Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of Liver
Uploaded by
siewv_10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views22 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views22 pagesAnatomy of Liver
Uploaded by
siewv_1Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
ANATOMY OF LIVER
Liver is a soft, dark brown highly vascular organ.
Largest gland in the body
Secretes bile & performs various metabolic functions
Occupies the whole of the right hypochondrium,
greater part of epigastrium & extends into the left
hypochondrium
Weight - 1400 – 1800 gms in males
1200 – 1400 gms in females.
Lobes
of liver
Large right lobe (5/6) and a small left lobe
Divided by the attachment of falciform ligament
(anteriorly & superiorly)
Fissure of ligamentum teres (inferiorly)
Fissure of ligamentum venosum (posteriorly)
Caudate lobe
- lies between the IVC & fissure for ligamentum venosum
- connected to the right lobe by the caudate process
Quadrate lobe
- lies between the gall bladder & the fissure for ligamentum
teres
The caudate & quadrate lobes are separated by the porta
hepatis
Surfaces of liver
Two surfaces, diaphragmatic surface & visceral surface
(posteroinferior)
Separated by the inferior border
Diaphragmatic surface
- smooth, dome-shaped
- conforms to the concavity of the inferior surface of the
diaphragm
-Separates the liver from thoracic structures
Visceral surface
- directed posteriorly, inferiorly & to the left
- many irregularities on this surface
Hepatic Segments
On the basis of blood supply and biliary drainage
there are four main hepatic sectors.
Left lateral
Left medial
Right anterior
Right posterior
These four sectors are further divided into eight
segments.
Relations
Diaphragmatic surface is related to the diaphragm and
right and left costal margins
Visceral surface is related to abdominal part of
oesophagus, the stomach, the duodenum, the right
colic flexure, transverse colon, the right kidney, right
suprarenal gland and the gall bladder
Areas not covered by peritoneum
- bare area
- groove for inferior vena cava
- fossa for the gall bladder
- porta hepatis
PORTAL SYSTEM
Large vein which collects blood from
- abdominal part of alimentary tract
- gall bladder
- pancreas
- spleen
begins as capillary plexus and ends by emptying
blood into the sinusoids of liver.
Formed by the union of splenic vein & superior
mesenteric vein
Posterior to the neck of pancreas
Level of L2
Relations
Runs behind first part of duodenum
Free margin of lesser omentum -anterior to bile duct (right)
and hepatic artery (left)
Ends at the right end of porta hepatis
Infraduodenal
- anterior: neck of pancreas
- posterior: IVC
Retroduodenal
- 1st part of duodenum
- CBD
- gastroduodenal artery
Portal Vein Tributaries
Splenic vein – it receives the inferior mesenteric
vein.
Superior mesenteric vein
Left gastric vein
Right gastric vein
Superior pancreaticoduodenal
Cystic vein
Porto-systemic anastomosis
Umbilicus
Lower end of oesophagus
Anal canal
Bare area of the liver
Posterior abdominal wall
Liver (rare)
References
Prof Dr. Nasaruddin’s notes
PM Dr. Jeya’s notes
http://www.radiologyassistant.nl
Gray’s Clinical Anatomy Textbook
You might also like
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1reeta yadav0% (1)
- SL NO Content NODocument12 pagesSL NO Content NOPdianghunNo ratings yet
- Importance of BADocument8 pagesImportance of BAGolden Gate Colleges Main LibraryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lymphoid Tissue & Immune System & Histology of Lymph Node & Thymus PDFDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Lymphoid Tissue & Immune System & Histology of Lymph Node & Thymus PDFhassam qaziNo ratings yet
- Pleurisy (Pleuritis)Document17 pagesPleurisy (Pleuritis)kamilahfernandezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Document9 pagesCardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Prince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Lu03 Moral Objectivism RelativismDocument4 pagesLu03 Moral Objectivism RelativismJocelynNo ratings yet
- Basilar Skull FractureDocument16 pagesBasilar Skull FractureRindahMDNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EmergenciesDocument73 pagesCardiac EmergenciesKristine CaringalNo ratings yet
- 5 - Respiratory AssessmentDocument61 pages5 - Respiratory AssessmentAbboud Ali100% (1)
- Tracheostomy Care: PhysiologyDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care: PhysiologyrajirajeshNo ratings yet
- Burns MGNT and CalculationDocument7 pagesBurns MGNT and CalculationPoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma Presented With Anemia of Chronic Disease As Microcytic Hypochromic TypeDocument3 pagesA Case Report of Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma Presented With Anemia of Chronic Disease As Microcytic Hypochromic TypeIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Guillan Barre Syndrome FinalDocument16 pagesGuillan Barre Syndrome FinalAswathy RCNo ratings yet
- Compartment SyndromeDocument3 pagesCompartment SyndromeTantyo Adi P100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesNursing Care PlanChic Dian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument2 pagesAbdominal Aortic AneurysmAria MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument14 pagesPulmonary EdemaRizzamwah Catague100% (1)
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAnatomy & Physiologyrachael80% (5)
- Case Stydy Angina PectorisDocument46 pagesCase Stydy Angina PectorissharenNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument10 pagesHeart Failureurmila prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulnonary Disease (Copd)Document3 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulnonary Disease (Copd)Richard TanNo ratings yet
- ATELECTASISDocument4 pagesATELECTASISAshley Jane MacapayadNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument2 pagesPneumothoraxAfif MansorNo ratings yet
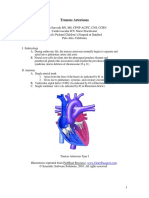
- Truncus ArteriosusDocument4 pagesTruncus ArteriosuskemalahmadNo ratings yet
- PresbycusisDocument5 pagesPresbycusisdarsunaddictedNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm PDFDocument20 pagesAneurysm PDFKV100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsDocument125 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsAyeNo ratings yet
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdMarion Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Fat Embolism SyndromeDocument26 pagesFat Embolism SyndromeAzni MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Treatments and Drugs: by Mayo Clinic StaffDocument23 pagesTreatments and Drugs: by Mayo Clinic StaffJr D BayzNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument9 pagesOtitis MediaMona Santi NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Management of Infective EndocarditisDocument14 pagesManagement of Infective Endocarditismhafzam2020No ratings yet
- Lab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDocument6 pagesLab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDaisy MellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study About: Cardiac Failure and Pulmonary EdemaDocument32 pagesCase Study About: Cardiac Failure and Pulmonary EdemaIan Simon DorojaNo ratings yet
- Colonic Carcinoma Case StudyDocument23 pagesColonic Carcinoma Case StudyGlaiza Claire Am-amlan OlayanNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction AssignmentDocument23 pagesMyocardial Infarction AssignmentPums100% (6)
- Mysthenia THEIORY APPLICATIONDocument35 pagesMysthenia THEIORY APPLICATIONPatel Himani100% (1)
- Gastric AnalysisDocument1 pageGastric AnalysisJose Paul RaderNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument2 pagesPulmonary Function TestsSafuan Sudin100% (1)
- 1.case Presentation CHDDocument23 pages1.case Presentation CHDDHARM MEENANo ratings yet
- Pre Op BabyDocument3 pagesPre Op BabyJmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument2 pagesHealth AssessmentrojeanrubinoNo ratings yet
- Endoscopicretrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)Document21 pagesEndoscopicretrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)Suman PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument43 pagesHeart FailuresimonjosanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Nursing ResearchDocument1 pageImportance of Nursing ResearchCathy Marie ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDDocument3 pagesAnatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument14 pagesPeritonitisaiya_sorayaNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderDocument15 pagesIsabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Administration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyDocument8 pagesAdministration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyRonald ThakorNo ratings yet
- Shock TypesDocument25 pagesShock TypesMuqeet76No ratings yet
- Valvularheart Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument9 pagesValvularheart Diseases: PathophysiologyVoid LessNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Presentation For A Patient With CABG: Subject: Medical Surgical Nursing-IIDocument10 pagesNursing Case Presentation For A Patient With CABG: Subject: Medical Surgical Nursing-IIanamika sharmaNo ratings yet
- SplenectomyDocument7 pagesSplenectomynessajoanNo ratings yet
- Cerebral HemorrhageDocument10 pagesCerebral HemorrhageJayd Lorenz Vicente ChuanNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Prof. Huiling Yang Dept. PathophysiologyDocument46 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy: Prof. Huiling Yang Dept. PathophysiologyAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument3 pagesLiverMamunNo ratings yet
- Anatomy LiverDocument6 pagesAnatomy LivercheaterxorcistNo ratings yet
- UyzxcvDocument100 pagesUyzxcvValentin RotaruNo ratings yet
- Radiological Anatomy of The Hepatobiliary System-1Document69 pagesRadiological Anatomy of The Hepatobiliary System-1Emmanuel OluseyiNo ratings yet
- Monitoreo Hemodinamico Funcional PinskyDocument23 pagesMonitoreo Hemodinamico Funcional PinskyJuan CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Nationa Institutes of HealthDocument5 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Nationa Institutes of HealthUtari UbNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Arterial DiseaseDocument161 pagesPeripheral Arterial Diseasec406400No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1ALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel (A) Biology A LevelDocument10 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel (A) Biology A LevelAmal Abu KhalilNo ratings yet
- JAAD CME Aug 2023 - Cutaneous Manifestations of Cardiovascular and Vascular DiseaseDocument39 pagesJAAD CME Aug 2023 - Cutaneous Manifestations of Cardiovascular and Vascular DiseasejchengwangNo ratings yet
- Apparent and True Resistant Hypertension Definition, Prevalence and OutcomesDocument6 pagesApparent and True Resistant Hypertension Definition, Prevalence and OutcomesDana MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MCQ IG BioDocument19 pagesChapter 9 MCQ IG BioAdanam käûñg khåṇṭ kÿāw šwãrNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II: Cardiovascular DrugDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry-II: Cardiovascular DrugMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology of The HeartDocument32 pagesElectrophysiology of The HeartJohn Carlo ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Ala 3Document30 pagesAla 3Alaz NellyNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidelines PDFDocument293 pagesTreatment Guidelines PDFgautambobNo ratings yet
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Coming To An ICU Near YouDocument8 pagesExtracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Coming To An ICU Near Youmuhamad abdul kodirNo ratings yet
- Hancock1 109 - Hancock II Brochure - FinalDocument4 pagesHancock1 109 - Hancock II Brochure - FinalLuisaoNo ratings yet
- AngioplastyDocument38 pagesAngioplastyBuyung HamzahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 1Document5 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 1Clement CheeNo ratings yet
- Evolocumab 2Document13 pagesEvolocumab 2Rania El-DesokyNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Document98 pagesNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Maylisa ManurungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Vasodilators and Angina PectorisDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Vasodilators and Angina PectorisChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Heart and Fetal CirculationDocument36 pagesEmbryology of Heart and Fetal CirculationRaviNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Case PresentationDocument4 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Case PresentationJunathan L. DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 16 Vascular Diseases of Nervous System-QDocument24 pages16 Vascular Diseases of Nervous System-QAdi PomeranzNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circulatory SystemWC - 12MA 669502 Central Peel SSNo ratings yet
- Rose Angina QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesRose Angina QuestionnaireAndra ZdocaNo ratings yet
- 2017 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients Presenting With ST Segment ElevationDocument66 pages2017 ESC Guidelines For The Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients Presenting With ST Segment ElevationMoises Torres AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsDocument27 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsSofia Rose Saniel Gonzales100% (1)
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument27 pagesCardiogenic ShockMuhammad Ikbar100% (1)
- A Prospective Study of Prescribing Pattern in The Management of Stroke at A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument6 pagesA Prospective Study of Prescribing Pattern in The Management of Stroke at A Tertiary Care HospitalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Limf NodeDocument34 pagesLimf NodeNika MtsituriNo ratings yet