Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro To HRM
Uploaded by
Asad AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro To HRM
Uploaded by
Asad AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Resource Management By Waheed Hamid
1 1
This course will develop the students basic understanding of the Human Resource Management with emphasis on the practical application of HRM and concepts. Specific HRM functions such as HR planning, Recruiting, Selection, Training, and Employees development and other contemporary HRM issues will be examined.
To Understand various HRM functions and its linkages with strategic management To Compare and contrast various Components of HRM HR planning, Job analysis, job design, diversity, and its challenges, gaining competitive advantage by best HRM practices Overview of current topics in HRM such as Compensations, Labor Unions, managing diversity, total quality management, leadership, motivation, change, and the decision-making process. Give an understanding to manage own career and development strategy.. Work as an effective HR manager
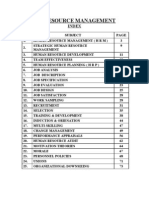
Definition of HRM Importance of HRM Functions of HRM Organization and Individual Distinguish b/w HRM and PM Line managers HRM responsibilities Staff managers HRM responsibilities A Basic Mental Map for HR The Human Resource Cycle Human behavior and relations Three stages of growth of HRM
Definition of HRM: Human resource management is to make the most productive use of human resource to the greatest benefits of the organization and individuals. Organization: profits and social commitments. Individuals: development and achievement.
(1) (2)
(3)
(4)
People is the key factor of production. Productivity is the key to measure a nations economic growth potential, and labor quality is the key to improving productivity. Competition today is the competition for talents. Since man is the most uncontrollable and unpredictable variable of all production variables, organizational success depends on the management of people.
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
Conducting job analysis. Planning future needs and supplies. Recruiting and selecting employees. Orienting and training employees. Managing wages and benefits. Performance appraisal. Communicating (discipline and services). Building employee commitment (incentives).
(1)
a.
b.
c.
d. e.
Management process Planning. Organizing. Staffing. Leading. Controlling.
(1)
Organization needs: Profits, productivity
and markets.
(2)
Individual needs: Maslows Need Hierarchy Physiological needs, security, belonging, self-respect and self-actualization.
(3) Coordinating organization and individual
needs: goal of HRM.
Frederic Taylor: Father of scientific management a. Definition: Systematic analysis and breakdown of work into the smallest mechanical components and rearranging them into the most efficient combination. b. Steps: Job analysisselectiontrainingrewards.
a. b. c. d. e. f. g.
Job placing. Orienting new employees. On-job training of employees. Interpreting company policies and procedures. Conducting job appraisals. Controlling labor costs. Labor protection and disciplines.
a. b. c.
A line function: directing and managing people in the HRM department. A coordinating function: coordinating HRM activities across the organization. Staff functions: Same as the HRM functions plus labor relations and collective bargaining with the trade unions.
Old viewcost center Keep track of forms Policy and procedure enforcement Payroll and insurance Cost reduction oriented Example: new employees go through orientation with a videotape and a package of forms
New viewstrategic partner
Example: developing a program to select employees for a dynamic work environment
Employee development Integration with the core operations of the organization Change management Results oriented
Introductory Lecture 1: Introduction to Human Resources
Develop an Overarching Strategy
What does the company do, with whom are they competing, what makes this company unique?
Acquire Staff
Who makes a good employee? How do we get these people to apply? How are people screened? How are people selected?
Train and Develop
Can we help new hires feel like part of the company? How do we teach employees the skills they need? How do we encourage civility? How do we measure performance?
Compensation and Benefits
How can we match our pay offers to the market?
Performance management
What are the things that motivate employees at work? What prevents employees from performing effectively? Are there incentives that we should be offering?
How do we pay people who are working in different job levels?
What types of non-cash benefits can we offer to employees?
Introductory Lecture 1: Introduction to Human Resources
a.
b. c. d.
The Hawthorne Studies by Westing House The happy workers are the most productive workers. (The Pet Milk theory) Max Weber: the Ideal Bureaucracy. Chris Argyris: Individual and organization mutual adjustment. Affected by the theories of behavioral science and system theory.
a. b. c.
File Management (1900-1964):collecting and storing data of each employee. Government Accountability (1964-1980): Compliance to government regulations. Human Resource Management: Treating human resource as an asset. Emphasizing joint responsibilities of line managers and staff managers.
Discussion
You might also like
- MBA Digital Notes on Human Resource ManagementDocument59 pagesMBA Digital Notes on Human Resource Managementme_sahaniNo ratings yet
- Strategy, Structure, Systems, Staff, Style, Skills and Shared ValuesDocument5 pagesStrategy, Structure, Systems, Staff, Style, Skills and Shared Valuessooraj2No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementArvind SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument58 pagesHuman Resource Managementpatelbikash492No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesHuman Resource ManagementDr-Shefali GargNo ratings yet
- HRM PPT RevisedDocument188 pagesHRM PPT Revisedzenebe zaffuNo ratings yet
- HRM BhuDocument135 pagesHRM BhuMakarand ChandaikerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Information SystemDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Information SystemXafiiska Al-IxsaanNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit1Document65 pagesHRM Unit1Suhani VermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON: Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesAssignment ON: Human Resource ManagementpuneetbabutaNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit 1 Revised-1Document53 pagesHRM Unit 1 Revised-1Punit SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Prof. Nidhi RaiDocument26 pagesHuman Resource Management: Prof. Nidhi RaifreebookNo ratings yet
- HRM NotesDocument73 pagesHRM NotesKashvi JindalNo ratings yet
- Course Code: Hrm353 L1Document26 pagesCourse Code: Hrm353 L1Jaskiran KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter - IDocument68 pagesChapter - ISai VivekNo ratings yet
- Contemporary issues in HRMDocument14 pagesContemporary issues in HRMTaruntej Singh0% (1)
- HRM Ppt's 16-17Document216 pagesHRM Ppt's 16-17sfdwhjNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument28 pagesHuman Resource ManagementhahireNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Strategic Role of HRMDocument42 pagesChapter One Strategic Role of HRMSoyed Mohammed Zaber HossainNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology-Ramapuram CampusDocument70 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology-Ramapuram CampusPritesh VekariyaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Roles of HRM: Functions, Evolution & ManagementDocument25 pagesStrategic Roles of HRM: Functions, Evolution & ManagementFahim BarakzaiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 HR IntroductionDocument46 pagesChap 1 HR IntroductionA1-40-Kiều VyNo ratings yet
- HRM in Insurance Sector WRT Recruitment and SelectionDocument57 pagesHRM in Insurance Sector WRT Recruitment and SelectionAnushriAdarshRathiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 HRMDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 HRMnikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- HRM functions challenges trendsDocument38 pagesHRM functions challenges trendsujjwalsingh027100% (2)
- HRM 1Document22 pagesHRM 1qari saibNo ratings yet
- HRM Module No 1Document47 pagesHRM Module No 1ashnajananNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Shrichand BhambhaniDocument64 pagesHuman Resource Management: Shrichand BhambhaniNikita GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Presentation On The Basics of Human Resource ManagementDocument28 pagesThe Presentation On The Basics of Human Resource ManagementAtif IqbalNo ratings yet
- SLM-Unit 01Document21 pagesSLM-Unit 01Dr. Smita ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Final PrintDocument63 pagesFinal PrintSai VivekNo ratings yet
- Professor: Dr. Abdus Samie Subject: Human Resource Management Group Members: Maham Sohail 2019-Ag-8680 Nida Baig 2019-Ag-8712 Dilawaiz 2019-Ag-8676 Sadia Munawar 2019-Ag-8690Document17 pagesProfessor: Dr. Abdus Samie Subject: Human Resource Management Group Members: Maham Sohail 2019-Ag-8680 Nida Baig 2019-Ag-8712 Dilawaiz 2019-Ag-8676 Sadia Munawar 2019-Ag-8690Maham SohailNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Notes MbaDocument70 pagesHuman Resource Management Notes MbaPrathap Vasu100% (9)
- Unit 01 - Introduction To Human Resource Management - Manipal UniversityDocument24 pagesUnit 01 - Introduction To Human Resource Management - Manipal UniversityPraveen ParocheNo ratings yet
- MBA Sem II - HRM NotesDocument59 pagesMBA Sem II - HRM Notesshyambgmi2No ratings yet
- HRM Guide on Human Resource ManagementDocument72 pagesHRM Guide on Human Resource ManagementSahil KapoorNo ratings yet
- Bba 301 ModuleDocument101 pagesBba 301 ModulefinleyNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - MergaDocument148 pagesHuman Resource Management - Mergameftuh abdiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to HRM FunctionsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to HRM FunctionsStuti Aggarwal 2K21/BBA/148No ratings yet
- HRM Assign 1.1Document16 pagesHRM Assign 1.1Saad ImranNo ratings yet
- R&S of Lakshmi HundaiDocument62 pagesR&S of Lakshmi Hundairajesh bathulaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Human Resource ManagementRajeswari RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Human Resource MGMNT 1Document150 pagesHuman Resource MGMNT 1Winny Shiru MachiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Inroduction To HRDocument38 pagesUnit 1 Inroduction To HRShrijana BaralNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Intro To Managing People - 5f41fd1b67eb4Document27 pagesSession 1 - Intro To Managing People - 5f41fd1b67eb4IreshaNadeeshaniNo ratings yet
- SV - Chap 1 HR IntroductionDocument36 pagesSV - Chap 1 HR IntroductionHoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - 0Document8 pagesCH 1 - 0wubeNo ratings yet
- ARH - Introducción - Whats Is HRM All AboutDocument34 pagesARH - Introducción - Whats Is HRM All AboutcataNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagmentDocument89 pagesHuman Resource ManagmentRUCHIT SAHAINo ratings yet
- Introduction To: Human ResourceDocument28 pagesIntroduction To: Human Resourcechin22No ratings yet
- Hrm Unit 1 NotesDocument22 pagesHrm Unit 1 NotesBorish LiffinNo ratings yet
- HRM core elements, objectives, scope, roles, functionsDocument27 pagesHRM core elements, objectives, scope, roles, functionsLandrito Armie UriNo ratings yet
- HRM ProjectDocument33 pagesHRM ProjectRajesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Defining HR Success: 9 Critical Competencies for HR ProfessionalsFrom EverandDefining HR Success: 9 Critical Competencies for HR ProfessionalsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Encyclopedia of Human Resource Management, Volume 3: Thematic EssaysFrom EverandThe Encyclopedia of Human Resource Management, Volume 3: Thematic EssaysNo ratings yet
- The ACE Advantage: How Smart Companies Unleash Talent for Optimal PerformanceFrom EverandThe ACE Advantage: How Smart Companies Unleash Talent for Optimal PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Voluntary Employee Withdrawal and Inattendance - ADocument227 pagesVoluntary Employee Withdrawal and Inattendance - AAmazia Pravianti100% (1)
- Department of Labor: MessageDocument2 pagesDepartment of Labor: MessageUSA_DepartmentOfLaborNo ratings yet
- Template Induction Checklist PDFDocument1 pageTemplate Induction Checklist PDFMohd Faizal Bin AyobNo ratings yet
- Excavation Trenching Daily Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesExcavation Trenching Daily Inspection ChecklistRajendraNo ratings yet
- Essential Steps to Complete an Employment Contract in RomaniaDocument2 pagesEssential Steps to Complete an Employment Contract in RomaniaTeodor CostacheNo ratings yet
- Traditional and Contemporary Issues and Challenges: Slide Content Created by Joseph B. Mosca, Monmouth UniversityDocument43 pagesTraditional and Contemporary Issues and Challenges: Slide Content Created by Joseph B. Mosca, Monmouth UniversityAnik AlamNo ratings yet
- Benefits Manager Director in Phoenix AZ Resume Lorraine CruzDocument2 pagesBenefits Manager Director in Phoenix AZ Resume Lorraine CruzLorraineCruzNo ratings yet
- Managerial Planning & Goal SettingDocument13 pagesManagerial Planning & Goal SettingAylalaNo ratings yet
- The Changing Nature of WorkDocument2 pagesThe Changing Nature of WorkSonal PalamNo ratings yet
- HBL HR Processes GuideDocument53 pagesHBL HR Processes GuideManan Butt100% (1)
- Workmen Compensation ActDocument22 pagesWorkmen Compensation ActLavkeshhNo ratings yet
- Equity TheoryDocument2 pagesEquity TheoryCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- SIHDocument25 pagesSIHangrishdeepakNo ratings yet
- Tour Claim FormDocument1 pageTour Claim FormGeeta VigNo ratings yet
- Negotiation and Bargaining Skills - Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesNegotiation and Bargaining Skills - Individual AssignmentRaunaq DashNo ratings yet
- Go P 38 2007Document10 pagesGo P 38 2007Upendra KumarNo ratings yet
- An Open Letter To Austin Council From AAHNDocument4 pagesAn Open Letter To Austin Council From AAHNAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundations of EducationDocument22 pagesPsychological Foundations of EducationDavid BlaneNo ratings yet
- Quit Claim SampleDocument3 pagesQuit Claim Samplelucky cudiaNo ratings yet
- Tattoo AirbrushDocument9 pagesTattoo AirbrushSimona WingNo ratings yet
- Jurnal InternasionalDocument16 pagesJurnal Internasionaldion syahraniNo ratings yet
- Softline Referral Program - EMDocument5 pagesSoftline Referral Program - EMbberryNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesExecutive SummaryM.V.S.A.M. KiranNo ratings yet
- Sterling Products International Inc V SolDocument2 pagesSterling Products International Inc V Solav783No ratings yet
- Human Resources GeneralistDocument2 pagesHuman Resources GeneralistCatalin BurdusaNo ratings yet
- Paper Industries Corporation VS LaguesmaDocument2 pagesPaper Industries Corporation VS LaguesmaColBenjaminAsiddao100% (1)
- Payroll 3Document49 pagesPayroll 3Bhanu PrkhashNo ratings yet
- Andrew Thornton - Group 2Document3 pagesAndrew Thornton - Group 2Ishmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Equitable Banking Vs SadacDocument22 pagesEquitable Banking Vs SadacLeslie LernerNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Work EnvironmentDocument3 pagesThe Ideal Work Environmentselina_kollsNo ratings yet