Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stages of Human Development
Uploaded by
Frances PidlaoanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stages of Human Development
Uploaded by
Frances PidlaoanCopyright:
Available Formats
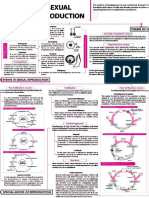
Fertilization consists in the union of the spermatozon with the mature ovum.
The process begins when sperms are deposited in the vagina and move through the uterus into the Fallopian tubes. Fallopian tubes /oviduct: tubes are two thin tubes, one on each side of the uterus, which help lead the mature egg from the ovaries to the uterus.
An ovum is a female reproductive cell or gamete.
If the sperm reach the fallopian tube within 36 hours during the female ovulation period an egg will be fertilized in one of the tubes. -the sperm cell penetrates the ovum and releases enzymes at the tip of its head(ACROSOME). They break down the jelly-like outer layers of the ovum. The sperm enters the ovum and they fuse together.
-after they fused, a zygote will develop into the entire organism. -zygote: The cell formed by the union of two gametes, especially a fertilized ovum before cleavage. - a zygote will travels back down the oviduct towards the uterus, a journey of six to seven days of fertilization.
-oviduct/fallopian tube: A tube, or duct, for the passage of ova from the ovary to the exterior of the animal or to the part where further development takes place. then the zygote becomes a small ball of cells that attaches itself to the uterine wall and process to implantation. It is now called and embryo.
Fertilization YouTube baby formation inside tummy - YouTube
The
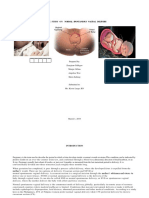
term embryonic development refers to changes that take place as an embryo matures.
The zygote forms in one of the mother's fallopian tubes, the tubes that connect the ovaries with the uterus.
By
the end of the first week, a protective sac, the amniotic cavity, begins to form around the embryoblast.
During week two of embryonic development, embryonic cells have begun the process of differentiation. The identical cells formed by the early divisions of the zygote are beginning to take on the different characteristic of muscle, blood, nerve, bone, and other kinds of cells. During week three, a thin membrane called the amniotic sac becomes filled w/ a liquid called Amniotic fluid, which helps cushion and protects the embryo. During the fourth week, the embryo becomes CShaped with an enlarged forebrain and a visible tail. Eye stalks and ear pits appear. Upper and lower limb buds are observable.
By the end of fifth week, the embryo has all of its internal organs. Much more brain development occurs at this time, and the head enlarges, causing it to bend forward and appear large compared to the body. During the sixth week, the trunk straightens and upper limb development continues. The neck, elbows, and wrists form. Mammary and pituitary gland buds appear, tooth buds appear. These buds will become the "baby" teeth that are lost in childhood.
Ex:A human embryo at five to six weeks of development.
During the seventh week, future fingers and thumbs are clearly visible on the hands. the tail begins to disappear, The heart has become divided into chambers. The cornea of the eye is also present. During the eighth week, remarkable development occurs. The top of the head becomes more rounded and erect. External genital (sex organ) differences begin to develop. All appearances of the tail are gone.
Embryonic development - YouTube
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PT-1 Bio (Set-B) 2023-24Document2 pagesPT-1 Bio (Set-B) 2023-24kopal94135No ratings yet
- EP - 02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - One Shot - NEET 2022 PreparationDocument85 pagesEP - 02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - One Shot - NEET 2022 PreparationSindhuja C SNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Sexual ReproductionDocument1 pageConcept Map Sexual ReproductionSalil ShauNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Our SensesDocument30 pagesThe Brain and Our Senseslolavillanueva81% (16)
- Demo Lesson Female Repro 19-20Document4 pagesDemo Lesson Female Repro 19-20Rhandy Buenecille100% (1)
- Heep 1 AnDocument48 pagesHeep 1 AnJuhnNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Second Periodical TestDocument23 pagesDepartment of Education Second Periodical TestcalindaganNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesModule 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMorgan BrownNo ratings yet
- PT Q2 Grade 5Document9 pagesPT Q2 Grade 5Janice Sumaylo BaluranNo ratings yet
- Mastery TestDocument3 pagesMastery TestThelma BajoNo ratings yet
- (A) Edward Jenner (B) Alexander Fleming (C) Carl Linnaeus (D) Rosalind FranklinDocument11 pages(A) Edward Jenner (B) Alexander Fleming (C) Carl Linnaeus (D) Rosalind FranklinTanya TyagiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisis Sperma - Analisis-spermatozoa-AsiaDocument8 pagesJurnal Analisis Sperma - Analisis-spermatozoa-AsiaMuzas88No ratings yet
- Biological Science Let Reviewer W AnswerDocument13 pagesBiological Science Let Reviewer W AnswerChupapi MunyanyoNo ratings yet
- Assiated Reproductive Technology IpDocument25 pagesAssiated Reproductive Technology IpBharati patil100% (1)
- Bio2 11 - 12 Q4 0801 FDDocument22 pagesBio2 11 - 12 Q4 0801 FDTeam KapappiesNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Q2 Science LASDocument69 pagesGrade 5 Q2 Science LASVince BulayogNo ratings yet
- Embryology Part 1Document34 pagesEmbryology Part 1Aira CorderoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/31Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/31Keisya TennayaNo ratings yet
- Juno Is The Egg Izumo Receptor and IsDocument16 pagesJuno Is The Egg Izumo Receptor and IsMike zombieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Biology 11Document46 pagesChapter 14 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Physical Self Care GuideDocument26 pagesPhysical Self Care GuideGemlo Gatillo71% (7)
- Apeejay School, Saket Holiday Homework 2021-22 Class-Xii Important Tips For Parents and StudentsDocument24 pagesApeejay School, Saket Holiday Homework 2021-22 Class-Xii Important Tips For Parents and StudentsManav Arya SinghNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Suppleme Nt-Ary Material S: Second QuarterDocument49 pagesEarth and Life Science Suppleme Nt-Ary Material S: Second QuarterKimberly LagmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Class 11Document4 pagesPlant Kingdom Class 11AnshnuNo ratings yet
- LESSONS ON MICROSCOPES AND LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATIONDocument28 pagesLESSONS ON MICROSCOPES AND LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATIONkentxy ddfsNo ratings yet
- Man and His OriginDocument16 pagesMan and His OriginUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Nengovhela Study GuideDocument129 pagesNengovhela Study Guidebrighton nyama100% (1)
- Human ReproductionDocument2 pagesHuman ReproductionGrace KatjiovaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy by WeekDocument78 pagesPregnancy by WeekIoana Influencers RebornNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryDocument20 pagesA Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryNyj QuiñoNo ratings yet