Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trends in Language Teaching
Uploaded by
loshini sivaraja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Trends in Language Teaching.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesTrends in Language Teaching
Uploaded by
loshini sivarajaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
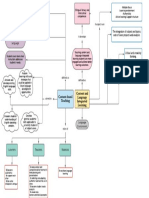
Trends in Language Teaching
Phase 1 traditional approaches (up to the
late 1960s)
Phase 2 classic communicative language
teaching (1970s to 1990s)
current communicative language
Phase 3 teaching (late 1990s to the
present)
Current Communicative Language Teaching.
Describes a set of Communicative
Why is it syllabus&
very general
principles implicated??? methodology
The classroom is a Second language
community where learning-learners are
learners learn through engaged in
collaboration and interaction&
sharing meaningful opportunities for students- Meaningful
communication. negotiate meaning, expand communication results
their language resources, from students
notice how language is processing content
used, and take part in that is relevant,
The role of the teacher -creates a meaningful intrapersonal purposeful, interesting
classroom climate conducive to exchange and engaging
language learning,provides
opportunities for students to use,
practice the language,to reflect on
language use and language
Core Assumptions
learning Communication is a holistic
of current
communicative process that calls upon the
language teaching use of several language
skills or modalities
Successful language
learning involves the use of
effective learning and
communication strategies Language learning is
Language learning, facilitated by activities that
process that involve inductive or
Learners develop their own involves creative use discovery learning of
routes to language learning, of language and trial underlying rules of language
progress at different rates, and error. use and organization, as well
have different needs and
as by those involving
motivations for language
language analysis and
learning
reflection
Communicative competence obviously does not mean the
wholesale rejection of familiar materials. There is nothing to
prevent communicatively-based materials from being subjected to
grammar-translation treatment.
CLT can be seen as describing a set of core What matters is the teacher’s conception
principles about language learning and
CONCLUSION of what learning a language is and how it
teaching. happens.
The basic principle involved is an orientation towards collective
participation in a process of use and discovery achieved by cooperation
between individual learners as well as between learners and teachers.
Shaping a Communicative Curriculum
begins with discovery of learner In an ESL setting, opportunities to use English
interests and needs and of outside the classroom abound. Systematic
Classroom visits to a courtroom trial, a
“field experiences” may successfully become
opportunities to not only respond to public auction, or a church bazaar
the core of the course, which then could
but, more importantly, to develop provide introductions to aspects of the
become a workshop in which learners can
those interests and needs through local culture that learners might not
compare notes, seek clarification, and expand
experience on their own.
English language use beyond the the range of domains in which they learn to
classroom itself. function in English.
You might also like
- Characteristics and Principles of Communicative Language TeachingDocument1 pageCharacteristics and Principles of Communicative Language TeachingAcro BleedNo ratings yet
- WPH002 - Ismael - AdditionalDocument7 pagesWPH002 - Ismael - Additionalkristine camachoNo ratings yet
- 1st Exam - EDENG 1Document3 pages1st Exam - EDENG 1Joy MagbutongNo ratings yet
- A. Communicative Language TeachingDocument7 pagesA. Communicative Language TeachingilhamNo ratings yet
- Teaching ApproachesDocument4 pagesTeaching Approacheschafiq jellasNo ratings yet
- Resumen Del Contenido de La Unidad 1 Communicative Language Teaching MethodsDocument9 pagesResumen Del Contenido de La Unidad 1 Communicative Language Teaching MethodsRoberto AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Pedro Ruiz Gallo National University: Foreign Language Teaching Approaches "Communicative Approach"Document3 pagesPedro Ruiz Gallo National University: Foreign Language Teaching Approaches "Communicative Approach"Kevin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Rationale: K12 CurriculumDocument1 pagePhilosophy and Rationale: K12 CurriculumElitiea KwonNo ratings yet
- THEME 4 Cooperative Language LearningDocument6 pagesTHEME 4 Cooperative Language LearningSusan VelaNo ratings yet
- Activities and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesActivities and-WPS OfficeMa Eloisa Juarez BubosNo ratings yet
- ELT Method - Cooperative Language LearningDocument5 pagesELT Method - Cooperative Language LearningYamith J. Fandiño100% (1)
- Lexical Approach - Exe 23bDocument2 pagesLexical Approach - Exe 23bMonse AlbeNo ratings yet
- A Summary Table of Four Methods: Methods Approach Design ProcedureDocument5 pagesA Summary Table of Four Methods: Methods Approach Design ProcedureVisalachi ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Colorful Pastel Childish Bubble Scheme Concept Mind Map GraphDocument2 pagesColorful Pastel Childish Bubble Scheme Concept Mind Map GraphAnghela Jhoselyn Cotrina DíazNo ratings yet
- Hunter Green Case 2020Document4 pagesHunter Green Case 2020api-539272799No ratings yet
- Improving Students Speaking Ability Through SimulDocument7 pagesImproving Students Speaking Ability Through SimulFathan GhotafaniNo ratings yet
- G.3 - Keep Movin FWD Fix BGTDocument31 pagesG.3 - Keep Movin FWD Fix BGTandri jupanoNo ratings yet
- Table Didactica InglesDocument2 pagesTable Didactica InglesCamila AmayaNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Methods and Techniques in English Language TeachingDocument8 pagesApproaches, Methods and Techniques in English Language TeachingAigul UrmatbekovaNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Improve As A Student: Learning Process Maria Fernanda MezaDocument3 pagesStrategies To Improve As A Student: Learning Process Maria Fernanda MezaKatherine OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Communicative Method: Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)Document14 pagesCommunicative Method: Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)Юлия ШакуроваNo ratings yet
- 18.0 PP 212 217 GlossaryDocument6 pages18.0 PP 212 217 GlossaryafsdgsadtgsadgNo ratings yet
- Colorful Pastel Childish Bubble Scheme Concept Mind Map GraphDocument2 pagesColorful Pastel Childish Bubble Scheme Concept Mind Map GraphAnghela Jhoselyn Cotrina DíazNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Language LearningDocument10 pagesIntercultural Language LearningSudiana NouraqcellNo ratings yet
- Methodology For The Development of Discursive Skills 1Document11 pagesMethodology For The Development of Discursive Skills 1Мерей КанагатоваNo ratings yet
- ApproachesDocument2 pagesApproachesJoyce Joyería100% (1)
- Communicative Language Teaching Group 10Document18 pagesCommunicative Language Teaching Group 10Azhar MoNo ratings yet
- Coaching - English Core Course M.6Document22 pagesCoaching - English Core Course M.6jimboy naquilaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Driessen 10Document8 pagesCSTP 3 Driessen 10api-678903282No ratings yet
- Integrating Language Skills Through A Dictogloss ProcedureDocument9 pagesIntegrating Language Skills Through A Dictogloss ProcedureMakoto ShishioNo ratings yet
- Mariya Olkhovych-Novosadyuk: Communicative Language Teaching: Managing The Learning ProcessDocument12 pagesMariya Olkhovych-Novosadyuk: Communicative Language Teaching: Managing The Learning ProcessAmeera I SuyansahNo ratings yet
- Mariya Olkhovych-Novosadyuk: Communicative Language Teaching: Managing The Learning ProcessDocument12 pagesMariya Olkhovych-Novosadyuk: Communicative Language Teaching: Managing The Learning ProcessUyenuyen DangNo ratings yet
- The Lexical ApproachDocument9 pagesThe Lexical ApproachIssam karchouchNo ratings yet
- StephensonDocument8 pagesStephensonweny yuniawatiNo ratings yet
- Plan de Refuerzo Académico NovenosDocument3 pagesPlan de Refuerzo Académico NovenosDanna VazquezNo ratings yet
- Name: Yves Gerald E. Giray Subject: Langlit 806 (Methods of Teaching Language Arts)Document8 pagesName: Yves Gerald E. Giray Subject: Langlit 806 (Methods of Teaching Language Arts)Yves GirayNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language TeachingDocument1 pageCommunicative Language TeachingRyan De la TorreNo ratings yet
- Term/word: Below You See A Glossary of Key Terms Used in ELT (Taken From Teaching Grammar Communicatively MOOC)Document5 pagesTerm/word: Below You See A Glossary of Key Terms Used in ELT (Taken From Teaching Grammar Communicatively MOOC)Ouafae ChaouqiNo ratings yet
- Week 7 CLTDocument29 pagesWeek 7 CLTCarolina HoyosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer KemeDocument3 pagesReviewer KemeMarc Lorenz AlbaridoNo ratings yet
- 2 Nur WasiahDocument15 pages2 Nur WasiahSisma rellyNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Principles and Guidelines: Suggested English Curriculum 6 TO 11 GradeDocument40 pagesPedagogical Principles and Guidelines: Suggested English Curriculum 6 TO 11 GradeYULEIDYS MARMOL GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Technology For Teaching and Learning 2 Lesson 2: K To 12 Curriculum Framework Components Goals-How To Achieve These GoalsDocument2 pagesTechnology For Teaching and Learning 2 Lesson 2: K To 12 Curriculum Framework Components Goals-How To Achieve These GoalsChina May SabanganNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument33 pagesChapter IINova PhaNo ratings yet
- Small TalkDocument12 pagesSmall TalkZilan DoğruNo ratings yet
- Hezha BakhtiyarDocument34 pagesHezha BakhtiyarHezha BANo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Observational Practice Step 1 Observation Matrix, Lisney GalvisDocument21 pagesPhase 2 Observational Practice Step 1 Observation Matrix, Lisney GalvisGREYS RICARDO NARANJONo ratings yet
- Area Lengua Extranjera Uerdg 2019Document13 pagesArea Lengua Extranjera Uerdg 2019Carmen Mera Del PieroNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapRosa HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Competence ActivitiesDocument8 pagesGrammatical Competence ActivitiesJojames GaddiNo ratings yet
- Communicative ApproachDocument23 pagesCommunicative Approachpramukh_swami100% (3)
- Principal of Lesson Planning: Stage 1: Pre-Lesson PreparationDocument6 pagesPrincipal of Lesson Planning: Stage 1: Pre-Lesson Preparationjaysel86No ratings yet
- Fundamentos de Educación Pre-Básica T Chart TareaDocument4 pagesFundamentos de Educación Pre-Básica T Chart TareaJennifer SaucedaNo ratings yet
- Myp Unit Plan g8 (Perspective)Document14 pagesMyp Unit Plan g8 (Perspective)Hesbon odhiambo OkelloNo ratings yet
- Active Methodologies in English Language TeachingDocument13 pagesActive Methodologies in English Language TeachingCarolina López AvilésNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language TeachingDocument1 pageCommunicative Language TeachingRyan De la TorreNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Cognitive, Metacognitive and Social Listening Comprehension Teaching Strategies in Kuwaiti ClassroomsDocument16 pagesEvaluating Cognitive, Metacognitive and Social Listening Comprehension Teaching Strategies in Kuwaiti ClassroomsAraceliRiveraEspindolaNo ratings yet
- Method of Teaching Chapter 3Document17 pagesMethod of Teaching Chapter 3Afiqah MuflihahNo ratings yet
- Conversation Strategies: Pair and Group Activities for Develping Communicative CompetenceFrom EverandConversation Strategies: Pair and Group Activities for Develping Communicative CompetenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Activity 1 Join The Google Meet (Video Call) With The Teacher. Slides Used in The Google MeetDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Join The Google Meet (Video Call) With The Teacher. Slides Used in The Google Meetloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- 18 Nov LP Wednesdayenglish 4GDocument3 pages18 Nov LP Wednesdayenglish 4Gloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development PRESENTATIONDocument3 pagesKohlberg's Theory of Moral Development PRESENTATIONloshini sivaraja100% (1)
- 20 Nov LP Friday LaDocument3 pages20 Nov LP Friday Laloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism VS MentalistDocument1 pageBehaviorism VS Mentalistloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- 19 Nov LP ThursdayDocument3 pages19 Nov LP Thursdayloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5B: Semantics: Language and Meaning: TASK (Pair Work)Document4 pagesTopic 5B: Semantics: Language and Meaning: TASK (Pair Work)loshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- LINGUISTICS Human Vs AnimalDocument4 pagesLINGUISTICS Human Vs Animalloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Love and TimeDocument3 pagesLove and Timeloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 TOSDocument40 pagesTopic 6 TOSloshini sivaraja100% (1)
- AJRE Phonol and Phon AwareDocument13 pagesAJRE Phonol and Phon Awarealialim83No ratings yet
- Topic 6 TOSDocument40 pagesTopic 6 TOSloshini sivaraja100% (1)
- ROMANCEDocument11 pagesROMANCEloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Private UniversitiesDocument4 pagesPrivate Universitiesloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Private UniversitiesDocument4 pagesPrivate Universitiesloshini sivarajaNo ratings yet
- Script Writing For TV Based InstructionDocument66 pagesScript Writing For TV Based InstructionJennifer Artiaga100% (2)
- 6 DLL HOPE 3 2019-2020 JulyDocument2 pages6 DLL HOPE 3 2019-2020 JulyCelia BautistaNo ratings yet
- CAPS - The Play-Friendly School HandbookofDocument73 pagesCAPS - The Play-Friendly School HandbookofBeriška AjinNo ratings yet
- Habits of MindDocument3 pagesHabits of MindRuba Tarshne :)No ratings yet
- 13 Reasons Why Discussion GuideDocument115 pages13 Reasons Why Discussion GuideEC Pisano RiggioNo ratings yet
- Early Childhood Ed 2010 UkDocument24 pagesEarly Childhood Ed 2010 UkTweetrudi WhyteNo ratings yet
- Emotional LeadershipDocument14 pagesEmotional LeadershipZdanne Ismail100% (1)
- Sculpture 1 Syllabus Final 2019-2020Document4 pagesSculpture 1 Syllabus Final 2019-2020api-418962958No ratings yet
- Prof Ed 5 Lesson 7 Preparing For Quality Teaching 20231022 003225 0000Document17 pagesProf Ed 5 Lesson 7 Preparing For Quality Teaching 20231022 003225 0000anniejill15No ratings yet
- IELTS Formal Letter TopicsDocument3 pagesIELTS Formal Letter TopicskiriakosNo ratings yet
- WLL 5 Agreement of Subject VerbDocument4 pagesWLL 5 Agreement of Subject VerbLorna TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Tpack SamrDocument17 pagesTpack Samrapi-245872335No ratings yet
- Lesson 25 Form Time Theme Topic Language / Grammar Focus Content StandardDocument4 pagesLesson 25 Form Time Theme Topic Language / Grammar Focus Content StandardgeethaNo ratings yet
- Heartland Horseshoeing School CatalogDocument52 pagesHeartland Horseshoeing School Catalogjkoehler8439100% (1)
- Assignment 2 Food TechnologyDocument15 pagesAssignment 2 Food Technologyapi-356883750No ratings yet
- Daily 5 CafeDocument13 pagesDaily 5 Cafeapi-261932242100% (4)
- DLL-Food Fish Processing 9-Q2-W6Document4 pagesDLL-Food Fish Processing 9-Q2-W6IlY-MyraTorresDeJesusNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design Task - Balloon CarDocument5 pagesEngineering Design Task - Balloon Carapi-357997977No ratings yet
- Can For Ability Lesson Plan PDFDocument6 pagesCan For Ability Lesson Plan PDFDiego Fernando GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Week 3-Day1 English LPDocument3 pagesWeek 3-Day1 English LPYoumar SumayaNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Social Studies SyllabusDocument4 pagesFoundation of Social Studies SyllabusPaulyne Pascual100% (4)
- Lab Week 1Document129 pagesLab Week 1Kacie LeedhamNo ratings yet
- Passion Project-Lesson 3Document2 pagesPassion Project-Lesson 3api-479524591No ratings yet
- Pet For Schools Examiner S CommentsDocument7 pagesPet For Schools Examiner S Commentsbenjo100% (1)
- FFC Lesson Plan - Dr.G.harinath GowdDocument3 pagesFFC Lesson Plan - Dr.G.harinath GowdHarinath GowdNo ratings yet
- Asking Giving Direction - MakalahDocument10 pagesAsking Giving Direction - MakalahAnonymous 6AKB6stNo ratings yet
- DLL3 Math 7 Week 2Document3 pagesDLL3 Math 7 Week 2Angela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4: Thursday, April 14Document10 pagesLesson Plan 4: Thursday, April 14api-319860340No ratings yet
- Adult Learning. Policies and PracticeDocument248 pagesAdult Learning. Policies and PracticeTamarNo ratings yet
- Capstone Project ModuleDocument12 pagesCapstone Project ModuleJeffrey MasicapNo ratings yet