Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By: Lalit Gautam Mohit Sharma Shishir Mishra Mohd. Frahim
Uploaded by
personifydOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Lalit Gautam Mohit Sharma Shishir Mishra Mohd. Frahim
Uploaded by
personifydCopyright:
Available Formats
By : Lalit Gautam Mohit Sharma Shishir Mishra Mohd.
Frahim
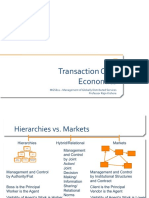
It is an autonomous business centre for which a manager is responsible for
Cost Revenue Acquisition of assets Disposal of assets
Classified into following parts
Expense centre Cost centre Revenue centre Profit centre Investment centre
The relationship between inputs and outputs of the responsibility centre determines the label.
responsibility centre can in practice consist of a department, a business unit, a legal entity, geographical unit etc.
A description of the type of activities which are common per responsibility centre
A number of examples per responsibility centre
The steering and control concept per responsibility centre The most common compensation method, both from a management and a tax perspective The legal framework.
Expense center Contract R&D services
Investment Center
IP owner/Parent company
Cost Center Contract manufacturing
Profit Center
Indian Entrepreneur (Principal company)
Revenue center Indian sales & distribution subsidiaries
Relationship : input/output
Inputs expressed in currencies($) and output in units. Output levels and costs are hard to determine.
Types of activities
Strategically and operationally necessary. Exclusively performed for group and is core in nature.
Examples
Highly creative and non repetitive tasks. e.g. core research
Corporate strategy department. E.g. strategy making.
Towards steering control
Determine expense level(budget) Monitor actual expense/cost per department. Focus on quality of processes, people and technology applied.
Common transfer pricing policy
actual cost are charged or allocated to recipient (budgeted costs +/- variances)
actual cost/benefit ratio is frequently reviewed profit margin is meaningless from a managerial point of view profit margin will be required for tax purposes
Legal framework
mostly development contract or service level agreement
Relationship: input/output
inputs are expressed in currencies($) and outputs in units. output level and cost standards can be determined
Type of activities
operational activities, managed by principal entity mostly performed for group mostly non-core
Examples
subcontracting of manufacturing activities facility management activities supporting activities of treasury department IT system maintenance activities
Towards steering/control
determine cost standards/targets per product etc. monitor actual costs per product etc focus on cost/quality relationship allows benchmarking of equivalent activities
Common transfer pricing policy
standard cost times actual volumes are charged to apply a profit mark-up creates pseudo profit centre profit margin could be applied from a managerial point of view profit margin will be required for tax purposes, unless a third party would not be able to charge a mark-up
Legal framework
mostly service level agreement.
Relationship input/output
inputs and outputs are expressed in currencies($) output level and cost level not directly related
Type of activities
market/customer driven activities mostly performed for external customers and is mostly core
Examples
sales and distribution activities
Towards steering/control
determine and monitor revenue levels maximize quantities or prices
Common transfer pricing policy
allocation of (contribution) margin of sales revenue
Legal framework
mostly service level agreements (e.g. distribution company)
Relationship input/output
inputs and outputs are expressed in currencies($) output level and cost standards can be determined
Type of activities
market/customer driven activities mostly performed for external customers and in mostly core
Examples
distribution activities speculative activities of treasury department
Towards steering/control
determine price levels and cost standards per product monitor turnover, costs and profits per product focus on profit contribution and quality analyse variances
Common transfer pricing policy
external/market price times actual volumes are charged operating profit margin should - as primary way of measuring profitability - provide an adequate return on capital employed for.
Legal framework
mostly service level agreement with cost centres.
Relationship input/output
inputs and outputs are expressed in currencies relates profits to assets/underlying capital (=input)
Type of activities
capital market/customer driven activities mostly performed for shareholders/MNO as a whole
Examples
intellectual property owners (return on investment on R&D)
Towards steering/control
determine minimum required return on investment monitor capital employed and profits per product analyse variances on return on investments focus on sustaining long term profitability of MNO
1
Common transfer pricing policy
EVA or RONA/ROCE measures should allow monitoring an adequate return on investment remuneration based on residual income
Legal framework
wide variety of legal agreements.
Positives (+) management is relieved of much day-to-day problem solving and is left free to concentrate on strategy, on higher level decision making, and coordinating activities.
Decentralization provides lower level managers with vital experience in making decisions. Without such experience, they would be ill-prepared to make decisions.
Negatives (-) Lower level managers may make decisions without fully understanding the "big picture."
In a truly decentralized organization, there may be a lack of coordination among autonomous managers. Lower-level managers may have objectives that are different from the objectives of the entire organization.
www.googlebooks.com www.tpa.au www.managerworld.com Management Control System by Ghosh
You might also like
- What is Financial Accounting and BookkeepingFrom EverandWhat is Financial Accounting and BookkeepingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Chart of Accounts: Assets Account Titles DescriptionDocument5 pagesChart of Accounts: Assets Account Titles DescriptionKent Dela Cruz Castillo100% (2)
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Internship Khybercements Soliha KhanDocument60 pagesInternship Khybercements Soliha KhanSoliha Khan100% (1)
- 3.2 Costs and RevenuesDocument22 pages3.2 Costs and RevenuesDanae Illia GamarraNo ratings yet
- 2A Income Statement and Statement of Stockholders EquityDocument5 pages2A Income Statement and Statement of Stockholders EquityKevin ChengNo ratings yet
- Investment Appraisal in BusinessDocument13 pagesInvestment Appraisal in BusinessAsimali AsimaliNo ratings yet
- Investment Centers and Transfer PricingDocument9 pagesInvestment Centers and Transfer PricingMohammad Nurul AfserNo ratings yet
- MAS Handout - Responsibility Accounting and Accounting For Decentralized Org, Balanced Scorecard and Transfer Pricing PDFDocument5 pagesMAS Handout - Responsibility Accounting and Accounting For Decentralized Org, Balanced Scorecard and Transfer Pricing PDFDivine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- BS Accountancy Qualifying Exam: Management Advisory ServicesDocument7 pagesBS Accountancy Qualifying Exam: Management Advisory ServicesMae Ann RaquinNo ratings yet
- Financial Due DiligenceDocument15 pagesFinancial Due Diligenceprateekkapoor24100% (1)
- Rothaermel Ch. 5 SummaryDocument5 pagesRothaermel Ch. 5 SummaryMichaelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Cost AccountingDocument15 pagesLecture 1 Cost AccountingVaibhav ChordiaNo ratings yet
- Assocham ValuationDocument34 pagesAssocham ValuationNiraj ThiraniNo ratings yet
- Definition of 'Time Value of Money - TVM'Document4 pagesDefinition of 'Time Value of Money - TVM'Chinmay P KalelkarNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument9 pagesCost AccountingPuneet TandonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BecDocument11 pagesChapter 3 BecStephen ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Cost Accounting - ESP Int - L Banking and FinanceDocument35 pagesUnit 10 - Cost Accounting - ESP Int - L Banking and FinanceDamMayXanhNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Planning and Performance Evaluation in Multinational EnterprisesDocument7 pagesChapter Five: Planning and Performance Evaluation in Multinational EnterprisesHunkar IvgenNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer ManagerialDocument7 pagesPrelim Reviewer ManagerialMargaux Julienne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Economic FeasibilityDocument40 pagesEconomic FeasibilityKristoffer Jesus Lopez OrdoñoNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument34 pagesRatio AnalysisavdhutshirsatNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis NotesDocument25 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis NotesparinNo ratings yet
- Income Statement, Its Elements, Usefulness and LimitationsDocument5 pagesIncome Statement, Its Elements, Usefulness and LimitationsDipika tasfannum salamNo ratings yet
- Entrep Business ModelDocument6 pagesEntrep Business ModelElena Salvatierra ButiuNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 25Document6 pagesFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 25RafaelNo ratings yet
- Income Statement 2022Document37 pagesIncome Statement 2022Vinay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable Cost PDFDocument29 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable Cost PDFitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- Drivers of Shareholder ValueDocument19 pagesDrivers of Shareholder Valueadbad100% (1)
- Essay FinalDocument27 pagesEssay FinalFadil Bin RafeekNo ratings yet
- Ques - Distinguish Between Operating Activities, Investing Activities and Financing Activities?Document12 pagesQues - Distinguish Between Operating Activities, Investing Activities and Financing Activities?Aniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Costing MBA Sem 1Document34 pagesIntroduction of Costing MBA Sem 1prashantmis452No ratings yet
- Funda NotesDocument14 pagesFunda NotesErika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- XCFBJJKMDocument33 pagesXCFBJJKMApurbh Singh KashyapNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable CostDocument29 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable CostitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- 404A - Hilton Irm Chapter 13Document14 pages404A - Hilton Irm Chapter 13Chloe Quirona PoliciosNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Section 3Document54 pagesFinancial Accounting: Section 3LOINI IIPUMBUNo ratings yet
- Finance For Non FinanceDocument32 pagesFinance For Non FinanceZhuwenyuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - INTRODUCTIONDocument54 pagesLecture 1 - INTRODUCTIONTgrh TgrhNo ratings yet
- 1Document34 pages1TOLENTINO, Julius Mark VirayNo ratings yet
- 19 19 Accounts Notes On Ratio and CfsDocument8 pages19 19 Accounts Notes On Ratio and Cfsrahul007.ajmeraNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument36 pagesIncome StatementTiffany VinzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Divisional Perfomance and BudgetingDocument34 pagesChapter 8 - Divisional Perfomance and BudgetingJeremiah NcubeNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management AccountingDocument29 pagesCost and Management AccountingAks SinhaNo ratings yet
- General and Administrative ExpensesDocument6 pagesGeneral and Administrative ExpensesmaresNo ratings yet
- FIN 408 - Ch.7Document24 pagesFIN 408 - Ch.7Shohidul Islam SaykatNo ratings yet
- R2R Unit 1Document16 pagesR2R Unit 1Bhavika ChughNo ratings yet
- What Are The Disadvantages of The Perpetual and Period Inventory System?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Disadvantages of The Perpetual and Period Inventory System?Siwei TangNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of New Business PDFDocument8 pagesEconomic Analysis of New Business PDFshule1No ratings yet
- Understanding Financial StatementsDocument77 pagesUnderstanding Financial Statementsshivam_dubey4004100% (1)
- A Analyzing of Cash Budgets and Hoe Its Used To Make Decisions Finance EssayDocument14 pagesA Analyzing of Cash Budgets and Hoe Its Used To Make Decisions Finance EssayHND Assignment HelpNo ratings yet
- MGS611 F15 TransactionCostEconomics PDFDocument11 pagesMGS611 F15 TransactionCostEconomics PDFSaiprasad VeluruNo ratings yet
- Session 5 and 6 PDFDocument32 pagesSession 5 and 6 PDFmilepnNo ratings yet
- Corporate ValuationDocument16 pagesCorporate ValuationJuBeeNo ratings yet
- Lean Bronze: Factors Affecting Customer RetentionDocument45 pagesLean Bronze: Factors Affecting Customer Retentionsherif mahmoudNo ratings yet
- ModelingDocument12 pagesModelingIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementDocument83 pagesFinancial StatementDarkie DrakieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - StudentsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - StudentsLynn NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On: "Business Valuation Methods and Techniques"Document39 pagesA Project Report On: "Business Valuation Methods and Techniques"Shish TNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementDocument16 pagesFinancial StatementCuracho100% (1)
- 2.the Life Cycle of A TradeDocument73 pages2.the Life Cycle of A TradeAnand Joshi100% (1)
- Investments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsFrom EverandInvestments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsNo ratings yet
- SPVG Quote SI-95692 Revision 0 PDFDocument4 pagesSPVG Quote SI-95692 Revision 0 PDFherrerafaridcrNo ratings yet
- Akun Impor Ud BuanaDocument1 pageAkun Impor Ud BuanaYusnita dwi kartikaNo ratings yet
- Wednesday June 13, 2012Document34 pagesWednesday June 13, 2012colomboanalystNo ratings yet
- Dividends and Share Repurchases: Basics: Presenter's Name Presenter's Title DD Month YyyyDocument20 pagesDividends and Share Repurchases: Basics: Presenter's Name Presenter's Title DD Month YyyyKavin Ur FrndNo ratings yet
- PESTEL Midterm Assignment Term 1Document12 pagesPESTEL Midterm Assignment Term 1humayunNo ratings yet
- How To Implement A Flexible Budget AcmaDocument6 pagesHow To Implement A Flexible Budget AcmaasmiNo ratings yet
- La Frutera vs. CIRDocument1 pageLa Frutera vs. CIRMaricar Corina CanayaNo ratings yet
- EssilorLuxottica - Credit AnalysisDocument4 pagesEssilorLuxottica - Credit AnalysisManfredi SopraniNo ratings yet
- Robin Nepal EnglishDocument1 pageRobin Nepal EnglishgpdharanNo ratings yet
- India Consumer: Wallet Watch - Vol 1/12Document6 pagesIndia Consumer: Wallet Watch - Vol 1/12Rahul GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 Questions and Practice Exercises Sab 101Document4 pagesChapter8 Questions and Practice Exercises Sab 101Zahar Zahur Kaur BhullarNo ratings yet
- Marketing PlanDocument11 pagesMarketing Planapi-300268103No ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument20 pagesFinancial StatementsOmnath BihariNo ratings yet
- 2014 Annual ReportDocument132 pages2014 Annual Reportnaveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Partnership Formation Operation and LiquidationDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Partnership Formation Operation and Liquidationanwaradem225No ratings yet
- GST Law 2017 Download GST PPT 2017Document34 pagesGST Law 2017 Download GST PPT 2017ShyamNo ratings yet
- XXXXXX / XXXXXX / XXXX: Frequently-Asked Questions (Faqs)Document9 pagesXXXXXX / XXXXXX / XXXX: Frequently-Asked Questions (Faqs)pmpanchalNo ratings yet
- Interloop: Investor InformationDocument2 pagesInterloop: Investor InformationALI SHER HaidriNo ratings yet
- Extremely Important Proforma of Projected P L Balance Sheet of Both Partnership Firm Sole Proprietorship Business With Cma Data Analysis For Cash Credit LoanDocument31 pagesExtremely Important Proforma of Projected P L Balance Sheet of Both Partnership Firm Sole Proprietorship Business With Cma Data Analysis For Cash Credit LoanMonty 20No ratings yet
- MRF RatioDocument27 pagesMRF RatioRushang PatelNo ratings yet
- Consumer - Outlook - 3jan22 - JM FinancialDocument14 pagesConsumer - Outlook - 3jan22 - JM FinancialBinoy JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HomeworkDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Homeworknadia0109No ratings yet
- RA 7496-Simplified Net Income Scheme For Self-Employed & Professionals...Document5 pagesRA 7496-Simplified Net Income Scheme For Self-Employed & Professionals...Crislene CruzNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management Quiz No. 1Document5 pagesStrategic Cost Management Quiz No. 1Alexandra Nicole IsaacNo ratings yet
- Part A Answer All The Question 4 1 4Document3 pagesPart A Answer All The Question 4 1 4jeyappradhaNo ratings yet
- 5 Methods of ValuationDocument14 pages5 Methods of Valuationmennakhla100% (1)
- Case Study 4Document11 pagesCase Study 4AmalMdIsaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan For A New ProductDocument27 pagesMarketing Plan For A New ProductFahadBinAzizNo ratings yet