Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WS Internacional SP2040: Apresentação Negócios
Uploaded by
sp2040Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WS Internacional SP2040: Apresentação Negócios
Uploaded by
sp2040Copyright:
Available Formats
Economic and Business Oportunities
2500000
2000000
Servios a Firmas e Pessoas Manufatura
1500000
Agricultura e extrativismo Transporte e Comunicaes
1000000
Sade
Instituies Financeiras Ensino
500000
Construo Civil Varejo
0 85 - 00 -500000 00 - 10
Atacado Hoteis e Restaurantes Adm. Pblica
-1000000
Indstria Comrcio de Eletrnicos Comrcio de Maquinas e Equipamentos Indstria intensiva em conhecimento Comrcio de Artigos de Uso Pessoal Mdia e comunicao Servios a Firmas Finanas Turismo e viagens Servios Profissionais P&D Restaurantes Educao Logstica Sade Comrcio de Alimentos Resduos Hospedagem
Estabelecimentos Trabalhadores 26,44% 36,13% 19,15% 27,47% 16,97% 15,12% 16,30% 21,64% 15,11% 22,44% 14,67% 18,31% 13,73% 24,17% 13,54% 22,64% 12,69% 18,93% 11,63% 5,53% 10,55% 13,99% 9,83% 9,98% 9,11% 12,52% 8,70% 14,90% 7,25% 8,15% 5,28% 8,92% 3,95% 6,24%
Ranking
Distrito 1 ITAIM BIBI 2 JD PAULISTA
3 VILA MARIANA
4 PINHEIROS 5 SANTO AMARO 6 MOEMA 7 SAUDE 8 REPUBLICA 9 TATUAPE 10 SANTANA
Broadening of infrastructure bottlenecks: mobility and large commuting distances Environmental resources degradation and urban degradation Scarcity of qualified technical workers (engineers, for instance) Bad educational quality: bottleneck regarding qualified workers.
In 2040, the economy of So Paulo will be characterized by a knowledge-intensive and diversified low-carbon productive structure, with plenty of opportunities for companies and workers, providing better life conditions for its inhabitants.
1) PROMOTION OF A BUSINESS-FAVORABLE ENVIRONMENT IN THE CITY Decrease of the bureaucracy required to set up, maintain and close down companies; Simplification of approval and licensing processes; Investment in the improvement of efficiency in all public services; Creation of entrepreneurship centers 2) STRENGTHENING OF THE CORPORATE PRESENCE IN THE CITY Promotion of a specific infrastructure; Development of innovative districts, with technology, financial and media areas; Appropriate management of the centralities and their respective implementations in the city and the transport system 3) ENCOURAGEMENT OF AN INTEGRATED ECONOMIC GROWTH IMPLEMENTED IN PERIPHERAL AREAS OF THE CITY Development of partnerships with community organizations; Formalization of small entrepreneurs and the labor market; Development of peripheral centralities, with special attention to the East Zone
4) ENCOURAGEMENT OF AND SUPPORT FOR ACTIVITIES INTENSIVE IN KNOWLEDGE, CREATIVITY, TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION: Creation of a fund for financing innovation-based companies Support for technology-based incubators Investments in infrastructure, like high speed (digital neighborhoods) Integration of the economy with urban development projects Government procurement policy rewarding high-tech firm estabilished in SP. 5) LABOR QUALIFICATION Encouragement for the offering of higher education positions in exact and applied sciences at the higher education institutions in the city of So Paulo; Attraction of major international universities to So Paulo Monitoring and evaluation of professional courses Labor requalification program for older people or those out of the labor market for a long period or unemployed 6) ATTRACTION OF QUALIFIED LABOR AND YOUNG TALENTS Intense investments for the strengthening and broadening of the amenities in So Paulo, Promotion of policies that include the interchange between students, researchers, professors and scientists in the city, and other regions in the country and the world.
How to differentiate the city from other cities? There is an idea that, by solving our structural problems mobility, safety, pollution the business environment will naturally be better and we will attract more businesses. Is that correct?
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Epigrammatum Anthologia Palatina 1 PDFDocument615 pagesEpigrammatum Anthologia Palatina 1 PDFdrfitti1978No ratings yet
- 9.1.13.5 Dry Type Transformer User ManualDocument6 pages9.1.13.5 Dry Type Transformer User ManualDindie GarvidaNo ratings yet
- 14 - Iso 17640 2018Document40 pages14 - Iso 17640 2018Md. Main UddinNo ratings yet
- BPS Impounded Vehicles List For Official Gazette November 2022Document3 pagesBPS Impounded Vehicles List For Official Gazette November 2022Anonymous UpWci5No ratings yet
- Course Title: OWASP Top 10 Threats and Mitigation Exam Questions - Single SelectDocument12 pagesCourse Title: OWASP Top 10 Threats and Mitigation Exam Questions - Single SelectBriar WoodNo ratings yet
- Cellular Gateway Release Notes Xe 17 11 XDocument6 pagesCellular Gateway Release Notes Xe 17 11 XceterelNo ratings yet
- P342 343 Generators ProtectionsDocument16 pagesP342 343 Generators ProtectionshieudaininhNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 2 SepmDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 2 SepmAKASH V (RA2111003040108)No ratings yet
- GE Digital Internship Cum PPO Recruitment Drive PPT On 8th June'23 For 2024 Graduating BatchDocument14 pagesGE Digital Internship Cum PPO Recruitment Drive PPT On 8th June'23 For 2024 Graduating BatchrandirajaNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Railway e Ticket PDFDocument1 pageBangladesh Railway e Ticket PDFShanto Mohammad Salah UddinNo ratings yet
- GRE140Document24 pagesGRE140Zainul ArifinNo ratings yet
- Scada Compone NTS: Prepared By:-Animesh Ghosh Roll No - 4 M.Tech (EE)Document28 pagesScada Compone NTS: Prepared By:-Animesh Ghosh Roll No - 4 M.Tech (EE)Animesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Tmu 220 EpsonDocument154 pagesTmu 220 EpsonHugo BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Ga Z77X D3H R101 PDFDocument41 pagesGa Z77X D3H R101 PDFTANo ratings yet
- Experiment 1:determination of Valve Timing of An Internal Combustion Engine Observation TableDocument18 pagesExperiment 1:determination of Valve Timing of An Internal Combustion Engine Observation Tableمحمد راشد بن زينNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Engineering Graphics Essentials 5th Edition by Kirstie PlantenbergDocument61 pagesEbook PDF Engineering Graphics Essentials 5th Edition by Kirstie Plantenbergdeborah.sheehan548100% (42)
- DineshDocument25 pagesDineshajeyan879No ratings yet
- Construction Experience ResumeDocument6 pagesConstruction Experience Resumef5dthdcd100% (2)
- 2020-03-04-Manuale-Tecnico-Louça Krupps - Uniko - Wi-Fi-rev03 - ENGDocument40 pages2020-03-04-Manuale-Tecnico-Louça Krupps - Uniko - Wi-Fi-rev03 - ENGLuis RolaNo ratings yet
- Client ListDocument6 pagesClient ListJayaseelan BaluNo ratings yet
- Using Plant 3D in A State Plane Coordinate Project EnvironmentDocument12 pagesUsing Plant 3D in A State Plane Coordinate Project EnvironmentRoobens SC LaraNo ratings yet
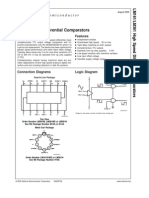
- LM361Document8 pagesLM361api-3825669No ratings yet
- AOLT-4000 OAM Manual PDFDocument546 pagesAOLT-4000 OAM Manual PDFBrenden CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- 0-By CPU - MT6571 - EMMC - 04-24-2023-18-37-04Document2 pages0-By CPU - MT6571 - EMMC - 04-24-2023-18-37-04abubakar qassimNo ratings yet
- Linux Administration: Unit 1Document59 pagesLinux Administration: Unit 1DerenNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Memory Interfacing - ComputerSCDocument7 pagesBasic Concepts of Memory Interfacing - ComputerSCParamartha BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Export Content To WordDocument2 pagesExport Content To Wordjulio50% (2)
- MEC469 Nontraditional and Computer Aided Manufacturing Laboratory 14443::guravtar Singh 0.0 0.0 2.0 1.0 Practical CourseDocument3 pagesMEC469 Nontraditional and Computer Aided Manufacturing Laboratory 14443::guravtar Singh 0.0 0.0 2.0 1.0 Practical CourseManoj MallickNo ratings yet
- Soccer AllDocument111 pagesSoccer AllKoall Tchang LindienNo ratings yet
- BYTE Job Description - Class of 2024 - SRM - 8th - 9th September'23Document2 pagesBYTE Job Description - Class of 2024 - SRM - 8th - 9th September'23SHIVANSH SRIVASTAVA (RA2011053010013)No ratings yet