Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecology Concept Map
Uploaded by
scribsunilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecology Concept Map
Uploaded by
scribsunilCopyright:
Available Formats
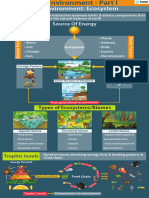
CONCEPT MAP
Ecology
Study of reciprocal relationship between
organisms and their environment
Climatic
• Light
• Temperature
• Wind
Organisms Abiotic factors • Rain(precipitati
• Basic unit of ecological hierarchy. on)
• Interact with physical environment • Atmospheric
comprised of atmosphere, hydrosphere humidity
and lithosphere.
• Adaptions enable them to survive and
reproduce in their habits.
• Environment factors (abiotic and biotic) Edaphic
influence the form and functioning of
organisms. Biotic factors • Mineral matter
• Organic matter
• Bacteria, Algae,
Levels of ecological organization
• Soil
Fungi, Parasites,
Saprophytes,
Symbionts, Animals
Tropographic
• Altitude
• Steepness of
Population Density slope
• Direction of slope
Characteristics of
• Organisms of the same kind form Natality
population Mortality Emigration
population
• They are capable of interbreeding Dispersal
among themselves Age distribution Immigration
Biotic potential
j-shaped (exponential)
Growth form
community
• Population of different species s-shaped(logistic)
occurring in a habitat Species composition
• Different kinds of plants and other organism
present in a community
Features
Dominance
• Only once or few species in a community
dominate and influence other species in terms of
numbers and biomass production
Ecosystem
• It includes biological
community, integrated with its Stratification
physical environment. • Vertical layering of vegetation in which different
layers are occupied by different species.
Mutualism
Positive Protocooperation
Commensalism
Biosphere Species
Competition
• Includes all ecosystems on the interaction
Negative Predation
earth.
Parasitism
You might also like
- ENVI SCI Lecture 3Document9 pagesENVI SCI Lecture 3Mary Rose SioNo ratings yet
- F5C09 Concept MapDocument1 pageF5C09 Concept MapLeena bsb.No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom ?Document20 pagesPlant Kingdom ?avika guptaNo ratings yet
- Ess Sa PreparationDocument16 pagesEss Sa Preparationilgyu1207No ratings yet
- 00a. High Sulfidation Epithermal Deposits - CookeDocument20 pages00a. High Sulfidation Epithermal Deposits - CookePatricio Castillo ManquecoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Science Framework in The K To 12 CurriculumDocument22 pagesLesson 4 - Science Framework in The K To 12 CurriculumBolasco, Aira Jeneva CelestialNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument14 pagesUntitled NotebookPanda ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Organisms and Population Flowchart - Telegram Ishita 4 UDocument11 pagesOrganisms and Population Flowchart - Telegram Ishita 4 Ulakshya singhalNo ratings yet
- Population Structure & DynamicsDocument8 pagesPopulation Structure & DynamicsKanika NahataNo ratings yet
- ExplorationDocument1 pageExplorationpmcclendonNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument9 pagesEcologymichealmuojNo ratings yet
- People and ServicesDocument6 pagesPeople and ServicesShantanu DasNo ratings yet
- Our Environment1Document2 pagesOur Environment1randahassanen2023No ratings yet
- Butterfly Diversity 3: Macroecology: What Is It?Document3 pagesButterfly Diversity 3: Macroecology: What Is It?Kellyta RodriguezNo ratings yet
- SBCOC by Bharat Panchal Class 11Document13 pagesSBCOC by Bharat Panchal Class 11kumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Genius-20 Examination 2022-23: For Class-8 Moving To Class-9Document3 pagesSyllabus For Genius-20 Examination 2022-23: For Class-8 Moving To Class-9sateek gamingNo ratings yet
- KS5 Curriculum Maps Biology A Level.303685701Document2 pagesKS5 Curriculum Maps Biology A Level.303685701Noh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Myp Science Syllabus Scope and Sequence ExampleDocument2 pagesMyp Science Syllabus Scope and Sequence ExamplewynotpointersNo ratings yet
- Mayoor School SyllabusDocument12 pagesMayoor School SyllabusSandeep PathakNo ratings yet
- Class 6-9 Science and Math Textbook SectionsDocument5 pagesClass 6-9 Science and Math Textbook SectionsAbhishant KumarNo ratings yet
- 11111Document1 page11111warenNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Lecture NoteDocument40 pages1 1 Lecture Notemeh jujubeNo ratings yet
- BLB - 14e - Ch01 - Lecture 학생Document44 pagesBLB - 14e - Ch01 - Lecture 학생huidamwooNo ratings yet
- PHA6113 LAB ViscosityDocument4 pagesPHA6113 LAB ViscosityPeter Jon SantiagoNo ratings yet
- POGIL Chemistry HandoutsDocument38 pagesPOGIL Chemistry HandoutsYunNo ratings yet
- Ecology Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEcology Cheat SheetJorge Aka-angel0% (2)
- Chap 1 Matter and MeasurementDocument49 pagesChap 1 Matter and MeasurementDiana ParkerNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Swarm IntelligenceDocument13 pages1-Introduction To Swarm IntelligenceivalenteNo ratings yet
- Content For General Science Capsule For DFCCIL 2021 Exam: Topics Covered in PHYSICS 2Document70 pagesContent For General Science Capsule For DFCCIL 2021 Exam: Topics Covered in PHYSICS 2Mahendra JenaNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument6 pagesBotanyCyrill Mae MagallonNo ratings yet
- TimelineDocument1 pageTimelineapi-574978257No ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy: Gpat Online ClassesDocument82 pagesPhysical Pharmacy: Gpat Online Classesshripathy1-1No ratings yet
- Hierarchy and Trophic LevelsDocument65 pagesHierarchy and Trophic LevelsJhofre VacaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Mutualism and Symbiosis Lecture 9: Mutualism and SymbiosisDocument5 pagesLecture 9: Mutualism and Symbiosis Lecture 9: Mutualism and SymbiosisBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Slide MembraneDocument1 pageSlide Membranebadrul aminNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - 23-07-2021 BBDocument7 pagesLecture 2 - 23-07-2021 BBpaulinemahlangu88No ratings yet
- Fun Farm SnacksDocument6 pagesFun Farm SnacksZafiriou MavrogianniNo ratings yet
- Definition and Characteristics of Therapeutic UltrasoundDocument7 pagesDefinition and Characteristics of Therapeutic Ultrasoundim. EliasNo ratings yet
- Abiotic vs. Biotic Factors: NameDocument2 pagesAbiotic vs. Biotic Factors: NameLinda BurgioNo ratings yet
- 1.680 ATP 2023 24 GR 8 Nat Sci Final 1Document5 pages1.680 ATP 2023 24 GR 8 Nat Sci Final 1kholofelomavis1988No ratings yet
- ME3400 Characteritics Types ProcessingDocument43 pagesME3400 Characteritics Types ProcessingWish SetsNo ratings yet
- IB MYP Chemistry Topic Coverage Map by ConceptDocument6 pagesIB MYP Chemistry Topic Coverage Map by ConceptSiddhant ShahNo ratings yet
- Oswaal_Olympiads_Class-4_Mind_Map_Science_for_2022_ExamDocument12 pagesOswaal_Olympiads_Class-4_Mind_Map_Science_for_2022_Examgunishgoyal0510No ratings yet
- Chemistry Topics MypDocument6 pagesChemistry Topics MypMaxwell WamaithaNo ratings yet
- CC2404 Revision Table 2009Document8 pagesCC2404 Revision Table 2009galaxy113No ratings yet
- L 1 Chemistry of LifeDocument10 pagesL 1 Chemistry of LifeDr Sonali PatleNo ratings yet
- Y3 CL T1 WK6 3rd October 2022 16th October 2022Document7 pagesY3 CL T1 WK6 3rd October 2022 16th October 2022RabbiyaNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument4 pagesMind MapPrincez Yuvasini NanthakumarNo ratings yet
- L-1 Bot 4-JuneDocument9 pagesL-1 Bot 4-Junedeekshitha 212521No ratings yet
- Ecology InteractionsDocument6 pagesEcology InteractionsAastha AvantikaNo ratings yet
- Imagen Promoción de La Salud MentalDocument1 pageImagen Promoción de La Salud Mentalale_bravo_schrothNo ratings yet
- YeteteaDocument5 pagesYeteteaAkbaraly Hayyan HoussenNo ratings yet
- MBS662 Session 2Document32 pagesMBS662 Session 2stgregNo ratings yet
- Ocean ActivitesDocument7 pagesOcean ActivitesritakeskitaloNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem l1 PpsDocument3 pagesEcosystem l1 Ppsapi-477189194No ratings yet
- 64f23ef6f8225c001887a474 - ## - Plant Kingdom Mind MapsDocument3 pages64f23ef6f8225c001887a474 - ## - Plant Kingdom Mind Mapsjai maa Durga aadi parashaktiNo ratings yet
- Biophilic Design As An Aid To HealingDocument13 pagesBiophilic Design As An Aid To HealingvartikaNo ratings yet
- PMC (NUMS) Syllabus Biology Chemistry PhysicsDocument2 pagesPMC (NUMS) Syllabus Biology Chemistry PhysicsAsad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Ac 7Document6 pagesAc 7scribsunilNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A 5 kVA InverterDocument22 pagesDesign and Implementation of A 5 kVA InverterscribsunilNo ratings yet
- FuseDocument8 pagesFusescribsunilNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To RuDocument1 pageClosed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To RuscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Maths 1 s15Document4 pagesMaths 1 s15scribsunilNo ratings yet
- Elite Academy, Nagpur Course: Fast Track (XII Mah'Board) TEST-1 Sub: Physics Date: 2 Dec 2018 Time: 1:00 Hrs. Max. Mark: 2/1/2019Document1 pageElite Academy, Nagpur Course: Fast Track (XII Mah'Board) TEST-1 Sub: Physics Date: 2 Dec 2018 Time: 1:00 Hrs. Max. Mark: 2/1/2019scribsunilNo ratings yet
- Advertisement For MHADA Recruitment 2021 DTD 17-9-2021Document18 pagesAdvertisement For MHADA Recruitment 2021 DTD 17-9-2021SureshSawantNo ratings yet
- Improve Power Factor Transmission Lines SVCDocument4 pagesImprove Power Factor Transmission Lines SVCscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Fuse1 PDFDocument16 pagesFuse1 PDFscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Sr Project Details and Funding StatusDocument3 pagesSr Project Details and Funding StatusscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To RuDocument1 pageClosed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To RuscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Improve Power Factor Transmission Lines SVCDocument4 pagesImprove Power Factor Transmission Lines SVCscribsunilNo ratings yet
- PhD Abroad Links With Low Expenses And Scholarship OptionsDocument2 pagesPhD Abroad Links With Low Expenses And Scholarship OptionsscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Power Electrnics Notes PDFDocument78 pagesPower Electrnics Notes PDFAditya SolankiNo ratings yet
- Arduino-Based Underground Cable Fault Detection SystemDocument6 pagesArduino-Based Underground Cable Fault Detection SystemscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Set 4Document1 pageSet 4scribsunilNo ratings yet
- What Next After School 1Document1 pageWhat Next After School 1scribsunilNo ratings yet
- 0BygiwGm pPHSZm5DaUJEXzBPMnc PDFDocument211 pages0BygiwGm pPHSZm5DaUJEXzBPMnc PDFMujthaba kauserNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 s16Document7 pagesPhysics 1 s16scribsunilNo ratings yet
- IfyDocument6 pagesIfyVibhor MittalNo ratings yet
- Wavelet SimpleDocument22 pagesWavelet SimplefarismohNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis (Gate Bits)Document90 pagesNetwork Analysis (Gate Bits)tvs_krishnavarma100% (3)
- DCOPFJTalk IEEEPESGM2007 PDFDocument31 pagesDCOPFJTalk IEEEPESGM2007 PDFscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Bhattacharaya Mathematical Academy: Topic: Mathematics and Statistics (Set Ii)Document2 pagesBhattacharaya Mathematical Academy: Topic: Mathematics and Statistics (Set Ii)scribsunilNo ratings yet
- 111 Lec 01Document54 pages111 Lec 01scribsunilNo ratings yet
- Chronology of Shivaji Maharaj's LifeDocument2 pagesChronology of Shivaji Maharaj's Lifescribsunil100% (1)
- Physics 1 w15Document5 pagesPhysics 1 w15scribsunilNo ratings yet
- TV - Ads QuoationDocument9 pagesTV - Ads QuoationscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document2 pagesSet 1scribsunilNo ratings yet
- Optimum Placement and Sizing Determination of Distributed Generation and DSTATCOM Using Penguins Search Optimisation AlgorithmDocument6 pagesOptimum Placement and Sizing Determination of Distributed Generation and DSTATCOM Using Penguins Search Optimisation AlgorithmscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Topic - 8Document29 pagesTopic - 8Cynthia GNo ratings yet
- Terminology Used in Livestock Production: TypeDocument5 pagesTerminology Used in Livestock Production: TypeBalajiNo ratings yet
- Competition Evolution ReadingDocument2 pagesCompetition Evolution Readingapi-242868690No ratings yet
- Amit Kumar Tyagi PHDDocument40 pagesAmit Kumar Tyagi PHDrohitNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological Analysis of Water: MPN Technique for Coliform CountDocument9 pagesBacteriological Analysis of Water: MPN Technique for Coliform CountGaurav MudaduNo ratings yet
- UGCNET Paper2 AnthropologyDocument56 pagesUGCNET Paper2 AnthropologyAryanNo ratings yet
- POCKIT Central SARS-CoV-2 Premix Reagent - User Manual (20200601) - US ...Document34 pagesPOCKIT Central SARS-CoV-2 Premix Reagent - User Manual (20200601) - US ...Anisa MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology The Essentials 3rd EditionDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Biology The Essentials 3rd EditionKristi Markus100% (33)
- HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY KEY FUNCTIONSDocument17 pagesHUMAN PHYSIOLOGY KEY FUNCTIONSplsssssNo ratings yet
- Iron-Oxidizing BacteriaDocument26 pagesIron-Oxidizing Bacteriagigio marinoNo ratings yet
- FY 2018 Self Identified Generic Drug Facilities Sites and OrganizationsDocument175 pagesFY 2018 Self Identified Generic Drug Facilities Sites and OrganizationsDavid Paul HensonNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning - Outbreaks, Bacterial Sources and Adverse Health Effects (2015) PDFDocument294 pagesFood Poisoning - Outbreaks, Bacterial Sources and Adverse Health Effects (2015) PDFAndré Campelo100% (1)
- Bioemergetics Cellular Respiration Electron Transport ChainDocument59 pagesBioemergetics Cellular Respiration Electron Transport ChainHassan Abib BasalNo ratings yet
- L. plantarum 299v Reduces Inflammation and Normalizes Motility in IBS Mouse ModelDocument6 pagesL. plantarum 299v Reduces Inflammation and Normalizes Motility in IBS Mouse ModelMarin GregurinčićNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science Chapter 2 MicrooganismDocument9 pagesClass 8 - Science Chapter 2 MicrooganismwandererNo ratings yet
- Christian EthicsDocument36 pagesChristian EthicsJoseph FordNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nano Priming On Seed Germination and Plant Growth of Forage and Medicinal PlantsDocument16 pagesInfluence of Nano Priming On Seed Germination and Plant Growth of Forage and Medicinal PlantsUriel González LemusNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom (L2) - 2nd JuneDocument43 pagesPlant Kingdom (L2) - 2nd JuneUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- GPB201 Unit-5 FullDocument51 pagesGPB201 Unit-5 FullAman MidhaNo ratings yet
- 2017 OL Biomolecule REVIEWDocument5 pages2017 OL Biomolecule REVIEWIan ZeigerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Anemia in CKDDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Anemia in CKDBazz DanteNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Olfaction in Parkinson's Disease and Related DisordersDocument63 pagesNIH Public Access: Olfaction in Parkinson's Disease and Related DisordersCarmen CiursaşNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Lab DNAReplication Bio1Document6 pagesUnit3 Lab DNAReplication Bio1DuckyRoblox YTNo ratings yet
- Curly Hair Genetics - Dominant or RecessiveDocument4 pagesCurly Hair Genetics - Dominant or RecessiveimnylaroseNo ratings yet
- Histologi Usus Ikan NilaDocument14 pagesHistologi Usus Ikan NilaOnnaSafuraNo ratings yet
- Primary Lymphoid Organs Generate Immune CellsDocument10 pagesPrimary Lymphoid Organs Generate Immune CellsKarthigaNo ratings yet
- (Dorothy Nelkin, M. Susan Lindee) The DNA MystiqueDocument314 pages(Dorothy Nelkin, M. Susan Lindee) The DNA MystiqueAntonella ParisiNo ratings yet
- Sophia Human Biology Lab SyllabusDocument6 pagesSophia Human Biology Lab SyllabusKoffi Agbéko HonsouNo ratings yet
- Fox Keller - The-Mirage-Of-A-Space-Between-Nature-And-Nurture PDFDocument117 pagesFox Keller - The-Mirage-Of-A-Space-Between-Nature-And-Nurture PDFBezafu100% (1)
- Snack Attack LabDocument3 pagesSnack Attack LabDavid YeeNo ratings yet