Professional Documents
Culture Documents
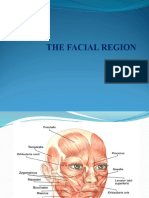
The Trigeminal Nerve
Uploaded by
Melanie GatchalianOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Trigeminal Nerve
Uploaded by
Melanie GatchalianCopyright:
Available Formats
THE TRIGEMINAL NERVE
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
BASIC POINTS
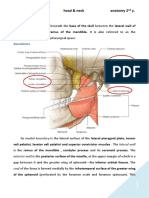
The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the twelve cranial nerves. It arises from the trigeminal ganglion or semilunar ganglion at the petrous portion on the temporal bone. It is a mixed nerve, with both motor and sensory fibers. The trigeminal nerve has three main divisions: 1. V1 or the ophthalmic division exits the skull thru the superior orbital fissure. This is the smallest division and is purely sensory. 2. V2 or the maxillary division exits the skull thru the foramen rotundum. The maxillary nerve is a purely sensory nerve. 3. V3 or mandibular division exits the skull thru the foramen ovale. This is the largest division and is a mixed nerve, containing both sensory and motor fibers.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Ophthalmic N. Maxillary N.
Mandibular N.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Mandibular N. Opthalmic N. Maxillary N.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
AREAS OF INNERVATION OF CNV
V1
V2
V3
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
The ophthalmic division (V1) exits the skull thru the superior orbital fissure. Its branches innervate the scalp, the upper eyelid. It is the smallest division of the trigeminal nerve and is a purely sensory or afferent nerve.
OPHTHALMIC NERVE (V1)
THE MAXILLARY NERVE
The maxillary nerve courses forward through the wall of the cavernous sinus and leaves the skull through the foramen rotundum. It crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, where it anastomoses with branches from the sphenopalatine ganglion, a parasympathetic ganglion. The maxillary nerve is a purely sensory nerve. The branches of the maxillary nerve are: 1. Inside the cranium nerve to the dura 2. At the pterygopalatine fossa area a. Branches from the sphenopalatine ganglion (click here) b. Zygomatic nerve i. Zygomaticofacial ii. Zygomaticotemporal c. Posterior superior alveolar nerve (PSAN) enters the alveolar canal thru the posterior superior alveolar foramina to innervate the pulps of the maxillary molars except the mesiobuccal root of the first molar.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
3. At the infraorbital canal a. Middle superior alveolar nerve (MSAN) innervates the pulps of the maxillary premolars and the mesiobuccal root of the first molar. b. Anterior superior alveolar nerve (ASAN) innervates the pulps of the maxillary anteriors. 3. Terminal branches (exit through the infraorbital foramen) a. Inferior palpebral sensory to the lower eyelid b. Lateral nasal sides of the nose c. Superior labial upper lip
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
F. ROTUNDUM
INFRAORBITAL FORAMEN
TRIGEMINAL GANGLION
INFRAORBITAL CANAL
PTERYGOPALATINE PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA AREA FOSSA AREA PETROUS PORTION OF THE TEMPORAL BONE
POST. SUPERIOR ALV. FORAMINA
THE MAXILLARY NERVE
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
NERVE TO THE DURA Z. FACIAL N. INF. PALPEBRAL INF. PALPEBRAL ZYGOMATIC N. LATERAL NASAL LATERAL NASAL SUPERIOR LABIAL SUPERIOR LABIAL ANT. SUP. ALV. N. ANT. SUP. ALV. N. (ASAN) (ASAN) INFRAORBITAL N. MIDDLE SUP. ALV. N. MIDDLE SUP. ALV. N. POST-SUP ALVEOLAR N. (PSAN) (MSAN) (MSAN) Z. TEMPORAL N.
SUPERIOR DENTAL PLEXUS
THE SPHENOPALATINE GANGLION
The sphenopalatine ganglion is part of the parasympathetic nervous system. This gangliion gives off several branches, containing visceral motor as well as sensory fibers, to the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose and pharynx. Its branches are: 1. Orbital branch 2. Posterior lateral nasal 3. Palatine nerves a. Nasopalatine nerve exits thru the nasopalatine or incisive foramen. Innervates the palatal mucosa of the anterior maxillary teeth b. Greater/ Anterior palatine nerve exits thru the greater/anterior palatine foramen. Innervates the palatal mucosa of the posterior maxillary teeth. c. Middle palatine nerve exits thru the lesser/posterior palatine foramen together with the lesser palatine nerve. Innervates the soft palate. d. Lesser/Posterior palatine nerve exits thru the lesser palatine
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
BRANCHES FROM THE SPHENOPALATINE GANGLION
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
ORBITAL NERVE
POSTERIOR LATERAL NASAL
SPHENOPALATINE GANGLION
NASOPALATINE N.
GREATER PALATINE OR ANTERIOR PALATINE N.
MIDDLE PALATINE N.
LESSER PALATINE OR POST. PALATINE N.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
THE MANDIBULAR NERVE
The mandibular nerve exits the skull thru the foramen ovale. For a short distance, the nerve is undivided where it gives of several branches to muscles of the inner ear, soft palate, mastication and dura. It then divides into an anterior trunk and a larger posterior trunk. The posterior trunk, after giving branches to the temporal area, mylohyoid muscle and the tongue enters the mandibular canal thru the mandibular foramen where it becomes known as the inferior alveolar nerve. Inside the canal, it gives off dental branches to innervate the roots of the mandibular teeth. At the area of the mandibular premolars, a small branch exits thru the mental foramen to innervate the lower lip and chin. Inside the canal, the inferior alveolar nerve continues as the incisive nerve to innervate the mandibular anterior teeth. The smaller anterior trunk gives off branches to the buccal mucosa of the mandibular posterior teeth and most of the muscles of mastication.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
THE BRANCHES OF THE MANDIBULAR NERVE
I. Undivided Nerve 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. 1. Nerve to the dura sensory Internal Pterygoid muscle - motor Tensor veli palatini - motor Tensor tympani - motor Nerve to the mastoid cells sensory Anterior Trunk a. b. c. d. Buccinator (long buccal) sensory External pterygoid ms. - motor Temporalis ms. - motor Masseteric nerve - motor
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Divided Nerve
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
2. Posterior trunk a. Auriculotemporal b. Lingual c. Mylohyoid nerve d. Inferior alveolar nerve ---- incisive nerve e. Mental nerve
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
DURA (N. TENTORII)
MASTOID CELLS
INT. PTERYGOID MUSCLE TENSOR VELI PALATINI ANT. TRUNK
UNDIVIDED N. TENSOR TYMPANI
POST. TRUNK
DIVIDED N.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
N. TO EXT. PTERYGOID MS.
N. TO TEMPORALIS
N. TO MASSETER
LONG BUCCAL N.
LINGUAL N.
MANDIBULAR FORAMEN
MD A IB NU LRA ACN A L
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
LINGUAL N.
MANDIBULAR FORAMEN
MD A IB NU LRA ACN A L
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
INFERIOR ALV. N. MYLOHYOID N. MENTAL FORAMEN
LINGUAL N.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
MENTAL N.
MENTAL FORAMEN
INCISIVE N.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
INNERVATION OF THE TONGUE
SENSORY ANTERIOR 2/3 Lingual Nerve branch of the Trigeminal Nerve MOTOR Hypoglossal Nerve (XII) innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
POSTERIOR 1/3
Glossopharyngeal Hypoglossal Nerve Nerve (IX) (XII)
Taste
Chorda Tympani branch from the Facial Nerve (VII)
THE CHORDA TYMPANI
Mandibular nerve
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Lingual n.
Chorda tympani, special branch from the Facial Nerve (CNVII) for the sensation of taste.
Inferior alveolar n.
Mylohyoid n.
Property of Dr. Michelle C. Sunico, UP College of Dentistry. Please do not copy without permission from the author.
Monheims Textbook of Dental Anesthesia http://medinfo.ufl.edu
Pictures are from:
You might also like
- Cranial Nerves 7-12Document62 pagesCranial Nerves 7-12jangyNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument82 pagesOral Cavitydavid100% (1)
- Facial Nerve and Its Applied AnatomyDocument37 pagesFacial Nerve and Its Applied Anatomyherojittlc100% (1)
- Trigeminal NerveDocument126 pagesTrigeminal NerveAsha Praveena100% (4)
- Assessing The Ear and HearingDocument32 pagesAssessing The Ear and HearingArlyn Mendenilla0% (1)
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument79 pagesMuscles of Facial ExpressionDr. Ektha PaiNo ratings yet
- Nerve Supply of TeethDocument45 pagesNerve Supply of TeethJayakumar Patil0% (3)
- Cosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBDocument11 pagesCosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBcirugia plastica uisNo ratings yet
- ENT Notes PDFDocument66 pagesENT Notes PDFBob Jenson100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Advanced Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument830 pagesA Textbook of Advanced Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryTabarak AdilNo ratings yet
- Fracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Document67 pagesFracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Arafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Trigeminal Nerve & Applied Anatomy: DR - Neha Mds 1 YearDocument37 pagesSeminar ON Trigeminal Nerve & Applied Anatomy: DR - Neha Mds 1 YearMAYANK MITTALNo ratings yet
- Basic Sinus AnatomyDocument71 pagesBasic Sinus AnatomyTalal AlanzyNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveDocument25 pagesFacial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveRafiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument68 pagesFacial NerveMédecin Adrian TGNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ReadingDocument32 pagesJurnal ReadingEva Ratnasari DinNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiAlexAlxNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiAlexAlxNo ratings yet
- OrlDocument186 pagesOrlMuli MaroshiNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument23 pagesFacial NerveAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- VTH CNDocument59 pagesVTH CNdoktergigikoeNo ratings yet
- 2d Facial Nerve-Dr GosaiDocument6 pages2d Facial Nerve-Dr GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Paranasal Sinuses by DR SharakyDocument21 pagesParanasal Sinuses by DR SharakyMobile AsdNo ratings yet
- Functions of Lateral V/s Medial Pterygoid Muscles: Branches of Facial NerveDocument4 pagesFunctions of Lateral V/s Medial Pterygoid Muscles: Branches of Facial NerveMubashir SheriffNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgeryDocument92 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgerySAMEENANo ratings yet
- Costen 1997Document15 pagesCosten 1997Lynda M. NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument63 pagesMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- Lect11-Facial Nerve (CNVII)Document17 pagesLect11-Facial Nerve (CNVII)Nayela AkramNo ratings yet
- 1 - Pratt Lung Surface Anatomy: Anterior MaleDocument19 pages1 - Pratt Lung Surface Anatomy: Anterior MaleNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Chronic TympanomastoiditisDocument25 pagesChronic Tympanomastoiditispatriciaberedo100% (1)
- Trigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsDocument77 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsHarees ShabirNo ratings yet
- Adhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanDocument51 pagesAdhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanErwin DiprajaNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument65 pagesFacial NerveprashanthsumsaiarjunNo ratings yet
- 7 Infratemporal FossaDocument7 pages7 Infratemporal FossaAaaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Essay - Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesNeuroscience Essay - Cranial NervesAkshaya RajangamNo ratings yet
- By DR Manah Chandra Changmai MBBS MSDocument31 pagesBy DR Manah Chandra Changmai MBBS MSKalaivaany RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Trigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordDocument18 pagesTrigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordBharathi GudapatiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of External EarDocument49 pagesAnatomy of External EarInderdeep AroraNo ratings yet
- Nervio MaxilarrDocument85 pagesNervio MaxilarrGermanLoopezzNo ratings yet
- Os 3Document11 pagesOs 3مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- NDBE Oral Surgery Cram NotesDocument14 pagesNDBE Oral Surgery Cram Notesayesha.medicozNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The NoseDocument19 pagesAnatomy of The NoseYuka Puspita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Paranasal SinusesDocument9 pagesParanasal SinusesSaima AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Facial NerveDocument6 pagesThe Facial NerveRahul Raj SNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs - EarsDocument37 pagesSensory Organs - Earsapi-324160601No ratings yet
- Paranasal Sinus Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyDocument12 pagesParanasal Sinus Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyKienlevy100% (1)
- BellDocument79 pagesBellvijay1234568883No ratings yet
- Applied Surgical AnatomyDocument52 pagesApplied Surgical AnatomyEmad AdelNo ratings yet
- 15-Sensory OrgansDocument23 pages15-Sensory OrgansMilad HabibiNo ratings yet
- Scalp With All DetailsDocument30 pagesScalp With All DetailsGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology of The EarDocument35 pagesAnatomy and Embryology of The EarVictor EnachiNo ratings yet
- Otic Disease and Ear Disorder MAINDocument27 pagesOtic Disease and Ear Disorder MAINJames AchuNo ratings yet
- EAR-4 Year PresentationDocument133 pagesEAR-4 Year Presentationeiuj497No ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy - Trigeminal NerveDocument8 pagesApplied Anatomy - Trigeminal NervefrabziNo ratings yet
- Mouth, 10 Nov 2006Document2 pagesMouth, 10 Nov 2006api-19921479No ratings yet
- Daphne Ganancial Janine Villas John Rev Lorenzo DDM Iii-BDocument57 pagesDaphne Ganancial Janine Villas John Rev Lorenzo DDM Iii-BDaphne GanancialNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Head and NeckDocument49 pagesMuscles of The Head and NeckMarili Camille CoquiaNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media AkutDocument24 pagesOtitis Media AkutBethari K AbiantiNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument26 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveMelanie GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Dog Skull ForaminaDocument1 pageDog Skull ForaminaVicio P. UntalNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia Head Neck Slides 060524Document84 pagesRegional Anesthesia Head Neck Slides 060524srisaivimalaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve V2 - Maxillary Nerve - FRCEM SuccessDocument1 pageCranial Nerve V2 - Maxillary Nerve - FRCEM SuccessJohn CoxNo ratings yet
- The Pterygopalatine FossaDocument6 pagesThe Pterygopalatine FossaxxyumeNo ratings yet
- Lec8 Sem2 Hnsweek3 20110822Document9 pagesLec8 Sem2 Hnsweek3 20110822Sazter AthiraNo ratings yet
- Pterygopalatine FossaDocument43 pagesPterygopalatine FossaAyaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve VDocument4 pagesTrigeminal Nerve Vm1m2mNo ratings yet
- Maxillary NerveDocument17 pagesMaxillary NerveSharan SamyNo ratings yet
- Pterygopalatine FossaDocument20 pagesPterygopalatine FossaGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthesia IV. Special Methods of Local Anaesthesia. Ganglion Blockade Intraligamental Anaesthesia. The Anaesthesia of Inflamed TissuesDocument26 pagesLocal Anaesthesia IV. Special Methods of Local Anaesthesia. Ganglion Blockade Intraligamental Anaesthesia. The Anaesthesia of Inflamed TissuesGeorge MKNo ratings yet