Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Review Renal System
Uploaded by
Carolyne CharvozOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Review Renal System
Uploaded by
Carolyne CharvozCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Review
Renal System
1-2
Classification of Hormones
Peptide or protein hormones (large, water soluble) chains of amino acids most hormones are peptide hormones; e.g., insulin (pancreas)
Steroid hormones (lipid soluble) derived from cholesterol e.g., adrenocorticosteroids (adrenal cortex), estrogen (ovaries), testosterone (testes) Biogenic amines (small, water soluble) derived from the amino acid tyrosine e.g., thyroxins (thyroid), epinephrine (adrenal medulla)
1-3
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
TSH -> thyroid
-> indicates tropic effect on hormonesecreting organs
GH -> liver; secretes somatomedin
increases growth & mitosis in most cells PRL -> testes secretes testosterone FSH & LH-> gonads; secrete sex hormones
increases lactation ACTH -> adrenal cortex; secretes corticosteroids
gamete maturation
increases melanin production
1-4
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
growth hormone prolactin acidophils
mnemonics for hormones: GH PRL A
b FSH LH ACTH TSH
basophils follicle stimulating hormone luteinizing hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone thyroid-stimulating hormone
1-5
Control of Posterior Pituitary Gland Secretions
The hypothalamus regulates the release of two hormones it secretes and stores in neurosecretory cells which project into the posterior pituitary (pars nervosa)
Oxytocin (OT) - regulated by positive feedback! stimulates uterine contractions & let down of milk prostate gland secretion in males Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys arteriole constriction
hypothalamohypophyseal tract
1-6
Adrenal Glands (suprarenal)
Paired, pyramid-shaped endocrine glands anchored on the superior surface of each kidney & therefore retroperitoneal
Yellow due to stored fat
Outer cortex
Inner medulla
1-7
Adrenal Cortex Hormones (Corticosteroids)
synthesis stimulated by ACTH produced by anterior pituitary >25 steroid hormones vital to survival regulate salt, sugar, & sex!
1-8
SALT mineralocorticoids: aldosterone increases salt & water retention from kidney; BP
SUGAR glucocorticoids: cortisol gluconeogenesis; anti-inflammatory; response to longterm stress
SEX regulates androgens
neural tissue; epinephrine
1-9
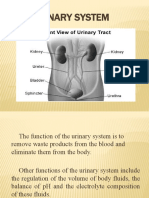
Pancreas
Digestion
Spongy, nodular organ between duodenum & spleen; posterior to stomach Exocrine:
pancreatic acini produce alkaline pancreatic juice that aids in digestion
Endocrine:
pancreatic islets (Islets of Langerhans) consists of four types of cells each producing a different hormone
1-10
Digestion
Pancreatic Hormones
Produced by the following cell types in the Islets of Langerhans (pancreatic islets)
Alpha cells - in response to blood glucose secrete glucagon blood glucose Beta cells in response to blood glucose secrete insulin blood glucose Delta cells in response to blood nutrient secrete somatostatin intestinal absorption F cells - stimulated by protein digestion
1-11
Disorder of Beta cells of Pancreas: Diabetes Mellitus
Digestion
Results in inadequate uptake of glucose from blood so glucose spills over into urine; (sweet urine)
Chronic high blood glucose damages small blood vessels retinal blindness, kidney failure, leg amputations, heart disease, stroke Type 1 diabetes Insulin-dependent DM Autoimmune disease Beta cells are destroyed Type 2 diabetes Insulin-independent DM Decreased insulin uptake by body cells
1-12
Ribs
12 pairs (both sexes)
true ribs (17)
1) connect individually to the sternum by separate cartilaginous extensions called costal cartilages costal cartilages do not attach directly to the sternum 810 fuse to the costal cartilage of rib 7 and thus are indirectly attached with the sternum 11 and 12 are floating ribs because they have no connection with the sternum
false ribs (812)
1) 2) 3)
1-13
Dense Connective Tissue: Dense Irregular
collagen bundles lie in different directions. Found in the dermis of the skin and fibrous capsules where pull is in different directions.
1-14
Loose Connective Tissue: Adipose
found with areolar under skin energy reserves insulating and protecting Signet ring appearance. Tightly packed adipocytes. Highly vascular.
1-15
Major Arteries of the Thorax & Abdomen
Subclavian arteries internal thoracic arteries intercostal a. thorax & abdominal walls
Abdominal aorta unpaired arteries to the unpaired organs of the gastrointestinal tract:
1. Celiac trunk
2. Superior mesenteric 3. Inferior mesenteric Abdominal aorta paired arteries to paired organs:
1. Renal kidneys
2. Gonadal gonads (ovaries or testes) Aorta bifurcates -> common iliac arteries -> internal iliac artery -> pelvis and perineum
1-16
Major Veins of the Thorax & Abdomen
Azygos system (unpaired)
drains thorax, pericardium, bronchi may also drain structures that normally drain into inf. vena cava or hepatic portal
merges into the superior vena cava
Following drain into the inferior vena cava: Hepatic veins drain liver Renal veins drain kidneys Internal iliac veins drain pelvis & perineum join common iliac veins merge w/ inferior vena cava
1-17
Tunics (Layers)
Correspond to heart wall layers 1. Tunica Intima (Interna) smooth endothelium; reduces friction 2. Tunica Media circularly arranged smooth muscle; under sympathetic innervation vasoconstriction thicker in arteries 3. Tunica Externa (Adventitia)- areolar CT w/ elastic & collagen fibers maintains integrity of vessel; anchors vessel to other tissues
Vaso vasorum small vessels w/in tunica externa; deliver blood to large vessels
thicker in veins
1-18
Centrifuge Separates Components of Whole Blood
Hematocrit or PCV = ratio of RBCs to total volume
straw-colored liquid
~42% in women
1-19
Functions of Blood
Transportation Erythrocytes carry oxygen and carbon dioxide Plasma carries nutrients, hormones, waste products (to kidneys) Regulation Body Temperature Plasma absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body To cool - blood vessels in dermis dilate and dissipate heat at surface To conserve heat - dermal blood vessels constrict, warm blood is shunted to deeper blood vessels in the body pH Levels (a measure of alkalinity or acidity; neutral is 7) Plasma pH is kept at ~7.4 for normal cellular functioning Fluid Levels Constant exchange between blood plasma & interstitial fluid in tissues Balance maintained by electrolyte & protein levels in blood Too much fluid absorbed in the blood - high blood pressure Too much fluid leaves blood for tissues - low blood pressure & edema
1-20
Simple Epithelium: Simple Cuboidal
One layer of cubeshaped cells Nucleus: usually round For secretion or absorption of fluids Examples: line kidney tubules, cover ovaries, line ducts of glands
1-21
Transitional
Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and surface cells are squamous or domeshaped Cells can slide over each other to allow distention from urine Examples: lines ureters, bladder and part of urethra
1-22
Body Membranes (coverings)
Epithelial membranes have epithelium on top of connective tissue
1) 2) Mucous membranes (mucosa) line passage ways and cavities open to the outside - digestive, respiratory, urinary, & reproductive tracts
Mucus secreted on surface prevents dessication
Serous membranes (serosa) line cavities not open to the outside pleura, pericardium, peritoneum
Secrete watery serous fluid (transudate) Always found as double membranes visceral and parietal
3)
Cutaneous membrane is skin (external membrane)
Connective tissue membranes are CT only
4) Synovial membranes line joints
1-23
Skeletal Muscle
Long, striated, multinucleated at periphery Voluntary movements, expressions Neural stimulation required Attached to skeleton usually
1-24
Smooth Muscle
No striations, tapered, single nucleus Often in sheets Involuntary May be autorhythmic Found in walls of hollow organs
1-25
Parasympathetic division:
Preganglionic axons: long
minimal divergence Postganglionic axons: short Ganglionic neurons near target:
myelinated
unmyelinated
terminal ganglia or
intramural ganglia in organ Sympathetic division:
Preganglionic axons: short
extensive divergence exit spinal cord with anterior roots of T1L2 spinal nerves Postganglionic axons: long Ganglionic neurons in: paravertebral ganglia, or prevertebral ganglia (collateral axons)
myelinated unmyelinated
1-26 PARASYMPATHETIC:
PARASYMPATHETIC
SYMPATHETIC
Conserves energy & replenishes nutrient stores
Most active when body is at rest or digesting a meal Origin: brainstem nuclei for CNs III, VII, IX, & X & S2-S4 of spinal cord
SYMPATHETIC:
Uses energy for mass activation in emergency
Increases metabolic activity Brain patterns change Skins electrical resistance changes (lie detector test) Increased alertness Origin: lateral horns of T1-L2
1-27
Parasympathetic Division
Spinal nerves S2-S4 give rise to pelvic splanchic nerves:
Distal end of large intestine & rectum 1. increased smooth muscle motility & secretory activity 2. defecation Bladder wall and distal ureter 1. contraction of smooth muscle
2. urination
Female clitoris and male penis 1. increased vasodilation 2. blood flow up -> erection
1-28
PARASYMPATHETIC
SYMPATHETIC
Neurotransmitters
Preganglionic axons: all release Ach; effect is always excitatory, short-lived & local
Post-ganglionic axons: Parasympathetic division all release Ach; can be inhibitory
Sympathetic division post-ganglionic axons which release Ach are always excitatory most sympathetic post-ganglionic axons release norepinephrine (NE); effect is long-lasting, widespread; can be inhibitory
1-29
Passive Transport Processes
Movement of substances along (down) a concentration or pressure gradient ATP is NOT required
Simple Diffusion (gas exchange in alveoli of lungs) Osmosis (diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane; IV solutions are isotonic (0.9% NaCl) to avoid hemolysis) Facilitated Diffusion Requires the participation of specific transport proteins to move particles from a region of high concentration to lower concentration (e.g., glucose, urea, vitamins, Cl ions) Bulk Filtration Involves the diffusion of both solvents and solutes together across the membrane from higher to lower fluid pressure side (e.g. blood against inside wall of a blood vessel)
1-30
Peroxisomes
Small sacs with powerful oxidase enzymes Detoxification
Toxins (ethanol, formaldehyde, phenol) converted to hydrogen peroxide Catalase converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
Especially found in kidney and liver Self-replicating
You might also like
- TEAS Science ReviewDocument49 pagesTEAS Science Reviewisapatrick8126100% (5)
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDump Acc 2100% (1)
- Organ System and FunctionDocument17 pagesOrgan System and FunctionLajilaNo ratings yet
- Watts Aggregate Autopsy ReportsDocument26 pagesWatts Aggregate Autopsy ReportsEKilloran85% (78)
- Cardiovascular System OverviewDocument19 pagesCardiovascular System OverviewRachel Kwong100% (2)
- Aortic Valve Preservation - Concepts and Approaches 1st EditionDocument251 pagesAortic Valve Preservation - Concepts and Approaches 1st EditionSergeNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DefectsDocument16 pagesCongenital Heart DefectsLara TomašićNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - ReviewerDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ PDFDocument73 pagesAnatomy MCQ PDFSmart NemoNo ratings yet
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- MDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample MaterialsDocument232 pagesMDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample Materialsbrihaspathiacademy100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument84 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMisaaaki CristinaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyDocument19 pagesTest Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyMichael Burger100% (33)
- Human Body Systems Unit-8 6404 Ppt-1Document53 pagesHuman Body Systems Unit-8 6404 Ppt-1chohan artsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckDocument20 pagesAnatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Radio Logical Anatomy For FRCR Part 1Document15 pagesRadio Logical Anatomy For FRCR Part 1Prashant Gupta100% (3)
- Encyclopedia of Gastroenterology PDFDocument2,352 pagesEncyclopedia of Gastroenterology PDFAndor Claudia Florentina100% (1)
- MRSM Biology Notes TransportDocument16 pagesMRSM Biology Notes TransportAhmad Hafize100% (2)
- Grade 10 Biology NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Biology Noteskatwal0986% (21)
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Document8 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Semifinal-Final)Jhason John J. CabigonNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Chest X-Ray GuideDocument11 pagesNeonatal Chest X-Ray GuideAhmad ApriansahNo ratings yet
- Fluid and electrolyte balance: Maintaining homeostasisDocument120 pagesFluid and electrolyte balance: Maintaining homeostasisAlessandra MercadoNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology NotesDocument32 pagesSPM Biology NotesAin Fza0% (1)
- Histology and Gross Pancreas 2019Document59 pagesHistology and Gross Pancreas 2019Azwaah Hassan100% (1)
- Primary Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland: Regulate Many Body SystemsDocument5 pagesPrimary Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland: Regulate Many Body SystemsGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Pankreas & LienDocument38 pagesPankreas & LienopimadridistaNo ratings yet
- Human Health and PhysiologyDocument61 pagesHuman Health and Physiologyainaa syuhadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Ana LabDocument40 pagesChapter 2 Ana LabJyrus Quim CrusperoNo ratings yet
- Bio ConceptDocument17 pagesBio Concept1 RNo ratings yet
- Endicronology Anatomy 3Document4 pagesEndicronology Anatomy 3shahab shamsiNo ratings yet
- Final AnaphyDocument11 pagesFinal Anaphypalmaresmhelchristelebsn3No ratings yet
- Unit 4 ReviewDocument53 pagesUnit 4 ReviewRoberta BansahNo ratings yet
- Human Body Functions and Anatomy PDF NotesDocument14 pagesHuman Body Functions and Anatomy PDF NotesreenajoseNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Visceral OrgansDocument5 pagesAbdominal Visceral OrgansYudi Kelsi KaharapNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemWayneNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport 2015Document6 pagesAnimal Transport 2015Jacob ZumaNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 6 SummaryDocument6 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 6 SummaryDana PorterNo ratings yet
- 3 Human Body SystemsDocument66 pages3 Human Body SystemsThe KhanNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ingles MédicoDocument14 pagesVocabulary Ingles MédicoMayra LandoNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 Section 3 Skin System Circulatory System: Date: 8 Sep, 2020 Preyanka - Nath@northsouth - EduDocument41 pagesBio 103 Section 3 Skin System Circulatory System: Date: 8 Sep, 2020 Preyanka - Nath@northsouth - EduMD Reyadus SalihenNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument75 pages9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiologydmnnfn8hkgNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy (Neonatalsepsis)Document16 pagesAnaPhy (Neonatalsepsis)rendelino01No ratings yet
- Human Biology v1Document6 pagesHuman Biology v1JNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Transport and ExchangeDocument44 pagesThe Circulatory System: Transport and ExchangeJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyDocument29 pagesThe Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyrajarshikNo ratings yet
- NPB 101 Lecture Notes 1Document4 pagesNPB 101 Lecture Notes 1Harika NanduriNo ratings yet
- Excretory and Endocrine System: Spgbio 2 12-NewtonDocument9 pagesExcretory and Endocrine System: Spgbio 2 12-NewtonElian BiadoNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Basics Document ExplainedDocument119 pagesVeterinary Basics Document ExplainedSaleem Ahmed Shahwani0% (1)
- Human Physiology: Circulatory and Digestive SystemsDocument57 pagesHuman Physiology: Circulatory and Digestive SystemsSalma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bio TrimestralDocument4 pagesBio TrimestralverduraNo ratings yet
- Integrated Function Organ - Kel 2Document20 pagesIntegrated Function Organ - Kel 2Rashif AnbiaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Pancreas: DR GaneshDocument42 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Pancreas: DR GaneshGanesh MarutinathNo ratings yet
- Endocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Document61 pagesEndocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Musfira KhalidNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems ppt2016Document53 pagesHuman Body Systems ppt2016RoryKurniawan100% (1)
- Endocrine and Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine and Urinary SystemShereen ManabilangNo ratings yet
- Content Practice TeachingDocument5 pagesContent Practice TeachingIshika RoyNo ratings yet
- The Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesThe Human AnatomyChristian D. RamatNo ratings yet
- Subiecte Engleza: 2. Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesSubiecte Engleza: 2. Human AnatomyMarius FeroiuNo ratings yet
- AP100 Final Exam Study GuideDocument27 pagesAP100 Final Exam Study Guidebhilligoss35100% (1)
- Six Levels of Biological OrganisationDocument35 pagesSix Levels of Biological OrganisationPianomanSuperman100% (2)
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY KEY FACTSDocument44 pagesANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY KEY FACTSHARI KRISHNA G LNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Endokrin Mei 2019Document64 pagesAnatomi Endokrin Mei 2019insiya insiyaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by ShakirullahDocument99 pagesPrepared by ShakirullahKhan AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 1Document1 pageEndocrine System 1grace_wong6051No ratings yet
- Histo CircDocument38 pagesHisto Circchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Fish Pathology - Anatomy Histology PDFDocument59 pagesFish Pathology - Anatomy Histology PDFvinimoja100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology FinalDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology FinalMhel Christele PalmaresNo ratings yet
- KMU-PGCN The Urinary System Shorter Colored 1Document101 pagesKMU-PGCN The Urinary System Shorter Colored 1M Shafique SadiqeeNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument2 pagesPancreasSam TagardaNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Cool Medic Golden File File 2Document345 pagesCool Medic Golden File File 2Zia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Measure Intracardiac Pressures & Assess Cardiac FunctionDocument41 pagesMeasure Intracardiac Pressures & Assess Cardiac Functionwaleed315No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument38 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentdpkkrsterNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Aspects On Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA)Document17 pagesEpidemiological Aspects On Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA)Janey Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Concept MappingDocument3 pagesAnaphy Concept MappingArlynn MartinezNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of the Aorta Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument26 pagesCoarctation of the Aorta Diagnosis and TreatmentMissDyYournurseNo ratings yet
- Aortic Aneurysm Info From Mass GeneralDocument8 pagesAortic Aneurysm Info From Mass Generalclubsingr28No ratings yet
- Prod Code Product DescriptionDocument76 pagesProd Code Product DescriptionMarivic Labartinos Bacungan0% (1)
- Fetal CirculationDocument5 pagesFetal CirculationJaime PorscheNo ratings yet
- Cardiology FMDocument25 pagesCardiology FMtrushaNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument125 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical Collegedomo domoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Chest, Dr. Hasan Nyambe PDFDocument45 pagesStructure of Chest, Dr. Hasan Nyambe PDFAndi Meidin AnugerahNo ratings yet
- Normal ChestDocument82 pagesNormal ChestMonica CherladyNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Natural History of Thoracic Aortic AneurysmDocument5 pagesEpidemiology, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Natural History of Thoracic Aortic AneurysmNathaliazuosNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Marfan StudiesDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Marfan StudiesemilydarkcoreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Workbook ThoraxDocument68 pagesAnatomy Workbook ThoraxClara AtiyehNo ratings yet
- 227 Full PDFDocument3 pages227 Full PDFanon_629352389No ratings yet