Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capital Gain
Uploaded by
Chikke Gowda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views19 pagescAPITAL gIAN
Original Title
CG
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentcAPITAL gIAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views19 pagesCapital Gain
Uploaded by
Chikke GowdacAPITAL gIAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Capital Gain
Capital Gain
“Any profit and gain arising on Transfer of a
capital asset”
known as Capital Gain
There are two types of Capital Gain
1. Short Term Capital gain
2.Long term Capital gain
Sections Applicable
1.Sec 45- Provides Chargeability
( Defines what is transfer of a capital asset for Capital Gain)
2. Sec 46 , 47 – Provides transactions, which are
not transfer of capital asset.
3. Sec 54, 54 B, 54 D, 54 EC, 54 F, 54 G, 54 GA &
54H - Gives the list of exemptions.
Conditions for
Capital gain tax liability
• There should be a capital asset
• The capital asset is transferred by the assessee
• Such Transfer takes place during the previous
year
• Any profit or gain arises as a result of transfer
• Such profit or gain is not exempt from tax
under Sec 54, 54B, 54D, 54EC, 54F, 54G, 54GA.
Important definitions
• Capital Assets:
• Short term / Long Term Capital Asset:
• Transactions are not regarded as Transfer:
• Cost of Acquisition (Sec 49):
• Cost of asset for the previous owner Sec 49(1):
• Transfer of Capital Assets:
• Slump sales ( Sec 50)
• Meaning of net worth
Capital Assets:
• A capital asset is defied to include property of
any kind, whether fixed or circulating,
movable or immovable, tangible or intangible
Short term / Long Term Capital Asset:
Transactions are not regarded as Transfer:
• Cost of Acquisition (Sec 49):
• Cost of asset for the previous owner Sec 49(1):
• Transfer of Capital Assets:
• Slump sales ( Sec 50)
• Meaning of net worth
Cost of Acquisition (Sec 49):
Cost of asset for the previous owner Sec 49(1):
Transfer of Capital Assets:
Slump sales ( Sec 50)
Meaning of net worth
Cost of Acquisition being the fair market value as on
April1, 1981:
The assessee may take at his option, either actual cost or the
fair market value of the asset ( other than a depreciable
asset) as on April 1, 1981 as cost of acquisition:
• Where the capital asset became the property of the
assessee before April 1, 1981.
• Where the capital asset became the property of the
assessee by any mode referred to in sec 49(1) and the
property was originally acquired before Aril 1, 1981.
Capital Gain in case of conversion of capital asset into stock in trade:
• The fair market value of the capital asset on
the date on which it was converted or treated
as stock in trade shall be deemed to be full
value of the consideration received or
accruing as a result of the transfer of the
capital asset
Important Situations of CG arrise
• Transfer of capital asset by a Partner to a firm:
• Distribution of capital asset on dissolution:
• Capital gain in case of self generated assets:
• Capital Gain arising form the transfer of the
residential Property (Sec
• Exemptions under following conditions are met.
• Capital Gain not to be charged on investment in
certain bonds (sec 54EC)
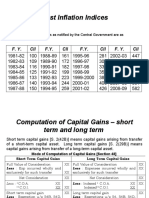
Calculation of CG
Computation of short term capital
gains ( STCG)
Computation of long term capital
gains (LTCG)
XXX
Full value of XXX
Full value of
consideration received consideration received or
or accrued accrued
XXX
(-) Expenses on Sale XXX
(-) Expenses on Sale
XXX
Net Sale Consideration XXX
Net Sale Consideration
XXX
Indexed cost of XXX
Indexed cost of
acquisition acquisition
XXX
Indexed cost of XXX
Indexed cost of
improvement improvement
XXX
Short term capital gain XXX
Long term capital gain
XXX
(-) deductions u/s 54B, XXX
(-)deductions u/s 54B,
54D, 54G,54GA 54D,54EC,54F
54G,54GA, 54GB
XXX
Net taxable STCG XXX
Net taxable LTCH
.
• Indexed cost of acquisition
Cost of acquisition x CII of the year of transfer
= ----------------------------------------------------------
CII of the year of acquisition
• Indexed cost of improvement
Cost of improvement x CII of the year of transfer
= ------------------------------------------------------------
CII of the year of improvement
• Cost of Transfer
= Cost of advertising + Brokerage paid + Legal
expenses incurred
Concept of Cost Inflation Index (CII)
Cost Inflation Index (CII) is an indexation declared every
year by the government for calculating capital gains
on long-term assets.
• Indexation is the procedure of adjusting prices based
on a standard index to factor in the inflation rate also
while calculating profits earned on the sale of assets.
• Indexation considers inflation and gives us a more
reasonable figure for long-term capital gains.
• Budget 2017 has revised the base year for
indexation from 1981 to 2001 and new index will be
notified in due course.
You might also like
- The McGraw-Hill 36-Hour Course: Finance for Non-Financial Managers 3/EFrom EverandThe McGraw-Hill 36-Hour Course: Finance for Non-Financial Managers 3/ERating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Income From Capital GainsDocument9 pagesIncome From Capital Gainsaysha banuNo ratings yet
- Intangible Finance Standards: Advances in Fundamental Analysis and Technical AnalysisFrom EverandIntangible Finance Standards: Advances in Fundamental Analysis and Technical AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Income From Capital GainsDocument5 pagesIncome From Capital Gainskeenu23No ratings yet
- Capital GainDocument41 pagesCapital GainKrrish KelwaniNo ratings yet
- Capital Gain 8th SemDocument10 pagesCapital Gain 8th SemAuthor SatyaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Capital Gains: After Studying This Unit, You Would Be Able ToDocument124 pagesUnit - 4: Capital Gains: After Studying This Unit, You Would Be Able ToGayatri KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Captal GainsDocument9 pagesCaptal GainsShivarajkumar JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Theory Capital GainDocument6 pagesTheory Capital GainRuthvik RevanthNo ratings yet
- Dtax Ii 2018Document11 pagesDtax Ii 2018GYANDEEP BONIANo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Capital Gains: Proforma For Computation of Income Under The Head "Capital Gains"Document33 pagesUnit - 4: Capital Gains: Proforma For Computation of Income Under The Head "Capital Gains"GauravNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Capital Gains: Proforma For Computation of Income Under The Head "Capital Gains"Document33 pagesUnit - 4: Capital Gains: Proforma For Computation of Income Under The Head "Capital Gains"GauravNo ratings yet
- Capital GainsDocument13 pagesCapital GainsGcs PreethikaNo ratings yet
- Captial Gain PresentationDocument18 pagesCaptial Gain Presentationvrmahajan59No ratings yet
- Capital GainDocument19 pagesCapital GainSAUJATYA BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Unit I Theory and ProblemsDocument7 pagesUnit I Theory and Problemssandy santhoshNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance Unit 4Document28 pagesAccounting and Finance Unit 4vasudhaNo ratings yet
- Bos 45796 CP 4 U 4Document116 pagesBos 45796 CP 4 U 4shrutichhalaniNo ratings yet
- 7 Capital GainsDocument116 pages7 Capital GainsSrinivas NuthalapatiNo ratings yet
- 1240330838-47 - Capital GainsDocument32 pages1240330838-47 - Capital GainsSHASWAT DROLIANo ratings yet
- Capital GainsDocument122 pagesCapital GainsVaibhav GawadeNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Short Term Capital Gain TaxDocument2 pagesCalculation of Short Term Capital Gain TaxSAGAR BALAGARNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Income From Capital GainsDocument10 pagesUnit 4 - Income From Capital GainsAvin P RNo ratings yet
- Income From Capital GainDocument9 pagesIncome From Capital Gain6804 Anushka GhoshNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains1Document56 pagesCapital Gains1api-3832224100% (3)
- Capital Gain: Unit IIIDocument44 pagesCapital Gain: Unit IIIvikas_is_stupidNo ratings yet
- Taxation Builders Developers Flat Purchasers VimalPDocument63 pagesTaxation Builders Developers Flat Purchasers VimalPS M SHEKAR AND CONo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Statement of Comprehensive IncomeKarylle EntinoNo ratings yet
- Computation of Capital GainsDocument25 pagesComputation of Capital GainsRamya GowdaNo ratings yet
- Diya 1Document4 pagesDiya 1Vipul I PanchasarNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains 1Document55 pagesCapital Gains 1apurvaapurvaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Profits Tax Computation and Capital Allowance Treatment - Firs June 2018 PDFDocument18 pagesPetroleum Profits Tax Computation and Capital Allowance Treatment - Firs June 2018 PDFObi MogboNo ratings yet
- 27 Capital Gain PCCDocument44 pages27 Capital Gain PCCbshah1989No ratings yet
- Capital GainDocument4 pagesCapital GainOnkar BandichhodeNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains ComputationDocument19 pagesCapital Gains ComputationNandini AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Accounting - Process of Identifying, Measuring, and Communicating EconomicDocument7 pagesFinancial Accounting: Accounting - Process of Identifying, Measuring, and Communicating EconomicKyle Daniel PimentelNo ratings yet
- Final Capital GainsDocument19 pagesFinal Capital GainsDisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains: Charging Section - Section 45Document42 pagesCapital Gains: Charging Section - Section 45Murugan SaralaNo ratings yet
- Afa CompilationDocument36 pagesAfa CompilationAnkur ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Income Under The Head Capital Gains: LTCG Arising From The Transfer of RHP and Is Reinvested in New RHP (Exemption U/s 54)Document14 pagesIncome Under The Head Capital Gains: LTCG Arising From The Transfer of RHP and Is Reinvested in New RHP (Exemption U/s 54)dosadNo ratings yet
- Income Statement and Balance SheetDocument20 pagesIncome Statement and Balance Sheetpankaj tiwariNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains: Presented by Dr. N.K.GuptaDocument53 pagesCapital Gains: Presented by Dr. N.K.Guptakeshav956No ratings yet
- Capital Gains Tax NEWDocument109 pagesCapital Gains Tax NEWRishi CharanNo ratings yet
- CFM 221 2023 Capital Budgets NotesDocument19 pagesCFM 221 2023 Capital Budgets NotesChantell KatlegoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Income (Accounting For Leasehold Improvements) Accounting Methods Accounting For Leasehold ImprovementsDocument10 pagesConcept of Income (Accounting For Leasehold Improvements) Accounting Methods Accounting For Leasehold ImprovementsShaina SamonteNo ratings yet
- RoadmapDocument2 pagesRoadmaplamslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - CompleteDocument15 pagesChapter 4 - Completemohsin razaNo ratings yet
- Income Statement ABC TRADING CORPORATION.Document5 pagesIncome Statement ABC TRADING CORPORATION.Mell Armonnd MonrealNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Impairment of AssetsDocument52 pagesModule 2 Impairment of AssetsRIZLE SOGRADIELNo ratings yet
- Acctg For LTCC - IllustrationsDocument13 pagesAcctg For LTCC - IllustrationsGalang, Princess T.No ratings yet
- DT Combined CA INTERDocument203 pagesDT Combined CA INTERkarthick rajNo ratings yet
- Correction in Income TaxDocument13 pagesCorrection in Income TaxchiragsmguptaNo ratings yet
- Income From Capital Gain, Income From Household Property, Income From Other SourcesDocument24 pagesIncome From Capital Gain, Income From Household Property, Income From Other Sourcesamol_more37No ratings yet
- Capital Gainsppt 180105192411Document58 pagesCapital Gainsppt 180105192411ozairsaiyedNo ratings yet
- Capital GainsDocument8 pagesCapital GainsSarfaraz Singh LegaNo ratings yet
- Slides - Module 4Document48 pagesSlides - Module 4Sunena KumariNo ratings yet
- Income From Capital Gain by Vishal GoelDocument57 pagesIncome From Capital Gain by Vishal Goelgoel76vishal100% (1)
- 1.0 Accounting Period and MethodDocument22 pages1.0 Accounting Period and MethodShiela Marie Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- SyovcgiDocument19 pagesSyovcgiSHIVAM SAHUNo ratings yet
- Final Course Content - General Knowledge - Old 1Document20 pagesFinal Course Content - General Knowledge - Old 1Chikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- Macr SyllabusDocument2 pagesMacr SyllabusChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- pENSION FOR PRIVATE WORKERSDocument2 pagespENSION FOR PRIVATE WORKERSChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- Final Course Content - General Knowledge-2Document32 pagesFinal Course Content - General Knowledge-2Chikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge (G K)Document45 pagesGeneral Knowledge (G K)Chikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge (G K)Document45 pagesGeneral Knowledge (G K)Chikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- DEPRECIATIONDocument14 pagesDEPRECIATIONChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- AC - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAC - Lesson PlanChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- The RBT Levels (Doenloaed From Google, Only For Educationalm Purpose, Dont Use Otherwise)Document5 pagesThe RBT Levels (Doenloaed From Google, Only For Educationalm Purpose, Dont Use Otherwise)Chikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- DEPRECIATIONDocument14 pagesDEPRECIATIONChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- AC - Lesson Plan FINAL - A SECDocument5 pagesAC - Lesson Plan FINAL - A SECChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- Accounting QuestionsDocument1 pageAccounting QuestionsChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- Tax - M-1 ProblemsDocument14 pagesTax - M-1 ProblemsChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- AC - Lesson Plan FINAL - A SECDocument5 pagesAC - Lesson Plan FINAL - A SECChikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- RBT Verbs-12-9-2018Document2 pagesRBT Verbs-12-9-2018Chikke Gowda100% (2)
- Papc June 2012Document3 pagesPapc June 2012Chikke GowdaNo ratings yet
- About Globalisation and IHRMDocument29 pagesAbout Globalisation and IHRMsharnagatNo ratings yet
- 12 Houses ExplainedDocument3 pages12 Houses ExplainedKoshi EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Sheet For RankingDocument6 pagesEvaluation Sheet For RankingSonny MatiasNo ratings yet
- Brochure 1st RMLNLU Kochhar Co. Arbitration Moot Court Competition 2023Document21 pagesBrochure 1st RMLNLU Kochhar Co. Arbitration Moot Court Competition 2023Rishi Raj MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Aarvee Denim & Export LTD.: CertificateDocument46 pagesAarvee Denim & Export LTD.: CertificateVinita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- SkripsiDocument101 pagesSkripsiNurul Maharani PutriNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Carbon Black On The Oxidative Induction Time of Medium-Density PolyethyleneDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Carbon Black On The Oxidative Induction Time of Medium-Density PolyethyleneMIRELLA BOERYNo ratings yet
- Food and Medicine Label 1-50Document11 pagesFood and Medicine Label 1-50Muthia KumalaNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesResearch Methodologysonal gargNo ratings yet
- 13 19 PBDocument183 pages13 19 PBmaxim reinerNo ratings yet
- Incremental and TwiceDocument12 pagesIncremental and TwiceAgung KaryawinaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-Operations and Management: There Are Four Main Reasons Why We Study OM 1)Document3 pagesChapter-1-Operations and Management: There Are Four Main Reasons Why We Study OM 1)Karthik SaiNo ratings yet
- 1.CH 211 IntraductionDocument13 pages1.CH 211 IntraductionCarlos BuchwaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of MoneyDocument9 pagesThe Importance of MoneyLinda FeiNo ratings yet
- Turn Taking and InterruptingDocument21 pagesTurn Taking and Interruptingsyah malengNo ratings yet
- Basic English: Unit 14 Guidelines Leisure ActivitiesDocument5 pagesBasic English: Unit 14 Guidelines Leisure ActivitiesDeyan BrenesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Form Day 2 / 3 (4) Webquest Data GatheringDocument1 pageLesson Plan Form Day 2 / 3 (4) Webquest Data GatheringMarkJLanzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9Document3 pagesUnit 9LexNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Science: N. Ratkovich, P.R. Berube, I. NopensDocument15 pagesChemical Engineering Science: N. Ratkovich, P.R. Berube, I. Nopensvasumalhotra2001No ratings yet
- Scientific Writing VerbsDocument3 pagesScientific Writing VerbsNejdetEXn100% (1)
- 1903 Er19031211Document22 pages1903 Er19031211Tullio OpattiNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Assignment 1 Solution: Name: Vivek Rana Roll No.: 1709113908Document5 pagesDeep Learning Assignment 1 Solution: Name: Vivek Rana Roll No.: 1709113908vikNo ratings yet
- Health Education ProgramDocument4 pagesHealth Education ProgramZari Novela100% (1)
- Types of Drills PDFDocument8 pagesTypes of Drills PDFSummer nightsNo ratings yet
- New Public Service (Denhardt & Denhardt)Document12 pagesNew Public Service (Denhardt & Denhardt)Ika Hartantiningsih100% (1)
- The Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes ServiceDocument9 pagesThe Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes ServiceKumar AvelNo ratings yet
- Akbar Early YearsDocument25 pagesAkbar Early YearsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Debate QuestionsDocument7 pagesDebate Questionsapi-522661051No ratings yet
- Fossils (DK Smithsonian Handbook) by DKDocument320 pagesFossils (DK Smithsonian Handbook) by DKAnthony Mello71% (7)
- APQP TrainingDocument22 pagesAPQP TrainingSandeep Malik100% (1)
- Topic 3 BatteryDocument40 pagesTopic 3 BatterynisaNo ratings yet