Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostic Tech
Uploaded by
drhemantt12790 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views80 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views80 pagesDiagnostic Tech
Uploaded by
drhemantt1279Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 80
DR HEMANT D. TO5HIKHANE DR HEMANT D.
TO5HIKHANE
M5(Ay.) M5(Ay.)
PROF& HOD DEPT. OF 5HALAYATANTRA
KLEU 5HRI B.M.K.Ayurvcda MahavIdya!ya 5hahapur
Bc!gaum Karnataka -
drhcmanttgmaI!.cnm
Achaia Sushiula - lho falhoi of suigoi
Aulhoi of sushiula sanhila
Iiisl ono lo dosciilo aloul suigicaI insliunonls and
lochniquos Dissoclion and doad lod piosoivalion ModoI
dissoclion
Iiisl ono lo poifoin pIaslic suigoi (Rhino-pIaslocuIai
suigoi Ano-ioclaI suigoi and vaiious aldoninaI
suigoiios
LIaloialo dosciiplion - fiacluios & lpos of landagos foi
diffoionl fiacluios
LIaloialo dosciiplion iog. fisluIa-in-Ano haonoiihoids
and sinus olc
Rofoioncos lo fisluIa-in-ano dalo lo anliquil.
Hippocialos nado iofoionco lo suigicaI lhoiap
foi fisluIous disoaso
Prnb!cm
A fisluIa-in-ano is a hoIIov liacl Iinod vilh
gianuIalion lissuo connocling a piinai
oponing insido lho anaI canaI lo a socondai
oponing in lho poiianaI skin. Socondai liacls
na lo nuIlipIo and fion lho sano piinai
oponing
ls a Chionic infIannaloi condilion a luluIai
sliucluio oponing in lho Ano-ioclaI canaI al ono ond
and suifaco of poiinoun oi poii-anaI skin on lho olhoi
ond.
CIassicaI fisluIa has lvo oponings ono inloinaI and
olhoi oxloinaI
Chionic on/off pus dischaigo
Doop soalod alscoss is lho souico of pus
On/off pain
Iiuiilis
Sono linos Iassing of slooI fion oxloinaI oponing
Frcqucncy
%ho piovaIonco ialo is 8.6 casos poi 1OOOOO popuIalion.
%ho piovaIonco in non is 12.3 casos poi 1OOOOO popuIalion.
n vonon il is 5.6 casos poi 1OOOOO popuIalion.
%ho naIo-lo-fonaIo ialio is 1.8:1. %ho noan ago of palionls
is 38.3 oais.
3
EtIn!ngy
IisluIa-in-ano is noaiI aIvas causod l a piovious
anoioclaI alscoss. AnaI canaI gIands silualod al lho donlalo
Iino affoid a palh foi infocling oiganisns lo ioach lho
inlianuscuIai spacos.
Olhoi fisluIao dovoIop socondai lo liauna Ciohn
disoaso anaI fissuios caicinona iadialion lhoiap
aclinoncosos luloicuIosis and chIandiaI infoclions.
Alscoss in ono oi noio polonliaI spacos
Souico of infoclion in AnaI fissuio
An uIcoi al lho iool of lho piIo nass
nfIanod anaI cipl nfoclion fion haii foIIicIo
nfoclod solacoous gIand
nfoclod svoal gIand
Ioioign lod injui
nfIanod /lhionlosod piIo nass
Rolainod suluios afloi haonoiihoidoclon
Ioioign lod ponolialing fion oul sido
Radialion luins fion x-ias and iadio lhoiap
5ystcmIc dIscascs can a!sn causc
FIstu!a-In-Ann
%uloicuIosis of nloslino
UIcoialivo coIilis
RogionaI iIoilis
Roc. Appondicilis
U.%.
Iioslalic infoclion
IiIo-nidaI sinusos
Iolls spino
Osloo-noIilis of poIvic lonos
ACCORD %O %S OIL .
.PARACHINA (BAHIRMUKHA)
2.ARVACHINA (ANTARMUKHA
ACCORD %O %HL DOSHA
.VATIK (5ATAPONAK)
2.PAITTIK (U5HTRA GRIVA)
.5HLE5HMIK (PARI5RAVI)
.5ANNIPATAJ (5AMBUKAVART)
.AGANTUJ (UNMARGI)
.ACCORD %O %HL DRLC%O OI IUS DCHARL
.RIJU (DIRECT)
2.VAKRA (CURVED)
Pc!vIc
5ub-mucnus
Rccta!
5ub-cutancnus
HIgh-ana!
Lnw-ana!
Illustration of anal canal anatomy in the coronal
plane. EAS = external anal sphincter, IAS = internal
anal sphincter, IS = intersphincteric space, LA =
levator ani, LM = longitudinal muscle, PR =
puborectalis muscle.
Illustrations in coronal plane show classification
of fistula in ano according to Parks et al
intersphincteric, transsphincteric,
suprasphincteric, and extrasphincteric.
Illustration in coronal plane shows fistula extensions
(secondary tracts): A = extension into roof of ischioanal
fossa, arising from apex of a transsphincteric fistula; B
= supralevator pararectal extension arising from apex
of a transsphincteric fistula; C = supralevator extension
originating from intersphincteric plane, D =
intersphincteric horseshoe.
Late diagnosis
lack of advanced diagnostic modalities
Avoidance of timely surgical intervention
Patient hesitation (esp. females)
Non-availability of kshar-sutra and surgical experts for
timely intervention
Natural& routine infection with urine stool etc.
Surgical technique limitations.
lack of awareness about the disease among the people
use of heavy Anti-biotics
ProbIems in diagnosing and treating
FistuIa-in-ano
use of Anti Biotics Proper
iagnosis procedures for fistuIa in ano
%rividha pariksha : darshana, sparsana and prashna
Astanga pariksha :Nadi,mala,mootra,jiwha
sabdam,sparsham,drik and akriti.
DRE : int.opening can be felt as a nodule
Dye injection (methylene blue or ndigo carmine
Hydrogen peroxide)
Procto-scopy :may reveal internal opening
Probing Probing : useful in exploring tracts. painful
sometimes. false passage one may create in
fibrosed tracts
nfoclion of anaI gIands Iocalod al lho laso of
lho anaI cipls al lho donlalo Iino.
Othcr causcs: anaI fissuio & ciohns disoaso.
Left lateral position, hips flexed to
90
0
, kness less flexed to 110
0
Stretch the buttocks- Inspect
the Anus & Perineum
Pulp of finger on Anus
%he Dreaded Digital Rectal Examination %he Dreaded Digital Rectal Examination
" "It still brings tears to my eyes!!! It still brings tears to my eyes!!!
Lnliio coIon
oxaninod vilh a fIoxilIo
coIonoscopo.
Suspicion of coIonic
disoidois - UIcoialivo
coIilis Ciohns disoaso
an MaIignanc olc.
istulo-graphy
C% Scan
MR (Endo-anal)
USG (%PUS,%RUS,%'S,EAUS)
Reservoir of feaces?
Recto-sigmoid junction 3rd sacral vertebra
Ant-posterior curvature is known as sacral flexure,
after passing pelvic diaphragm it passes downwards
backwards. %his curvature is known as perineal flexure.
3 lat. curvatures 2 in right 1 in left.
Relations: posteriorly :3rd sacra vertebra, coccyx median
sacral vessels and coccygeal vessels
Anteriorly : in male: bladder ,seminal vesicles, prostate
in female :uterus, upper part of vagina, recto uterine pouch.
Laterally :para-rectal fossa, pelvic sym.plexuses, sup.
rectal vessels.
%he anal canal is the terminal portion of the
intestinal tract
it begins at the ano-rectal junction (the point
passing through the levator-ani muscles),
t is about 4 cm long, and terminates at the anal
verge.
Anatomical : that extends from the dentate line to
the anal verge.
Anteriorly Male : bulb of urethra
emale : perineal body and vagina
Posteriorly : Coccyx and pubo-rectalis muscle
Laterally : schio-rectal fossa containing inferior
haemorrhoidal vessels and pudendal nerve
surrounded below by external and internal
cont. cont.
Mucous membrane folds are called crypts of morgagni. Mucous membrane folds are called crypts of morgagni.
columns join to form anal valves below and sinuses above columns join to form anal valves below and sinuses above
usually get infected. usually get infected.
anal glands form crypts at dentate line (crypts of anal glands form crypts at dentate line (crypts of
morgagni). morgagni).
imaginary line where the anal valves are situated is known imaginary line where the anal valves are situated is known
as as dentate line (pectinate line). dentate line (pectinate line).
N%ERNAL SPHNC%ER N%ERNAL SPHNC%ER : thickened cont. of the muscle coat of the : thickened cont. of the muscle coat of the
rectum. rectum.3 3 cm long. cm long.
EX% ANAL SPHNC%ER EX% ANAL SPHNC%ER: : 3 3 parts parts
1 1.sub cutaneous part .sub cutaneous part
2 2.superficial part .superficial part
3 3.deep part .deep part
SPACES ON %HE LA%ERAL SDE O REC%UM AND ANAL CANAL SPACES ON %HE LA%ERAL SDE O REC%UM AND ANAL CANAL: :
1 1.perineal space .perineal space 2 2.ischio rectal space .ischio rectal space 3 3.pelvirectal space .pelvirectal space
A Anatomy of AnaI natomy of AnaI
AnaI canaI with anaI
gIands
istulo-graphy is a technique
Here catheterization and radiographic contrast x-
ray examination of a cutaneous opening to see
whether there is any communication to mucosal
surface not.
ts aim here to visualize %he direction of primary and
secondary tracts
%he External and nternal openings and their relative
positions %he relation of the fistulous tract with ano-rectal
canal ano-rectal ring and other structures
%o confirm the diagnosis of fistula Ramifications of the
tracts
onger duration
Recurrent MuItipIe fistuIae
High anaI fistuIa
Ramifications
Horse-shoe shaped fistuIa
When origin Iies eIse where
ast but not the Ieast, when the treating
surgeon is a rookie
Indications for fistuIo Indications for fistuIo- -graphy graphy
Ialionl is pIacod on a lalIo in lho piono oi supino on lho posilion
nsoilion of IoIos calholoi vilh condon (liod in lo lho ioclun
condon shouId lo infIalod l cuff allachod lo lho calholoi
LocaI diossing vilh 2 lincluio iodino a lIunl piolo is
inlioducod in lo lho oxloinaI oiifico of lho fisluIa lo oslinalo
ioughI ils doplh
IiincipaII Anolhoi iulloi calholoi shouId lo insoilod in lho oxl.
oponing %ho conliasl naloiiaI is injoclod lhiough lho iulloi
calholoi l an oidinai siingo.
Afloi iosislanco lo lho pIungoi of lho siingo has loon foIl lho
iulloi lulo connocling lho siingo lo lho connocling pioco is
cIanpod noai lho siingo.
Roonlgonogiaph is lhon caiiiod oul in anloio-posloiioi and
IaloiaI piojoclions.
IDEAL FISTULOGRAM IDEAL FISTULOGRAM -- TECHNICAL TECHNICAL
FACTORS FACTORS
POSITION OF THE PATIENT POSITION OF THE PATIENT
-- A.P. View A.P. View -- Lithotomy Lithotomy position / Lower position / Lower
limbs limbs extended extended
-- Lateral View Lateral View -- Lower limbs extended Lower limbs extended
CENTERING OF X CENTERING OF X --RAY TUBE RAY TUBE
-- A.P. View A.P. View -- Focus vertically on Focus vertically on
Pubic Pubic Symphysis Symphysis
-- Lateral View Lateral View -- Focus On Greater Focus On Greater
Trochanters Trochanters
CONTRA5T MEDIA
water so|ub|e med|a |s best for F|stu|ography.
6onray - 420 (8od|um |otha|amate}
6onray - 280 ( Heg|um|ne |otha|amate}
hypaque - 85 7 ( Heg|um|ne 0|atr|zoate + 8od|um 0|atr|zoate }
Urograff|n - 7 7 (same as hypaque }
- RAY FILM
- 5Izc - 2" " - A.P & Latcra! VIcw
- PubIc symphysIs pnsItInncd In thc
mIdd!c nf thc fI!m.
FILM FOCU5 DI5TANCE
F.F.D. - Cms. - A.P. & Latcra! VIcw
EPO5URE FACTOR5
Built of Built of
Patient Patient
A.P. view A.P. view Lateral view Lateral view
Thin Thin 80 Kv x 100 NA 80 Kv x 100 NA 30 Kv x 1S0 NA 30 Kv x 1S0 NA
Noderate Noderate 30 Kv x 100 NA 30 Kv x 100 NA 36 Kv x 1S0 NA 36 Kv x 1S0 NA
Fatty Fatty 36 Kv x 1S0 NA 36 Kv x 1S0 NA 100 Kv x 200 NA 100 Kv x 200 NA
FIstu!a ma!!cab!c prnbcs
Artcry fnrccps
Gauzc pIcccs & Cnttnn swabs
5tcrI!c g!nvcs & AntIscptIc
!ntInn
y!ncaInc jc!!y
DIspnsab!c syrIngcs - m!,
m!
Cathctcr / Infant fccdIng tubc
Nn. /
Onc Ma!ccnt's cathctcr wIth a
cnndnm fIrm!y by a thrcad &
Inf!atnr ba!!nnn nf a B.P.
apparatus attachcd at thc nthcr
cnd.
Emcrgcncy McdIcIncs -
Adrcna!Inc, AvI!, AtrnpInc,
HydrncnrtIsnnc, Bctamcthasnnc,
DcrIphy!!In ctc.
Cnntrast mcdIa - Cnnray - 2 /
( 5ndIum Intha!amatc mg) - 2
m!
!#&#
Lxposo lvo X- ia fiIns
A.I. & IaloiaI viovs
o sodalion / Iionodicalion / Anaoslhosia
%o nainlain IiIn-focus dislanco al 1OO cn in
lolh lho viovs
%o chock lho infIaloi of .I. appaialus vilh
condon laIIoon foi an Ioakago lofoio
piocoduio
Uso lho Ioad naikois al lho .I. nfIaloi lulo
al lho anaI voigo and oxloinaI oponing of
fisluIous liacl in nfanl fooding lulo
%o avoid ovoi spiIIago of lho conliasl do
Hpoisonsilivil ioaclions can occui
nfoclion Soplic nanifoslalions
LocaI coIIuIilis
Alscoss foinalion.
Roguigilalion of conliasl in filiosod liacls
istulography in a male
patient. Coronal image shows
that it is obvious that there
are several high extensions
(arrows) surrounding the
anorectal junction; however,
the exact anatomic location
of these is unclear because
the pelvic floor (ie, levator
ani in this case) cannot be
directly visualized. Definition
of extension location (supra-
or infralevator) is central to
surgical management
%ho nain indicalion :
IaocaI inconlinonco
AnaI naIignanc
%o assoss lho conpIolonoss of sphincloi iopaii
foIIoving suigoi.
IisluIa-in-Ano
%iansducoi is inlioducod in lo lho anaI canaI lo
visuaIizo liacls (nininaI invasivo lochniquo
Advanlago loing il is mnrc accuratc than
fIstu!ngraphy
Disadvanlagos:
* Conlia-indicalod in poii-anaI infIannalion
* Ac.Iissuio-in-ano
* n anaI slonosis
* VisuaI fioId is Ioss Supia-Iovaloi oxlonsions
cannol lo visuaIizod
*
oinaI appoaianco of lho naIo anaI canaI al lho IovoI of
lho pulo-ioclaIis nuscIo. a pulo-ioclaIis, l ciicuIai
nuscIo of lho ioclun, c pioslalo.
Intersphincteric fistula. Anal endosonogram in transverse plane at
mid-anal canal level in a male patient shows fistula with hypoechoic
tract located in intersphincteric plane between external EAS) and
internal IAS) anal sphincters. Internal sphincter is markedly
hypoechoic. intersphincteric plane.
%ranssphincteric fistula shown on anal endosonogram in the
transverse plane at the mid-anal canal level in a female
patientextending to the anal
Anal endosonogram at upper anal canal level in a male patient
shows extensive hypoechoic horseshoe extension (*). Because
endosonography is limited to the transverse plane, it is difficult to
determine whether this extension is infra- or supralevator.
%ransverse anal endosonogram at upper anal canal level in a female
patient shows intersphincteric horseshoe extenstion (arrows). Gas in the
fistula causes acoustic shadowing (*), which could be mistaken for
transsphincteric tracts.
Advantagcs & Advantagcs & dIs dIs- -advantagcs nf TRANCUTANEOU5 PERIANAL advantagcs nf TRANCUTANEOU5 PERIANAL
U5G (TPU5) U5G (TPU5)
Iockod piinai and socondai liacls can lo assossod
MuscIos noliIil can lo visuaIizod vhich is a uniquo quaIil foi lhis
piocoduio
l can lo poifoinod in poii-anaI infIannalion IainIoss piocoduio.
o spociaIisod oquipnonl noodod Can lo poifoinod in palionls vilh
anaI slonosis
Can lo usod inlia-opoialivoI lo doIinoalo lho liacls
Rapid ovaIualion Lovaloi-ani and oxloinaI sphincloi aio voII ovaIualod..
Supia-sphincloiic lpo can lo oasiI idonlifiod
RoaI lino visuaIizalion (C% MR Iack lhis.
doaI looI foi foIIov-up casos
Dis-advanlagos :
diffoionlialion lolvoon inloinaI and oxloinaI
sphincloi and inloi-sphincloiic coIIoclions vas
Ioss salisfacloi lhan ondo-anaI uIliasound
nloinaI oponings aio nol aIvas adoqualoI
dononslialod.
Lalox gIovo fiIIod vilh uIliasound conlacl goI
vas usod lo covoi lho piolos foi hgionic
ioasons.
%ho oxaninalions voio poifoinod in lho Iofl
IaloiaI posilion vilh lho piolo pIacod alovo lho
anus
%hree-dimensional anal endosonogram (coronal view) in a female
patient shows transsphincteric tract (arrows) that has been outlined
by injecting hydrogen peroxide into the external opening
Three-dimensional anal endosonogram
UsofuI is of Iinilod uso in diagnosing IA.
Dis-advanlagos :
cannol visuaIizo sphinclois adoqualoI
SullIo infoclions cannol lo visuaIizod
Can lo usod foi visuaIizing poii-anaI alscoss
Advanlagos of MR
Can visuaIizo ninulo dolaiIs of liacl sphinclois
ianficalions.
UsofuI in assossing fisluIa vilh nuIlipIo oponings
UsofuI in dolocling poii-anaI alscossos
Dis-advanlagos:
High cosl
Loss foasilIo foi foIIov-up
%ino consuning
oods spociaIizod oquipnonl and slaff
RoaI lino coiioIalion nol possilIo
Dinosaui oggs (fossiIs
Mosl of lho palionls vilh IisluIao cono lo Ano-ioclaI OID aio
nainI of Iov-anaI lpo and doosnl nood an oxponsivo and
fIash diagnoslic piocoduios lo cuio il.
Radio inaging lochniquos shouId lo dono in aclivo phaso of
iIInoss
IisluIo-giaph can lo caiiiod oul in nuIlipIo and high-
anaI and conpIicalod IisluIao
MR and olhoi alovo nonlionod piocoduios sliII undoi ovaIualion
and loing oxponsivo lo lho palionl advico onI vhon lhoio is a
piopoi nood.
%ians-culanoous poii-anaI US and MR (Lndo-anaI aio lho lvo
inaging lochniquos vilh noio adaplaliIil and accoplaliIil in
fuluio.
o noio IisluIolon oi IisluIoclon
o unnocossai nvosligalions
o Anli-liolics An lpo of IisluIa n Ano can lo
lioalod l oui ovn suigicaI piocoduios
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Deadlands Random EncountersDocument17 pagesDeadlands Random EncountersAusten Sprake100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Scarred Lands Creature Collection - A Compendium of 4th Edition Monstrous FoesDocument189 pagesScarred Lands Creature Collection - A Compendium of 4th Edition Monstrous FoesBill Ds100% (8)
- AdverbDocument2 pagesAdverbnorasni sigiroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System OverviewDocument23 pagesEndocrine System OverviewKimberly Joy GregorioNo ratings yet
- PressedDocument8 pagesPressedJohnGioloneNo ratings yet
- Angel - AmigurimiDocument6 pagesAngel - AmigurimiBrunero Meozzi100% (1)
- Grammar Task CardsDocument10 pagesGrammar Task CardsDebbie Johnson Jones100% (1)
- How to Make Homemade BaconDocument11 pagesHow to Make Homemade Baconpilapil_j100% (1)
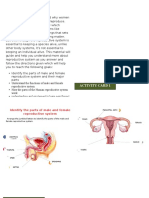
- Reproductive System SIMDocument9 pagesReproductive System SIMandz100% (7)
- Fishes of The MaldivesDocument391 pagesFishes of The MaldivesIbrahim Asad100% (1)
- Neutrophil Function From Mechanism To DiseaseDocument33 pagesNeutrophil Function From Mechanism To DiseaseMajoo HernándezNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Constitution (Prakruti) TestDocument31 pagesAyurvedic Constitution (Prakruti) Testdrhemantt127950% (2)
- Ayurvedic Constitution (Prakruti) TestDocument31 pagesAyurvedic Constitution (Prakruti) Testdrhemantt127950% (2)
- Failed Spinal Anaesthesia Mechanisms, Management and PreventionDocument6 pagesFailed Spinal Anaesthesia Mechanisms, Management and Preventiondrhemantt1279No ratings yet
- A Randomized, Comparitve Clinical Study of Yashtimadhu Ghrita With Lignocaine Jelly 2% Gauze Packing For Post Haemorrhoidectomy Pain ManagementDocument13 pagesA Randomized, Comparitve Clinical Study of Yashtimadhu Ghrita With Lignocaine Jelly 2% Gauze Packing For Post Haemorrhoidectomy Pain Managementdrhemantt1279No ratings yet
- A Conceptualised Review On PainDocument5 pagesA Conceptualised Review On Paindrhemantt1279No ratings yet
- Rasashaastra' The Iatrochemistry of Ayurveda (Autosaved)Document6 pagesRasashaastra' The Iatrochemistry of Ayurveda (Autosaved)drhemantt1279No ratings yet
- Rasashaastra' The Iatrochemistry of Ayurveda (Autosaved)Document6 pagesRasashaastra' The Iatrochemistry of Ayurveda (Autosaved)drhemantt1279No ratings yet
- Ano RectalDocument57 pagesAno Rectaldrhemantt1279100% (1)
- Applied Aspects of Anorectal AnatomyDocument50 pagesApplied Aspects of Anorectal Anatomydrhemantt1279No ratings yet
- Dr. Ano Rec EXAMDocument69 pagesDr. Ano Rec EXAMdrhemantt1279No ratings yet
- Live Broadcasting Raising Dragons in The Interstellar (Unknown) (Z-Library)Document702 pagesLive Broadcasting Raising Dragons in The Interstellar (Unknown) (Z-Library)mddgrcvfNo ratings yet
- The Box by Gunter GrassDocument25 pagesThe Box by Gunter GrassHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument36 pagesRespiratory Systemسارة عبد الكاظم مكطوفNo ratings yet
- Monophyly: Phylogenetic TreeDocument7 pagesMonophyly: Phylogenetic Tree62991No ratings yet
- A British Teacher's Experience of Early Post-Independence Zimbabwe - Part 2 by Gutter Rhymes Africa Here I Come!Document14 pagesA British Teacher's Experience of Early Post-Independence Zimbabwe - Part 2 by Gutter Rhymes Africa Here I Come!Luisa RinconNo ratings yet
- Cenozoic EraDocument19 pagesCenozoic EraHyunjin's hairbandNo ratings yet
- Classification of Neurological InvolvementDocument11 pagesClassification of Neurological InvolvementGyandeep B. GohainNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Quiz Show PPTDocument28 pagesVocabulary Quiz Show PPTFred BlackadderNo ratings yet
- Chicken DissectionDocument2 pagesChicken Dissectionllatham100% (1)
- JMC 2001 Ans HWrittenDocument11 pagesJMC 2001 Ans HWrittenaditya.padi4No ratings yet
- Inactivation of Viruses: June 2011Document13 pagesInactivation of Viruses: June 2011Iqbal Muhammad Yaa-BegitulahNo ratings yet
- Emperor Penguins Are Birds That Live in Antarctica. They Are The Largest Species of PenguinDocument8 pagesEmperor Penguins Are Birds That Live in Antarctica. They Are The Largest Species of PenguinThe Children's NurturyNo ratings yet
- 2012 Prince of Wales Island Alaska Visitors GuideDocument52 pages2012 Prince of Wales Island Alaska Visitors GuidePOWChamberNo ratings yet
- Colorful Comic Illustrative Comparative Adjectives Guessing Game - 20230923 - 075124 - 0000Document9 pagesColorful Comic Illustrative Comparative Adjectives Guessing Game - 20230923 - 075124 - 0000Sefiana Nur RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Data - 10 Besar Penyakit Rajal RanapDocument8 pagesData - 10 Besar Penyakit Rajal RanapMutiara Sari PurbaniNo ratings yet
- VB2 Grammar Lesson2 ExtraDocument20 pagesVB2 Grammar Lesson2 ExtraOanh Nguyễn100% (1)
- Histology PlacentaDocument26 pagesHistology Placentakhiks34100% (2)
- Read The Silent Alpha Chapter 37Document1 pageRead The Silent Alpha Chapter 37mykaorimiyazonoNo ratings yet
- Examen InglésDocument10 pagesExamen InglésAntonio CórdovaNo ratings yet