Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zygote Formation, Cleavage & Blastula Formation
Uploaded by
Mareeswaran RamachandranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zygote Formation, Cleavage & Blastula Formation
Uploaded by
Mareeswaran RamachandranCopyright:
Available Formats
5/4/12
5/4/12
Zygote formation, Cleavage & Blastula formation
Click to edit Master subtitle style R. Mareeswaran, (09BC011)
Second year M.Sc., Biochemistry
5/4/12
Early Embryonic Development
Cleavage starts Fertilization of ovum Ovary Oviduct
Secondary oocyte Blastocyst (implanted) Ovulation Endometrium Uterus
5/4/12
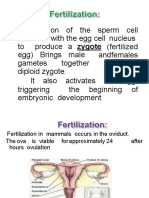
Fertilization.....
Fertilization is the process whereby two sex cells (gametes) fuse together to create a new individual with genetic potentials derived from both parents. known as Zygote formation a single event occurs in a series of steps
Also Not
5/4/12
Events
1. 2.
Contact and recognition
Regulation of sperm entry into the egg. Fusion of the genetic material of sperm and egg. Activation of egg metabolism
3.
4.
5/4/12
Sperm Capacitation..
Freshly Must
ejaculated sperm are unable or poorly able to fertilize. undergo a series of changes collectively known as Capacitation. is associated with removal of adherent seminal plasma proteins, reorganization of plasma membrane lipids and proteins.
Capacitation
5/4/12
Capacitation
occurs while sperm reside in the female reproductive tract for a period of time, as they normally do during gamete transport. appears to destabilize the sperm's membrane to prepare it for the acrosome reaction
Capacitation
5/4/12
Phases.
Phase Phase Phase
1 - Penetration of the corona radiata; 2 - Penetration of the zona pellucida
3 - Fusion of the oocyte and sperm cell membranes.
5/4/12
PHASE 1: PENETRATION OF THE CORONA RADIATA
Of
5/4/12
200 to 300 million spermatozoa only 300 to 500 reach the site of fertilization. one of these fertilizes the egg. sperm pass freely through corona
Only
Capacitated
cells
PHASE 2: PENETRATION OF THE ZONA PELLUCIDA
Zona
5/4/12
- glycoprotein shell
Facilitates
and maintains sperm binding and induces the acrosome reaction. binding and the acrosome reaction are mediated by the ligand ZP3, a zona protein. of acrosomal enzymes (acrosin) allows sperm to penetrate the zona, of the zona pellucida changes when the head of the sperm comes in contact with the oocyte surface. in release of lysosomal enzymes from cortical granules lining the plasma membrane
Both
Release
Permeability
Results
5/4/12
Acrosomal Reaction
The
acrosome reaction provides the sperm with an enzymatic drill to get throught the zona pellucida. same zona pellucida protein that serves as a sperm receptor also stimulates a series of events that lead to many areas of fusion between the plasma membrane and outer acrosomal membrane. fusion (actually an exocytosis) and vesiculation expose the acrosomal contents, leading to leakage of acrosomal enzymes from the sperm's head.
The
Membrane
As
the acrosome reaction progresses and the sperm passes through the zona pellucida, more and more of the plasma membrane and acrosomal contents are lost. the time the sperm traverses the zona pellucida, the entire anterior surface of its head, down to the inner acrosomal membrane, is denuded.
By
5/4/12
The
constant propulsive force from the sperm's flagellating tail, in combination with acrosomal enzymes, allow the sperm to create a tract through the zona pellucida. a sperm penetrates the zona pellucida, it binds to and fuses with the plasma membrane of the oocyte.
Once
PHASE 3: FUSION OF THE OOCYTE AND SPERM CELL MEMBRANES
Initial
5/4/12
adhesion of sperm to the oocyte - by the integrins & disintegrins penetration egg responds in three ways: Cortical and zona reactions.
After 1. 2.
Resumption of the second meiotic division Metabolic activation of the egg
3.
5/4/12
The Zona Reaction
The
cortical reaction refers to a massive exocytosis of cortical granules seen shortly after sperm-oocyte fusion. granules contain a mixture of enzymes, including several proteases alter the structure of the zona pellucida, inducing what is known as the zona reaction. of cortical granules may also interact with the oocyte plasma membrane.
Cortical
Proteases
Components
5/4/12
The critical importance of the zona reaction is that it represents the major block to polyspermy in most mammals. This effect is the result of two measurable changes induced in the zona pellucida:
1. 2.
The zona pellucida hardens. Sperm receptors in the zona pellucida are destroyed
5/4/12
The Zona Reaction Animation
5/4/12
Egg Activation
Prior
to fertilization, the egg is in a quiescent state, arrested in metaphase of the second meiotic division. binding of a sperm, the egg rapidly undergoes a number of metabolic and physical changes that collectively are called egg activation. effects include a rise in the intracellular concentration of calcium, completion of the second meiotic division and the so-called cortical reaction.
Upon
Prominent
5/4/12
5/4/12
Fusion Of Genetic Material
Pronuclear Male
migration takes about 12 hours
and female pronuclei are indistinguishable
5/4/12
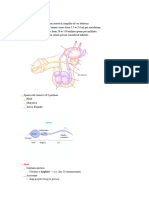
Summary.
1 The sperm
acrosomal enzymes digest the 3 Proteins on the eggs jelly SPERM sperm head bind coat to egg receptors 4 The plasma membranes of sperm and egg fuse Sperm head 5 The sperm nucleus enters Nucleus the egg cytoplasm Acrosome Acrosomal Plasma 6 A membrane enzymes fertilization envelope forms Receptor protein molecules Plasma Sperm membrane nucleus Vitelline Cytoplasm layer Egg Jelly nucleus coat 7 The nuclei EGG CELL of sperm Zygote and egg fuse nucleus
approaches the egg
2 The sperms
5/4/12
Results Of Fertilization
Restoration
of the diploid number of chromosomes of the sex of cleavage
Determination Initiation
5/4/12
Blocking Of Polyspermy
2
Types
Fast block Changing electric potential block Zona reaction
Slow
5/4/12
Cleavage.
Mitosis
and cytokinesis of the zygote produces an increasing number of smaller cells (Blastomeres), each with an exact copy of the genome present in the zygote. Tight junction & Gap junction 16 cell ends with the formation of a blastula.
Compaction Morula
Cleavage
5/4/12
Cleavage Pattern
5/4/12
Blastocyst Formation
Morula
enters the uterine cavity Embryoblast & Tropoblast
Blastocele Blastocyst
5/4/12
5/4/12
ENDOMETRIUM Inner cell mass
Cavity
Trophoblast
5/4/12
Th an Yo k u!
You might also like
- Biol 216 2020 Topic 2 Development - Powerpoint 2.0 Fertilization - TaggedDocument24 pagesBiol 216 2020 Topic 2 Development - Powerpoint 2.0 Fertilization - TaggedMichael HamoudiNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Çiğdem ElmasDocument49 pagesProf. Dr. Çiğdem ElmasMuhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- Phases of Embryonic DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPhases of Embryonic DevelopmentIshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document9 pagesLecture 2SultanNo ratings yet
- Human FertilizationDocument3 pagesHuman Fertilizationtamalbio7No ratings yet
- Topic: Fertilization: Print Self Learning MaterialDocument9 pagesTopic: Fertilization: Print Self Learning MaterialNihalNo ratings yet
- SAQ Unit 2Document9 pagesSAQ Unit 2Shilpa DuttaNo ratings yet
- Gamete Fusion and The Prevention of PolyspermyDocument9 pagesGamete Fusion and The Prevention of Polyspermyme and allNo ratings yet
- Gametes and FertilizationDocument3 pagesGametes and FertilizationCrystal Ann B. LaresmaNo ratings yet
- AlakeshBarman Zoology PG 2ND FERTILIZATIONDocument28 pagesAlakeshBarman Zoology PG 2ND FERTILIZATIONTrueAlpha 16No ratings yet
- Sperm Maturation:: FertilizationDocument4 pagesSperm Maturation:: FertilizationMuhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Gametogenesis and FertilizationDocument43 pagesLec 3 Gametogenesis and FertilizationDacks WangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 3 FertilizationDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Part 3 FertilizationSyeda Fizza BatoolNo ratings yet
- Cellular Mechanism of Sexual ReproductionDocument20 pagesCellular Mechanism of Sexual ReproductionJessa BelleNo ratings yet
- 1st WeekDocument25 pages1st WeekNamra NoorNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document10 pagesModule 5Phan MhiveNo ratings yet
- Acrosome ReactionDocument4 pagesAcrosome ReactionKuldip DwivediNo ratings yet
- HIMB Sea Urchin Fertilization LabDocument15 pagesHIMB Sea Urchin Fertilization LabAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Alakeshbarman Zoology PG 2nd FertilizationDocument28 pagesAlakeshbarman Zoology PG 2nd Fertilizationouafia liiamaniNo ratings yet
- 8673-2 Doc2Document13 pages8673-2 Doc2Imaan Khan ImaanNo ratings yet
- Fertilizacion RevisionDocument8 pagesFertilizacion RevisionAsistente IRP RESTREPONo ratings yet
- The State of The Union: The Cell Biology of Fertilization: ReviewDocument7 pagesThe State of The Union: The Cell Biology of Fertilization: ReviewIsabella ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Semen AnalysisDocument35 pagesSemen AnalysisSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ravichandran Doraiswamy Professor of AnatomyDocument70 pagesDr. Ravichandran Doraiswamy Professor of AnatomySiva SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 4 FertilizationDocument59 pages4 FertilizationQaiser InayatNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of The Mammalian Sperm Plasma Membrane in The Process of FertilizationDocument39 pagesDynamics of The Mammalian Sperm Plasma Membrane in The Process of FertilizationWachiel ArhamzNo ratings yet
- Conception 2021Document15 pagesConception 2021Dhinesh ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Embryo AssignmentDocument2 pagesEmbryo AssignmentA.j. MasagcaNo ratings yet
- Human Sperm Capacitation and The Acrosome Reaction : L.J.D.Zaneveld, C.J.De Jonge, R.A.Anderson and S.R.MackDocument10 pagesHuman Sperm Capacitation and The Acrosome Reaction : L.J.D.Zaneveld, C.J.De Jonge, R.A.Anderson and S.R.MackDaniel LunaNo ratings yet
- Pembelahan Embrio (Cleavage) S2 2017Document47 pagesPembelahan Embrio (Cleavage) S2 2017Desy NataliaNo ratings yet
- Devlopment Plasm GerminalDocument81 pagesDevlopment Plasm GerminalRian AbendaniNo ratings yet
- Fertilization: Recommended Reading: SummaryDocument10 pagesFertilization: Recommended Reading: SummaryKnjigeNo ratings yet
- Embryology - Fertilization: Paper 1 - Part BDocument5 pagesEmbryology - Fertilization: Paper 1 - Part BViswa GiriNo ratings yet
- The Sea Urchin Fertilization LabDocument5 pagesThe Sea Urchin Fertilization LabAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument10 pagesFertilizationdeepakshi rajputNo ratings yet
- Ferti Liz AreDocument13 pagesFerti Liz AreDontu MariaNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument8 pagesFertilizationAmy WuNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Fertilization in Plants and AnimalsDocument56 pages3.3 Fertilization in Plants and AnimalsAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- Human Fertilization - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesHuman Fertilization - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNadiya AfifahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Biology 2 Group 3 HN2Document3 pagesTutorial 4 Biology 2 Group 3 HN2Firdaus ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Mammalian Sperm Egg Interaction Leading To Fertilization 2161 0932.1000e107Document4 pagesMechanisms of Mammalian Sperm Egg Interaction Leading To Fertilization 2161 0932.1000e1071005 Siti Ainunnisa Lingga WinariNo ratings yet
- Biology: Find and Fuse: Unsolved Mysteries in Sperm - Egg RecognitionDocument11 pagesBiology: Find and Fuse: Unsolved Mysteries in Sperm - Egg RecognitionFlavio NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Fertilization - ImplantationDocument4 pagesFertilization - ImplantationEzeoke ChristabelNo ratings yet
- PolyspermyDocument2 pagesPolyspermyamnakhanak4748No ratings yet
- Human EmbryologyDocument7 pagesHuman Embryologyvinit cfuNo ratings yet
- اجنه الاخصابDocument12 pagesاجنه الاخصابFatimaAmmarNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis and FertilizationDocument10 pagesGametogenesis and FertilizationJustus MutuaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization: Beginning A New Organism: Lee Kui SoonDocument31 pagesFertilization: Beginning A New Organism: Lee Kui SoonSayapPutihNo ratings yet
- Fertilization by Rahmat Sarkani ADocument10 pagesFertilization by Rahmat Sarkani ARahmat Sarkani AipamaNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument16 pagesEmbryologyNikkNo ratings yet
- Embryology SummaryDocument23 pagesEmbryology SummaryChiderahNo ratings yet
- Review of Fetal DevelopmentDocument71 pagesReview of Fetal DevelopmentlisafelixNo ratings yet
- Fertilization Overview: Sperm PenetrationDocument13 pagesFertilization Overview: Sperm PenetrationAmira FahruddinNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument17 pagesFertilizationJahanvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 MouseDocument6 pagesChapter 10 MouseCarlo MendozaNo ratings yet
- CH 47 - Animal DevelopmentDocument70 pagesCH 47 - Animal DevelopmentSofiaNo ratings yet
- Sample EssayDocument4 pagesSample EssaySITI NABILA BINTI JAMALI KM-PensyarahNo ratings yet
- 02 FertilizationDocument6 pages02 Fertilizationhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Development and InheritanceDocument30 pagesDevelopment and InheritanceGeofry OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- @PAKET A - TPM BAHASA INGGRIS KuDocument37 pages@PAKET A - TPM BAHASA INGGRIS KuRamona DessiatriNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Tourism Laws CKSCDocument6 pagesSyllabus Tourism Laws CKSCDennis Go50% (2)
- Applied Chemistry-IDocument16 pagesApplied Chemistry-Islm.sbipNo ratings yet
- Social Legislation Cases On Kasambahay LawDocument12 pagesSocial Legislation Cases On Kasambahay LawLiee Raine100% (1)
- CV BTP AhokDocument2 pagesCV BTP AhokDiah Purwati N.No ratings yet
- ISDGTIE 2023 BrochureDocument9 pagesISDGTIE 2023 BrochureAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Vince - Michael - Intermediate - Language Assive 1Document5 pagesVince - Michael - Intermediate - Language Assive 1Николай КолевNo ratings yet
- Assignment On How To Increase Own Brand Mantras: Submition Date: January 29,2021Document5 pagesAssignment On How To Increase Own Brand Mantras: Submition Date: January 29,2021Ferari DroboNo ratings yet
- Eapp Las Q3 Week 1Document8 pagesEapp Las Q3 Week 1Maricel VallejosNo ratings yet
- MLHP Final ListDocument36 pagesMLHP Final Listswapnitha tummaNo ratings yet
- Napoleon Lacroze Von Sanden - Crony Capitalism in ArgentinaDocument1 pageNapoleon Lacroze Von Sanden - Crony Capitalism in ArgentinaBoney LacrozeNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument13 pagesNarrative ReportfranceNo ratings yet
- French Art of Not Giving A F-CK Chapter SamplerDocument19 pagesFrench Art of Not Giving A F-CK Chapter SamplerAllen & UnwinNo ratings yet
- Forum Discussion #7 UtilitarianismDocument3 pagesForum Discussion #7 UtilitarianismLisel SalibioNo ratings yet
- Delos Reyes Preliminary ExamDocument7 pagesDelos Reyes Preliminary ExamJp Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- 06 - Wreak Bodily HavokDocument40 pages06 - Wreak Bodily HavokJivoNo ratings yet
- GRP 15 Property Law Final DDocument15 pagesGRP 15 Property Law Final DBruno OsananNo ratings yet
- Dbms QuoteDocument2 pagesDbms QuoteAnonymous UZFenDTNMNo ratings yet
- HCM-C Ng-Hòa. 3kDocument300 pagesHCM-C Ng-Hòa. 3kTrí PhạmNo ratings yet
- Written Test 4-Book 3Document2 pagesWritten Test 4-Book 3Vinícius MoreiraNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Eschatology and ProtologyDocument48 pagesThe Impact of Eschatology and ProtologyJuan SteinNo ratings yet
- 2016 Biology CheckpointDocument14 pages2016 Biology CheckpointNicholas Leong100% (1)
- LESSON PLAN IN wRITING A REPORTDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN IN wRITING A REPORTMarkaton Dihagnos100% (4)
- Mapua Cwtsstudentsmodule (Ay08 09)Document62 pagesMapua Cwtsstudentsmodule (Ay08 09)anon-805332No ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1 (TPT630)Document7 pagesIndividual Assignment 1 (TPT630)MUHAMMAD HABIB HARRAZ ABDUL RAHMANNo ratings yet
- DIN EN 16842-1: in Case of Doubt, The German-Language Original Shall Be Considered AuthoritativeDocument23 pagesDIN EN 16842-1: in Case of Doubt, The German-Language Original Shall Be Considered AuthoritativeanupthattaNo ratings yet
- The Spartacus Workout 2Document13 pagesThe Spartacus Workout 2PaulFM2100% (1)
- The Java Collections Framework: InterfacesDocument22 pagesThe Java Collections Framework: InterfacesSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Electrofusion Jointing ProceduresDocument12 pagesElectrofusion Jointing ProcedureslfpachecoNo ratings yet
- Mercury and The WoodmanDocument1 pageMercury and The WoodmanLum Mei YeuanNo ratings yet