Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Disk Scheduling
Uploaded by
api-37032050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views18 pagesSecondary-storage DISK-SCHEDULING ALGOS Lecture Series By Er. Kanwalvir Singh Dhindsa. SSTF is common and has a natural appeal SCAN and C-SCAN perform better for systems that place a heavy load on the disk. Magnetic disks provide bulk of secondary storage of modern computers - transfer rate is rate at which data flow between drive and computer - Positioning time (random-access time) is time to move disk arm to desired
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSecondary-storage DISK-SCHEDULING ALGOS Lecture Series By Er. Kanwalvir Singh Dhindsa. SSTF is common and has a natural appeal SCAN and C-SCAN perform better for systems that place a heavy load on the disk. Magnetic disks provide bulk of secondary storage of modern computers - transfer rate is rate at which data flow between drive and computer - Positioning time (random-access time) is time to move disk arm to desired
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views18 pagesDisk Scheduling
Uploaded by
api-3703205Secondary-storage DISK-SCHEDULING ALGOS Lecture Series By Er. Kanwalvir Singh Dhindsa. SSTF is common and has a natural appeal SCAN and C-SCAN perform better for systems that place a heavy load on the disk. Magnetic disks provide bulk of secondary storage of modern computers - transfer rate is rate at which data flow between drive and computer - Positioning time (random-access time) is time to move disk arm to desired
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Secondary-Storage
DISK-SCHEDULING ALGOS
Lecture Series By : Er. Kanwalvir Singh Dhindsa
Website :: www.dhindsa.info
http://groups.google.com/group/os-2007
E-Mail :: sys.operating @ gmail.com
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Selecting a Disk-Scheduling Algorithm
• SSTF is common and has a natural appeal
• SCAN and C-SCAN perform better for systems that
place a heavy load on the disk
• Performance depends on the number and types of
request
• Requests for disk service can be influenced by the file-
allocation method
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Secondary-Storage Structures
• Magnetic disks provide bulk of secondary storage
of modern computers
– Transfer rate is rate at which data flow between
drive and computer
– Positioning time (random-access time) is time
to move disk arm to desired cylinder (seek time)
and time for desired sector to rotate under the disk
head (rotational latency)
– Head crash results from disk head making
contact with the disk surface
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Moving-head Disk Mechanism
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Secondary-Storage Structures
• Magnetic tape
– Was early secondary-storage medium
– Access time slow
– Random access ~ many times slower than disk
– Mainly used for backup, storage of infrequently-used
data, transfer medium between systems
– Kept in spool and wound or rewound past read-write
head
– Once data under head, transfer rates comparable to disk
– From MB’s to lots of GB’s of storage
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Disk Scheduling
OS is responsible for using hardware efficiently — for
the disk drives, this means having a fast access time
and disk bandwidth
Access time has two major components
– Seek time is the time for the disk to move the
heads to the cylinder containing the desired sector
– Rotational latency is the additional time waiting
for the disk to rotate the desired sector to the disk
head
Disk bandwidth is the total number of bytes
transferred, divided by the total time between the
first request for service and the completion of the
last transfer
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Disk Scheduling
• Several algorithms exist to schedule the
servicing of disk I/O requests
• Illustrate these with a request queue (0-199)
98, 183, 37, 122, 14, 124, 65, 67
Head pointer 53
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
FCFS SCHEDULING
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
SSTF SCHEDULING
Selects the request with the minimum
seek time from the current head position
SSTF scheduling is a form of SJF
scheduling; may cause starvation of
some requests
Not an optimal scheduling algorithm
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
SSTF (Cont.)
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
SCAN SCHEDULING
Disk arm starts at one end of the disk,
and moves toward the other end,
servicing requests until it gets to the
other end of the disk, where the head
movement is reversed and servicing
continues
Also called as Elevator algorithm
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
SCAN (Cont.)
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
C-SCAN SCHEDULING
Provides a more uniform wait time than SCAN
The head moves from one end of the disk to the
other, servicing requests as it goes. When it
reaches the other end, however, it immediately
returns to the beginning of the disk, without
servicing any requests on the return trip
Treats the cylinders as a circular list that wraps
around from the last cylinder to the first one
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
C-SCAN (Cont.)
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
C-LOOK SCHEDULING
Version of C-SCAN
Arm only goes as far as the last request
in each direction, then reverses direction
immediately,
without first going all the way to the
end of the disk
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
C-LOOK (Cont.)
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Characteristics of I/O Devices
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
Secondary-Storage
DISK-SCHEDULING ALGOS
Lecture Series By : Er. Kanwalvir Singh Dhindsa
Website :: www.dhindsa.info
http://groups.google.com/group/os-2007
E-Mail :: sys.operating @ gmail.com
O.S. by Er. K.S.Dhindsa © 2007
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Graphics 1Document8 pagesGraphics 1dajit1No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentapi-3703205100% (1)
- CpiDocument4 pagesCpiapi-3703205No ratings yet
- CNDocument5 pagesCNapi-3703205No ratings yet
- DaaDocument9 pagesDaaapi-3703205100% (2)
- B TECH SyllabusDocument80 pagesB TECH Syllabusapi-3703205100% (5)
- Sandy 1Document16 pagesSandy 1api-3703205No ratings yet
- Networking 2Document5 pagesNetworking 2api-3703205No ratings yet
- Test Takers Are Required To Take of The Following TestsDocument2 pagesTest Takers Are Required To Take of The Following Testsapi-3703205No ratings yet
- Write The Case Study of Open GLDocument6 pagesWrite The Case Study of Open GLapi-3703205No ratings yet
- SadDocument4 pagesSadapi-3703205100% (1)
- Flow ControlDocument36 pagesFlow Controlapi-3703205No ratings yet
- Technical Question and Answers in C, C++, DS, Oracle, UnixDocument176 pagesTechnical Question and Answers in C, C++, DS, Oracle, Unixapi-19750719No ratings yet
- Sandy 3Document14 pagesSandy 3api-3703205No ratings yet
- TrnsmsnmediaDocument19 pagesTrnsmsnmediaapi-3703205No ratings yet
- CH 13Document28 pagesCH 13api-3703205No ratings yet
- Sandp 2Document13 pagesSandp 2api-3703205No ratings yet
- NetworkDocument68 pagesNetworkapi-3703205No ratings yet
- IEEE11Document52 pagesIEEE11api-3703205No ratings yet
- CH 10Document48 pagesCH 10api-3703205No ratings yet
- TransportDocument50 pagesTransportapi-3703205No ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument22 pagesSwitchingapi-3703205No ratings yet
- ProtocolDocument34 pagesProtocolapi-3703205No ratings yet
- CH 12Document16 pagesCH 12api-3703205No ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument51 pagesOsi Modelapi-3703205No ratings yet
- DatalinkcntrlDocument9 pagesDatalinkcntrlapi-3703205No ratings yet
- ErrorDocument10 pagesErrorapi-3703205No ratings yet
- Protection 2007Document12 pagesProtection 2007api-3703205No ratings yet
- Virtual Memory1 March2007Document28 pagesVirtual Memory1 March2007api-3703205No ratings yet
- Security 2007Document18 pagesSecurity 2007api-3703205No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CalculusDocument101 pagesCalculuskusnoNo ratings yet
- Police Cranston School Committee Member Stole PTO FundsDocument1 pagePolice Cranston School Committee Member Stole PTO FundsashaydelineNo ratings yet
- Architech 06-2016 Room AssignmentDocument4 pagesArchitech 06-2016 Room AssignmentPRC Baguio100% (1)
- Tema & Htri by Bert BoxmaDocument5 pagesTema & Htri by Bert Boxmabloodterry2284No ratings yet
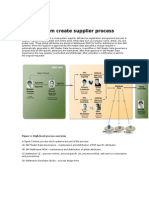
- Cross System Create Supplier ProcessDocument14 pagesCross System Create Supplier ProcesssakthiroboticNo ratings yet
- Impeller Velocity TrianglesDocument2 pagesImpeller Velocity TrianglesLorettaMayNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Ashok LeylandDocument120 pagesFinancial Analysis of Ashok LeylandSiva Kumaravel0% (1)
- Perfect Picture SummaryDocument3 pagesPerfect Picture SummaryReiaNo ratings yet
- College Invitation Letter - Managedia 2023Document2 pagesCollege Invitation Letter - Managedia 2023Sandeep DeyNo ratings yet
- Unseen Passage 2Document6 pagesUnseen Passage 2Vinay OjhaNo ratings yet
- RSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Document9 pagesRSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Kirsten WangNo ratings yet
- Imcp - RocketbookDocument11 pagesImcp - Rocketbookapi-690398026No ratings yet
- Final Lab Manual Main Ars 200280705008Document6 pagesFinal Lab Manual Main Ars 200280705008shalini pathakNo ratings yet
- Pe8 Mod5Document16 pagesPe8 Mod5Cryzel MuniNo ratings yet
- One God One People February 2013Document297 pagesOne God One People February 2013Stig DragholmNo ratings yet
- Memo ALS Literacy MappingDocument4 pagesMemo ALS Literacy MappingJEPH BACULINANo ratings yet
- General Arrangement, Isometric Views and B.O.M. A Midget Steam Car Using A Double Acting Oscillating EngineDocument3 pagesGeneral Arrangement, Isometric Views and B.O.M. A Midget Steam Car Using A Double Acting Oscillating EngineRobson Carlos0% (1)
- SS EN 1991-1-1-2008 (2017) - PreviewDocument16 pagesSS EN 1991-1-1-2008 (2017) - PreviewNg SHun JieNo ratings yet
- Digital ThermometerDocument12 pagesDigital Thermometershahpatel19No ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument44 pagesDocumentation19-512 Ratnala AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Esp8285 Datasheet enDocument29 pagesEsp8285 Datasheet enJohn GreenNo ratings yet
- 3S Why SandhyavandanDocument49 pages3S Why SandhyavandanvivektonapiNo ratings yet
- Daewoo SJ-210H DSJ-6000LHMDocument44 pagesDaewoo SJ-210H DSJ-6000LHMMarco Antonio100% (5)
- ENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Document3 pagesENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Analiza Dequinto BalagosaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentDocument8 pagesEpidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentRakib HossainNo ratings yet
- Advanced Packaging Polymers: Product Selection GuideDocument12 pagesAdvanced Packaging Polymers: Product Selection GuideDKNo ratings yet
- A Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument65 pagesA Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofMadhavpokale100% (1)
- Project Proposal DraftDocument1 pageProject Proposal DraftCarl Axel M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- Asme Bladder Accumulator DatasheetDocument3 pagesAsme Bladder Accumulator DatasheetSamad A BakarNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document22 pagesPresentation 1AILYN PECASALESNo ratings yet