Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Day 5 ICAO Atmosphere Standard 5 Oct 2015
Uploaded by
Ari Kurnia Ramadani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views15 pagesThe document outlines the ICAO standards for defining the layers of the atmosphere, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere, and describes characteristics of each layer such as temperature, presence of water vapor and ozone. It also discusses ICAO standards for atmospheric pressure measurements, pressure distribution, and how pressure varies with elevation based on mean sea level pressure and temperature. The standards provide average altitude, pressure, and temperature data used in aviation to a height of 20 km above sea level.
Original Description:
ICAO Atmosphere Standart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the ICAO standards for defining the layers of the atmosphere, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere, and describes characteristics of each layer such as temperature, presence of water vapor and ozone. It also discusses ICAO standards for atmospheric pressure measurements, pressure distribution, and how pressure varies with elevation based on mean sea level pressure and temperature. The standards provide average altitude, pressure, and temperature data used in aviation to a height of 20 km above sea level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views15 pagesDay 5 ICAO Atmosphere Standard 5 Oct 2015
Uploaded by
Ari Kurnia RamadaniThe document outlines the ICAO standards for defining the layers of the atmosphere, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere, and describes characteristics of each layer such as temperature, presence of water vapor and ozone. It also discusses ICAO standards for atmospheric pressure measurements, pressure distribution, and how pressure varies with elevation based on mean sea level pressure and temperature. The standards provide average altitude, pressure, and temperature data used in aviation to a height of 20 km above sea level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
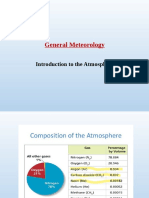
ICAO, Atmosphere Standard
Day 5: Unsurya 2015
Teknik Pengukuran Terbang
Division of Atmosphere
Troposphere
• In Contact With The Earth, The Warmest
• Create the Earth Weather Syatem
• The Intense of Water Vapour, Associated
with Strong Air Currents, Leads to Clouds
and Precipitation, Thunderstorms
• Strong Contrast Between Troposphere and
Stratosphere Generate the Very powerful
Winds Called Jet Streams, also Called
Earth’s Air Mass
Stratosphere
• Stratosphere is a 15 km, 50 000 feet Layer
, Temperature Increases to 0 C
• No Water Vapour, No Vertical Air Currents
• Main characteristic of the Stratosphere is
the Ultraviolet Shield, It Contains The
Ozone Layer.
• Stratospheric Warming Occurs as this
Layer Absorbs the Ultraviolet Rays from
the Sun.
Mesosphere
• The Only Significant Characteristic: Rarity
of Ozone and Consequently its Minimum
Temperature of about -80 C,
• 80 km from the Earth's surface. This is the
lowest temperature ever recorded in the
atmosphere.
• It is also in this layer that meteorites burn
up as they come into contact with the
atmosphere.
Thermosphere
• Air molecules are rare in this layer, which
is why the Sun's rays strike with such
force and temperatures can theoretically
rise to enormous levels.
ICAO Standard Atmosphere
• Data available for the first 20 km of the
atmosphere
• Basis of average altitude, pressure and
temperature conditions at 40 north
latitude.
ICAO Standard Atmosphere
• Values of particular significance are:
– MSL pressure: 1013 hectopascals (hPa or mb)
– MSL Temperature: 15ºC
– rate of decrease of temperature with height
(lapse rate) in the troposphere: 6.5ºC per km
(2ºC per 1000 feet)
– height of the tropopause: 11 kilometres
(36,000 feet) above MSL
– temperature of the tropopause: -56.5ºC
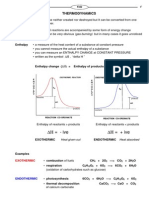
Thermodynamics Properties of Atmosphere
Thermodynamics Properties of Atmosphere
• Main Thermodynamics Parameters:
Pressure & Temperature
• Air Rises: Pressure & Temperature Go
Down, Volume.....
• Air Descends: Pressure & Temperature Go
Up, Volume.....
• Vertical Air Movement Plays Role of
Weather Changes: Cloud Formation
ICAO Atmospheric Pressure
• Pressure Distribution in the Atmosphere
Controls the Winds and, weather
phenomena such as cloud and
precipitation
• Atmospheric pressure is measured with
.......The simplest: Consists of a Vertical
Tube of Mercury
ICAO Atmospheric Pressure
• We can Easily Determine its Hydrostatic
Pressure, simply by Comparing
Atmospheric Pressure to the Pressure of
Mercury.
• In the world of aviation it is the
hectopascal (hPa) that is used to express
atmospheric pressure. This unit has the
same value as the MilliBar, the former unit
ICAO Atmospheric Pressure:
Station & MSL Pressure
ICAO Atmospheric Pressure:
Satation & MSL Pressure
• Atmospheric pressure at the elevation of the
station, measured with a barometer.
• How can we determine the pressure at different
elevations? Based on MSL pressure, since
pressure reaches its maximum at this level.
• We need to know its exact elevation and to
determine the mean temperature between this
elevation and sea level.
• The Importance of altimeter setting and mean
sea level (MSL) pressure.
ICAO Atmospheric Pressure:
Constant Pressure Chart
You might also like
- Concept of AgrometeorologyDocument43 pagesConcept of Agrometeorologybabloo08No ratings yet
- Aviation Meteorology - SPLDocument71 pagesAviation Meteorology - SPLGaurav NitnawareNo ratings yet
- Air, Atmospheric Pressure and WindsDocument42 pagesAir, Atmospheric Pressure and WindsVishnu PrasadNo ratings yet
- Tab 2 PMI Atmospheric BasicsDocument95 pagesTab 2 PMI Atmospheric BasicsAhmed ElgoharyNo ratings yet
- Conociminetos 5 Nociones de MeteorologiaDocument85 pagesConociminetos 5 Nociones de MeteorologiaBrunna Lopes de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Physics of AtmosphereDocument35 pagesPhysics of Atmosphereamro kirkisawiNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere - Structure & Composition - 2200687Document38 pagesAtmosphere - Structure & Composition - 2200687aamirzbhatt31No ratings yet
- Module 1 The Atmosphere Aviation MeteorologyDocument6 pagesModule 1 The Atmosphere Aviation MeteorologyadamNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Anshereena Mae Arines Patricia Estrada Nica Malantic Kenneth ParasDocument20 pagesPresented By:: Anshereena Mae Arines Patricia Estrada Nica Malantic Kenneth ParasSh3eNa..No ratings yet
- New PPL Bifa ProflightDocument512 pagesNew PPL Bifa ProflightThomas AmisimNo ratings yet
- Flight Mechanics Motes - Unit-IDocument40 pagesFlight Mechanics Motes - Unit-IHaroon RashidNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of TroposphereDocument24 pagesCharacteristics of Tropospheresukhjit78No ratings yet
- AER200 Lecture 3Document44 pagesAER200 Lecture 3Torin WicksNo ratings yet
- Meteorology: Private Pilot LicenseDocument93 pagesMeteorology: Private Pilot LicenseChristian Cesar C. CebrecusNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere and Layer of AtmosphereDocument38 pagesAtmosphere and Layer of AtmosphereAS Consultancy & TrainersNo ratings yet
- c15 Atmosphere and Air PollutionDocument94 pagesc15 Atmosphere and Air Pollutiontahlarab2No ratings yet
- Weather, Climate and Atmosphere-Lecture 1Document35 pagesWeather, Climate and Atmosphere-Lecture 1futurejnsNo ratings yet
- 6ENT1065 (6ENT1070) Aerospace Performance, Propulsion, Design (& Manufacture)Document51 pages6ENT1065 (6ENT1070) Aerospace Performance, Propulsion, Design (& Manufacture)samNo ratings yet
- Meto ReviewwwDocument10 pagesMeto Reviewwwmahmoud deyaaNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution MeteorologyDocument44 pagesAir Pollution MeteorologyJohnny BlazeNo ratings yet
- Class2 2022Document20 pagesClass2 2022Ashish v PhilipNo ratings yet
- Meteorology: Tropopause/TroposphereDocument19 pagesMeteorology: Tropopause/TroposphereDevanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- Fate and Transport of Air PollutantsDocument57 pagesFate and Transport of Air PollutantsKALESMI A/P AMARALATHAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Lecture Note, CC 511117Document143 pagesAerodynamics Lecture Note, CC 511117siamanwar893No ratings yet
- ClimatologyDocument61 pagesClimatologyVrushali ThokalNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument21 pagesMeteorologypilot maverickNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument93 pagesAtmosphereJohn Carlo Abala100% (1)
- AtmosphereDocument40 pagesAtmosphereJade Louise Patolilic100% (5)
- Composition and Origin of The AtmosphereFDocument28 pagesComposition and Origin of The AtmosphereFJoseph Wilson JuniorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1Estuardo MolinaNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE SYSTEMS 24mayDocument27 pagesPRESSURE SYSTEMS 24maygirishah92No ratings yet
- University of PNG - Earth Sciences: The AtmosphereDocument36 pagesUniversity of PNG - Earth Sciences: The AtmosphereTenielleNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Upsc Notes 20Document6 pagesAtmosphere Upsc Notes 20Tapas Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- BSMT-MET-O1-1B InstrumentsDocument36 pagesBSMT-MET-O1-1B InstrumentsJeycule BerendezNo ratings yet
- 11 AtmosphereDocument27 pages11 AtmosphereSakshi BhalewadikarNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument17 pagesAtmospheric PressureRagini khargNo ratings yet
- Meteorology and Air PollutionDocument50 pagesMeteorology and Air PollutionAsma Hairulla JaafarNo ratings yet
- Tananyag Fejlesztés Idegen Nyelven: Prevention of The AtmosphereDocument39 pagesTananyag Fejlesztés Idegen Nyelven: Prevention of The AtmospheremoxlindeNo ratings yet
- Meteorology AtplDocument17 pagesMeteorology AtplJavier Moreno Rodríguez100% (4)
- Let's Get Started - Ground School: Weather & MeteorologyDocument42 pagesLet's Get Started - Ground School: Weather & MeteorologyNirgunaRamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1stDocument42 pagesPresentation 1stHAFIAZ MUHAMMAD IMTIAZNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of The AtmosphereDocument36 pagesBasic Properties of The Atmospheregus ediNo ratings yet
- 2 MeteorologyDocument44 pages2 MeteorologyEhtisham MehmoodNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument3 pagesMeteorologyapi-330091099No ratings yet
- Dr. Sandip MondalDocument75 pagesDr. Sandip Mondalsignal jammerNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Evolution InteractionDocument26 pagesAtmosphere Evolution InteractionbynicioalvNo ratings yet
- ATPL - EASA2016 - MeteorologyDocument70 pagesATPL - EASA2016 - MeteorologyNuno Arnaud100% (1)
- Air Pollution SpaceDocument78 pagesAir Pollution SpaceMohd IqbalNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Atmosphere Atmospheric StructureDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Atmosphere Atmospheric StructureDc CheungNo ratings yet
- Chaptar 2 Hydrometerology (Final) PDFDocument35 pagesChaptar 2 Hydrometerology (Final) PDFHusnain WaleedNo ratings yet
- Climatology and Built Environment: Climate and Human ComfortDocument58 pagesClimatology and Built Environment: Climate and Human Comfortrekha vivek100% (1)
- 3 Standard AtmosphereDocument19 pages3 Standard AtmosphereRodrigo SantillanNo ratings yet
- 3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsDocument105 pages3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsvibiloceym2000No ratings yet
- Higher The Absolute Humidity.. SPECIFIC HUMIDITY Refers To The Weight (Amount)Document11 pagesHigher The Absolute Humidity.. SPECIFIC HUMIDITY Refers To The Weight (Amount)CPL MohanNo ratings yet
- International Standard Atmosphere (ISA)Document38 pagesInternational Standard Atmosphere (ISA)rahulsamyal100% (1)
- Chapter 01 The Earth's AtmosphereDocument34 pagesChapter 01 The Earth's Atmosphereannah piehNo ratings yet
- 1.atmosphere AviaCave 28 Days Met Program - 1Document7 pages1.atmosphere AviaCave 28 Days Met Program - 1Priyadharshini sRNo ratings yet
- 3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsDocument105 pages3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsVinoth Kumar100% (1)
- APCE Unit - 2Document50 pagesAPCE Unit - 2NAVEEN SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Interactions in The Ecosystem: 5.1 Habitats and Niches 5.2 Evolution and Adaptation 5.3 PopulationsDocument49 pagesChapter 5: Interactions in The Ecosystem: 5.1 Habitats and Niches 5.2 Evolution and Adaptation 5.3 PopulationsJan Marlon GoritNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument5 pagesHydrologic CyclesupermaneditNo ratings yet
- 1PH0 1H MSC 20210211Document30 pages1PH0 1H MSC 20210211RandomNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mass and Energy BalancesDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Mass and Energy BalancesdeltaoperativNo ratings yet
- 2018 BookDocument477 pages2018 Bookbrahim chalhoub100% (2)
- The Crust, Mantle, and CoreDocument30 pagesThe Crust, Mantle, and CoreKianNo ratings yet
- FuelsDocument47 pagesFuelsSheeraz Junejo100% (1)
- NA14631A - CristopiaDocument3 pagesNA14631A - CristopiaVietHienNo ratings yet
- Athem W. Alsabti, Paul Murdin (Eds.) - Handbook of Supernovae-Springer International PublishingDocument2,519 pagesAthem W. Alsabti, Paul Murdin (Eds.) - Handbook of Supernovae-Springer International PublishingMiroslav FilipovicNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration Test Rig Computerised Lab ManualDocument12 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration Test Rig Computerised Lab ManualAshish Verma50% (2)
- Rotational MotionDocument39 pagesRotational MotionKhushal BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Structures, Band Gaps, and Electronic StructuresDocument7 pagesInvestigation On Structures, Band Gaps, and Electronic StructuresbatistaufrnNo ratings yet
- AD5 Reading Task OCT 2020Document1 pageAD5 Reading Task OCT 2020LuisNo ratings yet
- Branches of Earth ScienceDocument26 pagesBranches of Earth ScienceSHEENANo ratings yet
- 77 ChaitraDocument83 pages77 ChaitraSubash PoudelNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Geology 4th Edition Murck Test BankDocument29 pagesVisualizing Geology 4th Edition Murck Test Bankazuragwencr8ud100% (24)
- Inorganic Biological Molecules - Water 0 MineralsDocument40 pagesInorganic Biological Molecules - Water 0 MineralsjonNo ratings yet
- Sullair FiltersDocument12 pagesSullair FiltersNicolás TomelínNo ratings yet
- IEEE 1125-1993 - SF6 Equipment - Dew PointDocument21 pagesIEEE 1125-1993 - SF6 Equipment - Dew Pointangela_pp100% (1)
- Dye Sensitized Solar CellDocument54 pagesDye Sensitized Solar Cellcharu agrawalNo ratings yet
- RM Cia 3Document60 pagesRM Cia 3RNo ratings yet
- 6323 12101 1 SMDocument7 pages6323 12101 1 SMElna PurwantiNo ratings yet
- The Mine Drainage Quality Prediction of Surface Coal Mine Rock Samples With Humidity Column Test-3-10Document8 pagesThe Mine Drainage Quality Prediction of Surface Coal Mine Rock Samples With Humidity Column Test-3-10Fanteri Aji DharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - 2 Precipitation (Background) Water VaporDocument4 pagesLecture Note - 2 Precipitation (Background) Water Vapornazifa nabilaNo ratings yet
- TE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 5 - Thermodyn Propertis of Moist AirDocument48 pagesTE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 5 - Thermodyn Propertis of Moist AirAkshay ChandoleNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Properties PDFDocument34 pagesEstimation of Properties PDFLee860531No ratings yet
- Ive + Ive: ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesIve + Ive: ThermodynamicsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Car 2016 9geo T4 ExamDocument12 pagesCar 2016 9geo T4 ExamPoTTie10No ratings yet
- Theoretical Assessment For The Mixing Properties of Almg Liquid Alloys at 1073KDocument9 pagesTheoretical Assessment For The Mixing Properties of Almg Liquid Alloys at 1073KShayista AhmadNo ratings yet
- Spring Cont PDFDocument7 pagesSpring Cont PDFphooolNo ratings yet