like atmospheric and pressurized fluidized beds, fuel and sorbent requirements, advantages of reduced emissions and ability to burn different fuels, and disadvantages like high dust loads and limited maximum operating temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views16 pages6 Combustion II
Uploaded by
raja.mtThe document discusses fluidized bed combustion, which involves passing air or gas through a bed of solid particles like sand at high velocities until the bed behaves like a fluid, allowing efficient combustion of fuels like coal. It explains the mechanisms, types like atmospheric and pressurized fluidized beds, fuel and sorbent requirements, advantages of reduced emissions and ability to burn different fuels, and disadvantages like high dust loads and limited maximum operating temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Combustion of solid fuels
Combustion of liquid fuels
Rules for combustion of oil
1. Atomize the oil completely to produce a fine
uniform spray
2. Mix the air and fuel thoroughly
3. Introduce enough air for combustion, but
limit the excess air to a maximum of 15%
4. Keep the burners in good condition
Fluidized bed combustion
When a air or gas is passed through an inert bed of solid
particles (supported on mesh) will initially sleek upward
through sand.
With Further increase in velocity the air starts bubbling
through bed and Particles attain a state of high
turbulence.
Under such conditions Bed attains the appearance of fluid
and exhibit the properties of Fluid.
MECHANISM OF FLUIDIZED BED
COMBUSTION
Temperature of bed should be at least equal to ignition
temperature of coal.
Bed temperature must not increase melting point of Ash.
Equilibrium temperature achieved through transfer
tubes immersed in bed and walls of combustor.
Gas velocity must be maintained between fluidization
velocity and the particle entrainment velocity.
Mechanism
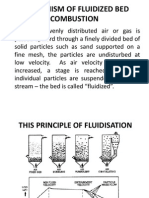
FIXING, BUBBLING AND FAST FLUIDIZED BEDS
As the velocity of a gas flowing
through a bed of particles
increases, a value is reaches
when the bed fluidizes and
bubbles form as in a boiling
liquid. At higher velocities the
bubbles disappear; and the solids
are rapidly blown out of the bed
and must be recycled to maintain
a stable system.
TYPES OF FBC
I. AFBC : Atmospheric Fluidized Bed Combustion
Bubbling fluidized bed combustion.
Circulating fluidized bed combustion.
II. PFBC : Pressurized fluidized bed combustion.
Circulating fluidized bed
Bubbling bed
PRESSURIZED FLUIDIZED BED COMBUSTION
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
Low volatile fuels such as Anthracite must be crushed to
smaller top size than higher volatile fuels
( approx 1/6 inch or less)
Larger fuel size are acceptable for higher volatile fuels.
SORBENT REQUIREMENTS:
Lime stone is crushed to a top size of 1000 microns
with average size 150 microns.
ADVANTAGE OF FBC BOILERS
Considerable reduction in boiler size is possible due to
high heat transfer rate.
Low combustion temp. of the order of 750-900 C
facilitates burning of coal with low ash fusion temp.
,prevent NOx- formation, reduces high temp. corrosion
and erosion.
High Sulphur coals can be burnt efficiently without much
generation of Sox by feeding limestone continuously.
The unit can be designed to burn a variety of fuels.
High turbulence of the bed facilitates quick startup
and shut down.
Efficiency of 80% and above can be achieved.
Lower coal crushing cost due to higher particle size.
High thermal inertia helps to overcome the problem
of flame stability.
DISADVANTAGES OF FBC
• The need for fuel particle size to be less than 300mm.
• A relatively high pressure-drop is required to fluidize a bed of
granular particles. The pressure drop is proportional to the weight
of the bed, but after incipient fluidization rises only slowly with
the gas velocity.
• The flue gas carries a high dust load.
• Although the operation of a bed is basically stable and the evolution
Of temperature is slow the problem of fluidized bed regulation and
control is not straightforward.
• The possibility of sintering of bed material limits the maximum
operating temperature, generally to a value of 850-950 °C, but
sometimes more.
• The operating experience with fluidized bed combustors is still
limited. Wear up on submerged surfaces, the occurrence of attrition
and elutriation upon bed particles, the evolution of the particle size
distribution and of the composition of the bed material cannot be
predicted with confidence.
You might also like
- Analytical Groundwater Modeling Theory and Applications Using PythonDocument243 pagesAnalytical Groundwater Modeling Theory and Applications Using PythonCesar Orlando Villalobos HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Boiler Stoker Firing PrincipleDocument4 pagesBoiler Stoker Firing PrincipleHefni OssyanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Oil ApplicationDocument3 pagesHydraulic Oil ApplicationRohit Ramamurthy TevnanNo ratings yet
- CFB BoilerDocument12 pagesCFB Boiler95113309No ratings yet
- Energy Auditors 2 6 FBC BoilerDocument13 pagesEnergy Auditors 2 6 FBC Boilervij2009100% (1)
- " (FBC) Fluidized Bed Combustion CombustionDocument4 pages" (FBC) Fluidized Bed Combustion CombustionAnil JadhavNo ratings yet
- Circulating Fluidised Bed Combustion 1Document4 pagesCirculating Fluidised Bed Combustion 1Prasaanna MoniNo ratings yet
- Fluidised Bed Combustion For Clean Energy (Contents)Document22 pagesFluidised Bed Combustion For Clean Energy (Contents)Manas Kumar SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Basic of FBC BoilerDocument25 pagesBasic of FBC BoilerJayam KondanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Introduction: Steam To ProcessDocument89 pagesBoiler Introduction: Steam To ProcessEngr M S MinhasNo ratings yet
- FBC Boilers: Syllabus FBC Boilers: Introduction, Mechanism of Fluidized Bed Combustion, AdvantagesDocument12 pagesFBC Boilers: Syllabus FBC Boilers: Introduction, Mechanism of Fluidized Bed Combustion, AdvantagesTejas T S TejasNo ratings yet
- An Overview of FBC Boiler: Compiled BY S.S.AcharyaDocument56 pagesAn Overview of FBC Boiler: Compiled BY S.S.AcharyaMusycal Fynnc100% (1)
- Hamada Boiler Catalogue Page 14 FBC 2Document1 pageHamada Boiler Catalogue Page 14 FBC 2Matias MancillaNo ratings yet
- CFBC DesignDocument28 pagesCFBC DesignThanga Kalyana Sundaravel100% (2)
- FBC Boilers in Power PlantDocument20 pagesFBC Boilers in Power PlantVenkatesan SundaramNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed CombustionDocument23 pagesFluidized Bed CombustionHawk EyeNo ratings yet
- Session Ii: Super Critical Boilers & Fluidized Bed Combustion BoilerDocument12 pagesSession Ii: Super Critical Boilers & Fluidized Bed Combustion BoilerHODEEE JP College of EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Boilers Training Topic Nov 2021Document24 pagesBoilers Training Topic Nov 2021mizharmuisstNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed Combustion System (FBC)Document41 pagesFluidized Bed Combustion System (FBC)ashishmathew0% (1)
- Flurized Bed CombustionDocument8 pagesFlurized Bed CombustionshpalyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Applied Thermodynamics-1Document175 pagesUnit 2: Applied Thermodynamics-1Riddhesh NawgajeNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 06: Pulverised FuelDocument6 pagesChapter No. 06: Pulverised FuelhananNo ratings yet
- Plate Type CFBC HotDocument192 pagesPlate Type CFBC HotManoj PaneriNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypesDocument14 pagesBoiler Typesaecsuresh35No ratings yet
- Principles of Fluidized Bed BoilersDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Fluidized Bed BoilersssNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed BoilerDocument5 pagesFluidized Bed BoilerSavita GuptaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of CFBC Boiler: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument88 pagesAn Overview of CFBC Boiler: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAakash Singh BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- 25.boiler Water Chemistry R1 26.06.2017Document312 pages25.boiler Water Chemistry R1 26.06.2017VINOTHINI R B.EdNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed CombustionDocument2 pagesFluidized Bed Combustionlaila salahNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Fluidized Bed CombustionDocument12 pagesMechanism of Fluidized Bed CombustionShami KouseNo ratings yet
- CFBCDocument84 pagesCFBCBottle Mani100% (3)
- Fuels and Combustion-Part2 PDFDocument57 pagesFuels and Combustion-Part2 PDFSugan NallaNo ratings yet
- Hamada Boiler Catalogue Page 15 FBC 3Document1 pageHamada Boiler Catalogue Page 15 FBC 3Matias MancillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Boiler Boiler: Boiler Types and ClassificationsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Boiler Boiler: Boiler Types and ClassificationsGH Eco RJNo ratings yet
- Classification of Stoker FiringDocument21 pagesClassification of Stoker FiringNaresh B100% (2)
- Fluidization Is A Method of Mixing Fuel and Air in A Specific Proportion, ForDocument2 pagesFluidization Is A Method of Mixing Fuel and Air in A Specific Proportion, ForSerajul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 WteDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Wtevarshh001No ratings yet
- CFBC Boiler DescriptionDocument9 pagesCFBC Boiler Descriptioncmani_bweNo ratings yet
- Coal GasificationDocument17 pagesCoal GasificationSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Pulveriser SystemDocument20 pagesPulveriser Systemmurthykeshava100% (3)
- By K.K.PARTHIBAN, Boiler Consultant Venus Energy Audit SystemDocument13 pagesBy K.K.PARTHIBAN, Boiler Consultant Venus Energy Audit SystemNogeshwar Kumar DewanganNo ratings yet
- Stoker Vs FBC PDFDocument11 pagesStoker Vs FBC PDFAsghar MirzaNo ratings yet
- Type of BoilersDocument5 pagesType of Boilersnagraj204No ratings yet
- Flame and Combustion Forcement Kilns KPK PDFDocument62 pagesFlame and Combustion Forcement Kilns KPK PDFPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Latest Technology CFB Boilers - 31st March 2022Document31 pagesLatest Technology CFB Boilers - 31st March 2022M.Srushanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Circulating Fluidized Bed: University of Engineering & Technology, LahoreDocument18 pagesCirculating Fluidized Bed: University of Engineering & Technology, Lahoreusman_uet08No ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed CombustionDocument32 pagesFluidized Bed CombustionAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Che 321 Power Pt.Document42 pagesChe 321 Power Pt.emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Power CyclesDocument66 pagesPower CyclesDomingo PintoNo ratings yet
- Experiments of Power Plant Engineering in SPPUDocument27 pagesExperiments of Power Plant Engineering in SPPUSiddiqui Adil Adnan100% (2)
- Principles of Non Ferrous Extraction Metallurgy Extraction MetallurgyDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Non Ferrous Extraction Metallurgy Extraction MetallurgykiranNo ratings yet
- Pulverized CoalDocument11 pagesPulverized CoalAdrian ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Different Zones in The Reactor-Chemistry of GasificationDocument6 pagesDifferent Zones in The Reactor-Chemistry of GasificationN.R. RishiNo ratings yet
- CFBC Boiler - A SurveyDocument11 pagesCFBC Boiler - A SurveygjanklesariaNo ratings yet
- Particle Technology: CHE 321 (3 Units)Document80 pagesParticle Technology: CHE 321 (3 Units)Temitope Aminu-EduNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Topics: 1. Flame Stabilization Methods 2. Shapes of Flames 3. Effect of TurbulenceDocument18 pagesMiscellaneous Topics: 1. Flame Stabilization Methods 2. Shapes of Flames 3. Effect of TurbulencechaitukblNo ratings yet
- Fluidization 180402101141Document13 pagesFluidization 180402101141suraj nakumNo ratings yet
- Coating RingsDocument8 pagesCoating RingsIrshad HussainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useFrom EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useNo ratings yet
- Chimneys & Fireplaces: They Contribute to the Health Comfort and Happiness of the Farm Family - How to Build ThemFrom EverandChimneys & Fireplaces: They Contribute to the Health Comfort and Happiness of the Farm Family - How to Build ThemNo ratings yet
- Aniline by ReductionDocument2 pagesAniline by Reductionraja.mtNo ratings yet
- ENCH-633 Tutorial - 2Document1 pageENCH-633 Tutorial - 2raja.mtNo ratings yet
- ENCH 633 - 2017 - Week 2 3Document100 pagesENCH 633 - 2017 - Week 2 3raja.mtNo ratings yet
- ENCH-633 2017 Week-4Document86 pagesENCH-633 2017 Week-4raja.mtNo ratings yet
- ENCH-633 2017 Week-1Document121 pagesENCH-633 2017 Week-1raja.mtNo ratings yet
- ENCH-633: Chemical Thermodynamics: Sathish Ponnurangam Fall 2018 Week - 5: Fugacities in Gas MixtureDocument28 pagesENCH-633: Chemical Thermodynamics: Sathish Ponnurangam Fall 2018 Week - 5: Fugacities in Gas Mixtureraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument55 pagesHeat Transferraja.mtNo ratings yet
- API - Cooling TowerDocument44 pagesAPI - Cooling TowerBilal0% (1)
- 02-Stoichiometric CalculationsDocument47 pages02-Stoichiometric CalculationsHandayani KesumadewiNo ratings yet
- Separator SizingDocument13 pagesSeparator Sizingraja.mt100% (1)
- Gas DehydrationDocument61 pagesGas Dehydrationraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Short Questions EditedDocument6 pagesUnit 9 Short Questions EditedNaveedAttaUllahNo ratings yet
- Aniline by ReductionDocument2 pagesAniline by Reductionraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Material of ConstructionDocument26 pagesMaterial of Constructionraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Magoosh Vocab Flashcard EbookDocument214 pagesMagoosh Vocab Flashcard EbookMohit G GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic ModelingDocument49 pagesBasic Modelingraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Material of ConstructionDocument26 pagesMaterial of Constructionraja.mtNo ratings yet
- 2 Liquid and Gaseous FuelDocument15 pages2 Liquid and Gaseous Fuelraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PROCESS MODELING AND SIMULATIONDocument47 pagesIntroduction To PROCESS MODELING AND SIMULATIONraja.mt50% (2)
- HeuristicsDocument13 pagesHeuristicsraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Important Title UpdatesDocument1 pageImportant Title Updatesraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Important Title Updates Bey AjigonaDocument1 pageImportant Title Updates Bey Ajigonaraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Usa Recognition ListDocument23 pagesUsa Recognition ListPavitra JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Basic ModelingDocument49 pagesBasic Modelingraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Numerical UploadDocument0 pagesUnit 1 Numerical UploadKhawaja Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document2 pagesLab 4raja.mtNo ratings yet
- 4 Carbonization of CoalDocument24 pages4 Carbonization of Coalraja.mt100% (4)
- PRP Garu PDFDocument34 pagesPRP Garu PDFraja.mtNo ratings yet
- Boiler Types: Advantages and Disadvantages: By: Dane HaysteadDocument6 pagesBoiler Types: Advantages and Disadvantages: By: Dane Haysteadraja.mtNo ratings yet
- AT6401 Applied Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument2 pagesAT6401 Applied Thermodynamics and Heat Transferkarthikeyan MNo ratings yet
- Important Membrane CalculationsDocument39 pagesImportant Membrane Calculationsarun kumar100% (1)
- Comsol Chemical Reaction Engineering SimulationsDocument26 pagesComsol Chemical Reaction Engineering Simulationsmagora0516No ratings yet
- Lip Thickness For Reduction of Supersonic Jet LengthDocument34 pagesLip Thickness For Reduction of Supersonic Jet LengthmadhanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SymbolsDocument15 pagesHydraulic SymbolsKo ZayNo ratings yet
- North Everest FieldDocument2 pagesNorth Everest FieldsmashfacemcgeeNo ratings yet
- Green Engineering - David T AllenDocument5 pagesGreen Engineering - David T AllenAbhishek AbhiNo ratings yet
- A 280224Document510 pagesA 280224Leo LonardelliNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Boundary LayerDocument110 pagesUnit 5 - Boundary LayerSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- Thesis CFD ChapterDocument12 pagesThesis CFD ChapterPrassanna PrabagaranNo ratings yet
- Thermal Work Limits Conversion Booklet: Vane AnemometerDocument24 pagesThermal Work Limits Conversion Booklet: Vane AnemometerCommando crawlerNo ratings yet
- Design of EquipmentDocument14 pagesDesign of EquipmentNaeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Turbo Machinery Validation Against Experimental ResultsDocument13 pagesOptimization of Turbo Machinery Validation Against Experimental ResultsSrinivasNo ratings yet
- Formation Damage 2Document21 pagesFormation Damage 2Suleiman Baruni100% (2)
- 5 PDFDocument28 pages5 PDFTysir SarhanNo ratings yet
- Me f215 Mel Lab ManualDocument105 pagesMe f215 Mel Lab ManualpankazspamNo ratings yet
- Studi Performa Membran Hidrofobik Berbasis Silika Dalam Proses Pemurnian BiodieselDocument5 pagesStudi Performa Membran Hidrofobik Berbasis Silika Dalam Proses Pemurnian BiodieselcessareNo ratings yet
- Vertical Bulk Storage Tanks: Taylor-Wharton Malaysia Sdn. BHDDocument2 pagesVertical Bulk Storage Tanks: Taylor-Wharton Malaysia Sdn. BHDSCALE Ingeniería y ConstrucciónNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Design MethodDocument23 pagesPlumbing Design MethodMechanicalLatestNo ratings yet
- W10 - Low Speed Airspeed Indicators (Incompressible Flow)Document6 pagesW10 - Low Speed Airspeed Indicators (Incompressible Flow)Patrick Lawrence PiasanNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control EquipmentDocument34 pagesAir Pollution Control EquipmentJanice OmadtoNo ratings yet
- Jet OilDocument8 pagesJet OilMarwa MandeelNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid: Ostwald's Process or Ammonia Oxidation Process Arc Process or Birkeland and Eyde ProcessDocument15 pagesNitric Acid: Ostwald's Process or Ammonia Oxidation Process Arc Process or Birkeland and Eyde ProcessSusbsisvNo ratings yet
- Catalytic ReformingDocument84 pagesCatalytic ReformingAlessio Scarabelli86% (7)
- EE Notes FULLDocument56 pagesEE Notes FULLAnonymous Q4MsQANo ratings yet
- Flujo Multifasico 4.4Document14 pagesFlujo Multifasico 4.4Ramses SuárezNo ratings yet
- Tks 324 Cyclone and Hydrocylone-07Document29 pagesTks 324 Cyclone and Hydrocylone-07Arosyidin Ayef0% (1)
- Cre QuestionDocument2 pagesCre QuestionChinu Routa100% (1)